 Understanding Tax Calculation
Understanding Tax CalculationThis chapter provides an overview of tax calculation and discusses how to:
Estimate the total annual income.
Calculate tax percentages.
View IRPF tax calculation results.
Review and update system information.
Enter payee tax data.
Run legal reports.
View delivered tax elements.
 Understanding Tax Calculation
Understanding Tax CalculationThis section discusses:
Tax calculation.
IRPF calculation overview.
Normalization.
IRPF in the pay process flow.

 Tax Calculation
Tax Calculation
Global Payroll for Spain enables you to manage the official withholding tax, Impuesto sobre la renta de las personas físicas (IRPF). The withholding amount originates from employee income and reductions and depends on which tax regulations are applicable to an employee.
Spain does not have one single set of tax regulations. There are general state tax regulations and four regions with specific tax calculations. Each tax location is known as a Fiscal Territory (Territorios Fiscales). An employee is associated with one fiscal territory depending on where the employee is living and working. Global Payroll for Spain calculates the IRPF for all the fiscal territories:
Hacienda Estatal (state territory).
Hacienda Foral de Navarra.
Hacienda Foral de Alava.
Hacienda Foral de Guipuzcoa.
Hacienda Foral de Vizcaya.
Note. The fiscal territories, Hacienda Foral de Navarra, Hacienda Foral de Alava, Hacienda Foral de Guipuzcoa, and Hacienda Foral de Vizcaya are known as historical territories.
Global Payroll for Spain provides the different calculation rules and setup data for each fiscal territory. Setup data is delivered using tax brackets and calculation variables. You can view and update the tax brackets and other tax data that Global Payroll for Spain delivers.

 IRPF Calculation Overview
IRPF Calculation Overview
To calculate an employee’s withholding percentage, the system:
Estimates the total annual income.
(State territory only) Estimates the social security contribution.
(State territory only). Calculates the available reductions.
These include deductions for dependents, any personal deductions due to age or disability, and any spousal garnishments.
(State territory only). Subtracts the social security contribution and the available reductions from the total annual income.
Note. The annual income for historical territories is reduced if needed by spousal garnishments, which will be the starting point for getting the IRPF percentage.
Calculates the withholding percentage.
The system generates the withholding percentage based on the previous steps. If needed, you may alter this percentage. You can only increase the withholding percentage; you can't enter a lower percentage than that calculated by the system.
See Reviewing and Updating System Information.

 Normalization
NormalizationTo avoid large differences between the estimated IRPF tax rate and the real tax contribution needed at the end of the year, the withholding percentage is calculated multiple times during the year. This process is called normalization. The percentage withholding normalization process accounts for incomes earned and taxes and contributions paid, as well as income, tax, and contribution estimates for the remainder of the contract period or year.
Global Payroll for Spain delivers a page where you can define the normalization schedule for IRPF calculation.
The Normalization Schedule page is read by the regular payroll process list to determine when to run the normalization process. The exception to this is that the process is always run for new hires in the month that they are hired and for all employees who are compensated on a net to gross basis. You may need more than one schedule if you have different tax calculation dates for different pay entities.
See Also
Reviewing Normalization Schedules

 IRPF in the Pay Process Flow
IRPF in the Pay Process FlowThis diagram illustrates how the IRPF calculation process fits into the overall pay process flow of Global Payroll for Spain.
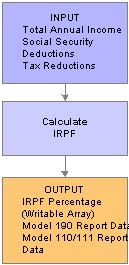
IRPF process flow

 IRNR Tax Reporting for Non-Residents
IRNR Tax Reporting for Non-ResidentsGlobal Payroll for Spain provides functionality for you to manage IRNR tax data that the payroll process generates for non-resident workers. This IRNR tax reporting functionality includes the ability to create the Model 216 and Model 296 reports.
See Also
Managing Displaced People and Expatriates
 Estimating the Total Annual Income
Estimating the Total Annual IncomeThis section provides an overview of estimated total annual income and discusses how to:
Estimate fixed income.
Estimate salary in kind income.
Estimate variable income.
Estimate recurring income from earnings assignments.
Estimate irregular income.
Define custom rules for tax base estimation.
Set up tax base estimation variables.
Override estimated tax base variables.

 Understanding Estimated Total Annual Income
Understanding Estimated Total Annual Income
The system calculates the estimation of annual income to use as the tax base for IRPF taxes. An employee’s total annual income includes fixed income, variable income, and benefits income. This estimation is necessary because the only time you can calculate the true tax base is in the December payroll run when the year is complete. The rest of the year therefore requires an estimation of the tax base for the remaining months.
Global Payroll for Spain calculates IRPF taxes for the state and all of the fiscal territories as a percentage of an employee's taxable income. The percentage of an employee's income that applies to IRPF taxes is based on the employee's annual income, minus reductions due to personal situations, number of dependents, salary level, and disability. You run the process that calculates the tax percentage as part of regular payroll. Whenever information affects an employee's taxes, the employer must recalculate the tax percentage by running the normalization process. The law states that employers must normalize tax percentages for their employees at least once quarterly even if no information changes.
When calculating an employee's tax percentage, whether through the regular payroll process or the normalization process, the system estimates the employee's annual income because the actual amount is not available until the end of the year.
The system performs the same tax base estimate calculations for all fiscal territories, both state and historical.
Global Payroll for Spain enables you to control the level of accuracy that you want to have for the tax base estimate defining how you want the system to estimate the annual taxable base during the calculation of IRPF taxes.
The system takes fixed income and benefits income amounts from the Compensation page of the Job Data component and the annual benefits base rate from the Benefits Program Participation page. These values are considered the theoretical annual compensation, so the system uses these values as the starting point of the estimation.
To estimate the variable income Global Payroll Spain use as the base the variable income from last year.
Calculation of Estimated Tax Base
The estimated tax base consists of three parts:
The amount paid from the beginning of the year through the last month.
The amount for the current month.
The amount estimated for the remainder of the year.
Each part of the estimated tax base consists of three different members:
Fixed income
In kind income
Variable compensation
The system performs a separate calculation for each part and stores the results of the tax base calculation details. The system calculates the total estimated tax base using the following equation:
Total Base = Accumulated values year-to-date + current month values + year remainder estimation
When estimating the tax base the system also considers compensation coming from earnings entered through the Earnings and Deduction Assignments menu components. The system adds these earnings to the corresponding member of the tax base: fixed income, in kind income, or variable compensation based on the nature of the compensation.
The system uses the TAX WA RSLT writable array to store the results of the tax percentage calculation, which includes the tax base and other information considered during the calculation. The system stores details in the in the GPES_TAX_RLST table for each of the different members of the tax base estimate as well as the total tax base value.
You can view the tax base calculation details through the IRPF Calculation Results ESP component.

 Estimating Fixed Income
Estimating Fixed IncomeEmployees with a net guarantee have a special treatment about tax percentage calculation. The system performs a normalization process each month, whether or not the normalization schedule is set up for the employee's pay entity and tax location, because the system needs to perform the net to gross process to calculate the fixed income part of the tax base. The system use the Target Compensation Rate field value on the Compensation page of Job Data component as guarantee net and retrieves a gross amount after an iterative process.
For employees that are not net-paid, the system calculates the estimated fixed income using the annual rate. The annual rate comes from the employee's compensation rate and frequency or the target compensation rate, depending on the employee, on the Compensation page of the Job component. The system prorates this value for the remainder of the year or contract. Note that the system does not perform an earning by earning estimation.
Note. If an employee finishes a contract during the year and you want the estimation of the tax base to consider that date as end date of the estimation, you must enter the Contract Expected End Date value in Contract Status/ Content page of Update Contracts component. If you do not enter a value in this field, the system estimates the income until the end of the year regardless of whether the employee finishes the contract finishes during the year.
The system considers the employee's current job records, accrued seniority earnings, the remaining days in the year, and pending extra periods in the calculation of estimated fixed income. For seniority earnings, the system uses the effective date data from the Job records. For pending extra periods, the system considers extra periods when estimating each member of the tax base through the calculation of pending days to be paid. The system uses a homogeneous distribution of salary along the different payments. The system does not perform an earning by earning estimation to determine which earning belongs to which extra period.
Global Payroll for Spain provides the option to include future job data events and future seniority events in the year as part of the calculation of estimated fixed income. Use the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable to control this functionality.
With the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable you can specify that the system consider job record data with future effective dates in the estimated fixed income. For example, perhaps an employees compensation rate in May is 1000 Euros but in August this value increases to 1500 Euros. To consider job records with future effective dates (future information in the Job record), set the character value of the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable to Y.
With the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable you can also specify that the system calculate future accrued seniority earnings in the year as part of the calculation of estimated fixed income. The system computes the values for each of seniority segments using the seniority compensation base elements as of each segment date. For example, if an employee is hired in August 2003 and receives a seniority amount every 3 years, then in August 2006 the employee is due the increase in seniority earnings. The system thus uses the current seniority earnings amount for January through August and the uses the future seniority amount for August through December during the calculation of the seniority portion of the estimated fixed income. Set the character value to Y to include the seniority earnings; set the character value to N to use the current value for the entire seniority earnings.
To perform the initial set up of the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable, navigate to Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Variables. Access the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable and set the this variable to the desired character value. The default value of this variable is N. The setting for this variable controls both the future job data and seniority events simultaneously. You can also control this setting at the by using the supporting element override functionality at the payee level.
See Also
Understanding Gross and Net Guarantee

