Programming WebLogic Web Services
|
|
Web Service Ant Tasks and Command-Line Utilities
The following sections describe WebLogic Web Service Ant tasks and the command-line utilities based on these Ant tasks:
- Overview of WebLogic Web Services Ant Tasks and Command-Line Utilities
- autotype
- clientgen
- servicegen
- source2wsdd
- wsdl2Service
- wsdlgen
- wspackage
Overview of WebLogic Web Services Ant Tasks and Command-Line Utilities
Ant is a Java-based build tool, similar to the make command but much more powerful. Ant uses XML-based configuration files (called build.xml by default) to execute tasks written in Java.
BEA provides a number of Ant tasks that help you generate important parts of a Web Service (such as the serialization class, a client JAR file, and the web-services.xml file) and to package all the pieces of a WebLogic Web Service into a deployable EAR file.
The Apache Web site provides other useful Ant tasks for packaging EAR, WAR, and EJB JAR files. For more information, see http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/manual/.
Note: The Apache Jakarta Web site publishes online documentation for only the most current version of Ant, which might be different from the version of Ant that is bundled with WebLogic Server. To determine the version of Ant that is bundled with WebLogic Server, run the following command after setting your WebLogic environment:
prompt> ant -version
To view the documentation for a specific version of Ant, download the Ant zip file from http://archive.apache.org/dist/ant/binaries/ and extract the documentation.
You can also run some of the Ant tasks as a command-line utility, using flags rather than attributes to specify how the utility works. The description of the flags is exactly the same as the description of its corresponding attribute.
Warning: Not all the attributes of the Ant tasks are available as flags to the equivalent command-line utility. See the sections that describe each Ant task for a list of the supported flags when using the command-line equivalent.
For further examples and explanations of using these Ant tasks, see Assembling WebLogic Web Services Using Ant Tasks.
List of Web Services Ant Tasks and Command-Line Utilities
The following table provides an overview of the Web Service Ant tasks provided by BEA and the name of the corresponding command-line utility.
Using the Web Services Ant Tasks
To use the Ant tasks, follow these steps:
On Windows NT, execute the
setEnv.cmdcommand, located in your domain directory. The default location of WebLogic Server domains isBEA_HOME\user_projects\domains\domainName, whereBEA_HOMEis the top-level installation directory of the BEA products anddomainNameis the name of your domain.On UNIX, execute the
setEnv.shcommand, located in your domain directory. The default location of WebLogic Server domains isBEA_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainName, whereBEA_HOMEis the top-level installation directory of the BEA products anddomainNameis the name of your domain.The following example shows a simple
build.xmlfile (with details of the Web Services Ant tasksservicegenandclientgenomitted for clarity):<project name="buildWebservice" default="build-ear">
<target name="build-ear">
<servicegenattributes go here...>
...
</servicegen>
</target>
<target name="build-client" depends="build-ear">
<clientgenattributes go here .../>
</target>
<target name="clean">
<delete>
<fileset dir="."
includes="example.ear,client.jar" />
</delete>
</target>
</project>Later sections provide examples of specifying the Ant task in the
build.xmlfile.- Execute the Ant task or tasks specified in the
build.xmlfile by typingantin the same directory as thebuild.xmlfile:
prompt> ant
Differences in Operating System Case Sensitivity When Manipulating WSDL and XML Schema Files
Many of the WebLogic Web Service Ant tasks have attributes that you can use to specify an operating system file, such as a WSDL or an XML Schema file. For example, you can use the wsdl attribute of the clientgen Ant task to create the Web Services-specific client JAR file from an existing WSDL file that describes a Web Service.
The Ant tasks process these files in a case-sensitive way. This means that if, for example, the XML Schema file specifies two complex types whose names differ only in their capilatization (for example, MyReturnType and MYRETURNTYPE), the clientgen Ant task correctly generates two separate sets of Java source files for the Java represenation of the complex data type: MyReturnType.java and MYRETURNTYPE.java.
However, compiling these source files into their respective class files might cause a problem if you are running the Ant task on Microsoft Windows, because Windows is a case insensitive operating system. This means that Windows considers the files MyReturnType.java and MYRETURNTYPE.java to have the same name. So when you compile the files on Windows, the second class file overwrites the first, and you end up with only one class file. The Ant tasks, however, expect that two classes were compiled, thus resulting in an error similar to the following:
c:\src\com\bea\order\MyReturnType.java:14:
class MYRETURNTYPE is public, should be declared in a file named MYRETURNTYPE.java
public class MYRETURNTYPE
^
To work around this problem rewrite the XML Schema so that this type of naming conflict does not occur, or if that is not possible, run the Ant task on a case sensitive operating system, such as Unix.
