| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for Microsoft Active Directory User Management Release 9.1.1 Part Number E11197-07 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Identity Manager Connector Guide for Microsoft Active Directory User Management Release 9.1.1 Part Number E11197-07 |
|
|
View PDF |
The procedure to deploy the connector can be divided into the following stages:
Note:
Some of the procedures described in this chapter are meant to be performed on the target system. The minimum permissions required to perform these procedures depends on the target system that you are using:If the target system is Microsoft Active Directory, then the permissions required are those assigned to members of the Domain Admins group.
If the target system is Microsoft ADAM, then the permissions required are those assigned to members of the Administrators group.
Preinstallation information is divided across the following sections:
This section contains the following topics:
The contents of the connector installation media directory are described in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 Files and Directories On the Installation Media
| File in the Installation Media Directory | Description |
|---|---|
|
configuration/ActiveDirectory-CI.xml |
This XML file contains configuration information that is used during the connector installation process. |
|
lib/xliActiveDirectory.jar |
This JAR file contains the class files required for provisioning. During connector installation, this file is copied into the following directory: OIM_HOME/xellerate/JavaTasks |
|
lib/xliADRecon.jar |
This JAR file contains the class files required for reconciliation. During connector installation, this file is copied into the following directory: OIM_HOME/xellerate/ScheduleTask |
|
Files in the resources directory |
Each of these resource bundles contains language-specific information that is used by the connector. During connector installation, these resource bundles are copied into the following directory: OIM_HOME/xellerate/connectorResources Note: A resource bundle is a file containing localized versions of the text strings that are displayed on the Administrative and User Console. These text strings include GUI element labels and messages. |
|
scripts/ProvTerminalServiceAttr.vbs |
This VBScript file is used to set values for Terminal Services Profile fields of the target system during provisioning operations. This script is called by the Remote Manager. While performing the procedure described in "Installing the Remote Manager", you copy this file into a directory on the target system host computer. |
|
scripts/ReconTerminalServiceAttr.vbs |
This VBScript file is used to fetch values from Terminal Services Profile fields of the target system during reconciliation runs. This script is called by the Remote Manager. While performing the procedure described in "Installing the Remote Manager", you copy this file into a directory on the target system host computer. |
|
test/config/config.properties |
This file is used to set input test data for the connector testing utility. |
|
test/config/log.properties |
This file is used to set log messages that must be displayed on the console when you run the connector testing utility. |
|
test/lib/xlapiclient.ear |
This EAR file contains the JAR files required to run the testing utility for Oracle Identity Manager running on IBM WebSphere Application Server. |
|
test/scripts/runADTest.bat test/scripts/runADtest.sh |
These scripts are used to run the testing utility. |
|
test/scripts/wsapiclient.cmd |
This file is used by the testing utility if Oracle Identity Manager is running on IBM WebSphere Application Server. |
|
xml/ActiveDirectory-ConnectorConfig.xml |
This XML file contains definitions for the connector components. These components include the following:
|
Note:
The files in the test directory are used only to run tests on the connector by using the testing utility. The Diagnostic Dashboard is an alternative to the testing utility. Chapter 5, "Testing the Connector" describes both testing options.You might have a deployment of an earlier release of the connector. While deploying the latest release, you might want to know the release number of the earlier release. To determine the release number of the connector that has already been deployed:
In a temporary directory, extract the contents of the following JAR file:
OIM_HOME/xellerate/JavaTasks/xliActiveDirectory.jar
Open the Manifest.mf file in a text editor. The Manifest.mf file is one of the files bundled inside the xliActiveDirectory.jar file.
In the Manifest.mf file, the release number of the connector is displayed as the value of the Version property.
Preinstallation on the target system involves performing the procedure described in the following section.
Oracle Identity Manager requires a target system user account to access the target system during reconciliation and provisioning operations. You provide the credentials of this user account while performing the procedure described in "Configuring the IT Resource for the Target System".
In Microsoft Active Directory
You can use a Microsoft Windows 2003 Server (Domain Controller) administrator account. Alternatively, you can create a user account and assign the minimum required rights to the user account.
Note:
If you want to enable the reconciliation of deleted target system records, then you must use an administrator account.To create the Microsoft Active Directory user account for connector operations:
See Also:
Microsoft Active Directory documentation for detailed information about performing this procedureCreate a group (for example, OIMGroup) on the target system. While creating the group, select Security Group as the group type and as Global or Universal as the group scope.
Make this group a member of the Account Operators group.
Assign all read permissions to this group.
Note:
You assign read permissions on the Security tab of the Properties dialog box for the user account. This tab is displayed only in Advanced Features view. To switch to this view, select Advanced Features from the View menu on the Microsoft Active Directory console.Create a user (for example, OIMUser) on the target system.
Make the user a member of the group (for example, OIMGroup) created in Step 1.
In Microsoft ADAM
To create the Microsoft ADAM user account for connector operations:
See Also:
Microsoft ADAM documentation for detailed information about these stepsCreate a user account in Microsoft ADAM.
Set a password for the user account.
Enable the user account by setting the msDS-UserAccountDisabled field to false.
Enter a value in the userPrincipalName field.
The value that you provide must be in the user_name@domain_name format, for example, OIMuser@mydomain.com.
Add the distinguished name of the user to the Administrators group.
Installation steps are divided across the following sections:
Installation on Oracle Identity Manager consists of the following procedures:
Note:
In this guide, the term Connector Installer has been used to refer to the Connector Installer feature of the Administrative and User Console.To run the Connector Installer:
Copy the contents of the connector installation media directory into the following directory:
OIM_HOME/xellerate/ConnectorDefaultDirectory
Log in to the Administrative and User Console by using the user account described in the "Creating the User Account for Installing Connectors" section of Oracle Identity Manager Administrative and User Console Guide.