 Estimating Salary In Kind Income
Estimating Salary In Kind IncomeDifferent salary in kind benefits for an employee can contribute to social security bases and taxable income either entirely or partially. To know whether salary in kind is exempt or not, you have to compare the sum of all the earnings considered as salary in kind to the 20 percent Professional Minimum Salary, which is a statutory rate published by the government annually. If the sum of all the earnings don't exceed 20 percent, the salary in kind won't contribute as regular contributing earnings to the social security base and taxable income. If there is an excess over 20 percent, the excess amount should be added to the contributing earnings and taxable income. If there is more than one type of salary in kind earning, the individual excess will have to be calculated separately for each earning in proportion to its value. The exempted amount must be shown in the 190 Annual Tax report.
Examples of different earnings that are salary in kind include housing, loans with an interest rate below the legal interest rate, cars, insurance contributions, and pension plan contributions.
The withholdings referred to the salary in kind can be paid by the employer (withholdings in kind not passed on) or by the employee (withholdings in kind passed on). If a withholding is passed on, it will be discounted in the payroll for the employee as a tax deduction (deduction in kind) (IRPF SPCR). If a withholding is not passed on, the employer will pay the deduction to the tax institution. All the withholdings in kind must be shown in an element IRPF SPC (Ingresos a cuenta efectuados) or “In kind withholdings made.”
To estimate salary in kind income, the system uses the value on the Annual Benefits Base Rate field on the Benefits Program participation page for estimation of in-kind income because this benefits compensation is equal to in kind compensation. You can access this field through the Benefits Program Participation link on the Job Data component.
The system uses the same effective date data from the Job Data component when calculating the estimated in kind income.
Use the TAX VR EST FUTURO variable to indicate whether to include rows of data with future effective dates within the current year in the calculation. Set the character value of the variable to Y to include future data. If you set the variable to N, the system uses the as of date value to perform the estimation of the remaining part of the year. You can set the value for this variable at the element level by accessing it through the Variables component. Navigate to Set up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll. Elements, Supporting Elements, Variables. You can also set the character value of this variable through the supporting element overrides functionality.
Note. The estimation method that Global Payroll for Spain uses takes a total annual amount as base of the estimation. The system does not perform an earning by earning calculation
If you enter in kind income through another means, the system includes that in kind income as part of that other category. For example, if you enter the in kind income through the Pay Components group box on the Compensation page of the Job Data component, the system manages the salary in kind as part of fixed income.

 Estimating Variable Income
Estimating Variable IncomeGlobal Payroll for Spain enables you to determine at the earning level which calculation method you want to use for estimating the variable compensation part of the tax base. For example, you might need to change how you estimate the variable compensation because the bonus is following a different schedule compared to last year or a bonus or commission is not being paid anymore this year when it was last year.
You can calculate the variable compensation part of the estimated tax base by using any of these three methods:
Method 1. Based on last year's values. Used for variable compensation that follows last year's schedule.
When you define an earning in Global Payroll for Spain, you must update some accumulators to define whether the earning is paid, taxable, and contributes to social security. When defining if the variable earning is taxable, you must assign CLI AC ING VR1 S accumulator to specific earnings to indicate this estimation method.
The estimated variable income (TAX VR HC VAR A) originates from the previous year’s variable incomes.
This method uses the array TAX AR ING VAR EST to retrieve values from record GPES_TAX2_RSLT, which stores every calculation result. The GPES_TAX_INC_VR1 the value of the accumulator value of GEN AC DEV VRBLS S. This array adds that part of the variable compensation to each slice between the pay period end date of the previous year and the end date of that same year. For example, if you calculate the estimated variable income for March 2006, the array totals every variable income from 1 April 2005 to 31 December 2005.
Method 2. Based on last year values. Used for variable compensation that does not follow last years schedule.
When you define an earning in Global Payroll for Spain, you must update some accumulators to define whether the earning is paid, taxable, and contributes to social security. When defining if the variable earning is taxable, you must assign CLI AC ING VR2 S accumulator to specific earnings to indicate this estimation method.
Use this calculation method when you expect differences in the earnings payment schedule but want to use the previous year's values in the estimation because you do not know the current year's values.
This calculation method uses the previous years total variable income, rather than a specific period, as the maximum variable compensation (base amount) value for the variable compensation part of the estimated tax base for the current year. Each month the calculation process subtracts the year-to-date variable compensation amount from this base amount to determine the tax base estimation for variable compensation. Once the payee reaches the base amount limit, the calculation process does not perform the variable compensation estimation anymore. For example, if last year a payee earns 10000 Euros and by June of this year the payee has already earned 9000 Euros, then the calculation process only uses the remaining 1000 Euros as part of the tax base estimation for the variable compensation. Once the payee reaches the 10000 Euros limit, the system stops calculating the variable compensation estimation.
Method 3. Based on current year values. Used for Variable compensation for which you know the current year values.
When you define an earning in Global Payroll for Spain, you must update some accumulators to define whether the earning is paid, taxable, and contributes to social security. When defining if the variable earning is taxable, you must assign CLI AC ING VR3 S accumulator to specific earnings to indicate this estimation method.
Use this calculation method when you know what is going to be paid this year for earnings of variable compensation. The calculation process estimates the variable compensation part of the tax base based on the information already in the system for current year variable income as entered through payee earnings and deduction assignment. To be able to perform that estimation you set the variable CLI VR EST ASIGN set to Y.
The system makes no differentiation between fiscal territories when estimating the variable compensation. The system performs the three calculation methods, including the corresponding earnings based on their setup (which CLI VR ING VRx S the earnings contribute to) in each method. The system calculates the variable tax base as a sum of year-to-date value, plus the current month value, plus the estimated value for the remaining months in the year.
You can also control whether the system looks for variable compensation coming from earnings and deduction assignments through the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable. By setting the character value of tis variable to Y, the system looks for variable income from earnings and deduction assignments, looking earning by earning at all earnings assigned to the payee.

 Estimating Recurring Income From Earnings Assignments
Estimating Recurring Income From Earnings AssignmentsUntil this point we have explained how the system calculates each member of the annual tax base (fixed income, in kind income, and variable compensation). We saw that in the case of fixed income and in kind income the starting point of the estimation are the values in the Job Data component. But what happens with other compensation you do not enter through the Job Data component, compensation that is recurring and which makes sense to consider as part of the tax base estimation? This other compensation is the type that is entered through the payee earning and deduction assignment functionality. Global Payroll for Spain enables you to decide whether to consider compensation coming from payee earning and deduction assignments when calculating the tax base.
Use the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable to control whether to include earnings entered through earnings and deduction assignments as part of the tax base estimation. This variable gives you the ability to include recurring earnings that are not entered through the Job record.
There are three possible levels at which you can override the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable:
Variable definition: The first level at which you can override the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable is at the variable definition level.
You can define the default value of this Global Payroll variable element during the implementation phase. If you set the default value of the variable to N, the system does not perform estimation for the values that you enter through earning and deduction assignments. There is no way to override the N value when set at as part of the variable definition. If you set the variable value to Y, the system does perform analysis of earning and deduction assignments as part of the tax base estimation. You can override the Y value that you set at the variable definition level at the other two levels.
Earning definition: The second level at which you can override the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable is at the earning definition level.
You can override the default value of the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable on the Supporting Element Overrides page of the earnings definition by setting it to N, provided that the default value of the variable at the variable definition level is set to Y. The system performs estimation of the amounts coming from earning and deduction assignments but skips the earnings for which you have set the variable override value to N. PeopleSoft recommends that if you are using earning and deduction assignments to override values coming from the Job record that you set the variable value of the earning to N at the earning level. Otherwise, the system might count the earning twice—once through the Job Data component and once through the earning and deduction assignment. This override level affects the specific earning for every employee.
Supporting element override:
(third level) You can override the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable value of a basic or recurring earning for a specific employee using the supporting element overrides functionality within the components of the Earnings and Deductions Assignments menu by changing the character value of the CLI VR EST ASIGN variable to N. This override level affects that specific entry (earning and payee combination) only.
Earnings are categorized as either fixed, in kind, or variable income at the earning level. When you create earnings in Global Payroll for Spain you must assign the earning to certain accumulators to define whether the earning is payable, taxable, and contributes to social security. Regarding taxes, you include the earning in a different accumulator depending on its categorization. For example, you include fixed income in the accumulator CLI AC ING DIN FJO. This categorization enables the tax base estimate calculation process to split earnings entered through earnings and deduction assignments into their appropriate categories for the estimation. The system determines which member of the tax base (fixed, in kind, variable) to which the earning belongs by checking which accumulators the earning is a member of in the earnings definition. The system then adds the earning to the corresponding member of the tax base.
When the take base estimation process reads the earning and deduction assignment and performs the corresponding calculation and frequency conversion, the process takes into account whether the earning is part of pending extra periods. For pending extra periods, the system considers extra periods when estimating each member of the tax base through the calculation of pending days to be paid. The system uses a homogeneous distribution of salary along the different payments. The system does not perform an earning by earning estimation to determine which earning belongs to which extra period.

