 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Overview
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Overview
This chapter discusses:
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications overview.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications business processes.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales application integrations.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales application implementation.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Overview
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Overview
You use the CRM Sales applications to successfully manage the organization's sales strategies, sales force, and sales opportunities. CRM Sales applications can be used to automate, standardize, maintain, and analyze sales information. For example, you can:
Create qualification scripts that the sales force can use to determine whether a sales lead or opportunity is worth pursuing.
Create sales methodologies, which the sales force can use to standardize and organize the activities associated with the sale of specific goods or services.
Track and maintain sales leads.
Track and maintain sales opportunities, customers and contacts.
Create sales quotes and sales orders directly from a sales opportunity.
Review and analyze the sales pipeline for many entities, such as employees, territories, or customers.
Create and analyze sales forecasts, which can provide the organization with the information it needs to determine whether sales strategies are successful.
Track and maintain information about competitors.
Provide sales information to the manufacturing department to assist in demand planning.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Business Process
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Applications Business Process
This process flow illustrates the Lead to Cash business processes, which is supported by JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications:
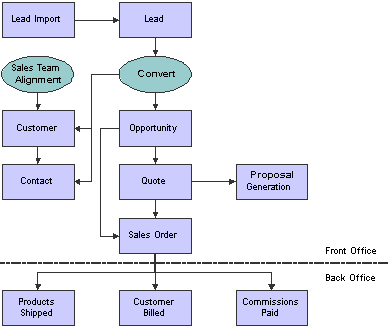
Lead to Cash Process Flow
We discuss these business processes in the business process chapters in this implementation guide.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Application Integrations
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Application Integrations
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications works with other JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications to ensure that all information is fully integrated. JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications integrate with these JD Edwards EnterpriseOne products from Oracle:
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Foundation
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Supply Chain Management
We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters of this implementation guide.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications integrate with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable to enable users to perform credit checks on sales opportunities. This enables sales representatives to determine, before the sale is finalized, whether the prospective customer has sufficient credit to purchase the goods and services in which they are interested.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications integrate with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book in many areas, including:
Employees
Partners
Contacts
Customers
Calendars
Activities
Action Plans
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Foundation
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Foundation applications provide the basis for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Force Automation system. CRM Constants are used to determine how the system processes sales information. You enter employees, customers, contacts, and partners using JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Foundation applications. You also use product catalogues and items during the sales cycle. You can also use email groups and email merge functionality to keep in close contact with customers, partners, and sales team members. These applications are all part of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Foundation product.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications integrate closely with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management. From the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Force Automation system, you can generate sales quotes and sales orders. Once the sales quotes and orders have been generated, you use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management system to update and process the orders.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Supply Chain Management
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Force Automation system integrates with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Supply Chain Management, enabling manufacturing organizations to utilize the information that is created by sales forecasts when determining the future demand for products. Using the SCBM Outbound Processor program, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Supply Chain Management systems can identify the active sales opportunities, and use that information to forecast product demand.
 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Application Implementation
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales Application Implementation
This section provides an overview of the steps that are required to implement JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications.
In the planning phase of your implementation, take advantage of all JD Edwards EnterpriseOne sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information. A complete list of resources appears in the preface in About This Documentation with information about where to find the most current version of each.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM Sales applications, use the EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant. EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant, a Java-based tool, reduces the time that is required to search for and download ESUs by 75 percent or more and enables you to install multiple ESUs at one time.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.98 Software Update Guide
For information about the Oracle Business Accelerator solution for implementation of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Customer Relationship Management, review the documentation available.
See http://www.peoplesoft.com/corp/en/iou/implement/rapid_start/rapid_start_prtr_notes.jsp

 Global Implementation Steps
Global Implementation Steps
This table lists the suggested global implementation steps for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CRM products:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
1. Set up global User Defined Code (UDC) tables. |
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.98 Foundation Guide |
|
2. Set up companies, fiscal date patterns, and business units. |
|
|
3. Set up next numbers. |
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools 8.98 Foundation Guide |
|
4. (Optional) Set up accounts, and the chart of accounts. |
|
|
5. (Optional) Set up the General Accounting constants. |
|
|
6. (Optional) Set up multicurrency processing, including currency codes and exchange rates. |
|
|
7. (Optional) Set up ledger type rules. |
|
|
8. Set up branch/plant constants. |

 Implementation Steps for CRM Sales Applications
Implementation Steps for CRM Sales Applications
This table lists the implementation steps for CRM Sales applications:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
1. Set up CRM Constants. |
|
|
2. Set up CRM Sales application UDCs |
|
|
3. Set up territories and industry groupings. |
|
|
4. Set up sales methodologies. |
|
|
5. Set up qualification scripts. |