


|

|
|
|
|
Batch Registry Command Reference
The following sections provide detailed explanations of the Batch Registry commands and command syntax:
Each Batch Registry utility command has syntax requirements. These syntax requirements are called character case, strings, and wildcards.
Using Character Case
Batch Registry utility commands have the following character case requirements:
To determine the case of a particular item, use the Batch Registry list commands, such as "List User" or "List Document".
Using Strings
You must enclose all character strings containing spaces, semi-colons, or quotes in single or double quotation marks. For example:
In addition, the following strings are equivalent:
Many commands let you use standard UNIX wildcards in file and document names, including asterisk (*) and percent (%).
Other commands use the `%' character to signify "all similar objects in the database."
For example, the following command lists all active processes and process definitions:
LIST JOB NAME %;
Individual command descriptions indicate when you can use the `%' wildcard for this purpose.
Overview of the Batch Registry Commands
The following table provides a brief description of each Batch Registry utility command.
The Batch Registry utility records errors in a file called batreg.log.
|
Category |
Command |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Users |
Create User |
Creates a user record in the eLink Business Process Option database. |
|
Create User with Pool |
Creates a user record in the Business Process database, simultaneously creating a pool record for the user. |
|
|
Delete User |
Deletes a user record from the eLink Business Process Option database. |
|
|
Update User |
Changes the name, password, email address, or other attribute of an existing eLink Business Process Option user. |
|
|
List User |
Lists information about eLink Business Process Option users. |
|
|
Pools |
Create Pool |
Creates a new pool. |
|
Delete Pool |
Deletes a pool from the database. |
|
|
Update Pool |
Renames an existing pool. |
|
|
Add User to Pool |
Adds an eLink Business Process Option user to an existing Pool. |
|
|
Remove User from Pool |
Removes a particular user from a pool. |
|
|
Remove All from Pool |
Removes all users from a pool. |
|
|
List Pool |
Lists information about all defined pools. |
|
|
Documents |
Create Document |
Creates one or more eLink Business Process Option document objects and associates these objects with an initial content file. |
|
Export Document |
Prepares a document for use on another server. |
|
|
Import Document |
Copies a document object and the associated content file from one Process Engine to another. |
|
|
Delete Document |
Deletes one or more document objects from the database. |
|
|
List Document |
Lists information about one or more documents. |
|
|
Processes |
Export Job |
Prepares a process definition and all related tasks, roles, placeholders, triggers, and task user interface documents for use on another server. |
|
Import Job |
Copies a process definition and all related tasks, roles, placeholders, triggers, and task user interface documents from one Process Engine to another. |
|
|
Delete Job |
Deletes a process definition from the database. |
|
|
List Job |
Lists information about one or more process definitions or active processes. |
|
|
Repository |
Create Repository |
Creates a new repository. |
|
Set Default Repository |
Changes the default repository. |
|
|
List Repository |
Lists information about repositories. |
|
|
Privileges |
Grant Privilege |
Provides one or more users with the privilege to manipulate a process, document, or trigger. |
|
Revoke Privilege |
Revokes privileges on processes, documents, and triggers. |
|
|
List Privilege |
Lists process, document, or trigger privileges. |
|
|
Class |
Create Subclass |
Creates a subclass of an existing class. |
|
Delete Class |
Deletes a class from the database. |
|
|
List Class Hierarchy |
Lists all defined classes and subclasses. |
|
|
List Class |
Lists information about an eLink Business Process Option class. |
|
|
Promote Class |
Promotes a class within its branch, retaining relationships to classes derived from it. |
|
|
Promote Instances |
Promotes the instances of a specified class so that they become instances of that class's parent. |
|
|
Update Class - Add Attribute |
Adds an attribute to a class definition. |
|
|
Update Class - Demote Attribute |
Demotes an attribute from a class to all of its subclasses. |
|
|
Update Class - Promote Attribute |
Promotes an attribute from a class to its parent. |
|
|
Update Class - Remove Attribute |
Removes an attribute from a class definition and from all of the target class's subclasses. |
|
|
Update Class - Rename Attribute |
Changes the name of an attribute in a class definition and in all subclasses of the target class. |
|
|
Update Class - Set Default |
Sets the default value for a user-defined attribute in a particular class. |
|
|
Triggers |
Create Trigger |
Creates a global object trigger or global event trigger. |
|
Delete Trigger |
Deletes a trigger from the database. |
|
|
List Trigger |
Lists information about global triggers with a particular event and action specification. |
|
|
Events |
Register Event |
Registers a user-defined event type for use in global trigger event specification. |
|
Unregister Event |
Removes a registered event type from the database. |
|
|
Signal Event |
Signals a registered event. |
|
|
List Event |
Lists all registered event types. |
|
|
Action |
Register Message Action |
Registers a triggered action specification that puts a message on a specific tuxedo queue. |
|
Register RPC Action |
Registers a user-written program for use in a global trigger action specification. |
|
|
Unregister Action |
Removes a registered action from the database. |
|
|
List Message Action |
Lists all registered MESSAGE actions. |
|
|
List RPC Action |
Lists all registered RPC actions. |
Command Reference
This section provides detailed descriptions of each of the Batch Registry commands.
Add User To Pool
|
Description |
Adds an eLink Business Process Option user to an existing Pool. |
|
|
Syntax |
ADD USER user_name TO POOL pool_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
user_name |
The name of an existing eLink Business Process Option user. |
|
pool_name |
The name of the pool to which the user is added. |
|
|
Example |
ADD USER Kelly TO POOL Finance; |
Note: A user must belong to a pool to perform an eLink Business Process Option task. Multiple eLink Business Process Option users can be added to the same pool and each user can belong to multiple pools. A typical installation has multiple pools and multiple users, as shown here.
Figure A-4 Typical Pool/User Organization
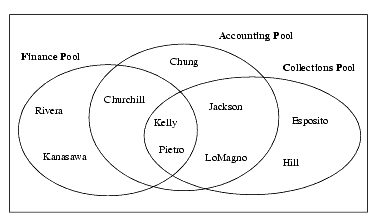
When you add users to a pool, they are granted the privileges of that pool while still retaining any pre-existing privileges.