 Estimating Irregular Income
Estimating Irregular IncomeIrregular income occurs due to having a generation period over two years. Irregular income has special tax treatment since the whole income is added to the annual fixed income but at the same time, 40, 50, or 70 percent of that amount is considered as a deduction as part of the tax calculation process (similar to the process described later in this chapter). Because of that the system consider just the taxable part of the irregular income when calculating the annual tax base.
See Calculating Available Deductions.

 Defining Custom Rules for Tax Base Estimation
Defining Custom Rules for Tax Base Estimation
Global Payroll for Spain provides an alternative way to calculate the tax base by delivering two configurable formulas that your implementation team can use to set up custom requirements for estimating tax base. These configurable formulas are distinct from the delivered tax base estimation formulas so that modification and use of these configurable formulas does not impact the maintenance of the standard delivered formulas.
The configurable formulas are:
CLI FM CALC ING A: Use this formula to write your own code on how to calculate the estimated tax base without using the delivered calculation method. The code that you enter in this formula overrides the whole tax base. You can use this formula to provide an override to the calculated tax base by assigning the value to the element through any mechanism that Global Payroll core provides to override supporting elements.
CLI FM EST OTROS: Use this formula to include other earnings in the tax base calculation in addition to the ones entered through the Job data component or the components in the Earning and deduction assignment menu.
Custom Designated Estimation
Implementation teams can define the details of the CLI FM CALC ING A formula to override the delivered tax base estimation functionality by developing custom requirements for estimating tax base. Global Payroll for Spain delivers this formula with no value. Implementers can add code to perform the tax base estimate calculation and retrieve a value. To override the calculated value for this formula, users can enter a value into this formula at the payee level as an override. The system then uses the override value rather than the calculated value.
Note. If the value of this formula is anything other than 0, the system assumes that you are using this formula to calculate estimated tax base through your own method rather than the delivered method, or that you are overriding the estimated tax base with a specific value. The system therefore does not use the delivered method to calculate the estimated tax base.
Custom Other Earnings Estimation
Implementation teams can define the details of the CLI FM EST OTROS formula if they want to use the delivered tax base estimation rules but have other earnings from other sources (such as from brackets, formulas, or custom compensation records) that they want to include in the estimate besides the ones from the job record or earnings and deduction assignments. These additional earnings are added on top of the tax base members (fixed, in kind, and variable).
To use this functionality, implementers can code the delivered CLI FM EST OTROS formula so that the system includes compensation from others sources in the estimated tax base. The system adds the results of this formula to the standard members of the tax base without affecting the delivered standard rules for the calculation.
Implementers need to take into account, when coding this formula, i to update values of the following variables:
TAX VR EST AÑO BR: Use this variable to add value from other compensation to the estimated fixed amount.
TAX VR EST AÑO VR: Use this variable to add value from other compensation to the estimated variable amount.
TAX VR EST AÑO SP: Use this variable to add value from other compensation to estimated in kind compensation amount.
These variables are added to each member of the tax base in the standard formulas. Implementers need to add their calculated amounts to those variables so that the customer design is integrated in the standard design. For example:
TAX VR EST AÑO BR + New Element1 = TAX VR EST AÑO BR
TAX VR EST AÑO VR + New Element2 = TAX VR EST AÑO VR
TAX VR EST AÑO SP + New Element3 = TAX VR EST AÑO SP
Where
New Element1 represents the amount calculated by CLI FM EST OTROS corresponding to fixed income.
New Element2 represents the amount calculated by CLI FM EST OTROS corresponding to variable income.
New Element3 represents the amount calculated by CLI FM EST OTROS corresponding to in kind income.
Tax Base Formula Overrides
The CLI FM CALC ING A formula has two functions. You can use the formula to write customer code that calculates the tax base using a customer method, but you can also use the formula to override a specific amount for a specific employee. The system uses the override values that you enter instead of the calculated values for the corresponding part of the tax base estimate. You perform these overrides using the supporting element override functionality.

 Setting Up Tax Base Estimation Variables
Setting Up Tax Base Estimation VariablesYou can use the following variables to define how you want the system to calculate the tax base estimation:
TAX VR EST FUTURO: At the variable definition level, use this variable to control when the system includes future information from the Job record (annual fixed income and annual in kind income) and future seniority increases in addition to current information.
CLI VR EST ASIGN: At the variable definition level use this variable to control whether the system includes future information for earnings that are entered through earning and deduction assignments as part of the tax base estimate calculation
TAX VR EST OVRD: At the earning level, use this variable to control whether the system includes the earning in the tax base estimate calculation when you enter the earning through an earning and deduction assignment.
Set the character value of these elements to Y to include the additional information as part of the tax base estimate calculation. Set the variable to N to exclude the information from the calculation. You can also override the value of these variable elements at the earning and deduction assignment level using the supporting element override functionality that is available in the Payee Assignment by Element or Element Assignment by Payee components. These variable element have a definition value as defined through the Variable component (Setup HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Elements, Supporting Elements, Variable, Definition). This value is the default value for every employee. You can override the default value at these different levels: pay entity, pay group, payee, calendar, element definition, and positive input (using Global Payroll core override functionality).

 Overriding Estimated Tax Base Values
Overriding Estimated Tax Base ValuesGlobal Payroll for Spain provides the ability to override each member of the estimated tax base or the final estimated tax base. Use the following elements to override the value of specific parts of the calculated tax base estimate:
CLI FM CALC ING A: Override the annual income calculation value.
CLI VR BRUTO SOB: Override the annual fixed income value.
CLI VR SPC SOB: Override the annual salary in kind value.
CLI VR BASE VRBLE: Override the annual variable income value.
The system uses the override values that you enter instead of the calculated values for the corresponding part of the tax base estimate. You perform these overrides using the supporting element override functionality.
 Calculating Tax Percentages
Calculating Tax Percentages
This section discusses how to:
Estimate the social security contribution.
Calculate available deductions.
Calculate the withholding percentage.
Calculate garnishment taxation.
Review taxable and non-taxable annual income sources.
See Also
Estimating the Total Annual Income

 Estimating the Social Security Contribution
Estimating the Social Security ContributionOnce the taxable base has been calculated, the system subtracts the employee’s annual social security contribution, if the employee is associated with the state territory.
Note. For employees associated with one of the historical territories, the social security contribution is not used in the IRPF calculation.
The system estimates social security contributions as two segments: the actual social security contributions year-to-date and the estimated value for the rest of the year. The amount remaining after subtracting the annual social security contribution from the estimated tax base is the Rendimiento neto del trabajo (RNT). To calculate RNT, the system uses the social security contribution accumulator (TAX AC SS CT A) for the actual year-to-date contribution and estimates future contributions. These calculations are made in the formula TAX FM CT SS EST.
RNT is subject to deductions for salary level, disability, personal minimum deductions, family minimum deductions (dependents), and alimony.
The sum of the RNT and all of its deductions is the BASE:
Taxable Base - Employee’s Social Security Contributions - Reductions over RNT - Personal Minimum Deductions - Family Minimum for Dependants Reductions − Spouse Support Garnishment = BASE
See Also
Calculating Social Security Benefits

 Calculating Available Deductions
Calculating Available DeductionsFor employees associated with the state territory, the third step in the IRPF calculation is the calculation of deductions.
Note. This step does not apply to employees associated with any of the historical territories.
The system calculates the ART18 reduction, the personal minimum reduction, and the familiar minimum reduction.
The ART18 reduction is based on income level and disability. Both values are compared to ranges in the system to determine the reduction amounts using the formula TAX FM RD ART 18.
The personal minimum reduction is based on age and disability. Both values are compared to values in the system to determine the reduction amounts using the formula TAX FM RD MN PERS.
The familiar minimum reduction is based on dependents, both children and adults. The system considers the total number of dependents, their ages, their degree of disability, and their level of dependency on the employee. The system calculates these deductions using the formulas TAX FM RD MN FAML and TAX FM RD FAM NUM.

 Calculating the withholding Percentage
Calculating the withholding PercentageOnce the taxable net base has been calculated, the system can calculate the withholding percentage. The system employs different formulas, depending on the fiscal territory:
For the state territory, the system uses the TAX FM CT IRPF EE formula to compare the taxable net base with the income ceilings, defined on the Tax Ceiling page, and generate the total contribution amount.
If the payee’s income is lower than the government’s annual minimum, the system applies a ceiling. This ceiling is 35 percent of the annual income minus a corresponding amount stored in ceiling brackets defined for the Fiscal Territories. You can view and update ceiling brackets using the Ceiling Brackets page.
For historical territories, the system uses the formula TAX FM HT PCT EE to calculate the Withholding percentage. The formula compares the taxable net base with the Withholding Brackets for the historical territory. For disabled payees, the system adjusts the percentage, by subtracting the Disability Bracket percentage from the Withholding Bracket percentage.
Global Payroll for Spain delivers and maintains tax brackets. You can view and update tax brackets using the Withholding Segments page.
Payees can increase their percentage using the Tax Percentage Override page. However, if the override is lower than the calculated percentage, the system uses the higher amount. You cannot use the Override Tax Percentage page to reduce the tax percentage.

