
| Bookshelf Home | Contents | Index | PDF |   |
|
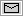
Siebel Connector for SAP R/3 > Installation and Configuration > Configuring ALE/IDOC ConnectivityALE communication occurs between entities known as logical systems. Logical system definitions must be created within SAP by an experienced SAP Basis Resource. You create a logical system definition for the external Siebel implementation and for the SAP client so that these two entities can communicate with one another through ALE. A logical system definition contains the list of IDOC Types and Message types allowed for communication with that logical system. It also specifies where the logical system exists on the network so that SAP can uniquely identify that system when it is connected to SAP. Figure 2 shows the data associated with defining a logical system. A Partner Profile, with both inbound and outbound message types communicates with a Port, which consists of an RFC Destination. An RFC Destination contains tRFC Parameters and a Program ID. The Program ID is written to the saprfc.ini file. You build logical systems from the bottom up. After you create a name for the logical system, then create an RFC Destination as shown in Figure 2. The most important part of the RFC Destination is the Program ID, as this value must exist in the TYPE=R destination entry of the After you have defined the RFC Destination, create a port definition and a Partner Profile definition. These are part of the logical system definition. These can be created manually or can be automatically generated by SAP if an SAP Distribution Model is created. The Distribution Model defines the list of Message Types that can be passed between any two logical systems. This information is used to create Partner Profiles in SAP. These Partner Profiles contain information for communication with an external system where data is transported outbound from SAP (Outbound Parameters) as well as information for communication with an external system where data is transported inbound to SAP (Inbound Parameters). Table 9 describes the Outbound Parameters. Table 10 describes the Inbound Parameters.
To interface to SAP using ALE, you must create a logical system in SAP with all of its associated information. The process in this document can be used to create a logical system and to perform the minimum amount of configuration necessary to work with the Siebel ALE Interfaces. Depending upon your own configuration requirements you may need to modify these steps accordingly. The SALE transaction handles all ALE configuration. This transaction takes you to the portion of the SAP Implementation Guide (IMG) that is relevant for ALE. The following procedures start with the SALE transaction. These procedures apply to SAP R/3 4.6C. Other versions of SAP differ slightly, but the SALE transaction still exists and the basic functions are available. |
 |
  |
| Siebel Connector for SAP R/3 |