







|
The following sections provide a complete reference to the engine tier configuration file, sipserver.xml:
The sipserver.xml file is an XML document that configures the SIP container features provided by a WebLogic SIP Server instance in the engine tier of a server installation. sipserver.xml is stored in the subdirectory DOMAIN_DIR/sipserver/config/ where DOMAIN_DIR is the root directory of the WebLogic SIP Server domain.
Figure 1-1 shows the element hierarchy of the sipserver.xml deployment descriptor file.
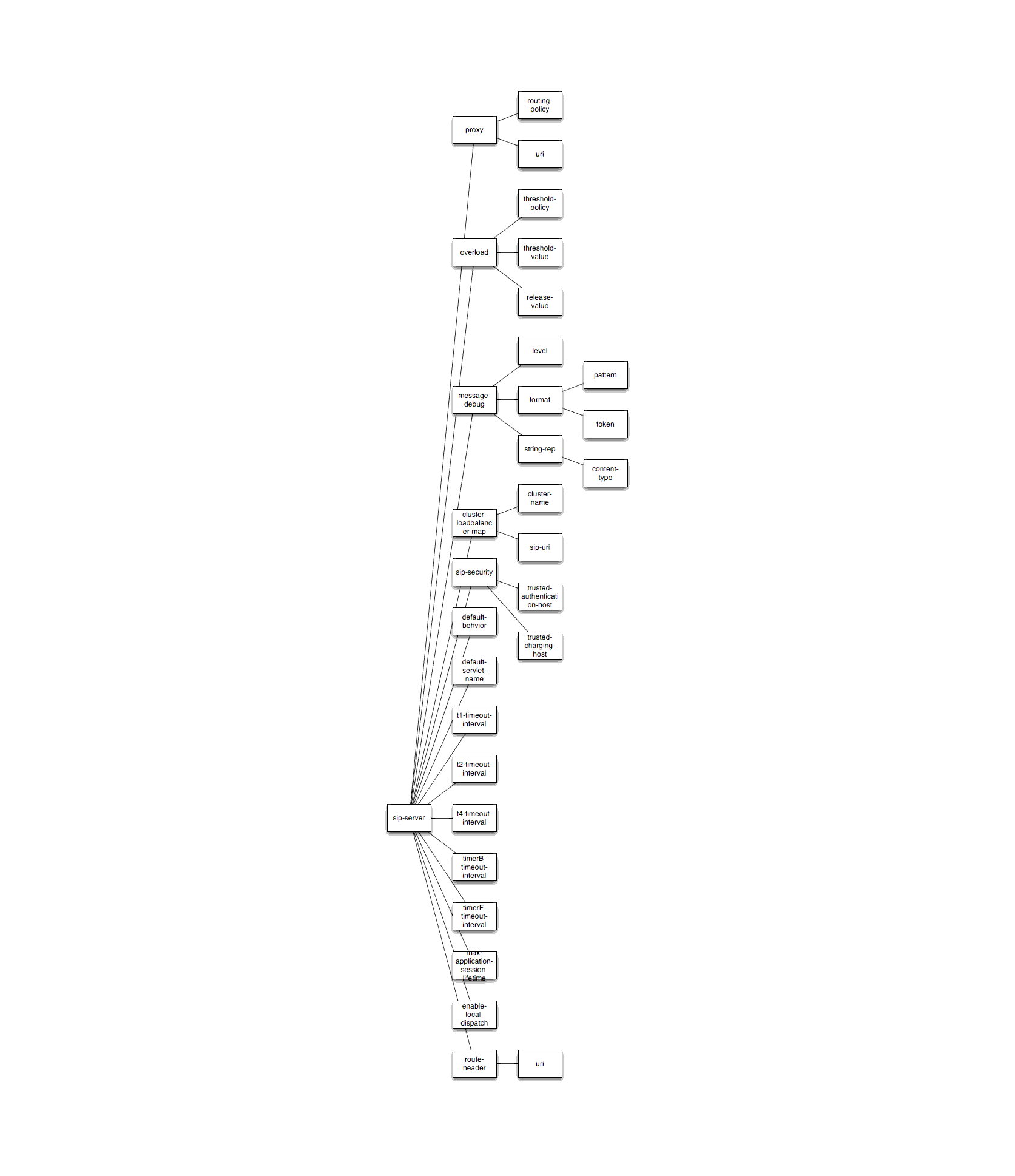
You should never move, modify, or delete the sipserver.xml file during normal operations.
