MobileAware Interaction Server Administration Guide
|
|
MobileAware Interaction Server Administration Guide
About This Manual
This manual introduces you to the various tasks required to configure and manage the MobileAware Interaction Server. The manual is divided into three parts:
Explains how to set up and configure the MobileAware Interaction Server. It describes the various files used by the MobileAware Interaction Server and the changes you need to make during configuration.
Explains how to set up device profiles and how to manage the various device profiles. These profiles are stored in the device database and are managed through the Administration Console, a Java-based GUI that provides a convenient way of setting up, retrieving and modifying the various attributes associated with each profile.
Appendix A - Device Attributes
Appendix B - web.xml Sample File
Further Reading
For further information on the MobileAware Interaction Server, see the following manuals:
- MobileAware Interaction Server, BEA WebLogic Edition Installation Guide
- MobileAware Interaction Server, BEA WebLogic Edition Getting Started Tutorials
- MobileAware Interaction Server, BEA WebLogic Edition User Guide
- BEA Sample Workshop Mobility Project Guide
- BEA Sample Mobility Portal Guide
System Administration
Deploying an Application
In order to develop Java Server Pages or Java Servlets, regardless of whether they are mobilised or not, you must establish a server-side environment that interprets, compiles, and executes the pages that you write. This section describes how to deploy a mobilised web application with the MobileAware Interaction Server servlet filter.
There are two key steps to deploying the MobileAware Interaction Server applications in a servlet environment:
Creating the Deployment Site
Servlet containers such as BEA Tomcat and WebLogic support the Java Servlet 2.3 specification that standardises how the various components in a web application are organised. Some things to remember:
- You store all the files for a web application under a root directory. This root directory also serves as the document root for this web application. Usually, you would place the root directory within the applications directory of your container. For example: ..\jakarta-tomcat\webapps\your_webapp
- You store all application files (such as the JSP pages, HTML pages and images) under the root directory.
- You must create a special directory named
"WEB-INF"under the root directory that contains the information describing the web application and how it should be configured and how it should behave. - For a new MobileAware Interaction Server deployment, copy the contents of
<installdir>\libdirectory toWEB-INF\lib.
Note: If you developed your mobilized application in BEA WebLogic Workshop with MobileAware Interaction Server, BEA WebLogic Edition installed, "Enable Multi-Channel" has already copied any necessary MobileAware Interaction Server files into the WEB-INF directory.
The following table shows the contents of the WEB-INF directory:
Table 1 WEB-INF Directory Contents
For additional information on deploying applications on BEA WebLogic Platform, Please refer to Developing Web Applications for BEA WebLogic Server documentation: http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs81/webapp/index.html:
Configuring the Web Deployment Descriptor
Before deploying a web application, you need to place a deployment descriptor (web.xml) into the WEB-INF directory. This file pulls together all the components of the Web application.
The following table describes the key elements in the web.xml file:
Table 2 Key Elements in web.xml File
Configuring the MIS Filter and Filter Mapping
An example of a web.xml file that has been configured for the MobileAware Interaction Server filter is shown below followed by an explanation of the settings.
<filter>
<filter-name>mobilityFilter</filter-name>
<display-name>MIS Mobility Filter</display-name>
<description>MIS Mobility Filter</description>
<filter-class>com.mobileaware.mcp.MobilityFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>propertiesname</param-name>
<param-value>/mis.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>mobilityFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
Table 3 MobileAware Interaction Server web.xml Filter Settings
|
A name for each parameter to be passed to the MobileAware Interaction Server: |
|
|
A value for each corresponding parameter name. In this case, the name and location of the properties file. |
Table 4 MobileAware Interaction Server web.xml Filter Mapping Settings
For more details on the Java Server specification and how to configure the web.xml file, please refer to the following URLs:
- Java Servlet Specification:
http://www.jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/final/jsr053/ - General Java servlet technology documents:
http://java.sun.com/products/servlet/docs.html
Developing Web Applications for BEA WebLogic Server documentation:
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs81/webapp/index.html
The MobileAware Interaction Server provides a set of sample JSP error handling pages and images:
Copy the error pages to your web application directory; you can place them in their own directory below the webapp root if you prefer.
Modify the following lines in the properties file so that they point to the appropriate error handlers.