Setting the Classpath for the WebLogic Ant Tasks
Each WebLogic Ant task accepts a classpath attribute or element so that you can add new directories or JAR files to your current CLASSPATH environment variable.
The following example shows how to use the classpath attribute of the servicegen Ant task to add to the CLASSPATH variable:
<servicegen destEar="myEJB.ear"
classpath="${java.class.path};my_fab_directory"
...
</servicegen>
The following example shows how to add to the CLASSPATH by using the <classpath> element:
<servicegen ...>
<classpath>
<pathelement path="${java.class.path}" />
<pathelement path="my_fab_directory" />
</classpath>
...
</servicegen>
The following example shows how you can build your CLASSPATH variable outside of the WebLogic Web Service Ant task declarations, then specify the variable from within the task using the <classpath> element:
<path id="myid">
<pathelement path="${java.class.path}"/>
<pathelement path="${additional.path1}"/>
<pathelement path="${additional.path2}"/>
</path>
<servicegen ....>
<classpath refid="myid" />
...
</servicegen>
Warning: The WebLogic Web Services Ant tasks support the standard Ant property build.sysclasspath. The default value for this property is ignore. This means that if you specifically set the CLASSPATH in the build.xml file as described in this section, the Ant task you want to run ignores the system CLASSPATH (or the CLASSPATH in effect when Ant is run) and uses only the one that you specifically set. It is up to you to include in your CLASSPATH setting all the classes that the Ant task needs to successfully run. To change this default behavior, set the build.sysclasspath property to last to concatenate the system CLASSPATH to the end of the one you specified, or first to concatenate your specified CLASSPATH to the end of the system one.
Warning: For more information on the build.sysclasspath property, see the Ant documentation.
Note: The Java Ant utility included in WebLogic Server uses the ant (UNIX) or ant.bat (Windows) configuration files in the WL_HOME\server\bin directory to set various Ant-specific variables, where WL_HOME is the top-level directory of your WebLogic Platform installation If you need to update these Ant variables, make the relevant changes to the appropriate file for your operating system.
Using the Web Services Command-Line Utilities
To use the command-line utility equivalents of the Ant tasks, follow these steps:
On Windows NT, execute the
setEnv.cmdcommand, located in your domain directory. The default location of WebLogic Server domains isBEA_HOME\user_projects\domains\domainName, whereBEA_HOMEis the top-level installation directory of the BEA products anddomainNameis the name of your domain.On UNIX, execute the
setEnv.shcommand, located in your domain directory. The default location of WebLogic Server domains isBEA_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainName, whereBEA_HOMEis the top-level installation directory of the BEA products anddomainNameis the name of your domain.
prompt> java weblogic.webservice.clientgen \
-ear myapps/myapp.ear \
-serviceName myService \
-packageName myservice.client \
-clientJarmyapps/myService_client.jar
autotype
The autotype Ant task generates the following components for non-built-in data types that used as parameters or return values of your Web Service operation:
- Serialization class that converts between the XML and Java representation of the data.
- Given an XML Schema or WSDL file, a Java class to contain the Java representation of the data type.
- Given a Java class that represents the non-built-in data type, an XML Schema representation of the data type.
- Data type mapping information to be included in the
web-services.xmldeployment descriptor file.
For the list of non-built-in data types for which autotype can generate data type components, see Non-Built-In Data Types Supported by servicegen and autotype Ant Tasks.
You can specify one of the following types of input to the autotype Ant task:
- A Java class file that represents your non-built-in data types by specifying the
javaTypesattribute. TheautotypeAnt task generates the corresponding XML Schemas, the serialization classes, and the data type mapping information for theweb-services.xmlfile. - A Java class file of the component that implements your Web Service by specifying the
javaComponentsattribute. If your Web Service is implemented with a Java class, then this attribute points to the Java class. If your Web Service is implemented with a stateless session EJB, then this attribute points to the remote interface of the EJB. TheautotypeAnt task looks for non-built-in data types used as parameters or return values in the component, then generates the corresponding XML Schemas, the serialization classes, and the data type mapping information for theweb-services.xmlfile. Be sure to include the Java class for your non-built-in data type in your CLASSPATH. - An XML Schema file that represents your non-built-in data type by specifying the
schemaFileattribute. TheautotypeAnt task generates the corresponding Java representations, the serialization classes, and the data type mapping information for theweb-services.xmlfile. - A URL to a WSDL file that contains a description of your non-built-in data type by specifying the
wsdlURIattribute. TheautotypeAnt task generates the corresponding Java representations, the serialization classes, and the data type mapping information for theweb-services.xmlfile.