 Calculating Garnishment Taxation
Calculating Garnishment TaxationFor the state territory, there are two garnishment types that affect tax calculations: child support and spousal support. For the historical territories, the only garnishment that affects tax calculation is the spouse support garnishment.
If a payee has a child support garnishment, the system estimates the annual value for this garnishment (or estimates the value for the remainder of the contract). Then, the system calculates separate contribution amounts for the garnishment and for the remainder of the taxable net base.
For example, assume a taxable net base of 22.625,19 EUR and an estimated annual garnishment amount of 2.704,55 EUR. The bracket calculations would be applied to 2.704,55 EUR and to 22.625,19 EUR (the sum of 22.625,19-2.704,55) generating two contribution amounts, TAX VR CT1 IRPF and TAX VR CT2 IRPF. The system then combines these amounts into TAX VR CT IRPF, which is used to calculate the tax percentage.
For the state territory, the system subtracts the spouse support garnishment annual estimation from TAX VR RNT as a special reduction.
For the historical territories, the system subtracts the spouse support garnishment from the annual income to calculate the taxable base.

 Reviewing Taxable and Non Taxable Annual Income Sources
Reviewing Taxable and Non Taxable Annual Income SourcesThese sources of revenue are subject to IRPF:
Base salary and complements.
Entertainment allowance.
Meals, lodging, and traveling expenses in excess of legal limits.
Example
You want to calculate the taxable annual income for the year 2004 for an employee hired on 01/01/1997 with this criteria:
Base Salary: 841,42 EUR/month.
Seniority: 24,04 EUR/month for each triennium.
Personal complement: 72,12 EUR/month.
Traveling expenses: 60,10 EUR/month.
Extra-periods: two extra periods containing base salary, seniority and personal complement.
The taxable annual income would be:
841,42 x 12 = 10.097,00 EUR.
24,04 x 12 x 2 (2 trienniums from 01/01/1997 to 12/31/2004) = 576,97 EUR.
72,12 x 12 = 865,46 EUR.
Traveling expenses are exempt and not added to the total.
2 extra periods x {base salary + (seniority rate x number of extra periods) + personal complement}.
2 x (841,42 + (24,04 x 2) + 72,12) = 1.923,24 EUR.
Total =10.097,00 + 576,97 + 865,46 + 1.923,24 = 13.462,67 EUR.
 Viewing IRPF Tax Calculation Results
Viewing IRPF Tax Calculation ResultsThis section provides an overview of tax calculation results, an overview of IRPF tax data review, an overview of the IRPF Comparison report, an overview of employee withholding percentage overrides, and discusses how to:
Review IRPF calculation results.
Review IRPF calculation details.
Review monthly IRPF tax data.
Review accumulated IRPF tax data.
Generate the IRPF Comparison report (GPESTAX2).
Update tax percentages.

 Understanding Tax Calculation Results
Understanding Tax Calculation ResultsOnce the system has calculated the taxable income base, the annual tax contribution and the withholding percentage, you can view the results by pay group on the IRPF Calculation Results ESP component. Use this component to view all information that the system uses to calculate the IRPF percentage, including personal data and financial data. Also use this component to review the earnings and deductions that make up a selected payee’s base amount for IRPF tax withholding. You may furthermore find this component useful for explaining IRPF percentage variations to employees.
Note. You can review IRPF data, including withholding percentages, after you run the standalone IRPF process or after you run the current payroll process. To have IRPF calculations reflect the payroll data computed for the current period, use the review the IRPF data after running the payroll process.

 Understanding IRPF Tax Data Review
Understanding IRPF Tax Data ReviewYou can use the IRPF Tax Data Review ESP component to view the monthly IRPF tax data that the payroll process generates for employees and, if necessary, to manually adjust this data. You can also use this component to view accumulated tax data for the year. In the case of special collectives for whom the payroll process does not calculate IRPF tax data, such as professionals, you can use this component to enter the IRPF tax data for the person. The system stores the data that is viewable through this component in the GPES_TAX_RSLT and GPES_TAX2_RSLT tables. The report generation processes use this data for the Model 110, Model 111, and Model 190 reports.
Global Payroll for Spain also provides the IRNR Tax Data Review ESP component for you to view tax data that the payroll process generates for non-resident workers. In addition, there is IRNR tax reporting functionality for creating the Model 216 and Model 296 reports, and pension plan reporting functionality for creating the Model 345 report.
See Also
Managing Displaced People and Expatriates
Generating the Model 345 File Report

 Understanding the IRPF Comparison Report
Understanding the IRPF Comparison Report
This new SQR report helps you identify changes in IRPF percentages and determine whether these changes are justified or adjustments are needed.
For each payee and month covered by the report, you see the following information:
Month to which the values pertain (1= January, 2 = February, and so on).
Information that affects the payee’s tax calculation, such as disability, help needed, mobility reduction, family situation, type of working relationship, and number of dependents as of the end of the reported month.
Amount of taxable earnings (the base amount) on which the IRPF percentage has been calculated.
The IRPF percentage.
Social security contribution.
Legal reductions to the base amount.
Irregular income.
Taxes paid from January through the reported month.
Accumulated taxable base from January through the reported month.
You can generate the report for all payees in selected companies, pay entities or pay groups, or you can produce the report for specific tax locations or selected employees. You can also have the report include only those payees for whom the difference in the last IRPF percentage and the new IRPF percentage meets or exceeds a certain percentage.

 Understanding Employee withholding Percentage Overrides
Understanding Employee withholding Percentage Overrides
The system automatically calculates employees' withholding percentage. However, employees can choose to increase their percentage using the Override Tax Percentage page.
Note. If the override is lower than the calculated percentage, the system uses the higher amount. You cannot use the Override Tax Percentage page to reduce the tax percentage.

 Page Used To View IRPF Tax Calculation Results
Page Used To View IRPF Tax Calculation Results
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPES_TAX_RSLT |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Absence and Payroll Processing, Review Absence/Payroll Info, IRPF Calculation Results ESP, IRPF Calculation Results |
View the tax withholding percentage, the taxable income base, and the annual tax contribution for employees in the selected calendar group. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_RSLT_DTLS |
Click the Details link on the IRPF Calculation Results page. |
Review values that make up the base amounts on which IRPF withholding is calculated. |
|
|
GPES_TAX2_RSLT |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, IRPF Tax Data Review ESP, IRPF Tax Review |
Review online the monthly tax data that the payroll process calculates for IRPF tax reporting. You can also adjust the calculated income and withholding amounts. For contingent workers or persons of interest, you can insert new rows of data for each specific job and salary type that a person might have. You can enter IRPF tax data for any person who is not processed through payroll. The system uses this data when you generate IRPF tax reports. |
|
|
GPES_TX2_RSL_VW |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, IRPF Tax Data Review ESP, Accumulated Values |
Review online the accumulated tax data that the payroll process calculates for IRPF tax reporting. The system uses this data when you generate IRPF annual tax reports. |
|
|
GPES_COMPARE_IRPF |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Absence and Payroll Processing, Reports, IRPF Comparison ESP |
Generate the IRPF Comparison report. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_RSLT_OVRD |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Payee Data, Taxes, Override Tax Percentage ESP, Override Tax Percentage |
Change an employee’s tax withholding percentage. |

 Reviewing IRPF Calculation Results
Reviewing IRPF Calculation ResultsAccess the IRPF Calculation Results page.
The following fields have been added to the IRPF Calculation Results page so that you can refine the list of employees to display in the results.
|
Difference >= |
Enter the minimum percentage by which a payee’s current IRPF percentage and last IRPF percentage must differ for the payee to be included in the report. |
|
Employee ID |
To review the results for a single payee, enter the employee ID here. |
Payee IRPF Calculation Results
View the details of the IRPF calculation results, including employee ID, employee name, withholding percentage, taxable base, and tax contribution.
|
Segment Number (segment number) |
The segment to which the results apply. |
|
Old Percentage |
The IRPF percentage that was applicable to the previous period. |
|
Difference |
The percentage difference between the current and previous IRPF withholding rates. |
|
Social Security Contribution |
The amount of social security contributions for the selected period. |
|
Total Reductions |
The total reductions for the selected period. |
|
Calculation Type |
The type of calculation performed on the corresponding data row. |
|
Details |
Click to access the Tax Calculation Details page where you can view a detailed listing of the current and prior values that make up an employee’s taxable earnings and personal data that affects the results. |

 Reviewing IRPF Calculation Details
Reviewing IRPF Calculation DetailsAccess the Tax Calculation Details page.
This page displays the values that make up the base amounts against which the IRPF percentage is applied or that affect the IRPF calculations.
|
Current Value |
Result of the most recent calculation. |
|
Prior Value |
Result from the previous calculation. |
|
Difference |
The difference between the current and prior value. |

