| Oracle® VM Manager User's Guide Release 2.1 Part Number E10901-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® VM Manager User's Guide Release 2.1 Part Number E10901-04 |
|
|
View PDF |
A server pool is logically an autonomous region that contains one or more physical servers. It presents a unified view of the storage in which the virtual machines reside.
Before creating a server pool, ensure you have:
Oracle VM Servers that you will deploy as the Server Pool Master, the Utility Server, or the Virtual Machine Server.
A repository that is used for live migration of virtual machines and for local storage on the Oracle VM Servers. For information on managing repositories, see the Oracle VM Server User's Guide.
IP addresses or host names of these servers.
Passwords to access Oracle VM Agent installed on these servers.
This chapter describes how to manage server pools. It includes the following sections:
Note:
Functions described in this chapter are only available to users who are granted theManager or Administrator role.This section guides you through the ways of designing a server pool to meet your requirements.
Before creating a server pool, you need to consider how many physical servers will be contained in the server pool, and what functions each physical server will perform. The more virtual machines you will run in the server pool, the more resources these virtual machines will consume, therefore the more physical servers are needed to provide sufficient resources for the server pool.
A server pool is scalable. If you find a server pool does not have sufficient resources, such as CPU and memory, to run the virtual machines and the applications inside, you can expand the server pool by adding more Virtual Machine Servers.
There are three typical server pool configurations: separate configuration, all-in-one configuration, and two-in-one configuration.
Separate Configuration
In separate configuration, one single Oracle VM Server functions as a Server Pool Master, one or more Oracle VM Servers function as Utility Servers, and one or more Oracle VM Servers function as Virtual Machine Servers.
This configuration is recommended when there is a large number of virtual machines running on the server, or when applications on the virtual machines consume most of the hardware resources. It ensures that the performance of the hosted virtual machines is not impacted by any significant management activity handled by the Server Pool Master or Utility Servers.
All-in-One Configuration
In the all-in-one configuration, a single Oracle VM Server acts as the Server Pool Master, the Utility Server, and the Virtual Machine Server at the same time.
This configuration is recommended when there are only a few virtual machines running. In this case, the hardware resources of the Oracle VM Server are sufficient to support the virtual machines and the management activity handled by the Server Pool Master and Utility Server.
Two-in-One Configuration
In the two-in-one configuration, the Server Pool Master function, and the Utility Server function are grouped together on the same Oracle VM Server, while the Virtual Machine Server function is implemented separately on different Oracle VM Servers.
Compared with the two structures described earlier, this configuration serves well for a scenario where the server pool resource consumption is moderate. Since virtual machines use more hardware resources than other servers, you can typically deploy both the Server Pool Master and Utility Server on the same Oracle VM Server.
To create a server pool, perform the following:
On the Server Pools page, click Create Pool. The Create Server Pool page is displayed.
Figure 3-4 Adding Servers to a Server Pool
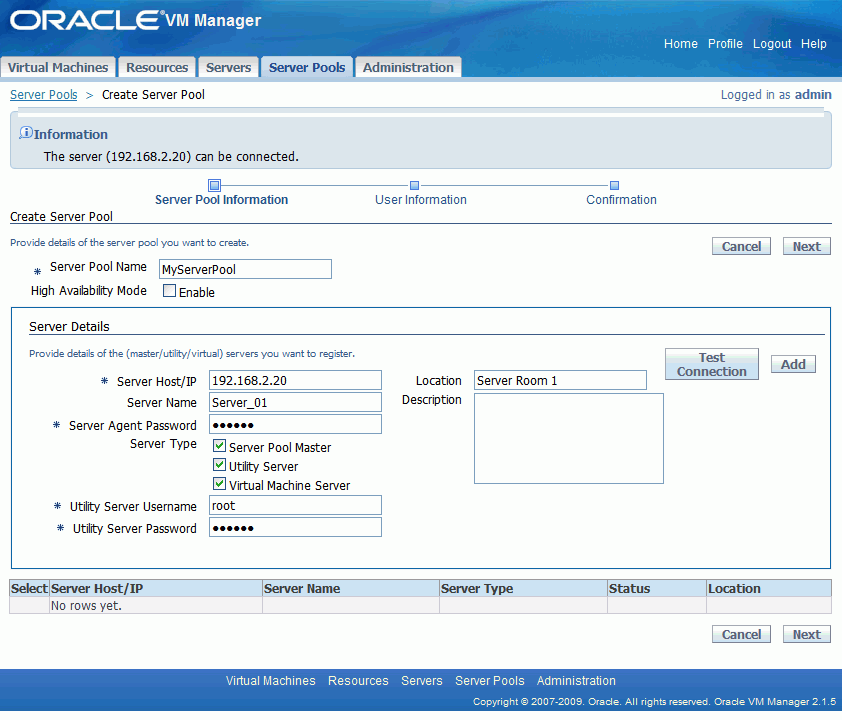
Enter the Oracle VM Server information and add the Oracle VM Server to the server pool. You can add multiple Oracle VM Servers to a server pool.