Use the destDir attribute to specify the name of a directory that contains the generated components. The generated XML Schema and data type mapping information are generated in a file called types.xml. You can use this file to manually update an existing web-services.xml file with non-built-in data type mapping information, or use it in conjunction with the typeMappingFile attribute of the servicegen or clientgen Ant tasks, or the typesInfo attribute of the source2wsdd Ant task.
Warning: The serialization class and Java and XML representations generated by the autotype, servicegen, and clientgen Ant tasks cannot be round-tripped. For more information, see Non-Roundtripping of Generated Data Type Components.
Note: The fully qualified name for the autotype Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.javaschema.JavaSchema.
Example
The following example shows how to create non-built-in data type components from a Java class:
<autotype javatypes="mypackage.MyType"
targetNamespace="http://www.foobar.com/autotyper"
packageName="a.package.name"
destDir="output" />
The following example is similar to the preceding one, except it creates non-built-in data type components for an array of mypackage.MyType Java data types:
<autotype javaTypes="[Lmypackage.MyType;"
targetNamespace="http://www.foobar.com/autotyper"
packageName="a.package.name"
destDir="output" />
Note: The [Lclassname; syntax follows the Java class naming conventions as outlined in the java.lang.Class.getName() method documentation.
The following example shows how to use the autotype Ant task against a WSDL file; it also shows how to specify that the Ant task keep the generated Java files for the serialization class:
<autotype wsdl="wsdls/myWSDL"
targetNamespace="http://www.foobar.com/autotyper"
packageName="a.package.name"
destDir="output"
keepGenerated="True" />
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the autotype Ant task.
|
Full pathname of the directory that will contain the generated components. The generated XML Schema and data type mapping information are generated in a file called |
|||
|
Specifies whether the The encoding is particularly important when generating complex XML data types, such as arrays. SOAP arrays are structurally different from non-SOAP arrays, so it is important to always use the correct one for the correct situation. If you are creating a document-oriented Web Service, you must specify that Use this attribute only when generating an XML Schema from an existing Java data type. Valid values for this attribute are |
Use this attribute only in conjunction with either the |
||
|
Comma-separated list of Java class names that implement the Web Service. For Java class-implemented Web Services, this attribute points to the Java class. For stateless session EJB-implemented Web Services, this attribute points to the remote interface of the EJB. The Java classes (of both the implementation of the component and the implementation of your non-built-in data type) must be compiled and in your CLASSPATH.
The |
You must specify one, and only one, of the following attributes: |
||
|
Comma-separated list of Java class names that represent your non-built-in data types. The Java classes must be compiled and in your CLASSPATH.
Note: Use the syntax |
You must specify one, and only one, of the following attributes: |
||
|
Specifies whether the Valid values for this attribute are |
|||
|
Specifies whether the components generated by this Ant task should be overwritten if they already exist. If you specify If you specify Valid values for this attribute is |
|||
|
Base package name of the generated Java classes for any non-built-in data types used as a return value or parameter in a Web Service. This means that each generated Java class will be part of the same package name, although the If you do not specify this attribute, the Note: BEA recommends you not use this attribute, but rather, specify the full package name using the |
If you specify this attribute, you cannot also specify |
||
|
Full package name of the generated Java classes for any non-built-in data types used as a return value or parameter in a Web Service. If you do not specify this attribute, the Note: Although not required, BEA recommends you specify this attribute in most cases.
|
If you specify this attribute, you cannot also specify |
||
|
Name of a file that contains the XML Schema representation of your non-built-in data types. |
You must specify one, and only one, of the following attributes: |
||
|
File that contains data type mapping information for non-built-in data types for which have already generated needed components, as well as the XML Schema representation of your non-built-in data types. The format of the information is the same as the data type mapping information in the The |
|||
|
Full path name or URI of the WSDL that contains the XML Schema description of your non-built-in data type. |
You must specify one, and only one, of the following attributes: |
Equivalent Command-Line Utility
The equivalent command-line utility of the autotype Ant task is called weblogic.webservice.autotype. The description of the flags of the utility is the same as the description of the Ant task attributes, described in the preceding section.
