Configuring Log Central
After you have ensured that all of the software components previously specified have been properly installed, and you have installed Log Central on the central host, you can proceed with configuring Log Central. To do so, you run the lc_config program. However, before running this program, you should be prepared to provide the information listed under "Required Information for Host Configuration Utility."
Required Information for Host Configuration Utility
Running the lc_config program brings up the form shown in Figure 2-1. You might want to fill out a worksheet first and have it handy.
The numbered list that follows the figure correspond to the numbers in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Host Configuration Utility
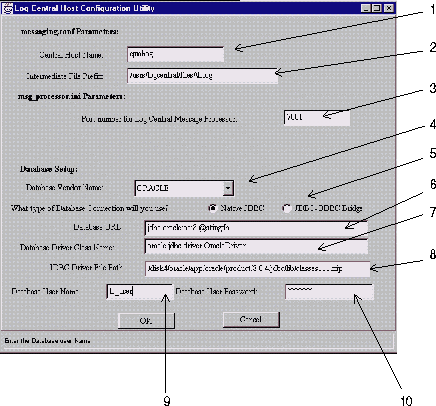
You need to ascertain the following: