









|
The following sections describe how to install and configure the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In:
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In allows requests to be proxied from an Apache HTTP Server to WebLogic Server. The plug-in enhances an Apache installation by allowing WebLogic Server to handle requests that require the dynamic functionality of WebLogic Server.
The plug-in is intended for use in an environment where an Apache Server serves static pages, and another part of the document tree (dynamic pages best generated by HTTP Servlets or JavaServer Pages) is delegated to WebLogic Server, which may be operating in a different process, possibly on a different host. To the end user—the browser—the HTTP requests delegated to WebLogic Server still appear to be coming from the same source.
HTTP-tunneling, a technique which allows HTTP requests and responses access through a company’s firewall, can also operate through the plug-in, providing non-browser clients access to WebLogic Server services.
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In operates as an Apache module within an Apache HTTP Server. An Apache module is loaded by Apache Server at startup, and then certain HTTP requests are delegated to it. Apache modules are similar to HTTP servlets, except that an Apache module is written in code native to the platform.
For information on configurations on which the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In is supported, see http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13196_01/platform/suppconfigs/configs92/92_over/add-ons.html.
Version 2.0 of the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In improves performance by using a reusable pool of connections from the plug-in to WebLogic Server. The plug-in implements HTTP 1.1 keep-alive connections between the plug-in and WebLogic Server by reusing the same connection in the pool for subsequent requests from the same client. If the connection is inactive for more than 30 seconds, (or a user-defined amount of time) the connection is closed and returned to the pool. You can disable this feature if desired. For more information, see “KeepAliveEnabled”.
The plug-in proxies requests to WebLogic Server based on a configuration that you specify. You can proxy requests based on the URL of the request (or a portion of the URL). This is called proxying by path. You can also proxy requests based on the MIME type of the requested file. Or you can use a combination of the two methods. If a request matches both criteria, the request is proxied by path. You can also specify additional parameters for each type of request that define additional behavior of the plug-in. For more information, see Configuring the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In.
Although this document refers to Apache 2.0, you can apply the same instructions to use Apache 2.2 with the libraries shown in Table 3-2.
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In is supported on Linux, Solaris, Windows, and HPUX11 platforms. For information on support for specific versions of Apache, see http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13196_01/platform/suppconfigs/configs92/92_over/add-ons.html.
You can install the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In as an Apache module in your Apache HTTP Server installation and link it as a Dynamic Shared Object (DSO).
A DSO is compiled as a library that is dynamically loaded by the server at run time, and can be installed without recompiling Apache.
The Apache plug-in is distributed as a shared object (.so) for Solaris, Linux, Windows, and HPUX11 platforms. BEA WebLogic supplies versions of shared object files that vary according to platform, whether or not SSL is to be used between the client and Apache, and the SSL encryption strength (regular or 128 bit—128 bit versions are only installed if you install the 128 bit version of WebLogic Server).
Table 3-1 shows the directories of your WebLogic Server installation that contain shared object files for various platforms (where WL_HOME is the top-level installation directory for the WebLogic platform).
Table 3-2 identifies the WebLogic Server Apache Plug-In modules for different versions of Apache HTTP Server and different encryption strengths.
export EXTRA_LDFLAGS="-lstd -lstream -lCsup -lm -lcl -ldld -lpthread" |
Choose the appropriate version of the plug-in shared object from the following table:
To install the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In as a dynamic shared object:
mod_so.c module is enabled.
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In will be installed in your Apache HTTP Server installation as a Dynamic Shared Object (DSO). DSO support in Apache is based on a module mod_so.c, which must be enabled before mod_wl_20.so is loaded. If you installed Apache HTTP Server using the script supplied by Apache, mod_so.c is already enabled. Verify that mod_so.c is enabled by executing the following command:
APACHE_HOME\bin\apache -l
(Where APACHE_HOME is the directory containing your Apache HTTP Server installation.)
This command lists all enabled modules. If mod_so.c is not listed, you must rebuild your Apache HTTP Server, making sure that the following options are configured:
...
--enable-module=so
--enable-rule=SHARED_CORE
...