The weblogic.webservice.autotype utility supports the following flags (see the equivalent attribute for a description of the flag):
-help (Prints the standard usage message)- -version (Prints version information)
- -verbose (Enables verbose output)
- -destDir
dir - -schemaFile
pathname - -wsdl
uri - -javaTypes
classname - -javaComponents
classname - -packageName
name - -packageBase
name - -encoding
name - -generatePublicFields
true_or_false - -typeMappingFile
pathname - -keepGenerated
true_or_false
clientgen
The clientgen Ant task generates a Web Service-specific client JAR file that client applications can use to invoke both WebLogic and non-WebLogic Web Services. Typically, you use the clientgen Ant task to generate a client JAR file from an existing WSDL file; you can also use it with an EAR file that contains the implementation of a WebLogic Web Service.
The contents of the client JAR file includes:
- Client interface and stub files (conforming to the JAX-RPC specification) used to invoke a Web Service in static mode.
- Optional serialization class for converting non-built-in data between its XML and Java representation.
- Optional client-side copy of the Web Service WSDL file
You can use the clientgen Ant task to generate a client JAR file from the WSDL file of an existing Web Service (not necessarily running on WebLogic Server) or from an EAR file that contains a Weblogic Web Service implementation.
The WebLogic Server distribution includes a client runtime JAR file that contains the client side classes needed to support the WebLogic Web Services runtime component. For more information, see Generating the Client JAR File by Running the clientgen Ant Task.
Warning: The clientgen Ant task does not support solicit-response or notification WSDL operations. This means that if you attempt to create a client JAR file from a WSDL file that contains these types of operations, the Ant task ignores the operations.
Warning: The serialization class and Java and XML representations generated by the autotype, servicegen, and clientgen Ant tasks cannot be round-tripped. For more information, see Non-Roundtripping of Generated Data Type Components.
Note: The fully qualified name of the clientgen Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.clientgen.ClientGenTask.
Example
<clientgen wsdl="http://example.com/myapp/myservice.wsdl"
packageName="myapp.myservice.client"
clientJar="myapps/myService_client.jar"
/>
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the clientgen Ant task.
|
Specifies whether the |
|||
|
Name of a JAR file or exploded directory into which the To create or update a JAR file, use a If you specify a JAR file or directory that does not exist, the |
|||
|
Name of an EAR file or exploded directory that contains the WebLogic Web Service implementation for which a client JAR file should be generated. Note: If the
|
|||
|
Specifies that the
Valid values for this attribute are |
|||
|
Specifies whether the clientgen Ant task, when generating the Java representation of any non-built-in data types used by the Web Service, should use public fields for the JavaBean attributes rather than getter and setter methods. |
|||
|
Specifies whether the |
|||
|
Specifies whether the Valid values for this attribute are |
|||
|
Specifies whether the components generated by this Ant task should be overwritten if they already exist. If you specify If you specify Valid values for this attribute is |
|||
|
Package name into which the generated JAX-RPC client interfaces and stub files should be packaged. |
|||
|
When set to |
|||
|
Web Service name for which a corresponding client JAR file should be generated. If you specify the If you do not specify the |
|||
|
File that contains data type mapping information, used by the If you specified the |
|||
|
Specifies the base package name of the generated Java class for any non-built-in data types used as a return value or parameter in a Web Service. This means that each generated Java class will be part of the same package name, although the If you specify this attribute, you cannot also specify If you do not specify this attribute and the XML Schema in the WSDL file defines a target namespace, then the Note: Rather than using this attribute, BEA recommends that you specify the full package name with the |
Required only if you specified the |
||
|
Specifies the full package name of the generated Java class for any non-built-in data types used as a return value or parameter in a Web Service. If you specify this attribute, you cannot also specify If you do not specify this attribute and the XML Schema in the WSDL file defines a target namespace, then the Note: Although not required, BEA recommends you specify this attribute. |
Required only if you specified the |
||
|
When set to true, specifies that the method names in the generated stubs have a lower-case first character. Otherwise, all method names will the same as the operation names in the WSDL file. |
|||
|
Specifies where the If this value is set to true, then operations take the name specified by the |
|||
|
Specifies where the Valid values are For the list of non-built-in data types for which |
|||
|
You can specify this attribute only in combination with the |
|||
|
Full path name or URL of the WSDL that describes a Web Service (either WebLogic or non-WebLogic) for which a client JAR file should be generated. The generated stub factory classes in the client JAR file use the value of this attribute in the default constructor. |
Equivalent Command-Line Utility
The equivalent command-line utility of the clientgen Ant task is called weblogic.webservice.clientgen. The description of the flags of the utility is the same as the description of the Ant task attributes, described in the preceding section.