Create Document File
|
Description |
Creates one or more eLink Business Process Option document objects and associates these objects with an initial content file. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE DOCUMENT file pathname |
|
|
Parameters |
pathname |
File(s) to be used as the initial document content; the file specification can include wildcards and full pathnames. |
|
name_pattern |
Name of the document(s) to be created. The name pattern can include wildcards. If unspecified, the document names are the same as the file names. |
|
|
keyword |
Keyword(s) for the new document(s); specify multiple keywords as a comma-separated string with no intervening spaces. |
|
|
class_name |
The class for the new documents. class_name must be an existing subclass of Document. If unspecified, the documents become members of the Document class. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be set or updated; the attribute must be defined for class_name or the Document class. |
|
|
attribute_value |
Value of attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
CREATE DOCUMENT FILE /usr/local/smith/report/*.txt |
Notes: A file is any information that can be stored, retrieved, or processed by the computer, such as an ASCII file, a scanned image, or word-processing file.
A file associated with an eLink Business Process Option document object is called a content file.
A document object is an ProductName database structure that describes one particular content file, such as the file name, creation date, and creator. Any file that you want to track or manage with ProductName must be associated with a document object.
One content file can be associated with multiple document objects. However, each object/file relationship is unique.
When you create a document, eLink Business Process Option copies the content file into the default repository.
Figure A-5 Document/Content File Associations
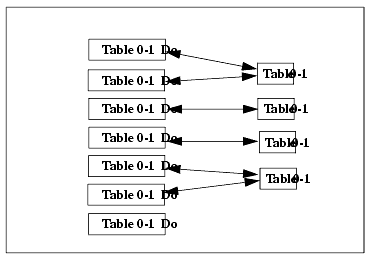
Document keywords describe the characteristics of the content file. For example, subject keywords might include annual report, product graphic, or insurance form. Keywords are used for document searches in the eLink Business Process Option application.
The optional class_name parameter let you categorize the document by class. By default, a new document becomes a member of the predefined Document class. You can use the class_name parameter to specify an existing subclass of Document; for example, Reports.
The ATTRIBUTE/VALUE keywords let you assign a value to a particular attribute for the class or override the default value; for example, writer name or document signoff date. You cannot create a new attribute, however; new class attributes can be defined only with "Update Class - Add Attribute".
An important document attribute is called IC_APPLICATION. This predefined attribute specifies the kind of application used to create or update the document content file. The default value is "ascii text", which means that the document is opened in whatever application you use to update ASCII files; for example, NotePad.
You map the value of IC_APPLICATION with an actual document-handling application using the setup program.
When you create a document, eLink Business Process Option grants you Update privilege on the document object; all members of the admin pool have Manage privilege on the document object; and all other users (PUBLIC) have Read privilege on the document object.
Create Document lists the following information for each new document:
|
Description |
Creates a new pool. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE POOL pool_name [ CLASS class_name ] |
|
|
Parameters |
pool_name |
Name of the new pool. |
|
class_name |
The class for the new pool. class_name must be an existing subclass of Pool. If unspecified, the pool becomes a member of the Pool class. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be set or updated; the attribute must be defined for class_name or the Pool class. |
|
|
attribute_value |
Value of attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
CREATE POOL Editors CLASS Writer; |
Notes: A pool is a group of users who perform the same job function. This command creates a pool record in the database. Once the pool record exists, you can populate the pool with "Add User To Pool".
There is no restriction on the number of pools you can create or on pool organization. Typically, a site has multiple pools and individual users often belong to several pools at once.
You should create a pool for each eLink Business Process Option user. This step allows tasks to be assigned, delegated, or routed to individual users.
Figure A-6 Pool/Task Association
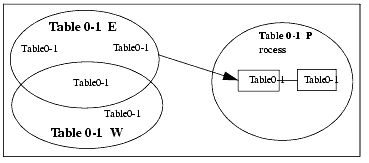
The optional class_name parameter lets you categorize the pool by class. By default, a new pool becomes a member of the predefined Pool class. You can use the class_name parameter to specify a user-defined subclass of Pool; for example, Writers.
The ATTRIBUTE/VALUE keyword lets you assign a value to a particular attribute for the class or override the default value. For example, security level, job description, or department name. You cannot create a new attribute, however; new class attributes can be defined only with "Update Class - Add Attribute".
Create Repository
|
Description |
Creates a new repository. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE REPOSITORY location { location | hostname:port } |
|
|
Parameters |
location |
Name of the repository host. For Repository Servers, hostname is the host in which the Repository Server is to run, and port is the port number in which the Repository Server is running. For NFS repositories, location is the name of the host on which the repository server is running. |
|
pathname |
Full pathname of the repository directory. |
|
|
type |
Repository type: 1 NFS 5 Repository Server |
|
|
class_name |
Optional. The class for the new repository. The class_name must be an existing subclass of Repository. If unspecified, the repository becomes a member of the Repository class. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Optional. Attribute to be set or updated; the attribute must be defined for class_name or the Repository class. |
|
|
attribute_value |
Optional, but required if ATTRIBUTE is specified. Value of attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
CREATE REPOSITORY LOCATION ServerA PARTITION /usr/local/ic/graphics_repos TYPE 1; |
Notes: A repository contains information about the directory used to store document content files, including the repository host name, directory pathname, and repository type. You can create multiple repositories to organize content files by, for example, file type, access privilege, or subject matter.
You must create the repository directory and start the respository server before running Create Repository (for example, with the UNIX mkdir command). Ensure that all eLink Business Process Option users have network access to this directory and can read and write files that are stored there.
If you change the default repository, existing documents remain in the original repository, including the system documents described above. As a result, you must keep all repositories accessible; otherwise, users may not be able to access old documents, their previously defined queries, or the system documents used to maintain folder persistence in the organizer windows.
The optional class_name parameter lets you categorize the repository by class. By default, a new repository becomes a member of the predefined Repository class. You can use the class_name parameter to specify a user-defined subclass of Repository; for example, Graphics.
The ATTRIBUTE/VALUE keywords let you assign a value to a particular attribute for the class or override the default value. For example, security level or kind of content file. You cannot create a new attribute, however; new class attributes can be defined only with "Update Class - Add Attribute".
Create Subclass
|
Description |
Creates a subclass of an existing class. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE SUBCLASS class_name OF parent_name ; |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the new class. The class name can include only the characters 0 through 9, a through z (upper and lower case), and underscore (_). |
|
parent_name |
Name of an existing class. Be sure that you specify the class name with its original case structure. Base class names begin with an uppercase letter. |
|
|
Example |
CREATE SUBCLASS SPR OF Document; |
Notes: A class is used to categorize ProductName objects by attributes. Attributes are inherited from the "parent" class, which is either one of the predefined base classes or a subclass of a base class. The base object classes include:
Binder
Document
Job
Link
Pool
Repository
Role
Task
Trigger
User
A Job class member is called a process definition and a Binder class member is called a placeholder.