BEA recommends using the Administration Console to modify sipserver.xml indirectly, rather than editing the file. Using the Administration Console ensures that the sipserver.xml document always contains valid XML. See also
Configuring Container Properties Using WLST (JMX) in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
You may need to manually view or edit sipserver.xml to troubleshoot problem configurations, repair corrupted files, or to roll out custom configurations to large number machines when installing or upgrading WebLogic SIP Server. When you manually edit sipserver.xml, you must reboot WebLogic SIP Server instances to apply your changes.
| WARNING: | Never redeploy or undeploy the sipserver implementation application on a running server. Always use the SIP Servers node in the Administration Console or the WLST utility, as described in
Configuring Engine Tier Container Properties in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server to make changes to a running WebLogic SIP Server deployment. |
If you need to modify sipserver.xml on a production system, follow these steps:
/sipserver/config/sipserver.xml file, where DOMAIN_DIR is the root directory of the WebLogic SIP Server domain.sipserver.xml file as necessary. See XML Schema for a full description of the XML elements.| WARNING: | Never redeploy or undeploy the sipserver implementation application on a running server. Always use the SIP Servers node in the Administration Console or the WLST utility, as described in
Configuring Engine Tier Container Properties in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server, to make changes to a running WebLogic SIP Server deployment. |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema targetNamespace="http://www.bea.com/ns/wlcp/wlss/220"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:wlss="http://www.bea.com/ns/wlcp/wlss/220"
elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xsd:element name="sip-server">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="proxy" type="wlss:proxyType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="overload" type="wlss:overloadControlType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="message-debug" type="wlss:messageDebugType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="cluster-loadbalancer-map" type="wlss:clusterLoadBalancerMapType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="sip-security" type="wlss:sipSecurityType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true" />
<xsd:element name="default-behavior" type="wlss:sipServerBehavior" default="proxy" minOccurs="0" />
<xsd:element name="default-servlet-name" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" />
<xsd:element name="t1-timeout-interval" default="500" type="xsd:unsignedLong" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="t2-timeout-interval" default="4000" type="xsd:unsignedLong" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="t4-timeout-interval" default="5000" type="xsd:unsignedLong" minOccurs="0" />
<xsd:element name="timerB-timeout-interval" default="32000" type="xsd:unsignedLong" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="timerF-timeout-interval" default="32000" type="xsd:unsignedLong" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="max-application-session-lifetime" default="-1" type="xsd:int" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="enable-local-dispatch" default="false" type="xsd:boolean" minOccurs="0"/>
<xsd:element name="route-header" type="wlss:routeHeaderType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="engine-call-state-cache-enabled" default="false" type="xsd:boolean" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:complexType name="overloadControlType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="threshold-policy" type="wlss:sipServerThresholdPolicy" default="queue-length"/>
<xsd:element name="threshold-value" type="xsd:long"/>
<xsd:element name="release-value" type="xsd:long"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="proxyType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="routing-policy" type="wlss:sipServerRoutingPolicy"/>
<xsd:element name="uri" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="messageDebugType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="level" type="wlss:sipServerDebugLevel" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" default="full"/>
<xsd:element name="format" type="wlss:formatType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
<xsd:element name="string-rep" type="wlss:string-repType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" nillable="true"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="formatType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="pattern" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="token" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="string-repType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="content-type" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="clusterLoadBalancerMapType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="cluster-name" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="sip-uri" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="sipSecurityType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="trusted-authentication-host"
type="xsd:string"
minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xsd:element name="trusted-charging-host"
type="xsd:string"
minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="routeHeaderType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="uri" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:simpleType name="sipServerBehavior">
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="proxy"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="ua"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:simpleType name="sipServerThresholdPolicy">
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="queue-length"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="session-rate"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:simpleType name="sipServerRoutingPolicy">
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="domain"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="proxy"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:simpleType name="sipServerDebugLevel">
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="full"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="basic"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="terse"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:schema>
The following shows a simple example of a sipserver.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sip-server xmlns="http://www.bea.com/ns/wlcp/wlss/220">
<overload>
<threshold-policy>queue-length</threshold-policy>
<threshold-value>200</threshold-value>
<release-value>150</release-value>
</overload>
</sip-server>
The following sections describe each element used in the sipserver.xml configuration file. Each section describes an XML element that is contained within the main sip-server element shown in Figure 1-1.
