


|

|
|
|
|
Basic Architecture of the BEA Tuxedo ATMI Environment
The following figure illustrates the basic architectural elements of a BEA Tuxedo ATMI environment: external interfaces to the environment, the ATMI layer, the MIB, BEA Tuxedo system services, and the environment's interface with standards-compliant resource managers.
The BEA Tuxedo ATMI Basic Architecture
As shown in this illustration, the BEA Tuxedo ATMI environment contains the following components: 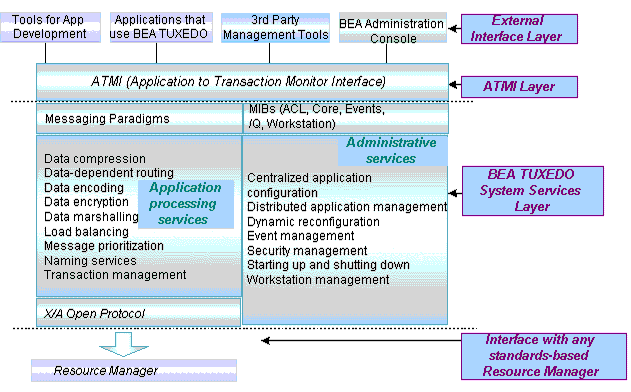
See Also

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2001 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|