<filter-name>mobilityFilter</filter-name>
Configuring the MobileAware Interaction Server
Configuring the MobileAware Interaction Server Filter
Configuring a MobileAware Interaction Server filter for each web application involves creating an mis.properties file that specifies:
- the database that the MobileAware Interaction Server needs to connect with
- the error pages to be returned in the event of any HTTP- or WAP-generated errors
- number of additional configuration settings as described in "Configuring the MobileAware Interaction Server"
There is a sample properties file, mis.properties.sample, in the lib folder of the installation directory. Copy this file into WEB-INF/classes folder and make the necessary changes for configuring the database and the error pages.
You can rename the file to a name of your own choosing, but you need to specify the name in <param-value> section of the web.xml file that has been configured for the filter. See the section "Configuring the MIS Filter and Filter Mapping" for further details.
This sectionchapter introduces the various properties used to manage the behaviour of the MobileAware Interaction Server. As an administrator, you will need to configure some of these properties to adjust the behaviour of the MobileAware Interaction Server.
Some of these properties will have been set during the install process, while others can be configured later when you want to activate other new features.
The mis.properties File
The main configuration file used by the MobileAware Interaction Server, which contains a number of user-modifiable parameters, is the mis.properties file.
This file can be found in the WEB-INF/classes folder. It is a plain text file that can be edited in any text editor.
This section describes configuration settings for the mis.properties file.
Configuring the MobileAware Device Database Connection
The following device database properties must be configured in order forthat the MobileAware Interaction Server tocan successfully communicate with the MobileAware Device Ddatabase used:
Table 5 Device Database Properties Settings
About Connection Pools
A dynamic web site often generates HTML pages from information stored in a database. Each request for a page results in a database access. Connecting to a database is time consuming since the database must allocate communication and memory resources as well as authenticates the user and set up the corresponding security context. Setting up the individual connections can become a bottleneck.
Establishing the connection once and using the same connection for subsequent requests can therefore dramatically improve the performance of a database driven web application. Connection pooling is a technique used to avoid the overhead of making a new database connection every time an application or server object requires access to a database. Rather than making and breaking connections as required, a "pool" of database connections is maintained by the system on the server. When the MobileAware Interaction Server needs a database connection, it simply requests an available one from the pool - if none is available, a new one is created & added to the pool.
The connection pool not only grows to specified limits, but also contracts as required, closing connections that have not been used for a specified time. This avoids taking up system resources by simply holding connections that are not currently required. This also handles databases which "time-out" their connections, and prevents handing a "stale" connection to an application object.
Configuration of XML File-based MobileAware Device Database
To configure MIS to use an XML File-based MobileAware Device Database instead of connecting to an external database (e.g. Oracle, MySQL) where the MobileAware Device Database has been installed, the database settings must be defined properly in the mis.properties file associated with the web application.
#######################################################
#
# Device Repository Type
# -----------------------------------------
# This setting indicates whether the MobileAware Device Database is
# deployed as an XML file or installed into a JDBC database.
# Possible values are: xml and db
#
# If not specified, db is assumed.
#deviceRepositoryType: xml
deviceRepositoryType: xml
#######################################################
#
# XML Device Repository File Location
# -----------------------------------------
# This setting indicates the location of the Device Repository XML file
# This setting must be set to the location of the xml file or the
# classpath will be checked (see deviceXML.resourceName)
#
# Example:
#C\:\\bea81sp3\\weblogic81\\mobileaware\\database\\DeviceRepository.xml
#
#deviceXML.location: C\:\\bea81sp3\\weblogic81\\mobileaware\\database\\DeviceRepository.xml
deviceXML.location: C\:\\bea81sp3\\weblogic81\\mobileaware\\database\\DeviceRepository.xml
# XML Device Repository Resource Name
# -----------------------------------------
# This setting indicates the name of the Device Repository XML file that
# should be used in the classpath.
#
# The default is "/DeviceRepository.xml"
#
# Example: deviceXML.resourceName: /DeviceRepository.xml
deviceXML.resourceName: /DeviceRepository.xml
Configuring Session Encoding of URLs (configuration optional)
Where session cookies are not supported by devices or gateways, session information can be automatically encoded into URLs :using the settings in the table below.
Table 6 Session Encoding of URLs Properties Settings
Configuring URL Compression
The URLs generated by portal frameworks and other content servers are often very long. If URL rewriting is used instead of cookies for session management the length of these URLs is extended further. Because the length of these URLs takes up valuable space within the limited memory of a small device, the output visible to the user is often very limited. In extreme cases, pages are limited to just 2 or 3 links.