See Apache 2.0 Shared Object (DSO) Support at http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.0/dso.html.
mod_wl_20.so file to the APACHE_HOME\modules directory and adding the following line to your APACHE_HOME/conf/httpd.conf file manually:LoadModule weblogic_module modules/mod_wl_20.so
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In recognizes the parameters listed in General Parameters for Web Server Plug-Ins. To modify the behavior of your Apache HTTP Server Plug-In, define these parameters:
APACHE_HOME\conf\httpd.conf file with the following command: APACHE_HOME\bin\apachectl -t
The output of this command reports any errors in your httpd.conf file or returns:
Syntax OK
/weblogic/”, which should bring up the default WebLogic Server HTML page, welcome file, or default servlet, as defined for the default Web Application on WebLogic Server. For example: http://myApacheserver.com/weblogic/
After installing the plug-in in the Apache HTTP Server, configure the WebLogic Server Apache Plug-In and configure the server to use the plug-in. This section explains how to edit the Apache httpd.conf file to instruct the Apache server to load the WebLogic Server library for the plug-in as an Apache module, and to specify the application requests that should be handled by the module.
Edit the httpd.conf file in your Apache HTTP server installation to configure the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In.
This section explains how to locate and edit the httpd.conf file, to configure the server to use the WebLogic Server Apache Plug-In, to proxy requests by path or by MIME type, to enable HTTP tunneling, and to use other WebLogic Server plug-in parameters.
httpd.conf file.
The file is located at APACHE_HOME\conf\httpd.conf (where APACHE_HOME is the root directory of your Apache HTTP server installation). See a sample httpd.conf file at Setting Up Perimeter Authentication.
httpd.conf file:LoadModule weblogic_module modules\mod_wl_20.so
IfModule block that defines one of the following:For a non-clustered WebLogic Server:
The WebLogicHost and WebLogicPort parameters.
For a cluster of WebLogic Servers:
The WebLogicCluster parameter.
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicHost myweblogic.server.com
WebLogicPort 7001
</IfModule>
MatchExpression line to the IfModule block. Note that if both MIME type and proxying by path are enabled, proxying by path takes precedence over proxying by MIME type.
For example, the following IfModule block for a non-clustered WebLogic Server specifies that all files with MIME type .jsp are proxied:
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicHost myweblogic.server.com
WebLogicPort 7001
MatchExpression *.jsp
</IfModule>
You can also use multiple MatchExpressions, for example:
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>WebLogicHost myweblogic.server.com
WebLogicPort 7001MatchExpression *.jsp
MatchExpression *.xyz
</IfModule>
If you are proxying requests by MIME type to a cluster of WebLogic Servers, use the WebLogicCluster parameter instead of the WebLogicHost and WebLogicPort parameters. For example:
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>WebLogicCluster w1s1.com:7001,w1s2.com:7001,w1s3.com:7001MatchExpression *.jsp
MatchExpression *.xyz
</IfModule>
Location block and the SetHandler statement. SetHandler specifies the handler for the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In module. For example the following Location block proxies all requests containing /weblogic in the URL:<Location /weblogic>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /weblogic
</Location>
The PathTrim parameter specifies a string trimmed from the beginning of the URL before the request is passed to the WebLogic Server instance (see General Parameters for Web Server Plug-Ins).
weblogic.jar, add the following Location block to the httpd.conf file:<Location /HTTPClnt>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
wlclient.jar, add the following Location block to the httpd.conf file:<Location /iiop>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In recognizes the parameters listed in General Parameters for Web Server Plug-Ins . To modify the behavior of your Apache HTTP Server Plug-In, define these parameters either:
If you want to keep several separate configuration files, you can define parameters in a separate configuration file called weblogic.conf file, by using the Apache Include directive in an IfModule block in the httpd.conf file:
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
# Config file for WebLogic Server that defines the parameters
Include conf/weblogic.conf
</IfModule>
The syntax of weblogic.conf files is the same as that for the httpd.conf file.
This section describes how to create weblogic.conf files, and includes sample weblogic.conf files.
