







|
An essential part of managing WebLogic Network Gatekeeper is dealing with service provider partners. Network Gatekeeper provides a partner administration model to help operators handle the needs and demands of their partners in a flexible and powerful way:
The separation of accounts and groups provides a flexible way defining class-of-service.
See Figure 2-1 for more information on the relationship among account types.
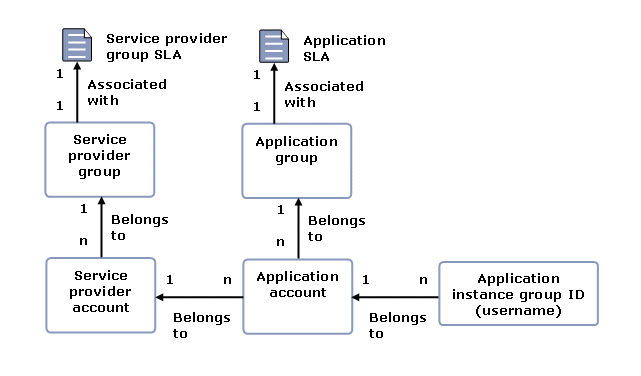
Service provider groups allow the Network Gatekeeper administrator to categorize different types of service providers (via service provider SLAs). For example, a Network Gatekeeper administrator might create three different categories:
Each of these would have different privileges when it comes to maximum throughput and QoS parameters. When a new service provider is provisioned, the service provider is associated with an appropriate group based on, for example, the amount of network traffic the service provider is projected to generate. If the outcome is not what was predicted, the service provider account can be reassigned to another service provider group with a different QoS parameter defined in the service provider level SLA.
Application groups allow the Network Gatekeeper administrator to categorize different types of applications (via application level SLAs).
For example, a Network Gatekeeper administrator may create three different categories:
Each of these groups would have different privileges when it comes to maximum throughput and QoS parameters. When a new application account is provisioned, that account is associated with an appropriate group based on, for example, the amount of network traffic the application is projected to generate. If the outcome is not what was predicted, the application account can be reassigned to another application group with a different QoS parameter defined in the application level SLA.
Service provider level SLAs have precedence over application level SLAs.
The service provider and application account and group registrations are performed either internally through the WebLogic Network Gatekeeper Management Console or through external management systems integrated with WebLogic Network Gatekeeper using the Network Gatekeeper Partner Relationship Management Interfaces. This guide describes many of the tasks associated with establishing and maintaining these accounts and groups using the WebLogic Network Gatekeeper Management Console.
The service provider accounts and application instance groups have states, which means that they can be temporarily be taken out of service. The states can be changed via OAM. If a state is changed for a service provider account, it affects all applications associated with the service provider.
| Note: | It is also possible to create unique SLAs and groups for an individual application. Accounts can be associated with other groups in runtime, so the class of service can be adjusted over time. |


|