To mitigate this, the MobileAware Interaction Server supports URL compression, which reduces the length of these URLs to a minimum, thereby allowing much more content to be delivered to the device. This is especially relevant where the device has limited memory but could also be important where limited bandwidth is an issue.
URL compression works by breaking the URL into fragments (query parameters) and replacing the fragments in the URL with shortened tokens. These shortened tokens are used by the MobileAware Interaction Server to map a request generated from the replacemen URL back to the original URL.
Examples
The following is an example of a URL of 359 characters produced by BEA WebLogic Portal:
/avitekfinancial/application?namespace=tracking&origin=searchResults.jsp&
event=link.clickContent&com.bea.event.type=com.bea.content.click.event&
com.bea.event.userid=null&com.bea.event.documentid=Avitek/DemoDocuments/Demo Features
List.xls&com.bea.event.documenttype=AvitekDocs&contentId=Avitek/DemoDocuments/Demo Features List.xls
With URL compression turned on in the MobileAware Interaction Server, this URL would be reduced to 99 characters, which is a saving of 260 characters:
/avitekfinancial/application?2=!!3&!!4=!!5&!!6=!!7&!!8=!!9&!!10=!!11&!!12=!!13&!!14=!!15&!!16=!!13
URL compression can be configured in the mis.properties file. mis.properties file.
The table below shows sample URL Compression configuration for the MobileAware Interaction Server running against a BEA WebLogic Portal server.
Table 7 URL Compression Properties Settings for MIS Running Against BEA WebLogic Portal
Note: When using the redirect URL for failed decompression it is recommended that content developers design JSP or XHTML pages that do not make use of, or depend on, the values of parameters passed in the URL.
Error Handling (configuration optional)
The location of Error handler JSPs for HTTP and WAP can be configured using the parameters in the table below. The location of the JSP error handlers is a webapp relative path.
Table 8 JSP Error Page Properties Settings
|
Location of the HTTP JSP error handler, or your own custom file. |
|
|
Location of the WAP JSP error handler, or your own custom file. |
Configuration Mode (configuration optional)
This configuration entry determines which mode of operation the MobileAware Interaction Server runs in.
Table 9 Configuration Mode Properties Setting
Generated URLs
The MobileAware Interaction Server automatically generates a number of URLs during content transformation. For content that the MobileAware Interaction Server produces for WAP phones, the MobileAware Interaction Server can produce `Next' and `Back to Top' links that contain the identifier of the required page. Similarly, when the MobileAware Interaction Server splits a form into multiple pages, the URLs generated by the MobileAware Interaction Server contain information about required form ID, current form ID and whether a form reset has been requested.
The parameter name that the MobileAware Interaction Server uses for these identifiers can be changed in the mis.properties file, in the event that they clash with those already used by content developers.
Table 10 URL Generation Properties Settings
Strict Attribute Handling and Delivery (configuration optional)
These configuration entries define whether the MobileAware Interaction Server rejects stand-alone `&' symbols, and whether it delivers them in HTML content.
<a href="/url?param1=value1¶m2=value">
Example of well-formed equivalent:
<a href="/url?param1=value1&param2=value">
Table 11 Strict Attribute Handling and Delivery Properties Settings
Diagnostics Subscriptions (configuration optional)
The MobileAware Interaction Server is configured by default to send certain important diagnostics messages, such as error messages, to the application server console. It is possible to configure these and additional diagnostic messages to be sent either to the console or to a specified file.
Example diagnostics messages published to file:
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.abcFile.topic: MIS.General.Startup
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.abcFile.level: verbose|normal
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.abcFile.filename: c:\\diagerrors.log
Note: "abc" is simply a placeholder for a unique identifier, to ensure that property names are unique. You are free to choose your own identifier.
Note: Each topic you subscribe to must be configured to output to a different file.
Note: At start-up, the specified file is overwritten, not appended to.
Example diagnostics messages published to the console:
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.xyzConsole.topic: MIS.General.Startup
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.xyzConsole.level: verbose|normal
By default, the MobileAware Interaction Server diagnostics are configured to publish start-up messages and diagnostic-audit messages (to track individuals connecting to diagnostics) to the console as follows:
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.startupConsole.topic:MIS.General.Startup
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.startupConsole.level:normal
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.diagnosticsauditConsole.topic:MIS.Diagnostics.Subscription
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.diagnosticsauditConsole.level:normal
Error messages could additionally be configured to publish to file as follows:
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.errorsFile.topic:
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.errorsFile.level:verbose
diagnostics.startup.subscriptions.errorsFile.filename:c:\\temp\\diagerrors.log
This is a special case where no topic is required.