Be aware of the following when constructing a weblogic.conf file.
weblogic.conf file is, via the Apache Include directive. PARAM_1 value1
PARAM_2 value2
PARAM_3 value3
MatchExpression in an IfModule block and a path specified in a Location block, the behavior specified by the Location block takes precedence.CookieName parameter, you must define it in an IfModule block. <VirtualHost> block, you must include all configuration parameters (MatchExpression, for example) for the virtual host within the <VirtualHost> block (see
Apache Virtual Host documentation).<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicCluster agarwalp02:8005,agarwalp02:8006
Debug ON
WLLogFile c:/tmp/global_proxy.log
WLTempDir "c:/myTemp"
DebugConfigInfo On
KeepAliveEnabled ON
KeepAliveSecs 15
</IfModule>
<Location /jurl>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicCluster agarwalp01:7001
</Location>
<Location /web>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /web
Debug OFF
WLLogFile c:/tmp/web_log.log
</Location>
<Location /foo>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /foo
Debug ERR
WLLogFile c:/tmp/foo_proxy.log
</Location>
MatchExpression statement instead of the <files> block.
The following examples of weblogic.conf files may be used as templates that you can modify to suit your environment and server. Lines beginning with # are comments.
# These parameters are common for all URLs which are
# directed to the current module. If you want to override
# these parameters for each URL, you can set them again in
# the <Location> or <Files> blocks. (Except WebLogicHost,
# WebLogicPort, WebLogicCluster, and CookieName.)
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicCluster w1s1.com:7001,w1s2.com:7001,w1s3.com:7001
ErrorPage http://myerrorpage.mydomain.com
MatchExpression *.jsp
</IfModule>
####################################################
In this example, the MatchExpression parameter syntax for expressing the filename pattern, the WebLogic Server host to which HTTP requests should be forwarded, and various other parameters is as follows:
MatchExpression [filename pattern] [WebLogicHost=host] | [paramName=value]
The first MatchExpression parameter below specifies the filename pattern *.jsp, and then names the single WebLogicHost. The paramName=value combinations following the pipe symbol specify the port at which WebLogic Server is listening for connection requests, and also activate the Debug option. The second MatchExpression specifies the filename pattern *.http and identifies the WebLogicCluster hosts and their ports. The paramName=value combination following the pipe symbol specifies the error page for the cluster.
# These parameters are common for all URLs which are
# directed to the current module. If you want to override
# these parameters for each URL, you can set them again in
# the <Location> or <Files> blocks (Except WebLogicHost,
# WebLogicPort, WebLogicCluster, and CookieName.)
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
MatchExpression *.jsp WebLogicHost=myHost|WebLogicPort=7001|Debug=ON
MatchExpression *.html WebLogicCluster=myHost1:7282,myHost2:7283|ErrorPage=
http://www.xyz.com/error.html
</IfModule>
# These parameters are common for all URLs which are
# directed to the current module. If you want to override
# these parameters for each URL, you can set them again in
# the <Location> or <Files> blocks (Except WebLogicHost,
# WebLogicPort, WebLogicCluster, and CookieName.)
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicHost myweblogic.server.com
WebLogicPort 7001
MatchExpression *.jsp
</IfModule>
# VirtualHost1 = localhost:80
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1:80>
DocumentRoot "C:/test/VirtualHost1"
ServerName localhost:80 <IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
#... WLS parameter ...
WebLogicCluster localhost:7101,localhost:7201
# Example: MatchExpression *.jsp <some additional parameter>
MatchExpression *.jsp PathPrepend=/test2
</IfModule>
</VirtualHost>
# VirtualHost2 = 127.0.0.2:80
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.2:80>
DocumentRoot "C:/test/VirtualHost1"
ServerName 127.0.0.2:80
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
#... WLS parameter ...
WebLogicCluster localhost:7101,localhost:7201
# Example: MatchExpression *.jsp <some additional parameter>
MatchExpression *.jsp PathPrepend=/test2
#... WLS parameter ...
</IfModule>
</VirtualHost> <IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
You must define a unique value for 'ServerName'or some Plug-In parameters will not work as expected.
This section contains a sample httpd.conf file for Apache 2.0. You can use this sample as a template and modify it to suit your environment and server. Lines beginning with # are comments.
Note that Apache HTTP Server is not case sensitive.
####################################################
APACHE-HOME/conf/httpd.conf file
####################################################
LoadModule weblogic_module libexec/mod_wl_20.so
<Location /weblogic>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /weblogic
ErrorPage http://myerrorpage1.mydomain.com
</Location>
<Location /servletimages>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /something
ErrorPage http://myerrorpage1.mydomain.com
</Location>
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
MatchExpression *.jsp
WebLogicCluster w1s1.com:7001,w1s2.com:7001,w1s3.com:7001
ErrorPage http://myerrorpage.mydomain.com
</IfModule>
Use perimeter authentication to secure WebLogic Server applications that are accessed via the Apache Plug-In.