 Reviewing Monthly IRPF Tax Data
Reviewing Monthly IRPF Tax DataAccess the IRPF Tax Review page.
Search Criteria
Upon entering the page select the company, fiscal territory, year, and month for which you want to review IRPF tax data.
|
Org Relation (organizational relationship) |
Select the type of organizational relationship of the persons for which you want to retrieve IRPF tax data. Your choices are Contingent Worker, Employee, or Person of Interest. |
|
EmplID (employee ID) |
Enter the employee ID to narrow the search results to a specific employee. |
|
Search |
Click this button to retrieve data for persons based on the search criteria. The system displays the data in the Detail of Payees grid. Fields vary depending on the selected organizational relationship. |
Detail of Payees - Earned Income
Use the fields on this tab to review IRPF tax-related data for employees. This tab shows the information that the payroll process generates. You cannot edit the information on this tab. This tab is not applicable to contingent workers or persons of interest and is therefore unavailable for these persons.
|
EmplID (employee ID) |
The person for which the data on a given row relates. |
|
Empl Rcd# (employee record number) |
The person’s employee record number. |
|
Name |
The first and last name of the person. |
|
National ID |
The national identification number or foreign identification number of the person. |
|
Key and Subkey |
The perception key and subkey that identifies the person’s work relationship with the company. If a person has more than one combination of key and subkey, the system displays a separate row for each combination. You define keys and subkeys on the Perception Keys ESP page. |
|
Salary Income |
The gross earned income in salary of the person. This amount is IRPF taxable. |
|
Variable 1 Income, Variable 2 Income, and Variable 3 Income |
The total variable income of the person according to the variable calculation method. |
|
Salary Withholding |
The amount subtracted from salary income that applies towards IRPF taxes. |
|
In Kind Income |
The total in-kind income of the person. This amount is IRPF taxable. |
|
In Kind Withholding |
The in-kind withholding tax amount. |
|
EE In Kind Withholding |
The in-kind withholding tax amount for the employee that was paid towards IRPF taxes by the employee. |
|
Reductions |
The total reductions that the payroll process calculated for each person and segment. |
|
Contribution |
The total amount considered as fiscally deductible expenses. This value is related to social security contributions. |
|
Calendar ID |
Identifies the calendar for which the row of data applies. |
Detail of Payees - Adjust
Access the Adjust tab.
Use this tab to adjust the IRPF tax data that the payroll process calculated for the selected fiscal period and month. For employees this tab shows the same fields as the earned Income tab except that many of the fields on this tab are editable. For contingent workers or persons of interest, you can enter new rows of data. The system differentiates between the data that the payroll process generates and the data that you enter manually.
|
EmplID (employee ID) and Empl Rcd# (employee record number) |
Select the ID of the person for whom you are entering data. When you press the Tab key the system displays the employee record number, name, and national ID of the person. If the person has multiple employee record numbers, select the one that is applicable. These two fields are available for edit only for contingent workers or persons of interest. |
|
Key and Subkey |
Select the perception key and subkey that describes the person’s work relationship with the company. These fields are available for edit only for contingent workers or persons of interest. You define keys and subkeys on the Perception Keys ESP page. |
|
Salary Income Adjust |
Adjust the gross earned income in salary of the person. This amount is IRPF taxable. |
|
Variable Income Adjust |
Adjust the total variable income of the person. |
|
Salary Withhold Adjust |
Adjust the amount subtracted from salary income that applies towards IRPF taxes. |
|
In Kind Income Adjust |
Adjust the total in-kind income of the person. This amount is IRPF taxable. |
|
In Kind Withhold Adjust |
Adjust the in-kind withholding tax amount that the company paid on the person’s behalf. |
|
EE In Kind Withholding Adjust |
Adjust the in-kind withholding tax amount for the employee that was paid towards IRPF taxes by the employee. |
|
Ceuta / Melilla |
Select this check box to indicate that the employee belongs to Ceuta or Melilla. This check box is available only for contingent workers and persons of interest. |
See Also
Maintaining IRPF Tax Review Information

 Reviewing Accumulated IRPF Tax Data
Reviewing Accumulated IRPF Tax DataAccess the IRPF Tax Data Review ESP - Accumulated Values page.
Review the sum of each of the IRPF tax data values for the selected calendar year from January 1 through the selected month. The system displays the data by employee, key, and subkey. If you are viewing accumulated data for December, the December data will be the same as the fiscal year data that gets included in the Model 190 file.
Note. You cannot make adjustments to accumulated values. You can only make adjustments for specific months, and this in turn affects the accumulated values.

 Generating the IRPF Comparison Report
Generating the IRPF Comparison ReportAccess the IRPF Comparison ESP page.
|
Year/Month |
Select the year and last month of data to include in the report. To be included in the report, a payee must have a calculation run for the selected month and year and must meet the other selection criteria that you enter on this page. |
Comparison Option
|
All Year |
Select to report for each payee, all calculations from the beginning of the fiscal year through the selected month. For example, to include payroll data from January 2005 through September 2005, enter 2005 / September in the Year/Month fields and select All Year. |
|
Comparative |
Select to include only those payees for whom the difference between the current IRPF percentage and the last IRPF percentage equals or exceeds the value in the Difference field. If this field is cleared, the report will include all payees that meet the other selection criteria. The report will include a row of payroll data for the month specified in the Year/Month fields and a row of data for the previous month. For example, if you enter 2005 / September in the Year/Month fields and select Comparative, the report will provide, for each payee, a row of data for September 2005 and a row of data for August 2005. |
|
Difference >= |
This field is displayed when you select Comparative. Enter the minimum percentage by which a payee’s actual IRPF percentage and last IRPF percentage must differ for the payee to be included in the report. For example, to include only those payees for whom the difference between the previous IRPF rate and the current IRPF rate is at least 5 percent, enter 5 here. |
|
Filter By |
Select a filter. Values are: Company, Pay Entity, Pay Group, Payee, and Tax Loc (tax location). |
Filter List
Select the companies, pay entities, pay groups, payees, or tax locations to include in the report. Your selection in the Filter By field determines what you can enter here.

 Updating Tax Percentages
Updating Tax PercentagesAccess the Override Tax Percentage page.
|
Withholding percentage |
Enter the new withholding percentage. |
 Reviewing and Updating System Information
Reviewing and Updating System InformationTo review tax ceilings, tax personal reductions, and tax family reductions, use the Calculation Variables ESP (GPES_TAX_VARIABLS) component. To review withholding segments, use the Withholding Segments ESP (GPES_TAX_BRKT_WHLD) component. To review ceiling brackets, use the Ceiling Bracket ESP (GPES_TAX_BRKT_CLNG) component. To review disability reductions, use the Disability Reduction ESP (GPES_TAX_BRKT_DSBL) component. To review fiscal territories and calculation data for the fiscal territory, use the Fiscal Territories ESP (GPES_TAX_LOCATN) component. To review the normalization schedule, use the Normalization Schedule ESP (GPES_TAX_CALENDAR) component. To set up garnishment elements, use the Garnishment Elements ESP (GPES_TAX_ELEMENTS) component. To review variable managers, use the View Variable Manager ESP (GPES_RATES) component.
This section provides an overview of system information and discusses how to:
Review tax ceilings.
Review personal tax reductions.
Review family tax reductions.
Review withholding segments.
Review ceiling brackets.
Review disability reduction brackets.
Review fiscal territories.
Review fiscal territory calculations.
Review normalization schedules.
Set up tax elements for garnishments.
View variable managers.

 Understanding System Information
Understanding System Information
Before the system calculates IRPF, ensure that the tax bracket and fiscal territories information is current. Also update the Normalization Schedule page to calculate withholding while running payroll. You can also run the IRPF percentage calculation separately by creating a specific calendar and calendar group for the IRPF percentage calculation.
Global Payroll for Spain provides the following information in accordance with government regulations:
Fiscal Territories and data for tax calculations.
Minimum annual contribution amounts.
Total contribution per taxable base.
Reduction amounts based on personal data (age and disability status), family data (number of dependents, disability status, and degree of dependency), and work situation (contract type and tax location).
Global Payroll for Spain enables you to calculate tax percentage independently or while running the payroll process. Use the Normalization Schedule page and the Fiscal Territories page to coordinate the tax calculation and payroll process.