Table 12 Diagnostics Subscriptions Properties Settings
|
Any diagnostic topic which can be selected from the MobileAware Interaction Server Diagnostics |
|
|
Specifies the level of diagnostics message required, either "verbose" or "normal" |
|
Back to Top (configuration optional)
This configuration entry defines whether the "Back to Top" feature is enabled or disabled.
When enabled, a shortcut "Back To Top" link is provided on the device, which will allow the user to return directly to the top of the group based on the hierarchy of the current document. If the user then uses this enhancement to navigate to the top-level navigation card of the current document hierarchy, they are provided with a "Back To Top" link that returns them to the referrer.
Table 13 Back to Top Properties Setting
Content Length Settings
The response.omitContentLength configuration entry defines whether or not the MobileAware Interaction Server will set the content length in the response. By default, response.omitContentLength is set to false, implying that the MobileAware Interaction Server will set the content length in the response. If it is set to true the MobileAware Interaction Server will not set the content length and chunked encoding will be used to deliver content
Table 14 Content Length Properties Setting
|
Indicates whether the content length should be included in the response from MobileAware Interaction Server |
Disallowed Output Encodings (configuration optional)
The MobileAware Interaction Server determines from the incoming device request which character encodings will give the best rendering of content. In some circumstances, however, a device may incorrectly report its quality of support for a given character encoding, or there may be no valid transformation from the original content encoding to the preferred device encoding. Specifying a comma-separated list of encodings for the disallowedOutputEncodings property instructs the MobileAware Interaction Server never to deliver content in any of these encodings.
Table 15 Disallowed Output Encodings Properties Setting
Optimizsing Performance with the JSP Tag Library (configuration optional)
There are several steps involved in the MobileAware Interaction Server transformation process. Some of these steps can by bypassed to achieve optimal performance using the MobileAware Interaction Server JSP tag library.
For full details on achieving optimal performance with the JSP Tag Library, see the chapter section "Optimising Performance with the JSP Tag Library" in the MobileAware Interaction Server, BEA WebLogic Edition. The properties involved in this process are summarised below.
Table 16 Optimizing JSP Tag Library Performance Properties Setting
Passthrough Pattern Configuration (configuration optional)
The following properties control which HTTP requests the MobileAware Interaction Server will act on. For performance reasons it is beneficial to be able to inform the MobileAware Interaction Server to not process any request that will not produce MMXHTML.
When an HTTP request is received, the MobileAware Interaction Server will check the URL against the "mis.patterns.url.nonmmxhtml" patterns. If it matches, the request will not be processed.
Otherwise, the MobileAware Interaction Server will check the "mis.patterns.url.mmxhtml" patterns. If these match, or the property "mis.patterns.url.unknown.mmxhtml" is set to true, the request is processed and the Content-Type is checked after the content has been produced.
The Content-Type check is done in much the same was as the url check. The Content-Type is checked against the "mis.patterns.contenttype.nonmmxhtml" property. If it matches, the content is delivered as produced. Otherwise, if either the "mis.patterns.contenttype.unknown.mmxhtml" is set to true or the "mis.patterns.contenttype.mmxhtml" pattern matches the content is transformed.
Note: If you need to modify or add to these lists you need to include the appropriate values from the default settings as you are overriding the property. Only remove from these lists if you are sure that is what you want to do. Configuring these properties incorrectly may cause the MobileAware Interaction Server to no longer process content.
In the following properties the "patterns" may be of the form:
XXX* - starts with XXX, for example /images/*
*XXX - ends with XXX, for example *.gif
*XXX* - contains XXX, for example */ignore/*
Table 17 Passthrough Pattern Properties Setting
BEA WebLogic Portal Settings (configuration mandatory for BEA Portal deployment)
Note: The following properties are to facilitate MIS Integration with BEA WebLogic Portal and Server. Do Not change these settings if running with BEA WebLogic Portal or Server.
Table 18 BEA WebLogic Portal Properties Setting
The ContentAssembly.properties File
This file contains additional configurable settings that relate to the way content appears on the screen. Most of these settings have to do with the text displayed in the automatically generated links, which aid navigation around sites being delivered to handheld devices. For example, Next, Back to:, Previous, and so on.