Click Deployment Management, and then click Install Connector.
From the Connector List list, select ActiveDirectory 9.1.1. This list displays the names and release numbers of connectors whose installation files you copy into the default connector installation directory:
OIM_HOME/xellerate/ConnectorDefaultDirectory
If you have copied the installation files into a different directory, then:
In the Alternative Directory field, enter the full path and name of that directory.
To repopulate the list of connectors in the Connector List list, click Refresh.
From the Connector List list, select ActiveDirectory 9.1.1.
Click Load.
To start the installation process, click Continue.
The following tasks are performed, in sequence:
Configuration of connector libraries
Import of the connector XML files (by using the Deployment Manager)
Compilation of adapters
On successful completion of a task, a check mark is displayed for the task. If a task fails, then an X mark and a message stating the reason for failure is displayed. Depending on the reason for the failure, make the required correction and then perform one of the following steps:
Retry the installation by clicking Retry.
Cancel the installation and begin again from Step 0.
If all three tasks of the connector installation process are successful, then a message indicating successful installation is displayed. In addition, a list of steps that you must perform after the installation is displayed. These steps are as follows:
Ensuring that the prerequisites for using the connector are addressed
Note:
At this stage, run the PurgeCache utility to load the server cache with content from the connector resource bundle in order to view the list of prerequisites. See "Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache" for information about running the PurgeCache utility.There are no prerequisites for some predefined connectors.
Configuring the IT resource for the connector
Record the name of the IT resource displayed on this page. The procedure to configure the IT resource is described later in this guide.
Configuring the scheduled tasks
Record the names of the scheduled tasks displayed on this page. The procedure to configure these scheduled tasks is described later in this guide.
When you run the Connector Installer, it copies the connector files and external code files to destination directories on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer. These files are listed in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2 Files Copied During Connector Installation
| File in the Connector Installation Media Directory | Destination Directory |
|---|---|
|
lib/xliActiveDirectory.jar |
OIM_HOME/xellerate/JavaTasks |
|
lib/xliADRecon.jar |
OIM_HOME/xellerate/ScheduleTask |
|
Files in the resources directory |
OIM_HOME/xellerate/connectorResources |
Installing the Connector in an Oracle Identity Manager Cluster
While installing the connector in a clustered environment, you must copy all the JAR files and the contents of the resources directory into the destination directories on each node of the cluster. See Table 2-2 for information about the files that you must copy and their destination locations on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer.
Table 2-3 lists the files that you must copy to the Oracle Identity Manager host computer.
Note:
The directory paths given in the first column of this table correspond to the location of the connector files on the installation media. See "Files and Directories On the Installation Media" for more information about these files.
If a particular destination directory does not already exist on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer, then create it.
The ldapbp.jar file is used by the connector to enable LDAP-based search of user records on the target system. You must download this file from the Sun Web site and copy it into the ThirdParty directory as follows:
Log on the Sun Web site at
Click Download JNDI 1.2.1 & More.
From the table on the page that is displayed, select and download the ldap-1_2_4.zip file.
Extract the contents of the ZIP file and copy the ldapbp.jar file from the lib directory to the OIM_HOME/xellerate/ThirdParty directory.
Note:
In an Oracle Identity Manager cluster, copy this JAR file into the ThirdParty directory on each node of the cluster.The IT resource for the target system is created during connector installation. This IT resource contains connection information about the target system. Oracle Identity Manager uses this information during reconciliation and provisioning.
You must specify values for the parameters of the ADITResource IT resource as follows:
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
Expand Resource Management.
Click Manage IT Resource.
In the IT Resource Name field on the Manage IT Resource page, enter ADITResource and then click Search. Figure 2-1 shows the Manage IT Resource page.
Click the edit icon for the IT resource.
From the list at the top of the page, select Details and Parameters.
If you are using a Remote Manager to provision to or reconcile from the Terminal Services Profile fields, then select the name of the Remote Manager.
Specify values for the parameters of the IT resource. Figure 2-2 shows the Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters page.
Figure 2-2 Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters Page

Table 2-4 describes each parameter of the IT resource.