A server pool consists of at least one Server Pool Master, one Utility Server, and one Virtual Machine Server. See Designing a Server Pool.
Note:
If you have registered a physical server to Oracle VM Manager, you cannot register it again, as this may result in duplicate host names or IP addresses.Enter the name of the server pool in the Server Pool Name field.
A server pool name must consist of alphanumeric characters, and must not contain spaces or special characters, except the underscore (_) character. The maximum length of a server pool name is 200 characters.
Select whether to enable HA with the High Availability Mode check box. To use HA, you must enable HA in the server pool, and on each virtual machine. For information about HA, see Enabling High Availability (HA). For more information on how to set up HA prerequisites, see the Oracle VM Server User's Guide.
Enter the following information on the Oracle VM Server in the Server Details box:
Server Host/IP
Enter the host name, or IP address of the Oracle VM Server, for example:
192.168.2.20
or
hostname.example.com
Server Name
Enter a name for the Oracle VM Server. This must be unique.
An Oracle VM Server name must consist of alphanumeric characters, and must not contain spaces or special characters, except the underscore (_) character. The maximum name length is 200 characters.
Server Agent Password
Enter the password to access Oracle VM Agent installed on the Oracle VM Server.
Select the checkbox for each role the Oracle VM Server should perform in the server pool:
Server Pool Master
Utility Server
Virtual Machine Server
If you select Utility Server, you must enter the Oracle VM Server login credentials in the Utility Server Username and Utility Server Password fields. The user must have read/write privileges for the /OVS folder.
Location
The location of the Oracle VM Server. For example, Server Room 1.
Description
A description of the Oracle VM Server.
To test the connection to the Oracle VM Server click Test Connection. If the information is incorrect, or the Oracle VM Server is not available, you cannot add it to the server pool.
When you have entered the information about the Oracle VM Server, click Add. The Oracle VM Server is added to the server pool and listed in the table at the bottom of the screen. You can select it, and then edit it or delete it with the Edit and Delete buttons.
To add more Oracle VM Servers to the server pool, enter the parameters for each Oracle VM Server, and click Add.
After adding the Oracle VM Server, click Next to proceed to the next page.
On the User Information page, select the users from the Non-Administration User Information table for which you want to grant access to the server pool. Users with the Administrator role are automatically granted access to the server pool.
To add new users, see Creating a User. To change a user role, see Changing a Role.
After adding users, click Next to proceed to the next page.
On the Confirmation page, confirm the information you have entered for the server pool. Click Confirm to create the server pool.
The Server Pools page is displayed and the new server pool is listed in the Server Pools table.
You can change the server pool name, check HA infrastructure and enable or disable HA. You can also edit the servers in a server pool, and add or remove users.
