







|
ALSB delivers message data and alerts to one or more reporting providers. Message data can be captured from the body of the message and from other variables associated with the message, such as header or inbound variables. Alert data contains information about Service Level Agreement (SLA) violations that you can configure to monitor proxy services. You can use the message or alert data delivered to the reporting provider for functions such as tracking messages or regulatory auditing.
ALSB includes a JMS reporting provider for message reporting. The Reporting module in the ALSB Console displays the information captured from this reporting provider. If you do not wish to use the JMS Reporting Provider that is provided with your ALSB installation, you can untarget it and create your own reporting provider using the Reporting Service Provider Interface (SPI). If you configure your own reporting provider for messages, no information is displayed in the ALSB Console. You must to create your own user interface. To capture SLA data, you must to create a reporting provider for alerts.
This chapter contains information about following topics
ALSB contains an extensible framework for creating one or more reporting providers for messages or alerts.
To enable message reporting you must first create a Report action in the message flow for the proxy service. The Report action allows you to extract information from each message and write it to the ALSB Reporting Data Stream. You do not need to configure a report action for alert reporting. Alert data is always available in the Reporting Data Stream. For more information, see How to Enable Message Reporting.
Information you need for creating your own reporting provider is located in com.bea.wli.reporting in the
Javadoc for AquaLogic Service Bus. The Javadoc provides information about what you need to do for implementing a reporting provider, including how to package it, where it goes, how to deploy it, and the order of deployment. The reporting schema is MessageReporting.xsd, located in ALSB_HOME/lib/common/reporting-api.jar.
Figure 5-1 shows the reporting framework.
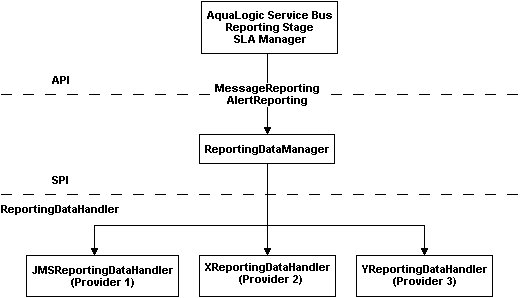
As shown in the Figure 5-1, both report messages and alerts are exported to reporting data streams. In the Report stage, information is extracted by the Report action from each message and written to the Reporting Data Stream with metadata that adheres to MessageReporting.xsd. Similarly, the SLA Manager uses Reporting Data Manager APIs to write to the Alert Reporting Stream with metadata that adheres to the AlertReporting.xsd. To develop a reporting provider for alerts or your own message reporting provider, you need to implement ReportingDataHandler interface and use the ReportingDataManager class.
The ReportingDataHandler interface takes the reporting or alert data stream and processes it. It can either process or store a stream, or do both in a relational database, file, JMS queue, and so on. Depending on which stream you want to use, you need to implement the appropriate handle methods to process the data stream:
handle(com.bea.xml.XmlObject metadata, String s)
handle(com.bea.xml.XmlObject metadata, com.bea.xml.XmlObject data)
handle method to write to the Alert Reporting Stream: handle(com.bea.xml.XmlObject metadata, com.bea.xml.XmlObject data)
The ReportingDataManager is a local server object that keeps a registry of reporting providers. Reporting providers implement the ReportingDataHandler interface. The ReportingDataManager provides operations to:
The JMS Reporting Provider provides a pluggable architecture to capture the reporting information from each message using a Report action. The default JMS Reporting Provider is automatically configured when you create an ALSB domain. All messages across the cluster are aggregated and stored in a JMS Reporting Provider Data Store in a database specific format. This provider displays information from the JMS Reporting Provider Data Store.
| Note: | If you do not wish to use this reporting provider, you must untarget it. For more information, see How to Untarget a JMS Reporting Provider. |
The JMS Reporting Provider consists of a producer and a consumer, which are decoupled to improve scalability. The producer is a JMS producer and the Message Driven Bean (MDB) acts as the JMS consumer, as shown in Figure 5-2.