Table 2-4 Parameters of the IT Resource for the Target System
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
ADAM Lockout Threshold Value |
If the target system is Microsoft ADAM, then enter the number of unsuccessful login attempts after which a user's account must be locked. If the target system is Microsoft Active Directory, then you need not enter a value. The value set in Microsoft Active Directory is automatically determined and used. Default value: |
|
This parameter holds the name of the lookup definition in which the names of group fields are stored after group lookup synchronization. Value: This value is the same as that of the Lookup Code Name attribute of the AD Group Lookup Recon scheduled task, which is discussed in "Scheduled Tasks for Lookup Field Synchronization". Note: You must not change the value of this parameter. |
|
|
Admin FQDN |
Enter the fully qualified domain name of the user account that you create by performing the procedure described in "Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations". You can use any one of the following formats to enter the domain name:
Sample values:
|
|
Admin Password |
Enter the password of the user account that you create by performing the procedure described in "Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations". |
|
AtMap ADUser |
This parameter holds the name of the lookup definition for user field mappings between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. This lookup definition is used during user provisioning operations. The default value of this parameter is If you are using Microsoft ADAM, then change the value to |
|
Enter the number of the port at which SSL is running on the target system host computer. Sample values: For Microsoft Active Directory:
For Microsoft ADAM:
The Use SSL parameter is described later in this table. This parameter is also mentioned in "Configuring SSL for Microsoft Active Directory". |
|
|
This parameter holds the name of the lookup definition that stores Terminal Services Profile field mappings between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. Value: Note: You must not change the value of this parameter. If you want to use Environment, Remote Control, or Sessions fields for provisioning operations, then see "Adding New Fields for Provisioning". |
|
|
Enter the full path and name of the ProvTerminalServiceAttr.vbs script file on the target system host computer. Sample value: RM_HOME\scripts\ProvTerminalServiceAttr.vbs See "Installing the Remote Manager" for more information. Note:
|
|
|
Root Context |
Enter the base DN on which reconciliation of deleted user data and provisioning are to be carried out. Sample values:
Note: You must enter a value for this parameter. |
|
Server Address |
Enter the host name or IP address of the Microsoft Windows computer (target system host computer) on which Microsoft Active Directory is installed. Sample values:
|
|
Invert Display Name |
Enter For example, if you enter Default value: Note:
|
|
Use SSL |
Enter Default value: Note: It is recommended that you configure SSL to secure communication with the target system. You must configure SSL if you want to set or change user passwords during provisioning operations. Refer to "Configuring SSL for Microsoft Active Directory" for information about enabling SSL. |
|
isADAM |
Enter Enter |
|
isLookupDN |
Use this parameter as follows to specify whether you want the Lookup.ADReconciliation.GroupLookup and Lookup.ADReconciliation.Organization lookup definitions to be populated with distinguished names (DNs) or relative DNs during lookup field synchronization:
Default value: Note: The value of this parameter is used during lookup field synchronization, provisioning, and reconciliation. After a lookup field synchronization run, you must not change the value of this parameter. This point is also mentioned in "Guidelines on Using the Connector". |
|
In Microsoft Active Directory, a user account can have other user accounts defined as its leaf nodes. Use the isUserDeleteLeafNode parameter to configure one of the following events to take place when a Delete User provisioning operation is carried out on a user account that has leaf nodes:
Default value: Note: This parameter is not used for Microsoft ADAM. You must not change the default value if the target system is Microsoft ADAM. |
|
|
Allow Password Provisioning |
Enter
Enter |
|
AtMap ADGroup |
Enter the name of the lookup definition that stores field mappings used for group provisioning: For Microsoft Active Directory: For Microsoft ADAM: |
|
UPN Domain |
Enter the name of the domain in which you want to provision and reconcile users. Sample value: On the Administrative and User Console, the User ID field is prepopulated with the User Login value from the OIM User form. In addition, the User Principal Name field is prepopulated with the concatenated value of the User ID field and UPN Domain parameter value separated by the at sign (@). For example, if you enter If required, you can change the User ID part of the User Principal Name field value during provisioning operations. |
|
Target Locale: TimeZone |
Enter the time zone of the target system. For example, enter |
To save the values, click Update.
This section discusses the following topics:
The Remote Manager enables you to include the Terminal Services Profile fields of the target system in reconciliation and provisioning operations.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you want to include Terminal Services Profile fields in reconciliation and provisioning operations.
In this guide, the directory in which you install the Remote Manager is referred to as RM_HOME.
To install the Remote Manager:
The Remote Manager installation files are shipped along with the Oracle Identity Manager installation files. You can install the Remote Manager on any computer that is a part of the domain. Depending on the application server that you use, perform the procedure to install the Remote Manager by following the instructions given in one of the following guides:
Oracle Identity Manager Installation and Configuration Guide for Oracle WebLogic Server
Oracle Identity Manager Installation and Configuration Guide for IBM WebSphere Application Server
Oracle Identity Manager Installation and Configuration Guide for JBoss Application Server
Oracle Identity Manager Installation and Configuration Guide for Oracle Application Server
Copy the following JAR files into the RM_HOME\xlremote\JavaTasks directory:
OIM_HOME\xellerate\lib\xlVO.jar
OIM_HOME\xellerate\lib\xlScheduler.jar
OIM_HOME\xellerate\lib\xlAPI.jar
OIM_HOME\xellerate\JavaTasks\xliActiveDirectory.jar
OIM_HOME\xellerate\ScheduleTask\xliADRecon.jar
Copy the ReconTerminalServiceAttr.vbs and ProvTerminalServiceAttr.vbs files from the OIM_HOME/XLIntegrations/ADUM/scripts directory to any directory that you create inside the RM_HOME directory.
Note:
Ensure that the directory into which you copy the scripts has the required read and write permissions for the target system user account used by Oracle Identity Manager. This user account is described in "Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations".
Ensure that the RM_HOME directory is secured using Microsoft Windows best practices. Only the target system user account for Oracle Identity Manager must have permissions to access the RM_HOME directory.
Use the following script to start the Remote Manager:
RM_HOME\xlremote\remotemanager.bat
Note the Remote Manager service name and URL. These values are displayed in the Remote Manager command window. You will need these values while creating the IT resource for the Remote Manager. The default values are RManager and rmi://HOST_NAME:12346. For example, for a Remote Manager running on ten.mydomain.com, the default values will be RManager and rmi://ten.mydomain.com:12346.
To enable logging in the Remote Manager:
Add the following lines in the RM_HOME\xlremote\config\log.properties file:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=LOG_LEVEL
In these lines, replace LOG_LEVEL with the log level that you want to set.
For example:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=INFO
In the log.properties file, use the following parameter to specify the name and location of the file in which you want log information to be recorded:
log4j.appender.logfile.File
To enable client-side authentication for the Remote Manager:
Open the RM_HOME/xlremote/config/xlconfig.xml file in a text editor.
Set the ClientAuth property to true as follows:
<ClientAuth>true</ClientAuth>
Ensure that the RMIOverSSL property is set to true as follows:
<RMIOverSSL>true</RMIOverSSL>
Perform Steps 2 through 3 in the OIM_HOME/config/xlconfig.xml file.