Figure 3-6 Editing Server Pool Page Links
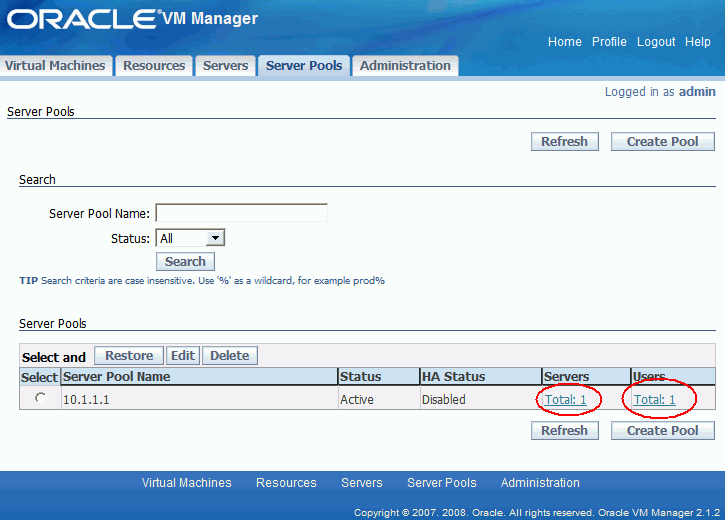
To edit a server pool:
Select the server pool in the Server Pools table and click Edit. The Edit Server Pool page is displayed.
Change the server pool name in the Server Pool Name field.
An Oracle VM Server name must consist of alphanumeric characters, and must not contain spaces or special characters, except the underscore (_) character. The maximum name length is 200 characters.
To check the HA infrastructure click Check in the High Availability Infrastructure field.
Enable or disable HA with the Enable High Availability check box.
Click OK or Apply to save your changes.
To edit the servers in a server pool, click the Servers link in the Server Pools table. For more information, refer to Chapter 4, "Managing Servers".
To add or remove users from the server pool:
Click the Users link in the Server Pools table. The Edit User Information for the Server Pool screen is displayed.
Select the users from the Non-Administration User Information table for which you want to grant access to the server pool. Users with the Administrator role are automatically granted access to the server pool. Click Apply.
To add new users, see Creating a User. To change a user role, see Changing a Role.
To search server pools, perform the following:
Enter the server pool name in the Server Pool Name field. Use % as a wildcard. All available server pools are displayed if you leave the Server Pool Name field empty.
Select the server pool status in the Status drop down. The server pool status reflects the status of the Server Pool Master.
Active
The server pool is available.
Inactive
The server pool is not available.
Click Search. The search results are displayed in the Server Pools table.
If the server pool data on the server pool master is damaged, you can restore this data by synchronizing it with the data from the Oracle VM Manager database.
Note:
When you restore a server pool, all the data stored in the server pool master will be deleted, and will be synchronized with the latest information from the Oracle VM Manager database.To restore a server pool, select it, and click Restore.
You can set up HA in Oracle VM to guarantee the availability of virtual machines if the Virtual Machine Server they are running on fails or restarts. When a Virtual Machine Server is restarted or shut down, the virtual machines running on it are either restarted on, or migrated to, another Virtual Machine Server.
You manage HA with Oracle VM Manager. To implement HA, you must create a cluster of Virtual Machine Servers in a server pool and have them managed by Oracle VM Manager. HA cannot be implemented with Oracle VM Server alone.
To use HA, you must first enable HA on the server pool, then on all virtual machines, as shown in Figure 3-8, "Enabling HA". If you enable HA in the server pool and then for virtual machines, when a Virtual Machine Server is shut down or fails, the virtual machines are migrated or restarted on another available Virtual Machine Server. HA must be enabled for both the server pool and for virtual machines. If HA is not enabled for both, HA is disabled.
If HA is enabled, when you restart, shut down, or delete the Virtual Machine Server in Oracle VM Manager, you are prompted to migrate the running virtual machines to another available Virtual Machine Server. If you do not migrate the running virtual machines, Oracle VM Agent attempts to find an available Virtual Machine Server on which to restart the virtual machines. The Virtual Machine Server is selected using the preferred server setting for the server pool when you create a virtual machine in Oracle VM Manager:
Auto selects an available Virtual Machine Server.