The weblogic.webservice.clientgen utility supports the following flags (see the equivalent attribute for a description of the flag):
-help (Prints the standard usage message)- -version (Prints version information)
- -verbose (Enables verbose output)
-wsdluri- -
earpathname - -
clientJarpathname -packageNamename-warNamename-serviceNamename-typeMappingFilepathname-useServerTypestrue_or_false- -typePackageName
name - -typePackageBase
name - -useLowerCaseMethodNames
true_or_false - -usePortNameAsMethodName
true_or_false - -generateAsyncMethods
true_or_false - -generatePublicFields
true_or_false - -saveWSDL
true_or_false - -autotype
true_or_false - -overwrite
true_or_false - -keepGenerated
true_or_false
servicegen
The servicegen Ant task takes as input an EJB JAR file or list of Java classes, and creates all the needed Web Service components and packages them into a deployable EAR file.
In particular, the servicegen Ant task:
- Introspects the EJBs and Java classes, looking for public methods to convert into Web Service operations.
- Creates a
web-services.xmldeployment descriptor file, based on the attributes of theservicegenAnt task and introspected information. - Optionally creates the serialization class that converts the non-built-in data between its XML and Java representations. It also creates XML Schema representations of the Java objects and updates the
web-services.xmlfile accordingly. This feature is referred to as autotyping. - Packages all the Web Service components into a Web application WAR file, then packages the WAR and EJB JAR files into a deployable EAR file.
You can also configure default configuration for reliable SOAP messaging, handler chains, and data security (digital signatures and encryption) for a Web Service using servicegen.
While you are developing your Web Service, BEA recommends that you create an exploded directory, rather than an EAR file, by specifying a value for the destEar attribute of servicegen that does not have an .ear suffix. You can later package the exploded directory into an EAR file when you are ready to deploy the Web Service.
Warning: The serialization class and Java and XML representations generated by the autotype, servicegen, and clientgen Ant tasks cannot be round-tripped. For more information, see Non-Roundtripping of Generated Data Type Components.
Note: The fully qualified name of the servicegen Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.servicegen.ServiceGenTask.
Example
<servicegen
destEar="ears/myWebService.ear"
warName="myWAR.war"
contextURI="web_services" >
<service
ejbJar="jars/myEJB.jar"
targetNamespace="http://www.bea.com/examples/Trader"
serviceName="TraderService"
serviceURI="/TraderService"
generateTypes="True"
expandMethods="True" >
</service>
</servicegen>
Attributes and Child Elements
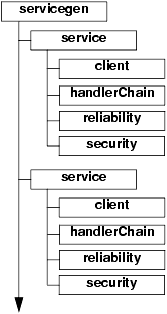
The servicegen Ant task has four attributes and one child element (<service>) for each Web Service you want to define in a single EAR file. You must specify at least one <service> element.
The <service> element has four optional elements: <client>, <reliability>, <handlerChain>, and <security>.
The following graphic describes the hierarchy of the servicegen Ant task.
Figure B-1 Element Hierarchy of servicegen Ant Task
servicegen
The servicegen Ant task is the main task for automatically generating and assembling all the parts of a Web Service and packaging it into a deployable EAR file.
The following table describes the attributes of the servicegen Ant task.
service
The <service> element describes a single Web Service implemented with either a stateless session EJB or a Java class.