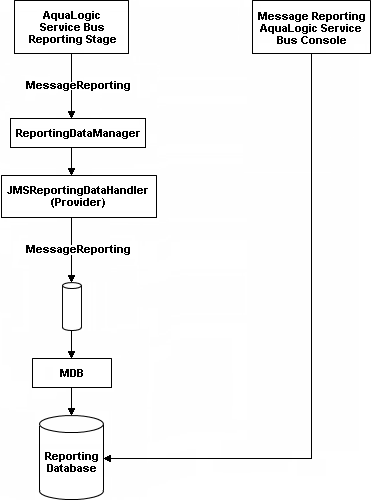
The Reporting stage contains the Report actions that collect the reporting information and dispatch the reporting stream to JMS Reporting Provider through various handle operations in the ReportingDataManager. The JMSReportingDataHandler is the JMS producer of the reporting provider. The JMSReportingDataHandler takes the reporting stream and logs the information to a JMS queue. The MDB listens to the JMS reporting queue, which processes the message asynchronously and stores the data in the JMS Reporting Provider Data Store.
To receive report messages from either the JMS Reporting Provider, which is provided with ALSB installation, or your reporting provider, you must first create a Report action in the message flow for the proxy service. The Report action allows you to extract information from each message and write it to the ALSB Reporting Data Stream. In the Report action, you must specify the information you want to extract from the message and add to the ALSB Reporting Data Stream.
You need not to configure a Report action for alert reporting. Alert data are always available in the Reporting Data Stream.
When configuring a Report action, use key values to extract key identifiers from the message. You can configure multiple keys. Information can be captured not only from the body of the message but any other variable associated with the message, such as header or inbound variables. For more information about message variables, see Message Context in AquaLogic Service Bus User Guide.
You can use any XML elements as a key:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<poIncoming>
<areacode>408</areacode>
<item-quantity>100</item-quantity>
<item-code>ABC</item-code>
<item-description>Medicine</item-description>
</poIncoming>
For example, you can specify the key as the itemcode, the value as .//item-code (an XPath expression), and the variable as message body (body), as shown in Figure 5-3.

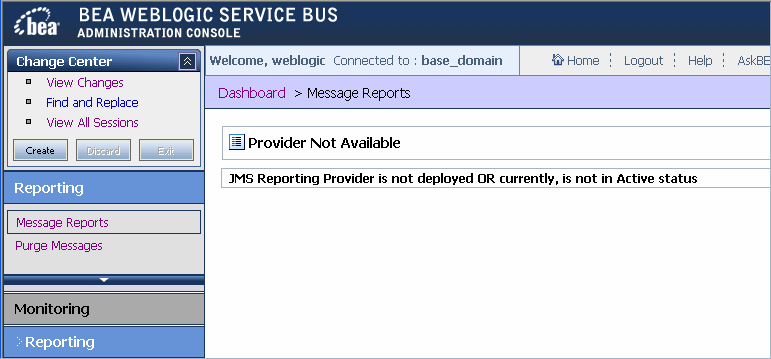
If you are using the default JMS Reporting Provider, the keys and associated values are displayed in the Report Index column of the Summary of Messages table. If you configure multiple keys, the key-value pairs are displayed in the Report Index column with each key-value separated by a comma, as shown in Figure 5-4.
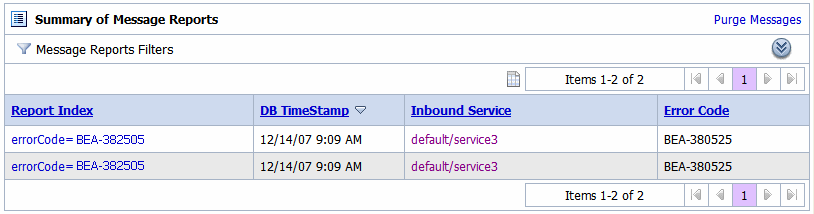
For information about creating a Report action or on how to view the Summary of Messages page, see the following in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console:
If you wish to stop a reporting provider when the server is running in the ALSB domain, do the following:
If you do not wish to use the default JMS reporting provider or any reporting provider, you must untarget it.
| Note: | If no reporting provider exists, you can still define a Report action. However, no data is be written. |
To untarget a reporting provider when the server is running in the ALSB domain, do the following:
| Note: | This step is only required for reporting providers that use their own data sources. To untarget the default JMS reporting provider in ALSB installation you must perform the following steps. |
 JDBC
JDBC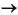 Data Sources.