Each parent class can have multiple subclasses and each subclass can be a parent of still other subclasses. You can list existing classes and subclasses with "List Class Hierarchy".
Once you create a subclass, you can add attributes to the class definition with "Update Class - Add Attribute".
Create Trigger
|
Description |
Creates a global object trigger or global event trigger. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE TRIGGER [ NAME trigger_name ] An action_specifier can take these forms: SENDMAIL POOL pool_name FORMAT mail_format [ text | file_name ] JOBCREATE process_definition POOL owner_pool NAME process_ID PROCEDURE action_name ARGUMENTS parameter MESSAGE action_name ARGUMENTS parameter ATTRIBUTES a1 a2 a3 |
|
|
Parameters |
trigger_name |
Name of the new trigger. If unspecified, the action type becomes the trigger name: either JOBCREATE, MESSAGE, SENDMAIL, or PROCEDURE. |
|
event_name |
Name of the event type that causes the trigger action to be performed. |
|
|
action_specifier |
The action to be performed when the event occurs. This parameter can take any of the forms listed above for JOBCREATE, MESSAGE, SENDMAIL, and PROCEDURE actions. |
|
|
Parameters for SENDMAIL action: |
||
|
pool_name |
Name of the pool to receive the mail message. |
|
|
mail_format |
Format of the mail message; either:
|
|
|
Parameters for JOBCREATE action: |
||
|
process_definition |
Process definition id from which the active process is created. |
|
|
owner_pool |
Name of the process's owner pool; a member of this pool is granted Manage and Update privileges on the process. |
|
|
process_name |
Name of the active process; the active process name can be the same or different than the process definition name. |
|
|
Parameters for PROCEDURE action: |
||
|
action_name |
Name of the registered action to send a message to when the trigger fires. Use "List Class" to list all registered actions. |
|
|
parameter |
Parameter(s) to be passed to the registered action; parameters must be enclosed in quotes. If the action takes no parameters, set this argument to null (""). |
|
|
Parameters for MESSAGE action: |
||
|
action_name |
Name of the registered action to send a message to when the trigger fires. Use "List Class" to list all registered actions. |
|
|
parameter |
Parameter(s) to be passed to the registered action; parameters must be enclosed in quotes. If the action takes no parameters, set this to null (""). |
|
|
a1, a2, a3 |
Attribute(s) of the object, such as JobName or JobType. |
|
|
Examples |
CREATE TRIGGER NAME new_job_trigger EVENT JOB_COPY ACTION SENDMAIL POOL mgrs FORMAT EVENT; CREATE TRIGGER NAME shutdown_trigger EVENT SERVER_SHUTDOWN ACTION SENDMAIL POOL everyone FORMAT STRING "The Process Engine has been shut down. Do not use InConcert until further notice."; CREATE TRIGGER NAME message_complete_trigger EVENT TASK_COMPLETE MESSAGE notify_manager ARGUMENTS parameter ATTRIBUTES TaskName; |
|
Notes: A trigger defines an action to be performed automatically when a particular eLink Business Process Option event occurs, such as a completed process or task. There are three kinds of trigger:
You can create object triggers only with InConcert's process design tools (for details, see the InConcert Process Designer's Guide). You can create global triggers only with "Create Trigger".
There are three kinds of trigger action:
For a SENDMAIL action:
EVENT - The message body has the following format:
(<date and time> GMT) <event name> by <username> - <text description of event>
STRING - The message body is the text string in the action specification.
STRING_AND_EVENT - The message body is the text string plus the event message above.
FILE - The message body is the contents of the file_name in the action specification.
FILE_AND_ EVENT - The message body is the contents of file_name plus the event message above.
Process Engine <servername> Event Report
SENDMAIL triggers support any MHS-compliant mail package that runs under your PC/UNIX connectivity software
For a CREATEJOB action:
For a PROCEDURE action:
You automatically acquire Manage and Update privilege on any trigger you create. This means that you can delete the trigger and modify attribute values for the trigger's class.
The following is a list of trigger actions:
|
BINDER_BIND_DOCUMENT |
JOB_COMPLETE |
TASK_ADD_RELATIVE |
|
BINDER_DELETE |
JOB_COPY |
TASK_ADD_TASK |
|
BINDER_UNBIND |
JOB_CREATE_ACTIVE |
TASK_COMPLETE |
|
CLASS_ADD_ATTRIBUTE |
JOB_CREATE_TEMPLATE |
TASK_CONVERT |
|
CLASS_CREATE_SUBCLASS |
JOB_DELETE |
TASK_COPY |
|
CLASS_DEMOTE_ATTRIBUTE |
JOB_RESUME |
TASK_DELETE |
|
CLASS_DESTROY |
JOB_SUSPEND |
TASK_DELETE_DEPENDENCY |
|
CLASS_PROMOTE |
LINK_COPY |
TASK_ITERATE |
|
CLASS_PROMOTE_ATTRIBUTE |
LINK_CREATE |
TASK_LATE_START |
|
CLASS_PROMOTE_INSTANCES |
LINK_DELETE |
TASK_OVERDUE |
|
CLASS_REMOVE_ATTRIBUTE |
LINK_SET_DESTINATION |
TASK_READY |
|
CLASS_RENAME_ATTRIBUTE |
POOL_ACQUIRE_FIRST_TASK |
TASK_RELEASE |
|
DOCUMENT_CANCEL_CHECK_OUT |
POOL_ADD_USER |
TASK_REPEAT |
|
DOCUMENT_CHECK_IN |
POOL_CREATE |
TASK_SET_ITERATE_CONDITION |
|
DOCUMENT_CHECK_OUT |
POOL_DELETE |
TASK_SET_PERFORM_CONDITION |
|
DOCUMENT_COPY_VERSION |
POOL_REMOVE_USER |
TASK_SET_ROLE |
|
DOCUMENT_CREATE |
REVOKE_PRIVILEGE_POOL |
TASK_SKIP |
|
DOCUMENT_DELETE_VERSION |
REVOKE_PRIVILEGE_PUBLIC |
TASK_SUBTASKS_COMPLETE |
|
DOCUMENT_DESTROY |
REVOKE_PRIVILEGE_USER |
TASK_TRANSFER |
|
DOCUMENT_RESTORE_VERSION |
ROLE_ASSIGN_POOL |
TASK_WAITING |
|
DOCUMENT_SET_CONTENT |
ROLE_DEASSIGN |
TRIGGER_CREATE |
|
GRANT_PRIVILEGE_POOL |
ROLE_DELETE |
TRIGGER_DELETE |
|
GRANT_PRIVILEGE_PUBLIC |
SERVER_STARTUP |
TRIGGER_FIRE |
|
GRANT_PRIVILEGE_USER |
TASK_ACQUIRE |
USER_CREATE |
|
JOB_ADD_BINDER |
TASK_ACTIVATE |
USER_DELETE |
|
JOB_ADD_ROLE |
TASK_ADD_DEPENDENCY |
Create User
|
Description |
Creates a user record in the eLink Business Process Option database. |
|
|
Syntax |
CREATE USER user_name ADDRESS email_address [ WITH POOL ] [ [ ATTRIBUTE attribute_name VALUE attribute_value ] ... ] ; |
|
|
Parameters |
user_name |
Name of the new user. |
|
address |
The new user's email address. |
|
|
WITH POOL |
When this clause is present, a pool is created with the same name as the user. The user is added to this new pool. |
|
|
class_name |
The class for the new user. class_name must be an existing subclass of User. If unspecified, the user becomes a member of the User class. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be set or updated; the attribute must be defined for class_name or the User class. |
|
|
attribute_value |
Value of attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
CREATE USER kelly ADDRESS kelly@InConcert.COM CLASS Manager ATTRIBUTE CACHE_POLICY VALUE "On Demand" ATTRIBUTE PC_CACHE_DIR VALUE C:\KELLY\CACHE_KE; |
Notes: Each eLink Business Process Option user must have a user record in the eLink Business Process Option database in order to use eLink Business Process Option. A user record consists of a user name, an email address, and one or more attributes.