The following table describes the attributes of the <service> element of the servicegen Ant task. Include one <service> element for every Web Service you want to package in a single EAR file.
|
JAR file or exploded directory that contains the EJBs that implement the back-end component of a Web Service operation. The |
You must specify either the |
||
|
Comma-separated list of EJB names for which non-built-in data type components should not be generated. If you specify this attribute, the The EJB names correspond to the |
|||
|
Specifies whether the |
|||
|
Specifies whether the Valid values are For the list of non-built-in data types for which servicegen can generate data type components, see Non-Built-In Data Types Supported by servicegen and autotype Ant Tasks. |
|||
|
Specifies that the Web Service ignore the Note: Be careful using this attribute. If you set the value of this attribute to |
|||
|
Comma-separated list of EJB names for which non-built-in data type components should be generated. If you specify this attribute, the The EJB names correspond to the |
|||
|
Comma-separated list of Java class names that implement the Web Service operation. The Java classes must be compiled and in your CLASSPATH.
Note: Do not include the The |
You must specify either the |
||
|
Specifies whether the client application that invokes this JMS-implemented Web Service sends or receives messages to or from the JMS destination. Valid values are Specify |
|||
|
JNDI name of the |
|||
|
Type of JMS destination. Currently only one type is supported: Queue. |
|||
|
Data type of the single parameter to the send or receive operation. Default value is If you use this attribute to specify a non-built-in data type, and set the |
|||
|
Name of the operation in the generated WSDL file. Default value is either |
|||
|
Name of the Web Service which will be published in the WSDL. Note: If you specify more than one |
|||
|
Web Service URI portion of the URL used by client applications to invoke the Web Service. Note: Be sure to specify the leading "/", such as The full URL to invoke the Web Service will be: |
|||
|
Specifies whether the RPC-oriented WebLogic Web Service operations use SOAP encoding. Document-oriented WebLogic Web Service operations use literal encoding. You can use the following two values to generate document-oriented Web Service operations: If you specify If you specify Valid values for this attribute are Note: Because the |
|||
|
File that contains additional XML data type mapping information and XML Schema representation of non-built-in data types. The format of the information is the same as the data type mapping information in a Use this attribute if you want to include extra XML data type information in the |
|||
|
Specifies whether to use SOAP 1.2 as the message format protocol. By default, WebLogic Web Services use SOAP 1.1. If you specify Valid values for this attribute are |
client
The optional <client> element describes how to create the client JAR file that client applications use to invoke the Web Service. Specify this element only if you want the servicegen Ant task to create a client JAR file.
Note: You do not have to create the client JAR file when you assemble your Web Service. You can later use the clientgen Ant task to generate the JAR file.
The following table describes the attributes of the <client> element.
|
Name of the generated client JAR file. When the Default name is Note: If you want a link to the client JAR file to automatically appear in the Web Service Home Page, you should not change its default name. |
|||
|
Package name into which the generated client interfaces and stub files are packaged. |
|||
|
When set to |
|||
|
Specifies where the Valid values are For the list of non-built-in data types for which servicegen can generate data type components, see Non-Built-In Data Types Supported by servicegen and autotype Ant Tasks. |
handlerChain
The optional <handlerChain> child element of the <service> element adds a handler chain component to the Web Service, and specifies that the handler chain is associated with every operation of the Web Service. A handler chain consists of one or more handlers. For more information on handler chains, see Creating SOAP Message Handlers to Intercept the SOAP Message.
Note: Setting this element in servicegen associates the handler chain with every operation in your Web Service. If you want only some operations to be associated with this handler chain, then you must edit the generated web-services.xml file and remove the handler-chain attribute of the corresponding <operation> element. For details of these elements and attributes, see WebLogic Web Service Deployment Descriptor Elements.
The following table describes the attributes of the <handlerChain> element.
|
Comma separated fully qualified list of Java class names that implement the handlers in the handler chain. You must include at least one class name. Note: If the Java class that implements a handler expects initialization parameters, you must edit the generated |
|||
|
The name of the handler chain. Default value is |
reliability
The optional <reliability> child element of the <service> element specifies that every operation of the Web Service can be invoked asynchronously using reliable SOAP messaging. For more information on reliable SOAP messaging, see Using Reliable SOAP Messaging.
Note: Setting this element in servicegen enables reliable SOAP messaging for every operation in your Web Service. If you want only some operations to have reliable SOAP messaging, then you must edit the generated web-services.xml file and remove the <reliable-delivery> child element of the corresponding <operation> element. For details of these elements, see WebLogic Web Service Deployment Descriptor Elements.
The following table describes the attributes of the <reliability> element.
security
The optional <security> child element of the <service> element adds default data security, such as digital signatures and encryption, to your Web Service. For more information about data security, see Configuring Security..