Data Sources.If the server is not running in the ALSB domain, you can use the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) to remove the JMS Reporting Provider from the ALSB domain. For more information about WLST, see WebLogic Scripting Tool in the WebLogic Server documentation.
To untarget a reporting provider, complete the following steps:
C:>java com.bea.plateng.domain.script.jython.WLST_offline
wls:/offline>readDomain("C:/bea/user_projects/domains/base_domain")
wls:/offline/base_domain>unassign("JdbcSystemResource", "wlsbjmsrpDataSource", "Target", "AdminServer")
wls:/offline/base_domain>unassign("AppDeployment", "JMS Reporting Provider", "Target", "AdminServer")
wls:/offline/base_domain>updateDomain()
wls:/offline/base_domain>closeDomain()
After the ALSB JMS reporting provider is untargeted, the Reporting module in the ALSB Console indicates that the reporting provider is not deployed, as shown Figure 5-7.
| Note: | In a cluster, the JMS Reporting Provider is targeted to Cluster. Therefore in a cluster, to view and purge messages, you must configure at least one managed server to run with the Administration server. If no managed servers are running, the ALSB Console displays the message shown in Figure 5-7. |
The reporting module in the ALSB Console displays the information collected by the JMS Reporting Provider Data Store. The first page of the Reporting module, called the Summary of Messages, displays a table containing the extracted information and other information, such as the time the message was written to the database and the service with which the message is associated. You can customize the display of information on this page by filtering and sorting the data. You can also drill down to view detailed information about specific messages, including error information.
The Reporting module provides a purge function to help you manage your message data. You can purge all of the messages from the reporting datastore or base the purge on a time-range.
The JMS Reporting Provider Data Store requires a database. An evaluation version of the PointBase database is installed with WebLogic Server. You can use PointBase for a development environment but not for production. ALSB also supports databases from other vendors. Be sure to apply standard database administration practices to the database hosting the JMS Reporting Provider Data Store. For more information, see How to Configure a Database for the JMS Reporting Provider Store.
For more information about the reporting module, see Reporting in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
When you click Message Reports in the Reporting module of the Operations navigation bar, the Summary of Messages page is displayed. This page contains a table that provides a list of report messages sorted by the database timestamp.
If the messages are not filtered, the Summary of Messages table displays up to 100 of the latest messages based on the database timestamp. If you filter the messages, up to 1000 messages are displayed.
| Note: | The filter is not reset automatically. The filter remains in effect until you update it or reset it. |
Table 5-1 describes the information in the Summary of Message Reports.
Displays the key-value pairs extracted from the message context variables or the message payload. For more information, see About the JMS Reporting Provider
|
|
Displays the error code associated with this message, if it exists. For more information about error codes, see Error Messages and Handling in
Proxy Services: Error Handlers in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
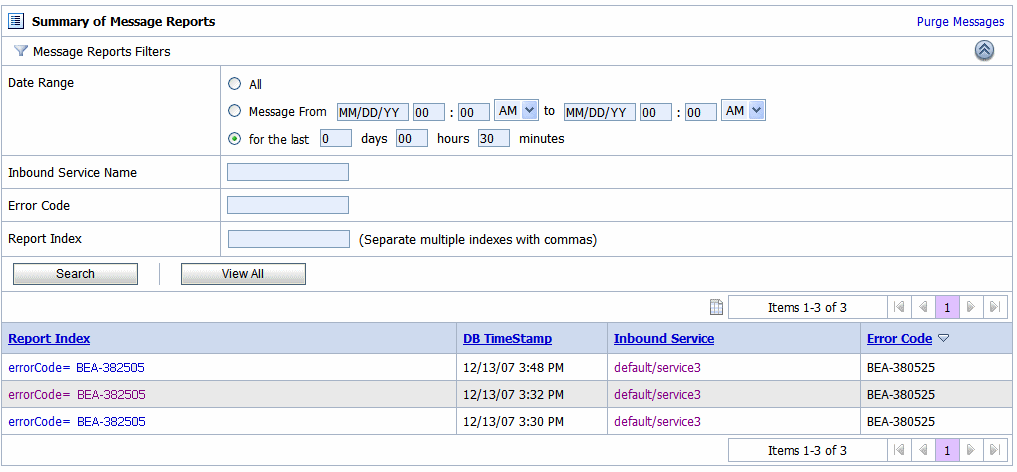
To search for specific messages, click Filter in the Summary of Messages Table to filter the display of messages. The available filtering is shown in Figure 5-9.