Manual selects an available preferred Virtual Machine Server.
If you do not select a preferred server when creating a virtual machine in Oracle VM Manager, Auto is set as the default.
If there is no preferred Virtual Machine Server or Virtual Machine Server available, the virtual machines shut down (Power Off) and are restarted when a Virtual Machine Server becomes available.
If the Server Pool Master fails, HA also fails for the Virtual Machine Servers running in that server pool.
The possible HA scenarios are:
If you shut down or restart a Virtual Machine Server in Oracle VM Manager, you are prompted which virtual machines to migrate to another available Virtual Machine Server. Any virtual machines which are not migrated, are restarted on an available Virtual Machine Server.
If you shut down or restart a Virtual Machine Server at the Oracle VM Server command-line, Oracle VM Agent restarts the virtual machines on an available Virtual Machine Server.
If a Virtual Machine Server fails, all running virtual machines are restarted automatically on another available Virtual Machine Server.
If a Virtual Machine Server fails and no other Virtual Machine Servers are available, all running virtual machines are restarted when a Virtual Machine Server becomes available.
In all the above scenarios, if any virtual machines running on the Virtual Machine Server are not HA-enabled, they are shut down (Powered Off).
Figure 3-9 shows a Virtual Machine Server failing and the virtual machines restarting on other Virtual Machine Servers in the server pool.
Figure 3-9 HA in Effect for a Virtual Machine Server Failure
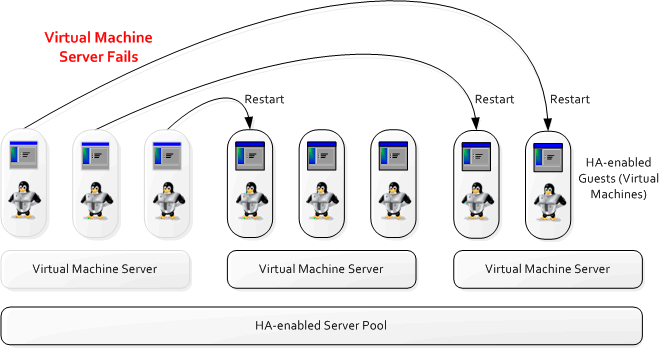
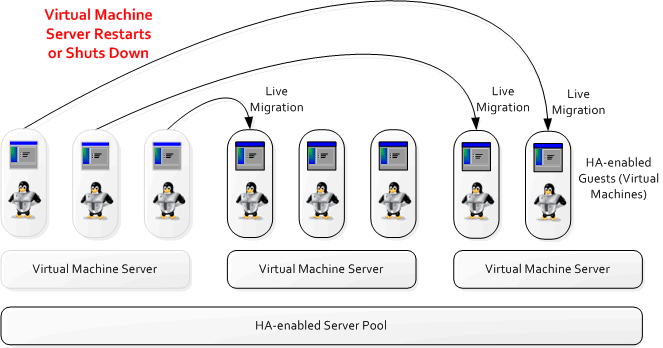
Figure 3-10 shows a Virtual Machine Server restarting or shutting down and the virtual machines migrating to other Virtual Machine Servers in the server pool.
Figure 3-10 HA in Effect for a Virtual Machine Server Restart or Shut Down
To delete a server pool, perform the following:
On the Server Pools page, select the server pool you want to delete, and click Delete.
On the Delete Confirmation page, select Remove all the working directories from the server pool if you want to delete all the related directories. If you do not select this option, only the server pool data is removed from the database, while the relevant directories and files of the server pool remain on the server. Select Force Remove to force the removal of the servers if one or more servers are unavailable.
Caution:
After you delete all the directories, all the servers and virtual machines on the server pool are then deleted as well. Ensure that the server pool is no longer in use before deleting it.