Postinstallation steps are divided across the following sections:
Configuring Oracle Identity Manager involves performing the following procedures:
Note:
In a clustered environment, you must perform these procedures on each node of the cluster.While you deploy the connector, the resource bundles are copied from the resources directory on the installation media into the OIM_HOME/xellerate/connectorResources directory. Whenever you add a new resource bundle in the connectorResources directory or make a change in an existing resource bundle, you must clear content related to connector resource bundles from the server cache.
To clear content related to connector resource bundles from the server cache:
In a command window, change to the OIM_HOME/xellerate/bin directory.
Note:
You must perform Step 1 before you perform Step 2. An exception is thrown if you run the command described in Step 2 as follows:OIM_HOME/xellerate/bin/BATCH_FILE_NAME
Enter one of the following commands:
On Microsoft Windows:
PurgeCache.bat ConnectorResourceBundle
On UNIX:
PurgeCache.sh ConnectorResourceBundle
Note:
You can ignore the exception that is thrown when you perform Step 2. This exception is different from the one mentioned in Step 1.In this command, ConnectorResourceBundle is the content category that you must delete from the server cache.
See Also:
The following file for information about content categories:OIM_HOME/config/xlconfig.xml
When you enable logging, Oracle Identity Manager automatically stores in a log file information about events that occur during the course of provisioning and reconciliation operations. To specify the type of event for which you want logging to take place, you can set the log level to one of the following:
ALL
This level enables logging for all events.
DEBUG
This level enables logging of information about fine-grained events that are useful for debugging.
INFO
This level enables logging of messages that highlight the progress of the application at a coarse-grained level.
WARN
This level enables logging of information about potentially harmful situations.
ERROR
This level enables logging of information about error events that may allow the application to continue running.
FATAL
This level enables logging of information about very severe error events that could cause the application to stop functioning.
OFF
This level disables logging for all events.
The file in which you set the log level and the log file path depend on the application server that you use:
Oracle WebLogic Server
To enable logging:
Add the following line in the OIM_HOME/xellerate/config/log.properties file:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=LOG_LEVEL
In this line, replace LOG_LEVEL with the log level that you want to set.
For example:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=INFO
After you enable logging, the log information is displayed on the server console.
IBM WebSphere Application Server
To enable logging:
Add the following line in the OIM_HOME/xellerate/config/log.properties file:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=LOG_LEVEL
In these line, replace LOG_LEVEL with the log level that you want to set.
For example:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=INFO
After you enable logging, log information is written to the following file:
WEBSPHERE_HOME/AppServer/logs/SERVER_NAME/SystemOut.log
JBoss Application Server
To enable logging:
In the JBOSS_HOME/server/default/conf/log4j.xml file, locate or add the following lines:
<category name="OIMCP.ADCS">
<priority value="LOG_LEVEL"/>
</category>
In the second XML code line of each set, replace LOG_LEVEL with the log level that you want to set. For example:
<category name="OIMCP.ADCS"> <priority value="INFO"/> </category>
After you enable logging, log information is written to the following file:
JBOSS_HOME/server/default/log/server.log
Oracle Application Server
To enable logging:
Add the following line in the OIM_HOME/xellerate/config/log.properties file:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=LOG_LEVEL
In this line, replace LOG_LEVEL with the log level that you want to set.
For example:
log4j.logger.OIMCP.ADCS=INFO
After you enable logging, log information is written to the following file:
ORACLE_HOME/opmn/logs/default_group~home~default_group~1.log
Suppose you have set up multiple, replicated installations of the target system for high availability. You can use the Lookup.AD.BackupServers lookup definition to ensure that if the primary target system installation becomes unavailable, then Oracle Identity Manager switches to one of the secondary target system installations. The Lookup.AD.BackupServers lookup definition is one of the lookup definitions created when you deploy the connector.
For a single primary installation, you can have any number of secondary installations. In addition, if you configure the connector to work with multiple primary installations, then you can specify secondary installations for each primary installation.
To use the Lookup.AD.BackupServers lookup definition, open it in the Design Console and enter code key and decode values for each combination of primary and secondary target system installation.
See Also:
Oracle Identity Manager Design Console Guide for information about working with lookup definitionsTable 2-5 shows samples entries for the Lookup.AD.BackupServers lookup definition.
Table 2-5 Samples Entries for the Lookup.AD.BackupServers Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode |
|---|---|
|
172.20.55.64 |
172.20.55.65 |
|
172.20.55.64 |
172.20.55.66 |
|
172.20.55.97 |
172.20.55.98 |
In this table, the first two entries represent two secondary installations (172.20.55.65 and 172.20.55.66) for one primary installation (172.20.55.64). The third entry shows a one-to-one combination of primary (172.20.55.97) and secondary (172.20.55.98) installations.
Postinstallation on the target system consists of the following procedure.
In Microsoft Active Directory, the "Passwords must meet complexity requirements" policy setting is used to enable or disable password policies.
The procedure that you must perform depends on whether or not you want to achieve either or both of the following objectives:
Enable password policies
Configure SSL between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system
Note:
The procedure to configure SSL is discussed later in this guide.Suppose there is a password policy on the target system for enforcing that the password field of user accounts is never left empty. At the same time, suppose you do not configure SSL. Under these conditions, the target system would reject provisioning operations that leave the password field empty. Therefore, you would not be able to perform such provisioning operations from Oracle Identity Manager. To enable provisioning operations under these conditions, you must disable password policies on the target system.
If you configure SSL and you want to enable both the default Microsoft Windows password policy and a custom password policy, then you must enable the "Passwords must meet complexity requirements" policy setting.