You must set the CACHE_DIR attribute for UNIX clients and may set PC_CACHE_DIR for PC clients. This attribute specifies the full pathname of the user's cache directory. If you do not set PC_CACHE_DIR, eLink Business Process Option uses a default cache directory location; CACHE_DIR has no default value.
You might also want to set the CACHE_POLICY attribute. This attribute can have the following values:
|
On Demand |
Copies the document content file to the cache directory when the user explicitly opens or checks out an InConcert document. This is the default value for CACHE_POLICY. |
|
On Task Start |
Copies all document content files for a task to the cache directory when the user starts to work on the task, including read-only documents. This policy applies only to UNIX clients. |
The optional class_name parameter lets you categorize the user by class. By default, a new user becomes a member of the predefined User class. You can use the class_name parameter to specify a user-defined subclass of User; for example, Manager.
The ATTRIBUTE/VALUE keywords allow you to assign a value to a particular attribute for the class or override the default value; for example, department name, job description, or years with the company. You cannot create a new attribute, however; new class attributes can be defined only with "Update Class - Add Attribute".
Delete Class
|
Description |
Deletes a class from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE CLASS class_name; [{WITH | PROMOTE} SUBCLASSES] [PROMOTE INSTANCES]; |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Class to be deleted |
|
Example |
DELETE CLASS NAME MyJobClass PROMOTE INSTANCES; |
Notes: The basic usage deletes a class with no subclasses or instances, and fails if any of these are present.
The WITH SUBCLASSES clause deletes the target class as well as its subclasses, provided that none have instances.
The PROMOTE SUBCLASSES clause promotes the target class's subclasses before deleting the target class, making the former subclasses direct subclasses of the target class's parent. Any attributes that these subclasses inherited from the target class become attributes of the (former) subclass. Any instances of the former subclasses are unchanged.
The PROMOTE INSTANCES clause promotes instances of the target class (and its subclasses, if the WITH SUBCLASSES clause is used), to become instances of the target class's parent. Any attributes inherited from the target class (or subclasses) are lost.
Note that use of the PROMOTE INSTANCES clause is the only way to delete a class that has instances. If the PROMOTE INSTANCES clause is not used, this command will not work (that is, if the class has instances, the command will not delete or promote subclasses).
Delete Document Name
|
Description |
Deletes one or more document objects from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE DOCUMENT NAME name_pattern; |
|
|
Parameters |
name_pattern |
Name or pattern of the document(s) to be deleted. |
|
Example |
DELETE DOCUMENT NAME Report*; |
Notes: A document object is an ProductName database structure that stores information about an associated content file. Delete Document deletes only the document object, leaving the content file intact. eLink Business Process Option classifies the content file associated with a deleted document object as an "unused content file."
This command deletes the document access control information, which removes any privilege relationships between the document and users and pools.
Delete Document lists the following information for each deleted document:
Delete Job Name
|
Description |
Deletes a process definition from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE JOB NAME name_pattern; |
|
|
Parameters |
name_pattern |
Name or name pattern of the process definition(s) to be deleted. |
|
Example |
DELETE JOB NAME AutoTheftClaim; |
Notes: A process definition describes a body of work that can be managed and tracked by eLink Business Process Option. When you delete a process definition, all information about the process is removed from the database.
This command deletes the process access control information, which removes any privilege relationships between the process definition and users and pools.
You cannot delete an active process. However, you can delete the associated process definition.
Delete Job lists the following information for each deleted process definition:
Delete Pool
|
Description |
Deletes a pool from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE POOL pool_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
pool_name |
Name of the pool to be deleted. |
|
Example |
DELETE POOL Editors; |
Notes: This command removes information about a pool from the database. The pool must be empty before you can delete it. To remove all users from the pool, use "Remove All From Pool".
You cannot delete a pool if any process definition or instance includes a reference to the pool. You must wait until the active process(es) complete, and/or remove the pool references from all process definitions.
Delete Trigger
|
Description |
Deletes a trigger from the database.. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE TRIGGER object_id; |
|
|
Parameters |
object_id |
Object ID of the trigger to be deleted. |
|
Example |
DELETE TRIGGER 000000050000115000010007000000C4; |
Notes: You cannot delete a trigger unless you have Manage privilege on the trigger object. Use "List Trigger" to obtain the trigger's object ID.
Delete Trigger lists the following information:
Delete User
|
Description |
Deletes a user record from the eLink Business Process Option database. |
|
|
Syntax |
DELETE USER user_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
user_name |
Name of the user to be deleted. |
|
Example |
DELETE USER Kelly; |
Notes: user_name cannot include wildcards.
This command removes all information about an eLink Business Process Option user from the database. Once you delete a user record, the user can no longer log in to eLink Business Process Option.
This command removes the user from all pools before deleting the user. If the user is currently working on one or more tasks, those tasks are released before the user is deleted.