Unlike the other two properties files discussed in this section, this file is located in the webapp's WEB-INF/lib/mmJSPtaglib.jar file. This file contains the default property values. If you wish to make changes to this file, unzip the jar, make a copy of the properties file, make the changes, then save it to:
WEB-INF/classes/com/mobileaware/i18n/resources/ContentAssembly.properties.
Multiple versions of this file can be created to provide locale specific property values. Which file is used depends on the language and region settings of the requesting device and the availability of a properties file matching those settings. This mechanism uses the Java Internationalization functionality that provides a standard for application designs that are adaptable to various languages and regions without engineering changes.
As an example, if you had customers in France and Germany who would be accessing your website, you would create two versions of the ContentAssembly.properties file and name them:
Modify the property values to conform to the language of the country.
# #
# Next Link #
# The text link that is inserted by MIS #
# during pagination of a group to take user to next #
# page of content within the group. #
# #
page.group.next.link: Suivant...
# #
# Previous Link #
# The text link that is inserted by MIS during #
# pagination of a group to return user to previous page #
# of the group. #
# #
#########################################################
page.group.previous.link: Précédent
Figure 1 Setting properties for French devices
For more information and a list of the fully supported locales and filename extensions, see the Java documentation at java.sun.com.
Table 19 Content Assembly Properties Settings
The oscache.properties File
The oscache.properties file is a text file containing the configuration settings that regulate the content caching mechanism. It is located in the WEB-INF/classes folder of each your webapps running with the MobileAware Interaction Server. It is a plain text file and can be modified in any text editor.
Normally, you do not need to modify anything in this file; however, you might want to change the directory that stores the caches. You can reset the directory by changing the cache.path property. By default, a cache directory called tempCache is created relative to the directory from which the MobileAware Interaction Server was launched.
Note: If you change the cache.path property, you must ensure that the cache has permission to write to the new directory.
Configuring the Error Pages
The MobileAware Interaction Server provides a set of sample JSP error handling pages and images. It is recommended that you replace these with your own error handling pages and images. This error pages can be found in the top directory of the sample BEA Workshop and BEA Portal projects installed during the installation process (see the MobileAware Interaction Server BEA WebLogic Edition Installation Guide).
Table 20 Sample JSP Error Handling Pages and Images
Copy the error pages to your web application directory or place them in their own directory below the <webapp> root if you prefer.
You will need to modify the following lines in the mis.properties file so that they point to the appropriate error handlers.
Table 21 JSP Error Page Settings
|
Location of the HTTP JSP error handler, or your own custom file |
|
|
Location of the WAP JSP error handler, or your own custom file |
Resource Administration
Getting Started
Device profiles are stored in the MobileAware Device Database. They are managed through the Administration Console, a Java-based GUI that provides a convenient way of setting up, retrieving and modifying the attributes associated with each profile.
This chapter introduces the Administration Console.
Quick Start
The following table introduces the basic steps in using the Administration Console.
Table 22 Administration Console Quick Start Guide
|
The MobileAware Tools Launcher Icon in BEA WebLogic Workshop or launch directly from <bea_home>/weblogic81/mobileaware/applications/MISAdmin/MISAdministrationConsole.exe or MISAdministration.bin. |
|
Logging In
- Enter the correct MobileAware Interaction Server IP address and web application address in the "Server" field, for example localhost:8080/<application>news/. (The "Server" field recalls the last four servers that the Administrator successfully connected to.)
Using the System Monitor
The System Monitor displays the Free Memory available and refreshes the console.
Refreshing the Console Automatically
Refreshing the Console Manually
Using the Administration Console Toolbar
The Administration toolbar provides a convenient method for accessing the administrative functions within the MobileAware Interaction Server. The following illustrates the tasks associated with each image on the toolbar.
Figure 2 Administration Console Toolbar
Managing Devices
Devices have a range of input and presentation capabilities, network connectivity and levels of scripting language support.
The MobileAware Interaction Server accommodates these differences by maintaining the device database, which contains profiles describing the properties and capabilities for a range of devices on the market.
These profiles enable the MobileAware Interaction Server to tailor the presentation and delivery of content to each device. This ensures clients receive content that they can display, store and which does not take too long to convey over the network.