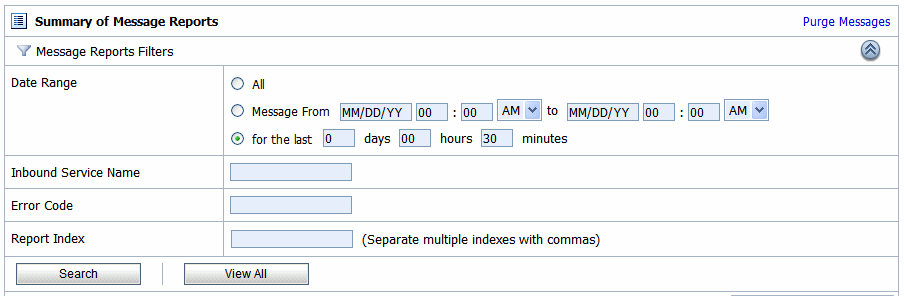
As shown in Figure 5-9, you can filter report messages for a specified period of time, by the name of a service, by error code, and by report index. After you filter the messages, the title of the page changes to Summary of Filtered Messages. For information about using the Summary of Messages filter, see Listing and Locating Messages in Reporting in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
To view more information about a report message, click the name of the message in the Report Index column. The View Message Details page is displayed.
The View Message Details page displays complete information about the report messages, as shown in Figure 5-10.
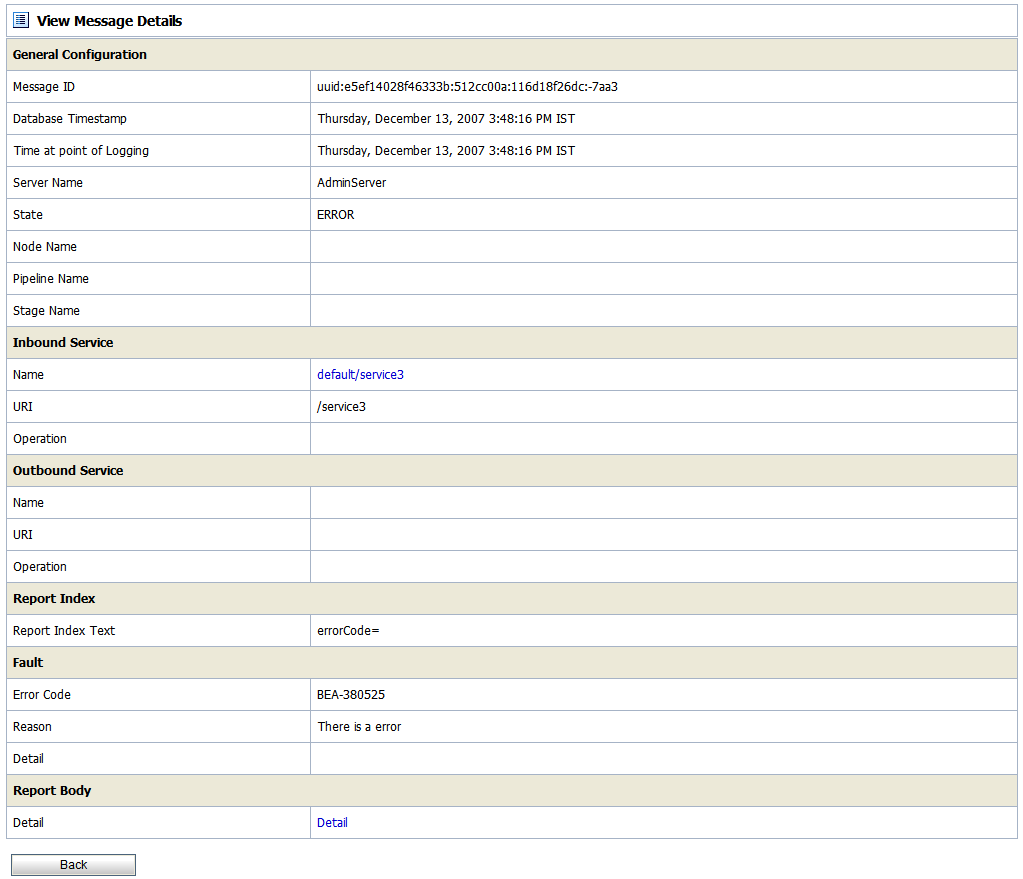
Table 5-2 describes the information displayed in Report Message Detail Page.