To enable or disable the "Passwords must meet complexity requirements" policy setting:
Note:
If you install Microsoft ADAM in a domain controller then it acquires all the policies of Microsoft Active Directory installed in the same domain controller. If you install Microsoft ADAM in a workgroup, then the local system policies are applied.On the Microsoft Windows computer hosting the target system, click the Start menu, Programs, Administrative Tools, and Domain Security Policy.
Select Security Settings, expand Account Policies, and then click Password Policy.
Double-click Passwords must meet complexity requirements.
In the Password Must Meet Complexity Requirements Properties dialog box, select Define this policy setting and then select:
Enabled, if you want to enable password policies
Disable, if you do not want to enable password policies
Click OK.
Restart the target system.
This section discusses the following topics:
Note:
The information in this section does not apply to Microsoft ADAM.
If the target system is Microsoft Active Directory, then perform this procedure only if you want to use the Terminal Services Profile fields of the target system during reconciliation and provisioning operations.
To create the IT resource for the Remote Manager:
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
Expand Resource Management.
Click Create IT Resource.
On the Step 1: Provide IT Resource Information section, perform the following steps:
IT Resource Name: Enter a name for the IT resource.
IT Resource Type: Select Remote Manager from the IT Resource Type list.
Remote Manager: Do not enter a value in this field.
Click Continue. Figure 2-3 shows the IT resource values added on the Create IT Resource page.
Figure 2-3 Step 1: Provide IT Resource Information
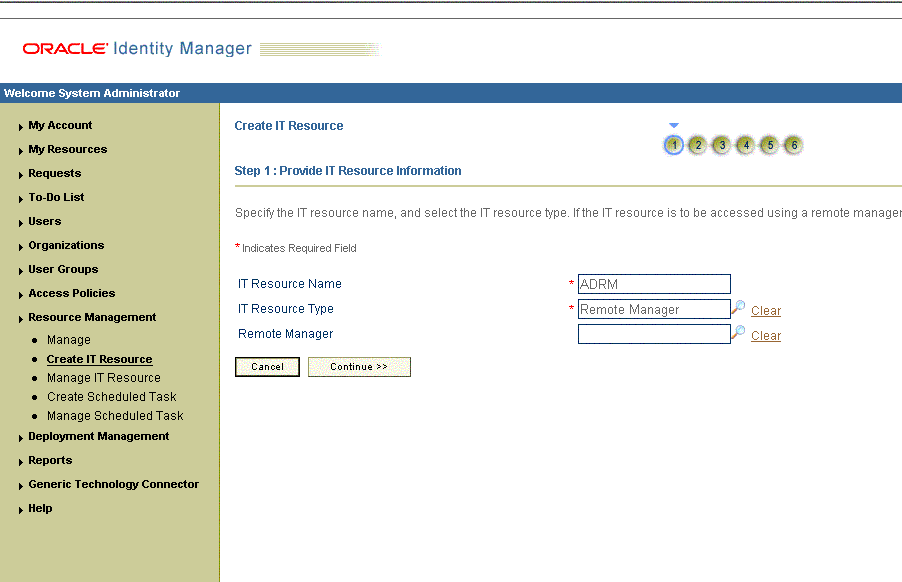
On the Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values section, specify values for the parameters of the IT resource and then click Continue. Figure 2-4 shows the Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values section.
Figure 2-4 Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values

Table 2-6 provides information about the parameters of the IT resource.
Table 2-6 Parameters of the IT Resource for the Remote Manager
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
service name |
Enter a name for the Remote Manager. Sample value: |
|
url |
Enter the IP address of the target system host computer and the port number at which the Remote Manager is listening. Sample value: |
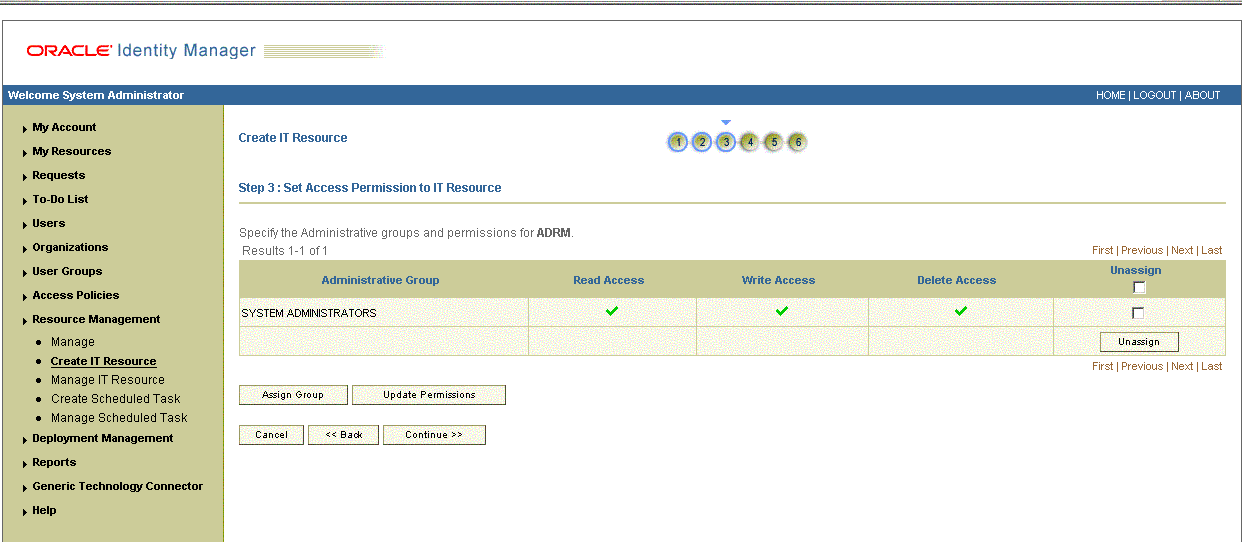
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, the SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORS group is displayed by default in the list of groups that have Read, Write, and Delete permissions on the IT resource that you are creating.