Device profiles are managed from within the Administration Console. From here, you can add, remove and modify devices and device attributes.
- The device database and device profiles
- How device profiles are used to tailor content.
- How to use the Administration Console to manage the device repository to add, delete and modify device profiles.
About Device Profiles
Each device in the device database has an associated set of properties (attribute-value pairs) that enable the MobileAware Interaction Server to identify the requesting device in order to deliver and present the content appropriately. In the event that the MobileAware Interaction Server does not find an exact match within its profiles, it uses the attributes to determine the closest match.
Composite Capabilities/Preferences Profile (CC/PP) is a standard developed by the W3C that is used to describe device capabilities and user preferences (i.e. the delivery context). This information can be used to develop device independent web content or applications. Based on this standard, the Open Mobile Alliance, the group that establishes open global standards for the mobile community has defined their own standard known as User Agent Profile (UAProf).
MobileAware has adopted this new standard for our device database. Currently, the database is CC/PP compliant, containing both the UAProf attribute set and a more comprehensive set of MobileAware Interaction Server proprietary device properties.
Each device is described by a set of attributes that make up a unique profile for that device. The two types of attributes are described below.
CC/PP Attributes
Following the standard, the CC/PP compliant attributes fall into one of seven categories. Each attribute begins with a prefix that indicates into which category it falls. The following table lists these categories and gives examples of the types of attributes that they encompass.
Table 23 CC/PP Attribute Category Prefixes and Example Attributes
MobileAware Attributes
Along with the CC/PP attributes are the MobileAware proprietary attributes that complete the database. These attributes describe device characteristics that are not yet included in the standard, but describe a number of extra characteristics that can be used when tailoring content to particular devices.
About the Device Database
The Organization of the Device Profiles
The database represents devices as a hierarchical arrangement, thus enabling devices to inherit attributes from a parent device.
The device database has three parent device classes: WML, XHTMLMP and HTML devices. When adding a new device, you can place it within one of these hierarchies or create your own parent device class.
The list of devices supported by the MobileAware Interaction Server is stored as a hierarchy or tree within the Devices section of the Administration Console.
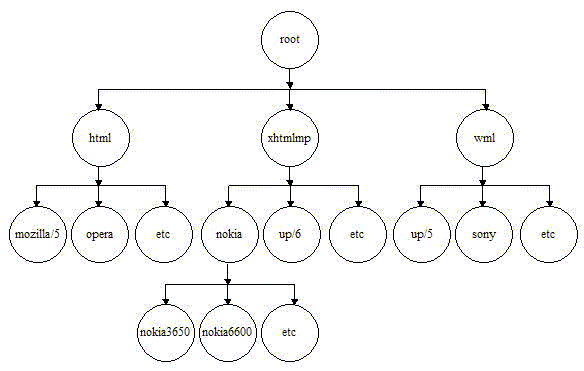
The tree is branched on the mark-up language used by the device with HTML, WML and XHTMLMP providing the main branches off the default root. Below the main branches, devices are categorised according to browser or model type, as illustrated in the device hierarchy below. An example fragment is shown below.
Figure 3 Device Repository Hierarchy
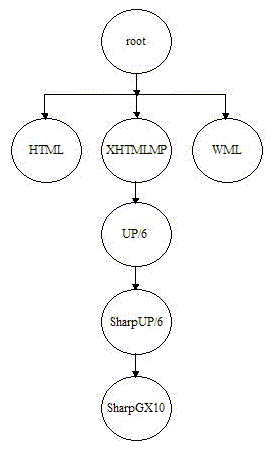
The hierarchy stores device attributes for the named devices detailing mark-up languages, screen sizes etc. The device name root represents the complete device tree within the MobileAware Interaction Server. All devices are subordinate to root, see example below. Tree nodes are device names, while all leaf nodes are device attributes.
Figure 4 Device Attribute Inheritance
A node in the device tree inherits any device attributes (markup language, screen size, etc.) from its parent. If the child node specifies values for any of these attributes, the child's values override the parent's.
Device Recognition
Comparing Incoming Requests to Device Attributes
When the MobileAware Interaction Server receives an end-user device request, it identifies the device using a combination of incoming request header information (which indicates the markup language of the device and often provides device model information) and stored device attributes.
The MobileAware Interaction Server achieves this by examining the details of the request and matching this request against device attributes contained in the device database.