Note: You can encrypt or digitally sign only the entire SOAP message body when you configure data security using the servicegen Ant task. If you want to specify particular elements of the SOAP message that are to be digitally signed or encrypted, see Configuring Message-Level Security: Main Steps. This section also describes the general security configuration tasks you must perform with the Administration Console before you can successfully invoke your secure Web Service.
The following table describes the attributes of the <security> element.
source2wsdd
The source2wsdd Ant task generates a web-services.xml deployment descriptor file from the Java source file for a stateless session EJB- or Java class-implemented WebLogic Web Service. You can also specify that the WSDL that describes the Web Service be generated.
The source2wsdd Ant task sets the name of the Web Service to the class name of the Java class or EJB that implements the Web Service. This name will also be the public name of the Web Service published in its WSDL.
The source2wsdd Ant task does not generate data type mapping information for any non-built-in data types used as parameters or return values of the methods of your EJB or Java class If your EJB or Java class uses non-built-in data types, you must first run the autotype Ant task to generate the needed components, then point the typesInfo attribute of the source2wsdd Ant task to the types.xml file generated by the autotype Ant task.
If your EJB or Java class refers to other Java class files, be sure to set the sourcePath attribute of source2wsdd Ant task to the directory that contains them.
Note: The fully qualified name of the source2wsdd Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.autotype.JavaSource2DD.
Example
The following example shows how to generate a web-services.xml file, generated into the ddfiles directory, for a Java class-implemented Web Service. The information about the non-built-in data types is contained in the autotype/types.xml file. The Web Service portion of the URI used to invoke the service is /MyService.
<source2wsdd
javaSource="source/MyService.java"
typesInfo="autotype/types.xml"
ddFile="ddfiles/web-services.xml"
serviceURI="/MyService"
/>
The following example shows how to generate both a web-services.xml file and the WSDL file (called wsdFiles/Temperature.wsdl) that describes a stateless session EJB-implemented Web Service. Because the ejbLink attribute is specified, the javaSource attribute must point to the EJB source file. The source2wsdd Ant task uses the value of the ejblink attribute as the value of the <ejb-link> child element of the <stateless-ejb> element in the generated web-services.xml file.
<source2wsdd
javaSource="source/TemperatureService.java"
ejbLink="TemperatureService.jar#TemperatureServiceEJB"
ddFile="ddfiles/web-services.xml"
typesInfo="autotype/types.xml"
serviceURI="/TemperatureService"
wsdlFile="wsdlFiles/Temperature.wsdl"
/>
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the source2wsdd Ant task.
|
Full pathname of the Web Services deployment descriptor file ( |
|||
|
Specifies the value of the Note: The The format of this attribute is as follows:
|
If you specify this attribute, the required |
||
|
Full pathname of the XML file that contains information about the SOAP message handlers and handler chains defined for the Web Service. You must create this file manually. The root element of the file is If you do not specify this attribute, the generated |
|||
|
Specifies that the Web Service ignore the Note: Be careful using this attribute. If you set the value of this attribute to |
|||
|
Name of the stateless session EJB or Java source file that implements your Web Service component. |
|||
|
Specifies whether the Valid values for this attribute are |
|||
|
Specifies whether the components generated by this Ant task should be overwritten if they already exist. If you specify If you specify Valid values for this attribute is |
|||
|
Web Service URI portion of the URL used by client applications to invoke the Web Service. Note: Be sure to specify the leading "/", such as The value of this attribute becomes the |
|||
|
Full pathname of the directory that contains any additional classes referred to by the Java source file specified with the javaSource attribute. |
|||
|
Name of the file that contains the XML Schema representation and data type mapping information for any non-built-in data types used as parameters or return value of the Web Service. The format of the data type mapping information is the same as that in the Typically you have already run the |
|||
|
Specifies that, in addition to the Set this value to the name of the output file that will contain the generated WSDL. |
wsdl2Service
The wsdl2Service Ant task takes as input an existing WSDL file and generates:
- the Java interface that represents the implementation of your Web Service based on the WSDL file
- the Java exception class for user-defined exceptions specified in the WSDL file
- an empty Java implementation class
- the
web-services.xmlfile that describes the Web Service
The generated Java interface file describes the template for the full Java class-implemented WebLogic Web Service. The template includes full method signatures that correspond to the operations in the WSDL file. You must then write a Java class that implements this interface so that the methods function as you want, following the guidelines in Implementing a Web Service By Writing a Java Class. You can generate a skeleton of the implementation class by specifying the generateImpl="True" attribute; add the business logic Java code to this class to complete the implementation.