The overload element enables you to throttle incoming SIP requests according to a configured overload condition. When an overload condition occurs, WebLogic SIP Server destroys new SIP requests by responding with "503 Service Unavailable" until the configured release value is observed, or until the capacity of the server's execute queues is exceeded (see Overload Control Based on Execute Queue Length).
User-configured overload controls are applied only to initial SIP requests; SIP dialogues that are already active when an overload condition occurs may generate additional SIP requests that are not throttled.
To configure an overload control, you define the three elements described in Table 1-1.
|
|
|
|
|
WebLogic SIP Server provides two different policies for throttling SIP requests:
session-rate policy throttles sessions when the volume new SIP sessions reaches a configured rate (a specified number of sessions per second).queue-length policy throttles requests after the sum of the sizes of the sip.transport.Default and sip.timer.Default execute queues reaches a configured size.| Note: | You can throttle SIP requests either using session-rate policy or a queue-length policy. You cannot use both policies simultaneously. |
The following sections describe each policy in detail.
WebLogic SIP Server calculates the session generation rate (sessions per second) by monitoring the number of application sessions created in the last 5 seconds. When the session generation rate exceeds the rate specified in the threshold-value element, WebLogic SIP Server throttles initial SIP requests until the session generation rate becomes smaller than the configured release-value.
The following example configures WebLogic SIP Server to begin throttling SIP requests when the new sessions are created at a rate higher than 50 sessions per second. Throttling is discontinued when the session rate drops to 40 sessions per second:
<overload>
<threshold-policy>session-rate</threshold-policy>
<threshold-value>50</threshold-value>
<release-value>40</release-value>
</overload>
By default, SIP messages are handled by an execute queue named sip.transport.Default and SIP timers are processed by an execute queue named sip.timer.Default. These execute queues are configured in the config.xml file for your WebLogic SIP Server installation.
WebLogic SIP Server performs execute queue-based overload control by monitoring the combined lengths of these default execute queues. When the sum of the lengths of the two execute queues exceeds the length specified in the threshold-value element, WebLogic SIP Server throttles initial SIP requests until the total length is reduced to the configured release-value.
Listing 1-1 shows the default overload configuration from sipserver.xml. In the default configuration, WebLogic SIP Server begins throttling SIP requests when the combined size of the sip.transport.Default and sip.timer.Default queues exceeds 200 requests. Throttling is discontinued when the combined length returns to 200 or fewer simultaneous requests.
<overload>
<threshold-policy>queue-length</threshold-policy>
<threshold-value>200</threshold-value>
<release-value>150</release-value>
</overload>
User-configured overload controls (defined in sipserver.xml) represent the first level of overload protection provided by WebLogic SIP Server. They mark the onset of an overload condition and initiate simple measures to avoid dropped calls (generating 503 responses for new requests).
If the condition that caused the overload persists or worsens, then the execute queues used to perform work in the SIP Servlet container may become full. At this point, the server can no longer generate 503 responses, so new message requests are simply dropped. In this way, the configured size of the SIP container's execute queues (sip.transport.Default and sip.timer.Default) represent the second and final level of overload protection employed by the server.
Always configure overload controls in sipserver.xml conservatively, and resolve the circumstances that caused the overload in a timely fashion. Overload conditions should never be permitted to last until the point where the execute queue capacities are exceeded.
The message-debug element is used to enable and configure access logging for WebLogic SIP Server. This element should be used only in a development environment, because access logging logs all SIP requests and responses. See
Enabling Access Logging in Developing Applications with WebLogic SIP Server for information about configuring and using access logging.
If you want to perform more selective logging in a production environment, see Logging SIP Requests and Responses in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
RFC 3261 defines an outbound proxy as "A proxy that receives requests from a client, even though it may not be the server resolved by the Request-URI. Typically, a UA is manually configured with an outbound proxy, or can learn about one through auto-configuration protocols."
In WebLogic SIP Server an outbound proxy server is specified using the proxy element in sipserver.xml. The proxy element defines one or more proxy server URIs. You can change the behavior of the proxy process by setting a proxy policy with the proxy-policy tag. Listing 1-2 describes the possible values for the proxy elements.