In matching a user request against a device each level of the tree is traversed. The pattern matcher starts at the root node and attempts to traverse the tree to as deep a level (hence as specific a device match) as possible.
Each node in the tree specifies a single header and associated values that are used to differentiate it from its parent node.
The HTTPMetadataKey attribute tells the matcher to match on either Accept header or User-Agent string.
The pattern matcher will determine from the Accept header whether it is to traverse the WML branch, the XHTMLMP branch, or the HTML branch of the device hierarchy. This is defined in the HTTPMetaDataString.
Note: The ordering of child nodes is important, as the pattern matcher will take the first match found and ignore all others.
Multiple Header Strings
If more than one string must be present in the header, pattern matching is achieved either by using more than one level of the hierarchy with one of the strings specified in each or by combining the strings in a single node with an ampersand (`&') character. For example, a menu-driven device could require that two strings be matched: "text/vnd.wap.wml&image/vnd.wap.wbmp". Similarly, an OR comparison may be performed using the bar (`|') character.
No Match
If an absolute match is not found a more general match is found at a higher level so that the MobileAware Interaction Server can deliver content in some format understandable by the given device.
If an unknown device sends a request, the MobileAware Interaction Server will find the closest match possible in the existing hierarchy (for example, an unknown UP 6.x browser-based phone will still match as far as UP 6.x). As such, the MobileAware Interaction Server does not need to have an exhaustive list of all devices on the market at present.
The MobileAware Interaction Server then uses the retrieved device attributes to assemble and deliver content in a manner suitable to the user's device. The content is tailored to suit the device, for example, content is restructured for smaller devices, such as WAP phones.
Transforming Content
Once the MobileAware Interaction Server has identified a device and matched it against one in its database, it seamlessly transforms the presentation of the content to the requesting device.
This transformation is managed through the use of Device Transformation Maps (DTMs). The DTM specifies how content marked up with the MobileAware Interaction Server mobility tags is transformed to tailor the delivered page to the capabilities of the requesting device.
DTMs make it possible to accommodate new devices or upgraded versions of existing models as soon as they come on the market; transformation rules can be built quickly to take into account the new capabilities.
Each device DTM forms part of the device's profile in the database. The DTM attribute specifies the location of the transformation map to be applied to the original marked up content before it is delivered to the requesting device. The transformation map specifies how the mark-up is transformed by associating each mmXHTML/HTML tag with a Java class file that is responsible for the transformation of that tag, or by directly specifying more rudimentary transformations, such as remove or replace element.
Tailoring Content
Device profiles enable the presentation and delivery of content to be tailored to accommodate the capabilities of the requesting device.
Within the MobileAware Interaction Server, tailoring of content takes place on three levels:
- When the MobileAware Interaction Server identifies the requesting device, it can automatically reconfigure the presentation of content to accommodate the device's capabilities, such as splitting up a large page across a number of decks on a WAP browser.
- The content author, using the conditional mobility tags, <mm-include> and <mm-exclude>, specifies how content should be altered when being delivered to different devices. For example, the length of a product description could be tailored to accommodate different-sized screens.
- The content author creates specific layouts to target different devices or device classes. Depending on the complexity of the content, the author may choose a static layout, where the dimensions (such as the number of columns and rows in a table) are fixed. Alternatively, they may choose dynamic layouts, using the delivery context API to identify the device and using JSP methods to generate the appropriate layout "on-the-fly". For example, the author can use the API to determine the width and height of a screen, and resize the table accordingly.
Creating and Modifying Device Profiles
Device profiles are configured from within the Administration Console. The existing profiles and attributes can be modified, or new ones can be created. This can be useful for capturing more device-specific information to finely tune your content delivery for a specific purpose.
Creating Device Profiles
Three steps are required when adding a new device profile to the MobileAware Interaction Server:
Adding a Device
Note: * Indicates a Required Field
When adding a device to the database, there is a standard set of attributes that need to be configured for the new device.
Adding a Device Attribute
To add a new Device Attribute:
Note: The Modifiable By option should be ignored. This is a legacy option and has been deprecated.
Configuring an Attribute
Modifying a Device Profile
You can add and delete attributes or change attribute values. Inherited attributes cannot be deleted: the Delete button will be graeyed if you select an inherited attribute.
Viewing an Attribute
Select the Attribute from the Attributes list and then click View.
Deleting Devices
You can only delete devices that you have added to the device hierarchy; you cannot delete pre-installed devices.