You can have more than one instance of the client running for the programming examples. However, you can only have one instance of the server running.
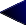
Figure B-1 shows how messages flow between a MessageQ client and an MQSeries server.
Figure B-1 DMQ_CLIENT and MQS_ECHO_SERVER
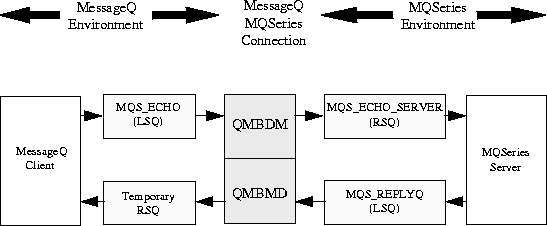
Figure B-2 shows how messages flow between an MQSeries client and a MessageQ server.
Figure B-2 MQS_CLIENT and DMQ_ECHO_SERVER
Prefixes for Clients and Servers
The prefix to the _ECHO_SERVER programs indicates the message queuing environment of the server program. The MQS_ECHO_SERVER and DMQ_ECHO_SERVER programs act like mirrors, and they return any messages they receive to the originators of the messages.
The prefix to the _CLIENT programs indicates the message queuing of the client program. For example, MQS indicates MQSeries. The MQS_CLIENT and DMQ_CLIENT programs act as drivers, making requests of echo servers running in the opposite queuing environment.
Building the Programming Examples
To build the programs, invoke the makefile by using the make command.
DMQ_ECHO_SERVER
DMQ_ECHO_SERVER is a MessageQ program designed to listen on a well-known address. It returns the message it just received to the sender of the message.
In this example, the address is named DMQ_ECHO_SERVER. In the MessageQ group initialization file, there must be an entry in the QUEUE CONFIGURATION SECTION or the GROUP NAME TABLE SECTION (if the server program is not run from the local group) for a queue named DMQ_ECHO_SERVER.
The command syntax for the DMQ_ECHO_SERVER program is as follows:
% DMQ_ECHO_SERVER [-d] [-?]
Table B-2 describes the DMQ_ECHO_SERVER parameters.