Export Document
|
Description |
Prepares a document for use on another server. |
|
|
Syntax |
EXPORT DOCUMENT document_id TO file_name_prefix; |
|
|
Parameters |
document_id |
Object ID of the document to be exported; use "List Document" to obtain the object ID. |
|
file_name_prefix |
Prefix for the output files produced during export. file_name_prefix can be a full path name but cannot include an extension; Export Document creates the extension automatically. |
|
|
Example |
EXPORT DOCUMENT 0000003000011500001000700000102 TO Doc1; |
Notes: Copying an eLink Business Process Option document from one server to another is a two-step process:
1. Export the document with Export Document.
2. Import the document on the destination server with "Import Document".
Export Document prepares the document for transfer to the other server by creating two special output files:
"Import Document" uses these files as input when run on the destination server.
Export Job
|
Description |
Prepares a process definition and all related tasks, roles, placeholders, triggers, and task user interface documents for use on another server. |
|
|
Syntax |
EXPORT JOB job_id TO file_name_prefix ; |
|
|
Parameters |
job_id |
Object ID of the process definition to be exported. |
|
file_name_prefix |
Prefix for the output file produced during export. file_name_prefix can be a full pathname but cannot include an extension; the extension is created automatically. |
|
|
Example |
EXPORT JOB 00000003000011500001000100000091 TO JobA; |
Notes: Copying a process definition from one server to another is a two-step process:
Export the process definition with Export Job.
Import the process definition on the destination server with "Import Job".
Export Job prepares the process definition for transfer to the other server by creating a special output file of the form file_name_prefix.xdm.
The Import Job command uses this file as input when run on the destination server.
In addition, for each task with a task user interface (created with the PC client), Export Job creates two more output files in the directory file_name_prefix.tui:
These files describe the task user interface in a portable format and are created by exporting the task user interface document. There is one such document for each task user interface in the process definition.
Grant Privilege
|
Description |
Provides one or more users with the privilege to manipulate a process, document, or trigger. |
|
|
Syntax |
GRANT PRIVILEGE privilege ON object_id TO subject ; subject can take these forms: USER user_name |
|
|
Parameters |
privilege |
Privilege to be granted: Manage Update Copy Read |
|
object_id |
Process, document, or trigger object ID. Use the List Job, List Document, or List Trigger command to obtain the object ID. |
|
|
subject |
Subject to be granted privilege USER, POOL, or PUBLIC. This parameter can take any of the three forms listed above. |
|
|
user_name |
Name of the user to be granted privilege. |
|
|
pool_name |
Name of the pool to be granted privilege. |
|
|
Example |
GRANT PRIVILEGE UPDATE ON 0000230000D09d000000002b00333300 TO POOL Editors; |
Notes: You can grant privilege to a particular user, to a pool of users, or to all users (PUBLIC). There are four kinds of privilege:
Manage privilege lets you grant and revoke privilege on a process, document, or trigger, as well as delete a process, document, or trigger.
On a process, manage privilege lets you modify the process state (for example, suspend and resume the process).
Manage privilege does not extend Update, Copy, or Read privilege, but does allow you to grant Update, Copy, or Read privilege to yourself or other users.
The meaning of Update privilege varies for processes, documents, and triggers.
Update privilege on a process allows you to modify the objects comprising the process (for example, attach pools to roles or change the task structure). It does not extend Copy privilege to the subject.
Update privilege on a document allows you to checkout and checkin a document and modify its contents. It does not extend Read privilege to the subject.
Update privilege on a trigger allows you to modify the value of any attribute in the trigger's class.
Copy privilege applies only to process definitions (not active processes). Copy privilege allows you to create an active process from a process definition or copy a process definition to create a new one.
Read privilege applies only to documents. Read privilege allows you to view the document content file and create a copy of the document object.
The following table summarizes the privileges that can be granted to a user, pool, or PUBLIC for processes, documents, and triggers:
|
Process |
Document |
Trigger |
|---|---|---|
|
Manage |
Manage |
Manage |
|
Update |
Update |
Update |
|
Copy |
Read |
N/A |
.
|
Process |
Document |
Trigger |
|
Manage |
Manage |
Manage |
|
Update |
Update |
Update |
|
Copy |
Read |
N/A |
Privileges need to be granted only when the default privileges do not meet your requirements.
|
|
Admin pool |
User |
Owner pool |
PUBLIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Base job template |
Manage |
- |
- |
Copy |
|
New process definition |
Manage |
Manage Update |
- |
Copy |
|
New active process |
Manage |
Manage Update |
Manage Update |
Copy |
|
New document |
Manage |
Manage Update |
- |
Read |
|
New trigger |
Manage |
Manage |
- |
- |
eLink Business Process Option grants special privileges to members of two pools:
Any pool that fills the predefined Owner role becomes the process owner pool. (The Owner role is associated with the process root task; this association cannot be removed. For more information, see the InConcert Process Designer's Guide.)
The Owner pool can be specified in the process definition or when the process is started. Members of the Owner pool receive Manage and Update privilege on the new active process. By default, members of the Owner pool also have the privilege to start the process because PUBLIC has Copy privilege on all process definitions.
Notes: If you want to restrict the users who can start a process, you must change the default privileges on process definitions.
Administrator privilege is a special privilege granted only to members of the internal admin pool. This privilege is not associated with any particular object but is needed to do the following:
The admin pool always has at least one member, the eLink Business Process Option administrator (default name, `icdba') who, for both practical and security purposes, cannot be removed from the pool; other users can be added to the admin pool with "Add User To Pool.
You should add eLink Business Process Option process designers to the admin pool. This is the only way they are permitted to create new attributes for the process definitions in use at your site.
Administrator privilege exists separately from the object-specific privileges described above and cannot be granted with Grant Privilege.
Import Document From
|
Description |
Copies a document object and the associated content file from one ProductName server to another. |
|
|
Syntax |
IMPORT DOCUMENT FROM file_name_prefix |
|
|
Parameters |
file_name_prefix |
File name prefix of the exported document, including the full path name if necessary. file_name_prefix must have been established previously with "Export Document". |
|
class_name |
The class for the new document. class_name must be the Document class or one of its subclasses. If unspecified, eLink Business Process Option uses class matching to determine the class. |
|
|
Example |
IMPORT DOCUMENT FROM Doc1 CLASS Document; |
Notes: Import Document reads the output files produced by Export Document and creates a new document on the destination server. The exported document files must be readable by the Batch Registry user and include:
If you specify a class when you import the document, eLink Business Process Option sets the class attributes to their default value. If you do not specify a class when you import the document, eLink Business Process Option uses class matching to determine the document's class and attribute values. The imported document retains the class and attribute values of the original (exported) document when all of the following conditions are true:
Class matching is concerned only with the exported document class name and attributes. Therefore, class matching can still succeed if a class on the destination server has additional (unexported) attributes. These additional attributes (if any) are set to their default value.