The inbound proxy service associated with this message. An inbound proxy service exchanges messages with client applications. The name is a link to the View a Proxy Service page. For more information about this page, see “Viewing and Changing Proxy Services” in Proxy Services in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
||
The outbound business service associated with this message. An outbound business service exchanges messages with an ALSB proxy service. Click on the link to go to View Business Service Details page.
For more information about this page, see “Viewing and Changing Business Services” in
Business Services in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
||
Displays the key-value pairs extracted by a Report Action from the message context variables or the message payload. For more information, see About the JMS Reporting Provider.
|
||
The code associated with the error, if any. For more information, see Error Messages and Handling in
Proxy Services: Error Handlers in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
||
The code associated with the error, if any. For more information, see Error Messages and Handling in
Proxy Services: Error Handlers in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
||
Opens a new browser window that displays the report body in a browser. You can use an XQuery expression in a Report action to capture the report body text. For more information, see Report in
Proxy Services: Actions and Using the Inline XQuery Expression Editor in
Proxy Services:XQuery Editors in Using the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
|
You can purge all of the messages from the reporting datastore or base the purge on a range of time. Message purging is an asynchronous process that occurs in the ALSB Console. This feature enables you to work with the Summary of Messages page in the ALSB Console while the purge occurs in the background.
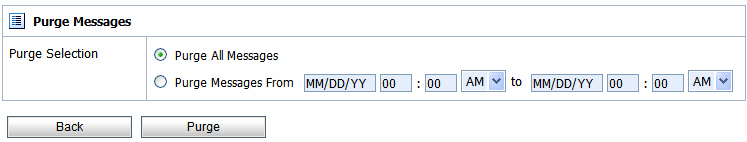
The duration of time it takes a purge to complete depends on how many messages are in the purge queue. The deletion of messages is slowed if you search for reporting messages during the purge process. Moreover, the Summary of Messages page may display incorrect data as some data may not yet be purged.
Because the purge process is asynchronous and occurs in the background, the ALSB Console does not display any messages to indicate that a purge is in process. However, if another user attempts to start a purge when a purge is in progress, the following message is displayed:
A Purge job is already running. Please try later.ALSB requires a database for the JMS Reporting Provider Data Store. The PointBase database that is installed with WebLogic Server is for evaluation purposes only and not intended for a production environment.
In a production environment you must use one of the supported databases. For the latest information about supported databases, see Supported Databases and Drivers in Supported Configurations for ALSB.
When you create an ALSB domain, the Configuration Wizard does not create database tables automatically. In a development environment, the default JMS Reporting Provider checks whether tables exist for the specified database at run time. If tables do not exist, the Reporting Provider creates them; if they do exist, the Reporting Provider uses them.
| Note: | If you are using Pointbase, you need not specify a database in the Configuration Wizard. |
You can specify which database is used by the JMS Reporting Provider in one of the following ways:
<BEA_HOME>/alsb_3.0/dbscripts>lswhere BEA_HOME represents the location in which you installed WebLogic products.
For complete information about configuring a database for production , see AquaLogic Service Bus Deployment Guide in the following chapters:


|