The wsdl2Service Ant task generates a Java interface for only one Web Service in a WSDL file (specified by the <service> element.) Use the serviceName attribute to specify a particular service; if you do not specify this attribute, the wsdl2Service Ant task generates a Java interface for the first <service> element in the WSDL.
The wsdl2Service Ant task does not generate data type mapping information for any non-built-in data types used as parameters or return values of the operations in the WSDL file. If the WSDL uses non-built-in data types, you must first run the autotype Ant task to generate the data type mapping information, then point the typeMappingFile attribute of the wsdl2Service Ant task to the types.xml file generated by the autotype Ant task.
Warning: The wsdl2Service Ant task, when generating the web-services.xml file for your Web Service, assumes you use the following convention when naming the Java class that implements the generated Java interface:
Warning: packageName.serviceNameImpl
Warning: where packageName and serviceName are the values of the similarly-named attributes of the wsdl2Service Ant task. The Ant task puts this information in the class-name attribute of the <java-class> element of the web-services.xml file.
Warning: If you name your Java implementation class differently, you must manually update the generated web-services.xml file accordingly.
Note: The fully qualified name of the wsdl2Service Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.wsdl2service.WSDL2Service.
Example
<wsdl2service
wsdl="wsdls/myService.wsdl"
destDir="myService/implementation"
typeMappingFile="autotype/types.xml"
packageName="example.ws2j.service"
/>
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the wsdl2Service Ant task.
wsdlgen
The wsdlgen Ant task generates a WSDL file from the EAR and WAR files that implement your Web Service. The EAR file contains the EJBs that implement your Web Service and the WAR file contains the web-services.xml deployment descriptor file.
The fully qualified name of the wsdlgen Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.wsdlgen.WSDLGen.
Example
<wsdlgen ear="myapps/myapp.ear"
warName="myapps/myWAR.war"
serviceName="myService"
wsdlFile="wsdls/myService.WSDL"
/>
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the wsdlgen Ant task.
Equivalent Command-Line Utility
The equivalent command-line utility of the wsdlgen Ant task is called weblogic.webservice.wsdlgen. The description of the flags of the utility is the same as the description of the Ant task attributes, described in the preceding section.
The weblogic.webservice.wsdlgen utility supports the following flags (see the equivalent attribute for a description of the flag):
-help (Prints the standard usage message)- -version (Prints version information)
- -verbose (Enables verbose output)
- -warName
name - -serviceName
name - -defaultEndpoint
address
wspackage
Use the wspackage Ant task to:
- package the various components of a WebLogic Web Service into a new deployable EAR file.
- add extra components to an already existing EAR file.
It is assumed that you have already generated the components, which can include:
- The
web-services.xmldeployment descriptor file - The EJB JAR file that contains the EJBs the implement a Web Service
- The Java class file that implements a Web Service
- A client JAR file that users can download and use to invoke the Web Service
- Implementations of SOAP handlers
- Components for any non-built-in data types used as parameters and return values for the Web Service. These components include the XML and Java representations of the data type and the serialization class that converts the data between its two representations.
Typically you use other Ant tasks, such as clientgen, autotype, source2wsdd, and wsdl2Service, to generate the preceding components.
When you use the wspackage Ant task to add additional components to an existing EAR file, be sure you specify the overwrite="false" attribute to ensure that none of the existing components are overwritten. Use the output attribute to specify the full pathname of the existing EAR file.
Note: The fully qualified name of the wspackage Ant task is weblogic.ant.taskdefs.webservices.wspackage.WSPackage.
Example
The following example shows how to use the wspackage Ant task to package WebLogic Web Service components into a new EAR file:
<wspackage
output="ears/myWebService.ear"
contextURI="web_services"
codecDir="autotype"
webAppClasses="example.ws2j.service.SimpleTest"
ddFile="ddfiles/web-services.xml"
/>
The following example shows how to add additional components to an existing EAR file called ears/myWebService.ear.
<wspackage
output="ears/myWebService.ear"
overwrite="false"
filesToEar="myEJB2.jar"
/>
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of the wspackage Ant task.