


|

|
|
|
|
Using the Batch Registry
The Batch Registry commands are used to perform administrative functions on users, pools, documents, processes, repositories, privileges, classes, triggers, events, and actions. Most of these functions are typically performed by the eLink Business Process administrator; others are performed by the Process Designer.
The Batch Registry utility may be run in one of the following two modes:
Note: Make sure that you installed the eLink Process Design Assistant. Otherwise, you cannot run the Batch Registry utility.
The following sections describe how to use the Batch Registry:
Using Client Data in the Batch Registry
The eLink Business Process Option uses client data to pass information back and forth between servers and clients. Typically, this data is stored in the IC_CLIENT environment variable, and the value is in the following form:
user/password@server
where:
|
user |
Name of the user to log in to the eLink Business Process server. |
|
password |
Password of user. |
|
server |
Logical name of the server to log in to (for example, Accounting). |
This form is also used whenever client data needs to be passed explicitly (for example, when launching the Batch Registry from the command line).
The ictimeout and icclient Parameters
You can pass parameters to the Batch Registry in either Interactive or Batch mode. The ictimeout and icclient parameters are optional, but can always be passed. Other parameters may also be available. The following table describes the ictimeout and icclient parameters.
.
|
-ictimeout seconds |
Optional. Specifies the timeout interval, in seconds, before the Batch Registry will stop trying to contact the eLink Business Process Engine. The default value is 120 |
|
-icclient client_data |
Optional. Overrides all or part of the IC_CLIENT environment variable setting. client_data must be in the following form: user/password@server |
Using the Batch Registry in Interactive Mode
Running the Batch Registry utility in Interactive mode lets you interactively issue Batch Registry commands. Interactive mode may be especially useful in performing one-time or non-routine tasks, such as creating a pool, deleting a user, or creating a subclass.
The PC and UNIX Batch Registry applications have different appearances, but they operate in the same way: they accept commands at a prompt and display the results.
To start the Batch Registry in interactive mode on a PC
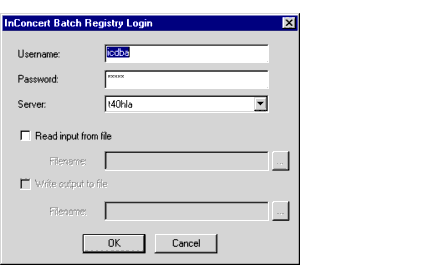
The Batch Registry Login dialog box appears, shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 The Batch Registry Login Dialog
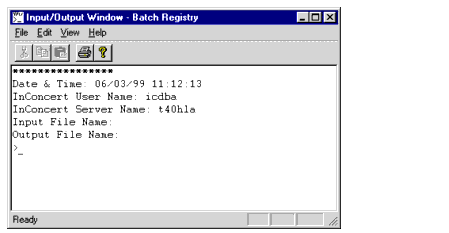
The Batch Registry window appears, shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 The Batch Registry Window
To start the Batch Registry in interactive mode on UNIX
IcBatchRegistry
An informational message displays and the Batch Registry command prompt appears. For example:
Host Name: Operations
System User Name: icadmin
Date & Time: 06/05/99 11:01:19
InConcert User Name: icdba
Process Engine Name: administration
Input File Name:
Output File Name:
Adding a Parameter to the Command Line
You can add the -icclient or -ictimeout parameters to the command line of the Batch Registry to override the IC_CLIENT environment variable.
Entering a Batch Registry Command in Interactive Mode
The procedure for entering a Batch Registry command on UNIX and PC platforms is identical. You enter a command at the prompt, specify parameters as necessary, and view the output.
To enter a Batch Registry command
>list user;
Note: If you enter a command incorrectly or the command action fails, an error message displays.
Exiting the Batch Registry Utility
To exit the Batch Registry on a PC
Choose File > Exit.
To exit the Batch Registry on UNIX
Enter quit at the prompt.
Using the Batch Registry in Batch Mode
When you run the Batch Registry in Batch mode, you specify the commands to be executed in a text file. Running the Batch Registry in Batch mode lets you:
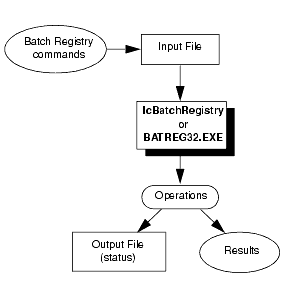
The following figure shows how the Batch mode reads the commands from a text file, executes the commands one at a time, and writes the status of each operation to an output file.
Figure 3-3 How the Batch Registry Works in Batch Mode
To start the Batch Registry in Batch mode on a PC:
Open a command window and enter:
BATREG32 [-icclient client_data ] [ -ictimeout seconds ] input_file [ output_file ]
To start the Batch Registry in Batch mode on UNIX:
From the command line, enter:
IcBatchRegistry [-icclient client_data ] [ -ictimeout seconds ] input_file [ output_file ]
Command Line Parameters
If you do not specify the icclient parameter, the Batch Registry uses the information in the IC_CLIENT environment variable. The following table describes the input_file and output_file parameters.
|
input_file |
Required. The input file parameter contains one or more of the Batch Registry commands. |
|
output_file |
Optional. If you specify this parameter, eLink Business Process appends the results of each batch operation to that file (the original contents are not overwritten). If you do not specify this parameter, eLink Business Process creates one with the name input_file.OUT. |
Note: The input_file and output_file filenames cannot be the same.
Input File Format
The input file is a text file containing one or more of the Batch Registry commands as explained in Batch Registry Command Reference, You can create this file with any text editor.
An example of an input file for the Batch Registry is as follows:
LIST USER;
REMOVE USER "jones" FROM POOL "Writers";
DELETE USER "jones";
LIST POOL;
LIST USER;
The input file has the following format:
batch_command; [ batch_command; ] [ ... ]
You can enter several commands on the same line by separating the commands with a semi-colon. Spaces, tabs, and line terminators are ignored, and treated as white space, unless you use quotes.
Enclose string parameter values in single or double quotes using the quoting rules. Wildcards are permitted as indicated.
Output File Format
Output files have Header, Command, and Summary sections. Each section is separated by a linefeed character (LF).
Header Section
The Header section contains the following information:
The command section contains the following information for each batch command:
LIST POOL
STATUS MESSAGE xxxxxxx
Writers
lee
jj
chris
Editors
luis
sri
kelly
The Summary section contains the following information:
Success: <# of commands>
Error: <# of commands>
Total: <# of commands>

|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|