If eLink Business Process Option cannot determine the document class, the import operation fails. There are two ways that this can happen:
eLink Business Process Option performs the following actions when a document is imported successfully:
Import Document lists the following information about the imported document:
Import Job From
|
Description |
Copies a process definition and all related tasks, roles, placeholders, triggers, and task user interface documents from one ProductName server to another. |
|
|
Syntax |
IMPORT JOB FROM file_name_prefix [ CLASS class_name ]; |
|
|
Parameters |
file_name_prefix |
File name prefix of the exported process definition, including the full pathname if necessary. file_name_prefix must have been established previously with "Export Job". |
|
class_name |
The class for the new Process Definition. class_name must be the Job class or one of its subclasses. If unspecified, eLink Business Process Option uses class matching to determine the class. |
|
|
Example |
IMPORT JOB FROM JobA CLASS Job; |
Notes: Import Job reads the output files produced by Export Job and creates a new process definition on the destination server. The following files must be readable by the Batch Registry user:
An imported job has task user interface documents only if it was created on the PC client. The document export files are stored in the file_name_prefix.tui directory.
If you do not specify a class name when you run this command, eLink Business Process Option uses class matching to determine the class of the imported process definition and its related roles, placeholders, tasks, and triggers. These objects retain their original class and attribute values when all of the following conditions are true:
If class matching fails, the imported object becomes a member of its base class (for example, Role) and its attributes are set to their default value.
Since class matching is concerned only with the exported class names and attribute names, class matching may still succeed if a class on the destination server has additional (unexported) attributes. These additional attributes (if any) are set to their default value.
If eLink Business Process Option cannot determine the class of the process definition itself, the import operation fails. There are two ways this can happen:
eLink Business Process Option performs the following actions when a process definition is imported successfully:
For a CREATEJOB action, a match occurs only if the original trigger specifies a process definition name and pool name that exists on the destination server.
For a SENDMAIL action, a match occurs only if the original trigger specifies a pool name that exists on the destination server.
For a PROCEDURE action, a match occurs only if the original trigger specifies a registered action that exists on the destination server.
If an error occurs while the import operation is in progress, the process definition is created with a subset of the exported roles, placeholders, tasks, and triggers.
The PerformCondition for an imported task remains blank (unset) if it refers to a process or task attribute that is not defined on the destination server.
Import Job lists the following information about the new process definition:
List Class
|
Description |
Lists information about an eLink Business Process Option class. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST CLASS class_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of class to list information about. |
|
Example |
LIST CLASS Application; |
Notes: Be sure to specify all eLink Business Process Option base class names with an initial cap; for example, Role, not ROLE or role.
See "Create Subclass" for more information about classes.
List Class lists the following information for each class attribute:
List Class Hierarchy
|
Description |
Lists all defined classes and subclasses. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST CLASS HIERARCHY [WITH COUNT]; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST CLASS HIERARCHY WITH COUNT; |
This function may take a few minutes to execute.
List Class Hierarchy lists the following information for each class:
When the WITH COUNT clause is present, the number of instances of each class is displayed along the class name. Instance counts are only for the indicated class and do not include subclasses of the indicated class.
List Document Name
|
Description |
Lists information about one or more documents. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST DOCUMENT NAME name_pattern; |
|
|
Parameters |
name_pattern |
Document name or name pattern; name_pattern can include wildcards. |
|
Example |
LIST DOCUMENT NAME Report%; |
List Document lists the following information for each document:
List Event
|
Description |
Lists all registered event types. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST EVENT; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST EVENT; |
Notes: Registered event types are user-defined events that can cause a trigger to fire. They are registered by the Register Event command and are specified during trigger creation.
List Event lists the following information for each registered event type:
List Job Name
|
Description |
Lists information about one or more process definitions or active processes. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST JOB NAME name_pattern; |
|
|
Parameters |
name_pattern |
Process name or name pattern; name_pattern can include wildcards (for, example, `%'). |
|
Example |
LIST JOB NAME %; |
List Job lists the following information for each process:
List Message Action
|
Description |
Lists all registered MESSAGE actions. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST MESSAGE ACTION; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST MESSAGE ACTION; |
Notes: Registered MESSAGE actions put a message on a named Tuxedo queue. They are registered by "Register Message Action" and specified during trigger creation with "Create Trigger".
List Class lists the following information for each registered action:
List Pool
|
Description |
Lists information about all defined pools. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST POOL; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST POOL; |
List Message Action lists the following information for each pool:
List Privilege
|
Description |
Lists process, document, or trigger privileges. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST PRIVILEGE ON object_id; |
|
|
Parameters |
object_id |
Object ID of the process, document, or trigger whose privileges are to be listed. Use the List Job, List Document, or List Trigger commands to obtain the object ID. |
|
Example |
LIST PRIVILEGE ON 00000002000030390000000100000400; |
List Privilege lists the following information for each privilege on the specified object:
List Repository
|
Description |
Lists information about repositories. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST REPOSITORY; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST REPOSITORY; |
List Repository lists the following information for each repository:
List RPC Action
|
Description |
Lists all registered RPC actions. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST RPC ACTION; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST RPC ACTION; |
Notes: Registered actions are user-written programs that can appear in a global trigger action specification. They are registered by "Register RPC Action" and specified during trigger creation with "Create Trigger".