Note:
This step is optional.If you want to assign groups to the IT resource and set access permissions for the groups, then:
Click Assign Group.
For the groups that you want to assign to the IT resource, select Assign and the access permissions that you want to set. For example, if you want to assign the ALL USERS group and set the Read and Write permissions to this group, then you must select the respective check boxes in the row, as well as the Assign check box, for this group.
Click Assign.
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, if you want to modify the access permissions of groups assigned to the IT resource, then:
Note:
This step is optional.
You cannot modify the access permissions of the SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORS group. You can modify the access permissions of only other groups that you assign to the IT resource.
Click Update Permissions.
Depending on whether you want to set or remove specific access permissions for groups displayed on this page, select or deselect the corresponding check boxes.
Click Update.
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, if you want to unassign a group from the IT resource, then:
Note:
This step is optional.
You cannot unassign the SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORS group. You can unassign only other groups that you assign to the IT resource.
Select the Unassign check box for the group that you want to unassign.
Click Unassign.
Click Continue. Figure 2-5 shows the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page.
Figure 2-5 Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource
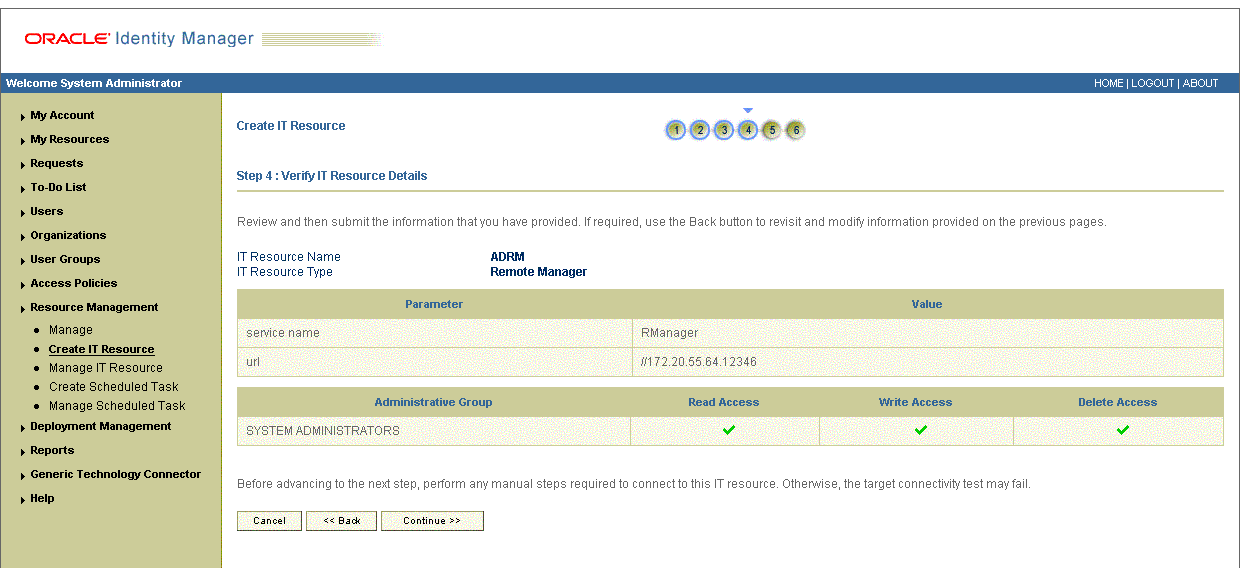
On the Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details page, review the information that you provided on the first, second, and third pages. If you want to make changes in the data entered on any page, click Back to revisit the page and then make the required changes.
To proceed with the creation of the IT resource, click Continue. Figure 2-6 shows Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details page.
Figure 2-6 Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details
The Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result page displays the results of a connectivity test that is run using the IT resource information. If the test is successful, then click Create. If the test fails, then you can perform one of the following steps:
Click Back to revisit the previous pages and then make corrections in the IT resource creation information.
Click Cancel to stop the procedure, and then begin from the first step onward.
Proceed with the creation process by clicking Create. You can fix the problem later, and then rerun the connectivity test by using the Diagnostic Dashboard.
Note:
If no errors are encountered, then the label of the button is Create, not Continue.Figure 2-7 shows the Step 5: Resource Connection Result page.
Figure 2-7 Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result

Click Finish. Figure 2-8 shows the IT Resource Created Page
To configure Oracle Identity Manager to trust the Remote Manager:
From the computer hosting the Remote Manager, copy the RM_HOME/xlremote/config/xlserver.cert file to a temporary directory on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer.
Note:
The server certificate in the OIM_HOME directory is also named xlserver.cert. Ensure that you do not overwrite that certificate.To import the certificate by using the keytool utility, run the following command:
JAVA_HOME/jre/bin/keytool -import -alias ALIAS -file RM_CERT_LOCATION/xlserver.cert -keystore OIM_HOME/xellerate/config/.xlkeystore -storepass PASSWORD
In the preceding command, replace:
JAVA_HOME with the location of the Java directory for your application server.
ALIAS with an alias for the certificate in the store.
RM_CERT_LOCATION with the full path of the temporary directory where you copied the certificate.
PASSWORD with the password of the keystore.
Copy the OIM_HOME/xellerate/config/xlserver.cert file to a temporary directory on the Remote Manager host computer.
To import the certificate by using the keytool utility on the Remote Manager host computer, run the following command:
JAVA_HOME/jre/bin/keytool -import -alias ALIAS -file OIM_CERT_LOCATION/xlserver.cert -keystore RM_HOME/xlremote/config/.xlkeystore -storepass PASSWORD
In the preceding command, replace:
JAVA_HOME with the location of the Java directory for your application server.