A WebLogic Identity Assertion Provider authenticates tokens from outside systems that access your WebLogic Server application, including users who access your WebLogic Server application through the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In. Create an Identity Assertion Provider that will safely secure your Plug-In as follows:
clientCertProxy to True in the web.xml deployment descriptor file for the Web application (or, if using a cluster, optionally set the Client Cert Proxy Enabled attribute to true for the whole cluster on the Administration Console Cluster-->Configuration-->General tab). The clientCertProxy attribute can be used with a third party proxy server, such as a load balancer or an SSL accelerator, to enable 2-way SSL authentication. For more information about the clientCertProxy attribute, see
context-param in Developing Web Applications, Servlets and JSPs for WebLogic Server.clientCertProxy, be sure to use a connection filter to ensure that WebLogic Server accepts connections only from the machine on which the Apache Plug-In is running. See
Using Network Connection Filters in Programming WebLogic Security. Change the alias name to obtain a different trusted CA file from the keystore.
To look at all of the keystore's trusted CA files, use:
keytool -list -keystore DemoTrust.jks
Press enter if prompted for password.
See Identity Assertion Providers in Developing Security Providers for WebLogic Server.
You can use the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to protect the connection between the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In and WebLogic Server. The SSL protocol provides confidentiality and integrity to the data passed between the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In and WebLogic Server.
The Apache HTTP Server Plug-In does not use the transport protocol (http or https) specified in the HTTP request (usually by the browser) to determine whether or not the SSL protocol is used to protect the connection between the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In and WebLogic Server.
Although two-way SSL can be used between the HTTP client and Apache HTTP server, note that one-way SSL is used between Apache HTTP Server and WebLogic Server.
To use the SSL protocol between Apache HTTP Server Plug-In and WebLogic Server:
WebLogicPort parameter in the httpd.conf file to the WebLogic Server SSL listen port configured in
step 2
.SecureProxy parameter in the httpd.conf file to ON.httpd.conf file that define information about the SSL connection. For a complete list of the SSL parameters that you can configure for the plug-in, see
SSL Parameters for Web Server Plug-Ins
.These known issues arise when you configure the Apache plug-in to use SSL:
* Select the root CA (at the top)
* Detail and then copy this certificate to a file using the Coded "Base
* Save the file, for example, to ýMyWeblogicCAToTrust.cerý (which is also a
<Location> tag. The following configuration is incorrect:
<Location /weblogic>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
WebLogicHost localhost
WebLogicPort 7001
PathTrim /weblogic
</IfModule> The following configuration is the correct setup:
<Location /weblogic>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /weblogic
</Location>Include directive does not work with Apache SSL. You must configure all parameters directly in the httpd.conf file. Do not use the following configuration when using SSL: <IfModule mod_weblogic.c>
MatchExpression *.jsp
Include weblogic.conf
</IfModule>
When the Apache HTTP Server Plug-In attempts to connect to WebLogic Server, the plug-in uses several configuration parameters to determine how long to wait for connections to the WebLogic Server host and, after a connection is established, how long the plug-in waits for a response. If the plug-in cannot connect or does not receive a response, the plug-in attempts to connect and send the request to other WebLogic Server instances in the cluster. If the connection fails or there is no response from any WebLogic Server in the cluster, an error message is sent.
Figure 3-1 demonstrates how the plug-in handles failover.
Failure of the WebLogic Server host to respond to a connection request could indicate the following problems:
Failure of all WebLogic Server instances to respond could indicate the following problems:
Under load, an Apache plug-in may receive CONNECTION_REFUSED errors from a back-end WebLogic Server instance. Follow these tuning tips to reduce CONNECTION_REFUSED errors:
AcceptBackLog setting in the configuration of your WebLogic Server domain.KeepAlive directive in the httpd.conf file to On. For example: # KeepAlive: Whether or not to allow persistent connections (more than
# one request per connection). Set to "Off" to deactivate.
#
KeepAlive On
See Apache HTTP Server 2.0 documentation at http://httpd.apache.org/docs-project/.
TcpTimedWaitDelay on the proxy and WebLogic Server servers to a lower value. Set the TIME_WAIT interval in Windows NT by editing the registry key under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\TcpTimedWaitDelay
If this key does not exist you can create it as a DWORD value. The numeric value is the number of seconds to wait and may be set to any value between 30 and 240. If not set, Windows NT defaults to 240 seconds for TIME_WAIT.