 Pages Used to Update System Information
Pages Used to Update System Information
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPES_TAX_VARIABLS1 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Calculation Variables ESP, Tax Ceilings |
Review the State Territory tax ceilings delivered by Global Payroll for Spain that define the minimum income required to pay tax. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_VARIABLS2 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Calculation Variables ESP, Tax Personal Reductions |
Review the State Territory personal reductions that are used in the tax calculation to reduce employees' tax amount. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_VARIABLS3 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Calculation Variables ESP, Tax Family Reductions |
Review the State Territory family reductions that are used in the tax calculation for employees with dependents. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET_DATA |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Withholding Segments ESP, Withholding Segments |
Review tax rates that define the percentage of tax withheld from employees based on income. For the historical territories, the tax withheld also varies according to the number of dependent children. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET_DATA |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Ceiling Bracket ESP, Ceilings Brackets |
Review ceiling brackets that define the minimum income required to pay tax, depending on the number of dependents. These values are for the state territory only. |
|
|
GP_BRACKET_DATA |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Disability Reduction ESP, Disability Reduction |
Review disability reduction rates that define disabled employees' reductions on tax. These values are for the historical territories only. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_LOCATN1 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Fiscal Territories ESP, Fiscal Territories |
Set up a tax office location and link the tax location to a pay entity and a tax calendar. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_LOCATN2 |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Fiscal Territories ESP, Calculation Data |
Define data and check tax brackets used in tax calculations for the fiscal territory. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_CALENDAR |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Normalization Schedule ESP, Normalization Schedule |
Establish a schedule for the normalization process in a payroll calculation. |
|
|
GPES_TAX_ELEMENTS |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Garnishment Elements ESP, Garnishment Elements |
Set up the elements that store garnishment values that could be paid by employees. This data is considered during the tax calculation. |
|
|
GPES_RATES |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, View Variable Manager ESP, View Variable Manager |
Specify which elements will be displayed in an specific component. Global Payroll for Spain delivers data for the component GPES_TAX_VARIABLS, so the elements are shown on different pages in this component: GPES_TAX_VARIABLS1 (Tax Ceilings), GPES_TAX_VARIABLS2 (Tax Personal Reductions), GPES_TAX_VARIABLS3 (Tax Family Reduction). |

 Reviewing Tax Ceilings
Reviewing Tax CeilingsAccess the Tax Ceilings page.
|
Ceilings |
Review the tax ceilings that define the minimum income required to pay tax. |

 Reviewing Personal Tax Reductions
Reviewing Personal Tax ReductionsAccess the Tax Personal Reductions page.
|
Personal Reductions |
Review the personal reductions that are used in the tax calculation to reduce employees' taxes. |

 Reviewing Family Tax Reductions
Reviewing Family Tax ReductionsAccess the Tax Family Reductions page.
|
Family Reductions |
Review the family reductions that are used in the tax calculation for employees with dependents. |

 Reviewing Withholding Segments
Reviewing Withholding SegmentsAccess the Withholding Segments page.
This page defines the tax rates for the Fiscal Territories. An employee's level of tax is determined by the employee's income.
Note. The fields on this page vary depending on the historical territory you select. For example, if you select the historical territory of Alava, fields pertaining to Alava will appear. The historical territories supported by Global Payroll for Spain include Alava, Guipuzcoa, Navarra, and Vizcaya.
Withholding Bracket <Fiscal Territory>
|
Search Key Number of Descendants |
The number of dependent children. An employee's children are considered as dependents if they are under the maximum age that is defined on the Fiscal Territory - Calculation Data page. |
|
Search Key Taxable Net Base |
Employee's annual income in Euros. The value in this field represents the top of the income range for the Withholding Bracket. |
|
Return Column Withholding Bracket <Fiscal Territory> |
The percentage of tax withheld for employees whose income is in the range defined by the Taxable Net Base and who have the number of children defined in the Number of Descendants field. |
|
Return Column Withholding Contribution and Return Currency |
The contribution amount withheld for paying employee's taxes for the state territory. |
|
Return Column Marginal Percentage |
The marginal percentage value used to calculate employee's taxes for the state territory. |
Example
This table illustrates how Withholding Segments work:
|
Number of Descendants |
Taxable Net Base |
Withholding Bracket |
|
0 |
8.340 |
0 |
|
0 |
8.800 |
1 |
|
0 |
9.310 |
2 |
Employees with no children would pay tax as follows:
An employee who earns 8.340 EUR or less pays 0% tax.
An employee earning 8.500 EUR pays 1% tax (for example).
An employee earning 9.310 EUR pays 2% tax.

 Reviewing Ceiling Brackets
Reviewing Ceiling BracketsAccess the Ceiling Brackets page.
This page defines the ceiling brackets for the state territory only. This page does not apply to the historical territories.
Personal Situation Exemptions
|
Search Key Family Situation |
The family situation for the employee. Values are 1 - General Situation, 2 - Less than 1 year relationship, and 3 - Special Relationship. |
|
Search Key Number of Descendants |
The number of dependent children. An employee's children are considered as dependents if they are under the maximum age that is defined on the Fiscal Territory - Calculation Data page. |
|
Return Column Personal Situation Exemptions and Currency |
The amount and currency for personal situation exemptions. |

 Reviewing Disability Reductions
Reviewing Disability ReductionsAccess the Disability Reduction page.
This page defines the reductions for disabled employees. This page does not apply to the state territory or the Navarra historical territory.
|
Search Key EE Disability Type |
The type of disability for the employee. Identifies the type of disability affecting the employee; Possible values are:
|
|
Search Key Taxable Net Base |
The total-taxable annual amount that is used to calculate the tax percentage. |
|
Return Column Disability Bracket <Fiscal Territory> |
The percentage that can be subtracted from the calculated tax percentage. For example, someone affected by disability has a smaller tax percentage and pays less. |

 Reviewing Fiscal Territories
Reviewing Fiscal TerritoriesAccess the Fiscal Territories page.
|
Effective Date |
Enter the effective date to track the history of the tax location. |
|
Pay Entity |
Select the pay entities associated with the Fiscal Territory. |
|
Tax Calendar |
Select the normalization schedule for the selected Pay Entity. This tells the system when to run the withholding percentage calculation for each Fiscal Territory during the payroll process. You can also run the calculation process separately whenever required. |

 Reviewing Fiscal Territory Calculations
Reviewing Fiscal Territory CalculationsAccess the Calculation Data page.
This page defines which brackets are used to calculate tax withholding percentages and various rates set by the Fiscal Territory. Global Payroll for Spain delivers the data for each Fiscal Territory. You can update the values as the tax regulations change.
|
Mileage Rate |
The exempted amount per mile reimbursement for mileage. |
|
Maintenance Domestic |
The exempted daily amount reimbursement for domestic traveling maintenance. |
|
Maintenance International |
The exempted daily amount reimbursement for international traveling maintenance. |
|
Night Domestic |
The exempted daily amount reimbursement for domestic overnight stays. |
|
Night International |
The exempted daily amount reimbursement for international overnight stays. |
|
Maximum Dependent Age |
The maximum age of fiscal dependents. |
|
Non-resident Withholding |
Enter the withholding percentage for non-residents. The default percentage is 25.00. If the payroll process identifies an employee as a non-resident it applies this percentage to the employee’s withholding instead of the withholding percentage that corresponds to IRPF taxes. |
|
Withholding Bracket |
The bracket used to calculate employees' withholding tax percentage. |
|
Ceiling Bracket |
The ceiling bracket that defines the minimum income required to pay tax, depending on the number of dependents. This field is displayed for the state territory only. Global Payroll for Spain delivers the bracket TAX BR MN EXENTO with these values. Note. The Ceiling Bracket field appears only if you selected the State Fiscal Territory (HE). |
|
Disability Bracket |
The bracket used to calculate the reduction in tax that applies for a disabled employee. This field is not displayed for the state fiscal territory. Note. The Disability Bracket field does not appear if you selected the State Fiscal Territory (HE). It appears for all other fiscal territories. |

 Reviewing Normalization Schedules
Reviewing Normalization SchedulesAccess the Normalization Schedule page.
Normalization Schedule
|
Tax Calculation Run |
Select the month that you want the tax percentage to be calculated during the payroll calculation. |

 Setting Up Tax Elements for Garnishments
Setting Up Tax Elements for GarnishmentsAccess the Garnishment Elements page.
|
Element Utility |
Define the type of garnishment element. Values are Child Support or Spouse Support. |
|
Element Name |
Select the element that stores the garnishment value for an employee. |

 Viewing Variable Managers
Viewing Variable ManagersAccess the View Variable Manager page.
|
Entry Type |
Identify the type of element being used. |
|
Element Name |
Select the element that will be shown in the component name. |
 Entering Payee Tax Data
Entering Payee Tax DataThis section provides an overview of payee tax data entry and discusses how to:
Enter payee tax data details.
Set up transnational mobility.

 Understanding Payee Tax Data Entry
Understanding Payee Tax Data Entry
When employees are hired, they must indicate their personal status, such as whether they have fiscal dependents, spouses to support, or neither. This information is required by the government in order to calculate an employee's taxes.

