Purpose
Generates or updates all necessary agent code to support a new private MIB group
Synopsis
imibgenall [ -u | -HHeaderfile]MIBRootName
Arguments
-u- Undo any code generation for the
MIBRootNameMIB group. -HHeaderFile- Specifies the file name containing customer-specific header information to be placed at the beginning of the generated files.
MibRootName- The root of the section of the MIB tree for which code will be generated.
Description
The imibgenall utility must be run from the $RELEASE_ROOT/agent_src/agentlib directory.
The imibgenall utility requires a MIBRootName argument. For scalar objects, indicate the name of the ancestor object (e.g., the name of the object above them in the tree). For tabular objects, indicate the name of the table object.
By default, the imibgenall utility creates agent source code to support your private MIB. When the -u argument is specified, the utility removes any code previously generated for any portion of your MIB.
If you are creating code to support your MIB, this utility creates several files to support the specified MIB in the SNMP agent: agent hook and access functions files, and their supporting header files. It also updates the makefiles that are needed to build an SNMP agent. You need only modify the generated access functions file:
$RELEASE_ROOT/agent_src/agentlib/MIBRootName.c
where MIBRootName is the same as the argument passed to imibgenall. Once the code is created, your only concern is with filling in the access function skeletons in a single source file, and perhaps tuning of constants defined in its associated header file:
$RELEASE_ROOT/agent_src/agentlib/MIBRootName.h
Environment Variables
RELEASE_ROOT- Contains the root directory of the Agent Development Kit installation.
Examples
Assume a private MIB such as in the following diagram, where objects a through g are scalar, and objects h through n are columnar objects (i.e., scalar-valued objects that can have multiple instances).
Figure 3-1 Sample Private MIB Tree
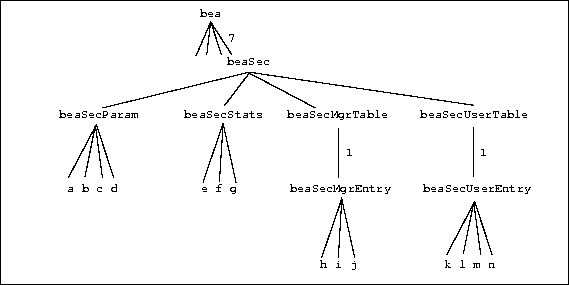
The imibgenall utility must be run four times to create four agent hook files, their corresponding access function files, and other files. The four commands would be the following:
imibgenall beaSecParam
imibgenall beaSecStats
imibgenall beaSecMgrTable
imibgenall beaSecUserTable
The following creates code associated with the MIB group item beaSecParam:
imibgenall beaSecParam
Several files will be created. Usually, you will only need to modify the file beaSecParam.c, but you may be required to make some changes to the beaSecParam.h file. You can undo these operations by entering:
imibgenall -u beaEm
Warning:
The imibgenall -u command will delete the MIBRootName.c and MIBRootName.h files. Before invoking imibgenall with this option, you may wish to make a backup copy of any changes in the MIBRootName.c and MIBRootName.h files that you want to preserve.
imibgenall -u command will also delete any entries in the makefiles for the specified MIB group.