TcpTimedWaitDelay by editing the registry key under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
tcp_time_wait_interval to one second (for both the WebLogic Server machine and the Apache machine, if possible):$ndd /dev/tcp
param name to set - tcp_time_wait_interval
value=1000
limit (.csh) or ulimit (.sh) directives, you can make a script to increase the limit. For example:#!/bin/sh
ulimit -S -n 100
exec httpd
If you are running only a single WebLogic Server instance the plug-in only attempts to connect to the server defined with the WebLogicHost parameter. If the attempt fails, an HTTP 503 error message is returned. The plug-in continues trying to connect to that same WebLogic Server instance until ConnectTimeoutSecs is exceeded.
When you use the WebLogicCluster parameter in your httpd.conf or weblogic.conf file to specify a list of WebLogic Servers, the plug-in uses that list as a starting point for load balancing among the members of the cluster. After the first request is routed to one of these servers, a dynamic server list is returned containing an updated list of servers in the cluster. The updated list adds any new servers in the cluster and deletes any that are no longer part of the cluster or that have failed to respond to requests. This list is updated automatically with the HTTP response when a change in the cluster occurs.
When a request contains session information stored in a cookie or in the POST data, or encoded in a URL, the session ID contains a reference to the specific server instance in which the session was originally established (called the primary server) and a reference to an additional server where the original session is replicated (called the secondary server). A request containing a cookie attempts to connect to the primary server. If that attempt fails, the request is routed to the secondary server. If both the primary and secondary servers fail, the session is lost and the plug-in attempts to make a fresh connection to another server in the dynamic cluster list. See Figure 3-1 Connection Failover.
| Note: | If the POST data is larger than 64K, the plug-in will not parse the POST data to obtain the session ID. Therefore, if you store the session ID in the POST data, the plug-in cannot route the request to the correct primary or secondary server, resulting in possible loss of session data. |
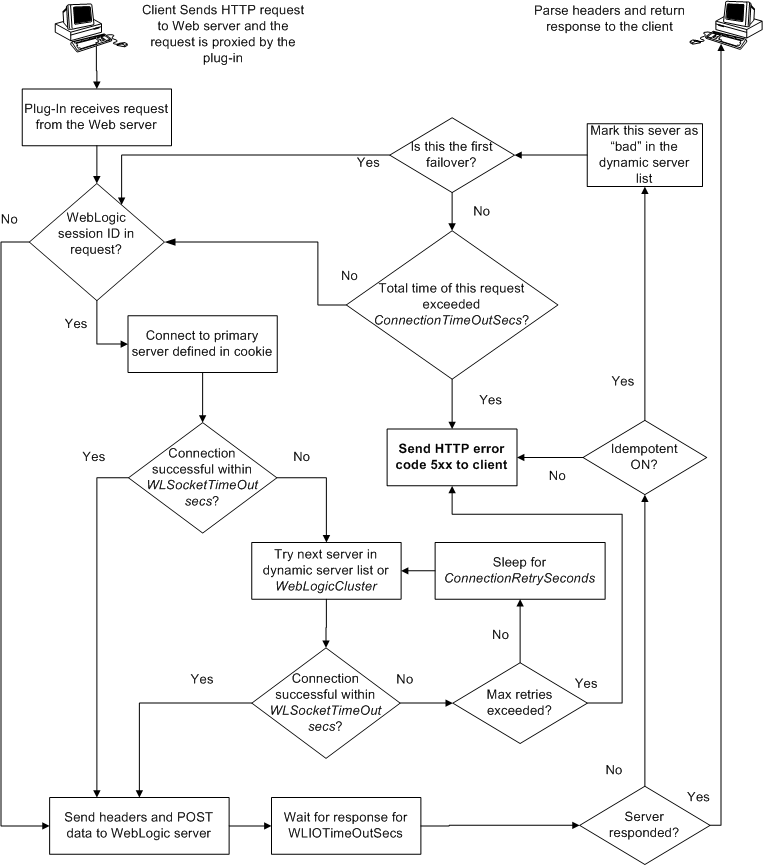
In the preceding figure, the Maximum number of retries allowed is equal to ConnectTimeoutSecs ÷ ConnectRetrySecs.


|