The default behavior is as if domain policy is in effect. The proxy policy means that the request is sent out to the configured outbound proxy and the route headers in the request preserve any routing decision taken by WebLogic SIP Server. This enables the outbound proxy to send the request over to the intended recipient after it has performed its actions on the request. The proxy policy comes into effect only for the initial requests. As for the subsequent request the Route Set takes precedence over any policy in a dialog. (If the outbound proxy wants to be in the Route Set it can turn record routing on).
Also if a proxy application written on WebLogic SIP Server wishes to override the configured behavior of outbound proxy traversal, then it can add a special header with name "X-BEA-Proxy-Policy" and value "domain". This header is stripped from the request while sending, but the effect is to ignore the configured outbound proxy. The X-BEA-Proxy-Policy custom header can be used by applications to override the configured policy on a request-by-request basis. The value of the header can be "domain" or "proxy". Note, however, that if the policy is overridden to "proxy," the configuration must still have the outbound proxy URIs in order to route to the outbound proxy.
Listing 1-2 shows the default proxy configuration for WebLogic SIP Server domains. The request in this case is created in accordance with the SIP routing rules, and finally the request is sent to the outbound proxy "sipoutbound.bea.com".
<proxy>
<routing-policy>proxy</routing-policy>
<uri>sip:sipoutbound.bea.com:5060</uri>
<!-- Other proxy uri tags can be added. -->
</proxy>
This element sets the value of the SIP protocol T1 timer, in milliseconds. Timer T1 also specifies the initial values of Timers A, E, and G, which control the retransmit interval for INVITE requests and responses over UDP.
Timer T1 also affects the values of timers F, H, and J, which control retransmit intervals for INVITE responses and requests; these timers are set to a value of 64*T1 milliseconds. See the SIP: Session Initiation Protocol for more information about SIP timers. See also Configuring NTP for Accurate SIP Timers in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
If t1-timeout-interval is not configured, WebLogic SIP Server uses the SIP protocol default value of 500 milliseconds.
This elements sets the value of the SIP protocol T2 timer, in seconds. Timer T2 defines the retransmit interval for INVITE responses and non-INVITE requests. See the SIP: Session Initiation Protocol for more information about SIP timers. See also Configuring NTP for Accurate SIP Timers in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
If t2-timeout-interval is not configured, WebLogic SIP Server uses the SIP protocol default value of 4 seconds.
This elements sets the value of the SIP protocol T4 timer, in seconds. Timer T4 specifies the maximum length of time that a message remains in the network. Timer T4 also specifies the initial values of Timers I and K, which control the wait times for retransmitting ACKs and responses over UDP. See the SIP: Session Initiation Protocol for more information about SIP timers. See also Configuring NTP for Accurate SIP Timers in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
If t4-timeout-interval is not configured, WebLogic SIP Server uses the SIP protocol default value of 5 seconds.
This elements sets the value of the SIP protocol Timer B, in milliseconds. Timer B specifies the length of time a client transaction attempts to retry sending a request. See the SIP: Session Initiation Protocol specification for more information about SIP timers. See also Configuring NTP for Accurate SIP Timers in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
If timerB-timeout-interval is not configured, the Timer B value is derived from timer T1 (64*T1, or 32000 milliseconds by default).
This elements sets the value of the SIP protocol Timer F, in milliseconds. Timer F specifies the timeout interval for retransmitting non-INVITE requests. See the SIP: Session Initiation Protocol specification for more information about SIP timers. See also Configuring NTP for Accurate SIP Timers in Configuring and Managing WebLogic SIP Server.
If timerF-timeout-interval is not configured, the Timer F value is derived from timer T1 (64*T1, or 32000 milliseconds by default).
This element sets the maximum amount of time, in minutes, that a SIP application session can exist before WebLogic SIP Server invalidates the session. By default there is no limit for SIP session lifetimes.
enable-local-dispatch is a server optimization that helps avoid unnecessary network traffic when sending and forwarding messages. You enable the optimization by setting this element "true." When enable-local-dispatch enabled, if a server instance needs to send or forward a message and the message destination is the engine tier's cluster address or the local server address, then the message is routed internally to the local server instead of being sent via the network. Using this optimization can dramatically improve performance when chained applications process the same request as described in
Composing SIP Applications in Developing Applications with WebLogic SIP Server.