List Class lists the following information for each registered action:
List Trigger
|
Description |
Lists information about global triggers with a particular event and action specification.. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST TRIGGER EVENT event_name |
|
|
Parameters |
event_name |
Event that causes the trigger to execute. |
|
action_type |
Trigger action type: JOBCREATE, SENDMAIL, MESSAGE, or PROCEDURE. |
|
|
Example |
LIST TRIGGER EVENT job_copy ACTIONTYPE SENDMAIL; |
List Trigger lists the following information for each matching trigger:
JOBCREATE: process, pool, name
SENDMAIL: pool, format, type, text
MESSAGE: action name, arguments, attributes
PROCEDURE: action name, arguments
List User
|
Description |
Lists information about eLink Business Process Option users. |
|
|
Syntax |
LIST USER; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
LIST USER; |
List User lists the following information for each user:
Promote Class
|
Description |
Promotes a class within its branch, retaining relationships to classes derived from it. Any attributes formerly inherited from classes between it and its new parent become attributes of the promoted class. |
|
|
Syntax |
PROMOTE CLASS class_name [TO SUBCLASS OF parent_name]; |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Class to be moved in hierarchy. |
|
parent_name |
Class that will be new parent of moved class; if you do no specify a parent, the class is promoted to be a sibling of its current parent. |
|
|
Example |
PROMOTE CLASS MyDetailedJobClass TO SUBCLASS OF Job; |
Notes: This command is typically used during process design, when you decide that a class should have a more general usage than the usage originally implied by the class's position in the hierarchy.
Another use is to "preserve" a class, preparatory to deleting its current parent classThis command is used primarily to preserve instances prior to deleting a class. This functionality already exists in "Delete Class".
Promote Instances
|
Description |
Promotes the instances of a specified class, so that they become instances of that class's parent. Any attributes defined by the former class are lost. |
|
|
Syntax |
PROMOTE INSTANCES OF CLASS class_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Class to which instances are to be promoted. |
|
Example |
PROMOTE INSTANCES OF CLASS MyJobClass; |
|
Description |
Exits the Batch Registry. |
|
|
Syntax |
QUIT; |
|
|
Parameters |
None. |
|
|
Example |
QUIT; |
Notes: On UNIX, use Quit to exit the Batch Registry. Another way to exit is with the key sequence Ctrl + D.
On Windows, choose File > Exit to exit the Batch Registry.
Register Message Action
|
Description |
Registers a triggered action specification that puts a message on a specific Tuxedo queue. |
|
|
Syntax |
REGISTER MESSAGE ACTION action_name QUEUE queue_name QUEUESPACE space_name |
|
|
Parameters |
action_name |
Name of the action to be registered. |
|
queue_name |
Name of message queue. |
|
|
space_name |
Name of queue space. |
|
|
Example |
REGISTER MESSAGE ACTION test QUEUE tuxedo_queue QUEUESPACE tuxedo_queue_space create trigger name tuxedo_queue event JOB_COPY action MESSAGE TestActionSpec "testing one two three" ATTRIBUTE ATTRIBUTE1 ATTRIBUTE2; |
Notes: A global trigger can place a message on a named Tuxedo message queue if it is registered with eLink Business Process Option as a registered message action. Registering an action makes eLink Business Process Option aware of the action's general operating characteristics.
Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute "Register Message Action".
Do not use the same name for an RPC action and a MESSAGE action.
Register RPC Action
|
Description |
Registers a user-written program for use in a global trigger action specification. |
|
|
Syntax |
REGISTER RPC ACTION action_name |
|
|
Parameters |
action_name |
Name of the action to be registered. |
|
agent_address |
Name of host on which action is run. |
|
|
program# |
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) program number for agent_address; program# must be an integer in the range allocated for user-defined RPC services. |
|
|
rpc_version |
RPC version; this argument typically is set to 1 but can be any integer representing the RPC version. |
|
|
procedure# |
Integer procedure number to call within action_name. |
|
|
Example |
REGISTER ACTION run_status ADDRESS Bluefish CREATE TRIGGER NAME status_trigger EVENT job_complete ACTION PROCEDURE run_status ARGUMENTS ""; |
Notes: A global trigger can execute a user-written program if it is registered with eLink Business Process Option as a registered RPC action. Registering an action makes eLink Business Process Option aware of the program's general operating characteristics. The program itself is usually written in C or C++ with embedded eLink Business Process Option API function calls. The program must conform with the guidelines for agent applications described in the ICAgent documentation.
Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute "Register RPC Action".
Do not use the same name for an RPC action and a MESSAGE action.
Register Event
|
Description |
Registers a user-defined event type for use in a global trigger event specification. |
|
|
Syntax |
REGISTER EVENT event_name TYPE event_#; |
|
|
Parameters |
event_name |
Name of the event type to be registered; this name must be unique among registered event types. |
|
event# |
Event type # of event_name; this integer must be unique among registered event types and must be greater than 10000. |
|
|
Example |
REGISTER EVENT daily TYPE 10001; SIGNAL EVENT daily AT "06/07/99 16:30:00"; CREATE TRIGGER NAME status_trigger EVENT daily ACTION JOBCREATE group_status POOL mgr |
Notes: A global trigger can fire on a user-defined event type if it is registered with eLink Business Process Option. Registered event types are usually time-based, and are signalled periodically using the timing information established with "Signal Event".
Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute the Register Event command.
Remove All From Pool
|
Description |
Removes all users from a pool.. |
|
|
Syntax |
REMOVE ALL FROM POOL pool_name ; |
|
|
Parameters |
pool_name |
Pool whose members are to be removed. |
|
Example |
REMOVE ALL FROM POOL Editors; |
Notes: Remove All From Pool has two uses:
This command does not delete the pool itself.
Remove User From Pool
|
Description |
Removes a particular user from a pool. |
|
|
Syntax |
REMOVE USER user_name FROM POOL pool_name ; |
|
|
Parameters |
user_name |
Name of the user to be removed. |
|
|
pool_name |
Name of the pool from which the user is to be removed. |
|
Example |
REMOVE USER Kelly FROM POOL Editors; |
Notes: You might need to remove a user from a pool for any of these reasons:
This command does not remove the user record from the database; use "Delete User".
Revoke Privilege
|
Description |
Revokes privileges on processes, documents, and triggers. |
|
|
Syntax |
REVOKE PRIVILEGE privilege ON object_id FROM subject; subject can take these forms: USER user_name |
|
|
Parameters |
privilege |
Privilege to be revoked:
|
|
object_id |
Process, document, or trigger object ID. Use the List Job, List Document, or List Trigger commands to obtain the object ID. |
|
|
subject |
Subject from which to remove privilege. This parameter can take any of the three forms listed above. |
|
|
user_name |
Name of the user from which the privilege is to be removed. |
|
|
pool_name |
Name of the pool from which the privilege is to be removed. |
|
|
Example |
REVOKE PRIVILEGE UPDATE ON |
Notes: You cannot revoke Manage privilege from the admin pool or any of its members.
You need to revoke privileges on a process, document, or trigger if the current settings exceed the requirements of your application.
Copy privilege applies only to process definitions. Read privilege applies only to documents.