 Page Used to Define Payee Tax Data
Page Used to Define Payee Tax Data
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPES_PAYEE_DATA |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Payee Data, Taxes, Maintain Tax Data ESP, Maintain Tax Data |
Enter information about employees and their dependents as it relates to payroll calculation. |
|
|
GPES_EXPATR_MOB |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Payee Data, Taxes, Maintain Tax Data ESP, Transnational Mobility |
Indicate whether employees are affected by transnational mobility. If so, also indicate whether the employee receives compensation, pays taxes, and contributes to social security. |

 Entering Payee Tax Data Details
Entering Payee Tax Data DetailsAccess the Maintain Tax Data page.
Payee Data
In the Payee Data group box, define the details for an employee as they relate to tax calculation.
|
Effective Date |
You must enter a new effective date every time any information related to tax calculation changes, including data that appears as display-only. |
|
Disabled |
Selected if you indicate the employee is disabled on the Disability page in Human Resources. |
|
Handicap Percent |
If the employee is disabled, the handicap percent appears. This information comes from the Disability page in Human Resources. |
|
Fiscal Territory |
Select the Fiscal Territory to which the employee pays tax. The Fiscal Territory you select affects the fields that are displayed on the page. Values are Alava Fiscal Territory, Guipuzcoa Fiscal Territory, Navarra Fiscal Territory, State Fiscal Territory, and Vizcaya Fiscal Territory. |
|
Relationship Type |
Define the contract type as agreed between the employee and the company: 1. - General Relationship: For all other situations. 2. - Less 1 year relationship: For contracts with a duration of less than 1 year. 3. - Special Relationship: For special contracts, such as those for special collectives (for example, for consultants). |
|
Family Situation |
This field is displayed if you select the State Fiscal Territory in the Fiscal Territory field. Select the family situation of the employee, as defined by the government: 1. - With fiscal dependent: If the employee has dependents to support. Some dependents are recognized by Hacienda as fiscal dependents. Qualifying someone as a fiscal dependent has an impact on an employee's tax calculation. 2. - With spouse to support: If the employee has a spouse to support. 3. - Other situations: If the employee does not have fiscal dependents or a spouse to support. |
|
Address Type |
Select the address type to be used in tax reporting. Values are HOME and MAIL. |
|
Help to Go to Work |
Selected if you indicate that the employee needs help to go to work on the Disability page in Human Resources. |
|
Ceuta/Melilla |
Select if the employee lives in the cities of Ceuta or Melilla. Employees who reside in these two Spanish cities, which are located in Africa, get special tax treatment. |
|
Geographical Mobility |
Select if IRPF taxes will be reduced for the employee if the employee has geographical mobility limitations. |
|
Work life Extension |
Select if IRPF taxes will be reduced for the employee if the employee qualifies for worklife extension status. |
|
NIF Spouse |
This field is displayed if you select the State Fiscal Territory in the Fiscal Territory field and 2 – With spouse to supportfor the Family Situation. Enter the spouse fiscal identification number. |
Dependent Data
In the Dependent Data group box, define the details for an employee's dependents as they relate to tax calculation.
|
Dependent ID |
Select the dependent/beneficiary ID for the employee. |
|
Name |
The name of the dependent. |
|
Relation |
The relation of the dependent to the employee. |
|
Birthdate |
The birth date of the dependent. |
|
Adoption Date |
Enter the date that a dependent is adopted. |
|
Disabled |
This field is displayed if you select the State Fiscal Territory in the Fiscal Territory field only. It displays disability information entered for the dependent on the Dependent Data page in Human Resources. This information is used in calculating an employee's taxes. |
|
Handicap Percent |
This field is displayed if you select the State Fiscal Territory only. Define the percentage of the handicap for the dependent. This information is used in calculating an employee's taxes. |
|
Reduced Mobility |
Indicates reduced mobility for the dependent. |
|
Dependency Percentage |
This field is displayed if you select the State Fiscal Territory only. Enter a percentage that indicates the level of dependency. For example, 100% means that the person is completely dependent on the employee. |
|
Need Assistance |
Indicates whether the dependent needs assistance or not. |

 Setting Up Transnational Mobility
Setting Up Transnational MobilityAccess the Transnational Mobility page.
By default the system assumes that employees are not expatriates or displaced, so if an employee is displaced or an expatriate you need to identify them as such on this page. Once employees become expatriates or displaced, you can use this page to define each employee’s specific compensation, taxation, and social security contribution scenario to comply with regulatory requirements.
Transnational Geographic Mobility
|
Transnational Mobility |
Select this check box to indicate that the employee is displaced and this transnational mobility requires changes to the employee’s payroll calculations. By default, the system clears this check box. |
|
Country of Residence |
Select the country where the employee resides. The system reports this value when you create the Model 296 file. If the employee’s country of residence changes, you must update this value so that the Model 296 file reports the change. |
Payment Features
|
Pay Compensation |
Select this check box to have the payroll process pay the net pay amount. Clear this check box to have the payroll process calculate the net pay amount and then add a deduction to force the net pay amount to zero, thus canceling the employee’s compensation. This is necessary if you want to calculate just the employee’s social security contributions or tax withholding. The system uses the DD COMP EXPTR deduction element to store the deduction amount that forces the net pay to zero balance. The system selects this check box by default. To have the payroll process calculate compensation for displaced and expatriate employees, you must also assign to the employee the applicable earning and deduction elements according to the employee’s situation. |
|
Taxes Calculation |
Select how the payroll process calculates taxes for the employee. Your choices are:
|
|
Social Security Calculation |
Select this check box to have the payroll process calculate social security contributions for the employee and the employer. Clear this check box if you do not want the payroll process to calculate social security contributions. Global Payroll for Spain provides functionality to allow reimbursement of the amount paid directly by the employee to the social security agency. The system selects this check box by default. To have the payroll process calculate social security contributions, you must also assign to the employee the applicable earning and deduction elements according to the employee’s situation using the Assign Elements By Payee page. |
See Also
Managing Displaced People and Expatriates
 Running Legal Reports
Running Legal ReportsTo define reporting results for Process 111, Process 110, and Process 190, use the Processes ESP (GPES_TAX_SETUP) component.
This section provides an overview of tax reports, an overview of the Tax Deductions Report, lists the common elements used in this section, and discusses how to:
Run the Model 111/110 report.
Run the Model 190 report.
Run the Tax Deductions report.
Select payees for the Tax Deductions report.

 Understanding Tax Reports
Understanding Tax ReportsWith Global Payroll for Spain, you can create these tax reports:
Model 111 report (Modelo de declaración de retenciones e ingresos a cuenta de grandes empresas) used for large companies to declare employee deductions. This report is run every month.
Model 110 report (Modelo de declaración de retenciones e ingresos a cuenta) used for companies to declare employee deductions. The report is required from companies with an annual turnover of less than 6 million EUR. This report is run every quarter.
Model 190 report, an annual summary of deductions.
Note. The Model 110 report is for reporting to the Hacienda Estatal only. The report is not suitable for reporting to the other Fiscal Territories.
Global Payroll for Spain provides functionality to facilitate completion of the Model 111 and Model 110 reporting for historical territories. If you select to generate report data for an historical territory, the process generates a free format file that contains the information that needs to be reported. You can then use this file as a reference when entering reporting data on the official website of the historical territory.
In addition, Global Payroll for Spain provides functionality that enables you to print the Model 110 report for the state territory using the printing module that the state territory provides through its official web service.
See Also
Generating the Model 345 File Report

 Understanding the Tax Deductions Report
Understanding the Tax Deductions Report
Global Payroll for Spain provides an additional tax report, the Tax Deductions Report (Certificado de Haberes). The system generates a the report in two different formats, the format depending on whether the employee is a resident or non-resident. For residents, the system generates the Annual Deduction Report (GPESTXDG). For non-residents, the system generates the IRNR Annual Deduction Report (GPESIRNR).
As an employer, you are obliged to issue the Annual Deductions certificate for every employee before the beginning of the income tax return period.
The report must include fiscal data on the employer and the employee, as well as all of the deductions for an employee, including annual social security deductions and annual tax deductions. Use this document to submit employee income tax returns.
The information in the Tax Deductions Report has the same data as the 190 Model, but for individual employees.
Use the tax process component to determine which accumulators will appear on this report.

 Common Elements Used in This Section
Common Elements Used in This Section
|
Fiscal Territory |
Select the fiscal territory to which the report will be submitted. |
|
Company |
Select the company for which the report will be submitted. |
|
Calendar Year |
Select the reporting year. |
|
Person ID |
Select the ID for the person who sends the report. |
|
File Name |
Enter the flat file name and location. |
|
Contact Name |
Select the contact’s name. |
|
Contact Phone |
Displays the contact’s phone number. |

 Pages Used to Run Legal Reports
Pages Used to Run Legal Reports
|
Page Name |
Object Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GPES_TAX111_SETUP |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Processes ESP, Process 111 Setup |
List the accumulators used to generate the Model 111 report. The 111 Model is a flat file containing monthly withholding data. |
|
|
GPES_TAX110_SETUP |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Processes ESP, Process 110 Setup |
List the accumulators used to generate the Model 110 report. |
|
|
GPES_TAX190_SETUP |
Set Up HRMS, Product Related, Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Processes ESP, Process 190 Setup |
List the accumulators used to generate the Model 190 report. |
|
|
GPES_RC_TAX_111 |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Taxes, Create 111/110 Model File ESP, Create 111/110 Model File |
Select the parameters with which the system generates the Model 111 or Model 110 report. Use the Tax Process page to establish the reported elements. |
|
|
GPES_RC_TAX_190 |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Year-End Processing, Create 190 Model File ESP, Create 190 Model File |
Select the run control parameters used to generate the 190 Model report. |
|
|
GPES_PP_EMPL_ASS |
Click the Employees link on the Create 190 Model file page. |
Select the employees that the system will process. Use this page only if you select to process a complimentary type of statement. |
|
|
GPES_RC_TAX_10T |
Global Payroll & Absence Mgmt, Year-End Processing, Tax Deductions Report ESP, Tax Deductions Report |
Generate the Tax Deductions report (GPESTAX1) for resident or non-resident employees. The Application Engine (AE) processes generate a flat file containing annual tax deduction information for each employee. You can run the applicable AE process by itself or as part of a PSJob. The job first runs the applicable AE process to generate the flat file. Then the job uses a Microsoft Word template to merge the data from the text file into a Word document with the required format. |
|
|
GPES_TAX010_SEC |
Click the Payee List link on the Tax Deductions Report page. The Payee List link is only available if the Listed Payees option is selected on the Tax Deductions Report page. |
Select the employees to include in the Tax Deduction report. |