ALIAS with an alias for the certificate in the store.
OIM_CERT_LOCATION with the full path of the temporary directory where you copied the certificate.
PASSWORD with the password of the keystore.
Note:
It is recommended that you follow security best practices and change the default passwords used for the Remote Manager keystore. To change the Remote Manager keystore password, follow the instructions given in Oracle Identity Manager Installation and Configuration Guide for your application server.To verify that the Remote Manager is running:
Use the following script to start the Remote Manager:
RM_HOME\xlremote\remotemanager.bat
Log in to the Design Console.
Expand Administration, and double-click Remote Manager.
Search for and open the Remote Manager that you have created.
Click the Refresh icon. The screen displays details of the Remote Manager that you have configured. The "running" check box should be selected for the Remote Manager. This implies that the status of the Remote Manager is active.
To configure SSL communication between Oracle Identity Manager and Microsoft Active Directory, you must perform the following tasks:
To install Certificate Services on the target system host computer:
Note:
Before you begin installing Certificate Services, you must ensure that Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed on the target system host computer.Insert the operating system installation media into the CD-ROM or DVD drive.
Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel.
Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
Click Add/Remove Windows Components.
Select Certificate Services.
In the Windows Components Wizard, follow the instructions to start Certificate Services.
Note:
While providing input to the wizard, select Enterprise root CA as the CA type. This is required for adding a policy with the Domain Controller template, which is a step that you perform in the next procedure.The target system host computer must have LDAP over SSL (LDAPS) enabled. To enable LDAPS:
On the Active Directory Users and Computers console, right-click the domain node, and select Properties.
Click the Group Policy tab.
Select Default Domain Policy.
Click Edit.
Click Computer Configuration, Windows Settings, Security Settings, and Public Key Policies.
Right-click Automatic Certificate Request Settings, and then select New and Automatic Certificate Request. A wizard is started.
Use the wizard to add a policy with the Domain Controller template.
At the end of this procedure, the certificate is created and LDAPS is enabled on port 636. You can use an LDAP browser utility to verify that LDAPS is working.
Note:
While performing the procedure described in "Configuring the IT Resource for the Target System", you specify the port number as the value of the Port Number parameter.If the Microsoft Active Directory certificate is not issued or certified by a CA, then set it up as a trusted certificate. To do this, you first export the certificate and then import it into the keystore of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer as a trusted CA certificate.
To export the Microsoft Active Directory certificate:
Click Start, Programs, Administrative Tools, and Certification Authority.
Right-click the Certification Authority that you create, and then select Properties.
On the General tab, click View Certificate.
On the Details tab, click Copy To File.
Use the wizard to create a certificate (.cer) file using base-64 encoding.
To import the target system certificate into the certificate store of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer:
Note:
All application server releases supported by Oracle Identity Manager release 9.1.0 are supported.In a clustered environment, you must perform this procedure on all the nodes of the cluster.
Copy the target system certificate to the Oracle Identity Manager host computer.
Change to the directory where you copy the certificate file, and then enter a command similar to the following:
keytool -import -alias ALIAS -file CER_FILE -keystore MY_CACERTS -storepass PASSWORD
In this command:
ALIAS is the alias for the certificate (for example, the server name).
CER_FILE is the full path and name of the certificate (.cer) file.
Table 2-7 shows the location of the certificate store for each of the supported application servers.
Table 2-7 Certificate Store Locations
| Application Server | Certificate Store Location |
|---|---|
|
Oracle WebLogic Server |
|
|
IBM WebSphere Application Server |
|
|
JBoss Application Server |
JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/cacerts |
|
Oracle Application Server |
ORACLE_HOME/jdk/jre/lib/security/cacerts |
To confirm whether or not the certificate has been imported successfully, enter a command similar to the following:
keytool -list -alias ALIAS -keystore MY_CACERTS -storepass PASSWORD
For example:
keytool -list -alias MyAlias -keystore C:\mydir\java\jre\lib\security\cacerts -storepass changeit
For a nonclustered configuration of IBM WebSphere Application Server, download the jsse.jar file from the Sun Web site and copy this file into the WEBSPHERE_HOME/java/jre/lib/ext directory.
For a clustered configuration of IBM WebSphere Application Server, download the jnet.jar, jsse.jar, and jcert.jar files from the Sun Web site and copy these files into the WEBSPHERE_HOME/java/jre/lib/ext directory.
To configure SSL communication between Oracle Identity Manager and Microsoft ADAM, you must perform the following tasks:
Note:
Before you begin generating the certificate, you must ensure that Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed on the target system host computer.To generate the certificate in Microsoft ADAM, perform the following procedures:
To submit a request for the certificate:
On the target system host computer, open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
You can use one of the following methods to open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
Use the following URL:
http://localhost/certsrv
Open Control Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click IIS Service.
Expand Web Sites, and then expand Default Web Site.
Right-click CertSrv, and then select Browse.
Click Request a certificate.
Click Advanced certificate request.
Click Create and submit a request to this CA.
On the Advanced Certificate Request page, perform the following actions:
Note:
There are instructions for only some of the fields on this page. For the remaining fields, you can enter values according to your requirements.In the Name field, enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the target system host computer. For example, enter hk128.corp.example.com.
Note:
On your target system installation, if a value is already selected in this field, then you need not change it.You need not enter values in the remaining fields of the Identifying Information region.
Select Store certificate in local computer certificate store.
Select PCKS10 as the format.
In the Friendly name field, enter the FQDN of the target system host computer. For example, enter hk128.corp.example.com.
Click Submit.
When a message asking you to confirm that you want to request a certificate is displayed, click Yes.
