| Bookshelf Home | Contents | Index | PDF |   |
|
Siebel Business Rules Administration Guide > Configuring the Business Rules Development Environment > Understanding Building and Deploying RulesIn order to invoke rules in a Siebel application, the following events take place:
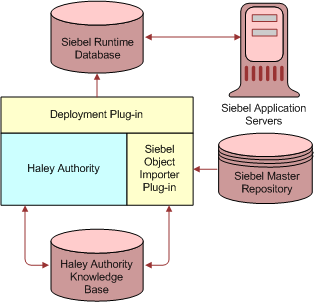
Figure 2 represents the interaction among the HaleyAuthority knowledge base, Siebel runtime database, and Siebel Master Repository database when rules are created, deployed, and invoked. The following three databases participate in implementing rule modules.
The following processing occurs when you create, deploy, and invoke rule modules. About Rule Modules CreationWhenever you use Object Importer, a COM Data Control (CDC) connection to a Siebel Master Repository database is created and a CDC connection to a Siebel runtime database is created. When you import Siebel objects using Object Importer:
As expected, the length of time to import objects depends on the number of objects you import. When you subsequently create statements and rule modules, they are written to the HaleyAuthority knowledge base. For information about tables provided for rules data in the Siebel runtime database, see Rule Tables in the Siebel Runtime Database. For detailed information about importing Siebel objects and creating rules, see Using Siebel Object Importer and Creating and Deploying Rules. About Rule Modules DeploymentWhen you deploy rule modules from HaleyAuthority:
For information about tables provided for rules data in the Siebel runtime database, see Rule Tables in the Siebel Runtime Database. For detailed information about deploying rule modules, see Deploying Rule Modules. About Rule Modules Invocation: Loading, Using, and CachingYou can implement rule modules to execute in various scenarios; for example, in a runtime event or in a business service within a Siebel workflow. Independent of how a rule module is invoked, the activity that occurs consists of loading the binaries (object model and rule modules) that exist in the runtime database into the Haley's runtime knowledge base for execution. Haley's runtime knowledge base is instantiated in the Application Object Manager when the object manager process starts, and persists until the object manager process stops. NOTE: Haley's runtime knowledge base is neither the Siebel runtime database nor the HaleyAuthority knowledge base. For more information on the Siebel runtime database and the HaleyAuthority knowledge base, see Understanding Building and Deploying Rules. A rule module is loaded into Haley's runtime knowledge base for execution when the rule module is first invoked. Haley's runtime knowledge base is loaded with rule modules on demand and shared among different user sessions. Once a rule module is loaded into the Haley's runtime knowledge base, it is ready to be used until it needs to be excised. When a rule module is re-deployed or deactivated, the loaded rule module is excised from Haley's runtime knowledge base. The next time the rule module is invoked, the newly deployed or re-activated rule module is loaded into the runtime knowledge base. |
  |
| Siebel Business Rules Administration Guide | Copyright © 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. | |