 Running the Model 111/110 Report
Running the Model 111/110 ReportAccess the Create 111/110 Model File page.
Note. Only fields that are unique to the Model 111/110 report are discussed here. Fields common to all tax reports are defined elsewhere in this chapter.
See Common Elements Used in This Section.
For the state territory the process generates a flat file that you can electronically import into the official program provided by the tax authorities. For historical territories the process generates a free format file that contains a readable summary of the information that you need to report. You can then use this file as a reference when entering reporting data on the official website of the historical territory. The file name that the process generates for historical territories is the file name that you specify plus the letter S at the end.
Report Request Parameters
|
Model |
Select the report you want to run: Model 110 or Model 111. The model you select here determines whether the system displays a Quarter or Month field. |
|
Fiscal Territory |
Select the fiscal territory for which you are generating the model file. The system prompts you to select from the available tax locations. Based on your selection, the process properly formats the files that it generates for the state or historical territory. |
|
Month |
This field is displayed if you select Model 111. Select the year and reporting month. |
|
Quarter |
This field is displayed if you select Model 110. Select the year and the quarter for the report. |
|
Pay Type |
Select whether the payment of the Model 110 report for the state territory will be done in cash or by bank transfer. The value that you select appears in the Pay Type box of the report when you are using the printing module that the fiscal territory provides on its official website. |
|
Declaration Type |
Select declaration type of the Model 110 report for the state territory. The value that you select appears in the Declaration Type box of the report when you are using the printing module that the fiscal territory provides on its official website. Valid values are:
|
Signature
Use this group box to enter the values for the Signature City and Signature Date boxes of the report when you are using the printing module that the state fiscal territory provides on its official website to generate the Model 110 report.
|
Signature City |
Select the location where the file is generated. The location appears in the corresponding box on the printed version of the report. |
|
Signature Date |
Select the date the file is generated. The date that you select appears in the corresponding box on the printed version of the report. |

 Running the Model 190 Report
Running the Model 190 ReportAccess the Create 190 Model File page.
Note. Only fields that are unique to the Model 190 report are discussed here. Fields common to all tax reports are defined elsewhere in this chapter.
See Common Elements Used in This Section.
The process generates a flat file that you can electronically import into the official program provided by the tax authorities. The process uses different formats for the file depending on the selected fiscal territory.
Report Request Parameters
|
Fiscal Territory |
Select the fiscal territory for which you are generating the model file. The system prompts you to select from the available tax locations. Based on your selection, the process properly formats the files that it generates for the state or historical territory. |
|
Calendar Year |
Select the calendar year for which you are generating the model file. |
|
Device CD |
Select the device CD. |
|
File Name |
Enter the path where you want the process to store the model file. Include the name of the file that you want the process to use for the model file. Entering a file extension type is optional. The system stores the data in a text file by default. |
Sender Data
Companies can manage their own tax reporting or give that responsibility to another company. In cases where one company is sending information for other companies, use this group box to enter contact data for the company that is sending the information. Then use the Contact Data tab in the Companies to Process group box to enter the contact information specific to each company. If you are sending data for your own company only, leave this group box blank and enter contact information only in the Contact Data tab.
|
Company |
Enter the name of the company that is sending the model file. |
|
Person ID |
Enter the ID of the person who is sending the model file. |
|
Name and Phone |
Enter the name and contact phone number of the person who is sending the model file. The system displays these values when you select the person ID. |
Companies to Process - Reporting Type
|
Company |
Select the companies for which you are sending the model file. The process creates a report for each company that you specify. |
|
Description |
The system displays the name of the selected company. |
|
Type of Statement |
Select the type of model statement that you want to generate. Your choices are:
|
|
Related ID Number |
The system displays this field when the statement type is either complement or substitute. Enter the ID of the previously generated model file that you want to complement with more employees or substitute with new data. |
|
Employee |
Click this link to access the Employees to Process page, where you can select the employees who the system will process. The system displays this link only if you select to process a complimentary type of statement. When your system displays the Employees to Process page, use the EmplID field to select the employees that you want to include in the model file. The system enables you to select only the employees who are in the related reporting table for the selected year. |
Companies to Process - Contact Data
Use this tab to enter the contact information for each of the companies for which you are sending the model file.
|
Employee ID |
Enter the ID of the person who is the contact for the model file at the company. |
|
Contact Name |
Enter the name of the person who is the contact for the model file at the company. |
|
Contact Phone |
Enter the contact phone number of the person who is the contact for the model file at the company. |

 Running the Tax Deductions Report
Running the Tax Deductions ReportAccess the Tax Deductions Report page.
|
Company |
Select the company for which this report will be run. |
|
Fiscal Territory |
Select the fiscal territory to which the Company submits tax reporting information. Note. Global Payroll for Spain provides functionality for the generating Tax Deductions Report just for the state fiscal territory. For other fiscal territories you can generate this report through the programs that each fiscal agency provides when you report the Model 190. You can download these programs directly from the official websites of the historical territories. |
|
Calendar Year |
Select the calendar year to report. |
|
Signature City |
Enter the city where the report was signed. |
|
Signature Date |
Enter the date that the report was signed. |
|
Responsible ID |
Enter the ID of the person who is responsible for signing the report. |
|
Payee Selection Option |
Select All Payees to include all the employees in the Company in the report. Otherwise, select Listed Payees and click the Payee List link to select the employees for the report. |

 Selecting Payees for the Tax Deductions Report
Selecting Payees for the Tax Deductions ReportAccess the Payee List page.
|
EmplID (employee ID) |
Select the employee that you want to run the Tax Deduction report for. |
 Viewing Delivered Tax Elements
Viewing Delivered Tax ElementsThis section discusses:
Delivered tax deductions.
Delivered earnings for historical territories.
Delivered tax process lists.

 Delivered Tax Deductions
Delivered Tax DeductionsThis table lists the delivered tax deductions in Global Payroll for Spain:
|
Deduction |
Description |
|
IRPF |
Salary taxes. This deduction is defined as Base * Percent, where: Base is TAX AC DIN S Percent is TAX VR PCT IRPF |
|
IRPF AFW |
Tax to be forwarded. This deduction is calculated during a retroactivity process and is used to forward values to the current period. |
|
IRPF EXT AFW |
Exempt income to be forwarded. |
|
IRPF EXT FWD |
Exempt income from previous years. |
|
IRPF EXT RTR |
Exempt income from retro. |
|
IRPF FWD |
IRPF deduction for retro of periods in the previous year. |
|
IRPF RTR |
IRPF deduction for retro of periods in the current year. |
|
IRPF SPC |
Salary in kind IRPF. This deduction is defined as Base * Percent, where: Base is TAX AC SPC S Percent is TAX VR PCT IRPF |
|
IRPF SPC AFW |
Salary in kind IRPF to be forwarded. This deduction is calculated during a retroactivity process and is used to forward values to the current period. |
|
IRPF SPC EXA |
Exempt in-kind to be forwarded. |
|
IRPF SPC EXF |
Exempt in-kind from previous years. |
|
IRPF SPC FWD |
Salary in kind IRPF for retro of periods in the previous year. |
|
IRPF SPC RTR |
Salary in kind IRPF for retro of periods in the current year. |
|
IRPF SPRC |
IRPF in-kind employee. |
|
IRPF SPCR AF |
IRPF in-kind employee to be forwarded. |
|
IRPF SPCR FW |
IRPF in-kind employee from previous years. |
|
IRPF SPCR RT |
IRPF in-kind employee from current year. |

 Delivered Earnings for Irregular Income
Delivered Earnings for Irregular Income
The following table lists the new delivered earnings elements related to calculation of irregular income reductions for employees who belong to historical territories:
|
Earning |
Description |
|
RDTO IRREGUL |
Irregular income. |
|
RDTO IRR 50 |
Irregular income affected by 50% reduction. This earning corresponds to income accrued in more than five years. |
|
RDTO IRR 50D |
Irregular income affected by 50% reduction. This earning is used in the Navarra historical territory. It corresponds to income that has been derived from disability benefits. |
|
RDTO IRR 70 |
Irregular income affected by 70% reduction. This earning is used in the Navarra historical territory. It corresponds to income that has been derived from death benefits. |

 Delivered Tax Process List
Delivered Tax Process ListGlobal Payroll for Spain delivers the TAX PR CALC IRPF process list specifically for running the tax percentage calculation separately from the payroll process. The process list has a run type of IRPF_CALC.
Note. The PeopleSoft system delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Spain. Instructions for running the query are provided in thePeopleSoft Enterprise Global Payroll 9.0 PeopleBook.
See Also
Understanding How to View Delivered Elements