To issue the certificate:
On the target system host computer, open Control Panel.
Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Certification Authority.
In the Certification Authority window, expand Administrator and then open Pending Requests.
The request that you created earlier is displayed on the right pane.
Right-click the request, select All Tasks, and then select Issue.
Open the Issued Certificates folder.
The certificate is displayed on the right pane.
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
Expand Web Sites, and then expand Default Web Site.
Right-click CertSrv, and then select Browse.
Click View the status of pending certificate request.
Click the link for the certificate request.
Click Install this certificate.
When a message asking you to confirm that you want to add the certificate is displayed, click Yes.
A message saying that the certificate has been successfully installed is displayed.
To add the certificate to the personal store of the Microsoft ADAM service:
On the target system host computer, use the Run dialog box to run the command for opening the Microsoft Management Console:
mmc
On the Microsoft Management Console, click File and then select Add/Remove Snap-in.
On the Standalone tab of the Add/Remove Snap-in dialog box, click Add.
From the list of snap-ins, select Certificates and then click Add.
In the Certificates snap-in dialog box, select Service account.
In the Select Computer dialog box, select Local computer and then click Next.
From the Service account list in the Certificates snap-in dialog box, select the Microsoft ADAM service instance and then click Finish.
In the Certificates snap-in dialog box, select My user account and then click Finish.
In the Certificates snap-in dialog box, select Computer account and then click Next.
In the Select Computer dialog box, select Local computer and then click Finish.
Click Close, and then click OK.
In the Microsoft Management Console window, expand Certificates - Local Computer, expand Personal, and then open Certificates.
Right-click the certificate that you have added and copy it.
The name of this certificate is the FQDN of the host computer.
Paste the certificate into the following folders:
Personal folder under the Certificates - Service (ADAM_INSTANCE_NAME) on Local Computer folder
Personal folder under the Certificates - Current User folder
To save the changes that you have made to the Microsoft Management Console, click File and then select Save.
To assign the required permissions to the folder containing the certificate key:
In Microsoft Windows Explorer, navigate to the MachineKeys folder. The path to this folder is similar to the following:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeys
Right-click the MachineKeys folder, and then select Properties.
Use the Add button to add the following groups and users:
Administrators
Everyone
NETWORK SERVICE
The user name of the account used to install Microsoft ADAM
SYSTEM
From the Permissions list, select Full Control.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
In Microsoft Windows Explorer, expand the MachineKeys folder and select the certificate key. The time stamp for this certificate key is the date and time at which you created the certificate.
Note:
Refresh the folder if the certificate key that you created is not displayed.Right-click the key, and select Properties.
Use the Add button to add the following groups and users:
Administrators
Everyone
NETWORK SERVICE
The user name of the account used to install Microsoft ADAM
SYSTEM
From the Permissions list, select Full Control.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
To restart the Microsoft ADAM instance:
Open Control Panel.
Double-click Administrative Tools, and then select Services.
In the Services window, right-click the Microsoft ADAM instance and then select Restart.
To test the certificate:
To open the ADAM Tools Command Prompt window on the target system host computer, click Start, Programs, ADAM, and ADAM Tools Command Prompt.
In the ADAM Tools Command Prompt window, enter ldp and then press Enter.
From the Connection menu of the LDAPS dialog box, select Connect.
In the Connect dialog box:
In the Server field, enter the FQDN of the target system host computer.
In the Port field, enter the SSL port number.
Select SSL.
Click OK.
If SSL has been successfully configured, then status messages about the connection are displayed on the right pane of the LDAPS window.
If the Microsoft ADAM certificate is not issued or certified by a CA, then set it up as a trusted certificate. To do this, you first export the certificate and then import it into the keystore of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer as a trusted CA certificate.
To export the Microsoft ADAM certificate:
Open the Microsoft Management Console.
In the Microsoft Management Console window, expand Certificates - Local Computer, expand Personal, and then open Certificates.
Right-click the certificate, select All Tasks, and then select Export.
Use the wizard to create a certificate (.cer) file using base-64 encoding.
To import the target system certificate into the certificate store of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer:
Note:
All application server releases supported by Oracle Identity Manager release 9.1.0 are supported.In a clustered environment, you must perform this procedure on all the nodes of the cluster.
Copy the target system certificate to the Oracle Identity Manager host computer.
Change to the directory where you copy the certificate file, and then enter a command similar to the following:
keytool -import -alias ALIAS -file CER_FILE -keystore MY_CACERTS -storepass PASSWORD
In this command:
ALIAS is the alias for the certificate (for example, the server name).
CER_FILE is the full path and name of the certificate (.cer) file.
Table 2-8 shows the location of the certificate store for each of the supported application servers.
Table 2-8 Certificate Store Locations
| Application Server | Certificate Store Location |
|---|---|
|
Oracle WebLogic Server |
|
|
IBM WebSphere Application Server |
|
|
JBoss Application Server |
JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/cacerts |
|
Oracle Application Server |
ORACLE_HOME/jdk/jre/lib/security/cacerts |
To confirm whether or not the certificate has been imported successfully, enter a command similar to the following:
keytool -list -alias ALIAS -keystore MY_CACERTS -storepass PASSWORD
For example:
keytool -list -alias MyAlias -keystore C:\mydir\java\jre\lib\security\cacerts -storepass changeit
For a nonclustered configuration of IBM WebSphere Application Server, download the jsse.jar file from the Sun Web site and copy this file into the WEBSPHERE_HOME/java/jre/lib/ext directory.
For a clustered configuration of IBM WebSphere Application Server, download the jnet.jar, jsse.jar, and jcert.jar files from the Sun Web site and copy these files into the WEBSPHERE_HOME/java/jre/lib/ext directory.