Since you can only revoke one privilege at time, you may need to execute Revoke Privilege several times to remove all the privileges you want.
Set Default Repository
|
Description |
Changes the default repository. |
|
|
Syntax |
SET DEFAULT REPOSITORY repository_id; |
|
|
Parameters |
repository_id |
Object ID of the new default repository. Use "List Repository" to obtain the object ID. |
|
Example |
SET DEFAULT REPOSITORY 00000002000030390000000B00000403; |
Notes: The default repository is typically the repository used most often by the majority of users. The software installation procedure establishes the initial default repository. You can change the default repository to another repository with the Set Default Repository command. The new default repository must have been created previously with "Create Repository".
Once you change the default repository, it is used to store the document content files for new eLink Business Process Option documents. Existing documents, created when a different repository was the default, remain in the repository in which they were originally created, and can still be accessed from a task.
Signal Event
|
Description |
Signals a registered event. |
|
|
Syntax |
SIGNAL EVENT event_name |
|
|
Parameters |
event_name |
Name of the registered event to be signaled. |
|
|
date_time |
Date and time for signalling the event. You must include both the date and the time. The date_time value must be entered in double quotes, in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
repeat_interval |
Repeat interval (in seconds) for signaling the event; repeat_interval must be greater than or equal to 3600. |
|
|
Example |
SIGNAL EVENT weekly AT "06/07/99 12:00:00" REPEAT 604800; SIGNAL EVENT update NOW; |
Notes: This command establishes the timing information for a registered event - a user-defined event created with "Register Event". Registered events must be signalled explicitly for an associated trigger to fire. There are three kinds of timing specification:
Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute the Signal Event command.
Unregister Action
|
Description |
Removes a registered action from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
UNREGISTER ACTION action_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
action_name |
Name of the action to be unregistered. |
|
Example |
UNREGISTER ACTION run_status; |
Notes: Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute the Unregister Action command.
Unregister Action removes the value given by action_name from either the Action RPC Table or the Action Message Queue Table.
Unregister Event
|
Description |
Removes a registered event type from the database. |
|
|
Syntax |
UNREGISTER EVENT event_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
event_name |
Name of the event type to be unregistered. |
|
Example |
UNREGISTER EVENT weekly; |
Notes: Only users who belong to the admin pool can execute the Unregister Event command.
Unregister Event lists the following information:
Update Class - Add Attribute
|
Description |
Adds an attribute to a class definition. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name ADD data_type |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be updated. |
|
|
data_type |
The attribute's data type:
|
|
attribute_name |
Name of the new attribute. Use only the characters 0 through 9 and A through Z (no lowercase characters). |
|
|
default |
Default value for the new attribute. |
|
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS Appraisers ADD STRING ATTRIBUTE COUNTY DEFAULT MONROE; |
Notes: This command adds a user-defined attribute to an eLink Business Process Option base object class (for example, Role) or one of its subclasses. You can list existing classes with "List Class Hierarchy".
A subclass inherits the attributes of its parent; user-defined attributes are inherited like any other attribute. .
Update Class - Demote Attribute
|
Description |
Demotes an attribute from a class to all of its subclasses. The attribute is removed from all instances of the target class. Instances of the target class's subclasses are unchanged. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be updated. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be demoted. |
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS MyJobClass DEMOTE ATTRIBUTE JobNumber; |
Note: This command is typically used during workflow design, to rearrange attributes that were incorrectly assigned to a class.
Update Class - Promote Attribute
|
Description |
Promotes an attribute from a class to its parent. The attribute becomes inherited by the target class, its siblings, and all their subclasses. Instances of the target class and its subclasses are unchanged. Instances of the target class's siblings and their subclasses receive the default value of the attribute. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be modifed. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be promoted. |
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS MyJobClass PROMOTE ATTRIBUTE JobNumber; |
Note: This command is typically used during workflow design, to rearrange attributes that were incorrectly assigned to a class.
Update Class - Remove Attribute
|
Description |
Removes an attribute from a class definition, and by extension from all of the target class's subclasses. The attribute is removed from instances of the class and its subclasses. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be updated. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be removed. |
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS MyJobClass REMOVE ATTRIBUTE JobNumber; |
Note: This command is typically used during workflow design, to rearrange attributes that were incorrectly assigned to a class.
Update Class - Rename Attribute
|
Description |
Changes the name of an attribute in a class definition and, by extension, all subclasses of the target class. The attribute is renamed for all instances of the target class and any of its subclasses. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be updated. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be renamed. |
|
new_name |
New name of attribute. |
|
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS MyJobClass RENAME ATTRIBUTE JobNumber TO JobNum;
|
Note: This command is typically used during workflow design.
Update Class - Set Default
|
Description |
Sets the default value for a user-defined attribute in a particular class |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE CLASS class_name |
|
|
Parameters |
class_name |
Name of the class to be updated. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Name (in uppercase letters) of the attribute to be updated. |
|
default |
Default value for attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format: mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
UPDATE CLASS Appraisers SET ATTRIBUTE COUNTY DEFAULT WESTFORD; |
Notes: Use this command to modify only user-defined attributes. Modifying predefined attributes can sometimes confuse the eLink Business Process Option software.
Update Pool
|
Description |
Renames an existing pool. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE POOL pool_name NAME new_name; |
|
|
Parameters |
pool_name |
Old pool name. |
|
|
new_name |
New pool name. |
|
Example |
UPDATE POOL Engineer NAME Test Engineer; |
|
Description |
Changes the name, password, email address, or other attribute of an existing eLink Business Process Option user. |
|
|
Syntax |
UPDATE USER user_name [ NAME new_name ] [ PASSWORD new_password ] [ ADDRESS new_address ] [ [ ATTRIBUTE attribute_name VALUE attribute_value ] ]; |
|
|
Parameters |
user_name |
Name of the user whose database record is to be updated. |
|
|
new_name |
User's new name. |
|
new_password |
User's new password. |
|
|
new_address |
User's new email address. |
|
|
attribute_name |
Attribute to be set or updated; the attribute must be defined for the class in which the user was originally created. |
|
|
attribute_value |
Value of attribute_name. The attribute value can be a string, integer, or date/time in the format mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss |
|
|
Example |
UPDATE USER Kelly NAME Kelly PASSWORD xyz ADDRESS Kelly@InConcert.COM ATTRIBUTE CACHE_POLICY VALUE "On Task Start" ATTRIBUTE PC_CACHE_DIR VALUE C:\KELLY\CACHE_KE; |
Notes: Two common uses for this command are to:

|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|