You may want to disable this optimization if you feel that routing internal messages could skew the load on servers in the engine tier, and you prefer to route all requests via a configured load balancer.
By default enable-local-dispatch is set to "false."
The cluster-loadbalancer-map element is used only when upgrading WebLogic SIP Server software, or when upgrading a production SIP Servlet to a new version. It is not required or used during normal server operations.
During a software upgrade, multiple engine tier clusters are defined to host the older and newer software versions. A cluster-loadbalancer-map defines the virtual IP address (defined on your load balancer) that correspond to an engine tier cluster configured for an upgrade. WebLogic SIP Server uses this mapping to ensure that engine tier requests for timers and call state data are received from the correct "version" of the cluster. If a request comes from an incorrect version of the software, the cluster-loadbalancer-map entries are used to forward the request to the correct cluster.
Each cluster-loadbalancer-map entry contains the two elements described in
Listing 1-3 shows a sample cluster-loadbalancer-map entry used during an upgrade.
<cluster-loadbalancer-map>
<cluster-name>EngineCluster</cluster-name>
<sip-uri>sip:172.17.0.1:5060</sip-uri>
</cluster-loadbalancer-map>
<cluster-loadbalancer-map>
<cluster-name>EngineCluster2</cluster-name>
<sip-uri>sip:172.17.0.2:5060</sip-uri>
</cluster-loadbalancer-map>
This element defines the default behavior of the WebLogic SIP Server instance if the server cannot match an incoming SIP request to a deployed SIP Servlet (or if the matching application has been invalidated or timed out). Valid values are:
proxy is used as the default if you do not specify a value.
When acting as a User Agent (UA), WebLogic SIP Server acts in the following way in response to SIP requests:
When acting as a stateless proxy requests are automatically forwarded to an outbound proxy (see proxy—Setting Up an Outbound Proxy Server) if one is configured. If no proxy is defined, Weblogic SIP Server proxies to a specified Request URI only if the Request URI does not match the IP and port number of a known local address for a SIP Servlet container, or a load balancer address configured for the server. This ensures that the request does not constantly loop to the same servers. When the Request URI matches a local container address or load balancer address, WebLogic SIP Server instead acts as a UA.
This element specifies the name of a default SIP Servlet to call if an incoming initial request cannot be matched to a deployed Servlet (using standard servlet-mapping definitions in sip.xml). The name specified in the default-servlet-name element must match the servlet-name value of a deployed SIP Servlet. For example:
<default-servlet-name>myServlet</default-servlet-name>
If the name defined in default-servlet-name does not match a deployed Servlet, or no value is supplied (the default configuration), WebLogic SIP Server registers the name com.bea.wcp.sip.engine.BlankServlet as the default Servlet. The BlankServlet name is also used if a deployed Servlet registered as the default-servlet-name is undeployed from the container.
BlankServlet's behavior is configured with the default-behavior element. By default the Servlet proxies all unmatched requests. However, if the default-behavior element is set to "ua" mode, BlankServlet is responsible for returning 481 responses for CANCEL and BYE requests, and 500/416 responses in all other cases. BlankServlet does not respond to ACK, and it always invalidates the application session.
WebLogic SIP Server enables you to configure one or more trusted hosts for which authentication is not performed. When WebLogic SIP Server receives a SIP message, it calls getRemoteAddress() on the SIP Servlet message. If this address matches an address defined in the server's trusted host list, no further authentication is performed for the message.
The sip-security element defines one or more trusted hosts, for which authentication is not performed. The sip-security element contains one or more trusted-authentication-host or trusted-charging-host elements, each of which contains a trusted host definition. A trusted host definition can consist of an IP address (with or without wildcard placeholders) or a DNS name. Listing 1-4 shows a sample sip-security configuration.
<sip-security>
<trusted-authentication-host>myhost1.mycompany.com</trusted-authentication-host>
<trusted-authentication-host>172.*</trusted-authentication-host>
</sip-security>
3GPP TS 24.229 Version 7.0.0 requires that IMS Application Servers generating new requests (for example, as a B2BUA) include the S-CSCF route header. In WebLogic SIP Server, the S-CSCF route header must be statically defined as the value of the route-header element in sipserver.xml. For example:
<route-header>
<uri>Route: sip:wlss1.bea.com</uri>
</route-header>


|