8 Setting Up Quality Management
This chapter contains the following topics:
8.1 Understanding Quality Management Setup
Before you use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Blend Management system from Oracle, you must set up information that directs the system to accommodate specific business requirements. For example, you must set up the quality tests that you will perform on a blend lot as well as the equipment and consumables that you will use during the test. You can also set up the time durations after which test results expire. Additionally, you can group tests into panels and test results into test result names.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Blend Management system integrates with the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Quality Management system. You must activate the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Quality Management system before using the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Blend Management system.
You should set up the functionality for quality testing for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Blend Management system in this order:
-
Test result names.
-
Test conversion.
-
Sample containers.
-
Test definition and result duration.
-
Test equipment.
-
Test consumables.
-
Test panels.
8.1.1 Prerequisite
Activate quality control.
8.1.2 Common Fields Used in This Chapter
- Allowed Maximum
-
Enter the highest value for a passing test result.
- Allowed Minimum
-
Enter the lowest value for a passing test result.
- Conversion ID or Result Conversion ID
-
Enter the conversion table ID to use to convert a test result to a common unit of measure. The common unit of measure is defined in test result names. For example, if you enter a test value in degrees Fahrenheit, the test result name is defined as degrees Celsius. The system stores both the entered and converted test results.
- Display Decimals
-
Enter a value to designate the number of decimals in the amount or quantity fields that appear.
- Numeric
-
Select to indicate that the result value is numeric and right-justified. Clear to indicate that the result value is alphanumeric and left-justified.
Tests that use alphanumeric result values can have user-defined code (UDC) tables set up that contain alpha to numeric translations. The purpose of these tables is to supply result evaluations with a way of determining whether a result is within the range of the minimum and maximum values.
- Preferred Maximum
-
Enter the highest value for the preferred test result. This value must be less than or equal to the value that you enter in the Allowed Maximum field. Use the preferred maximum value to measure quality to a more precise specification than a customer requests.
Processing options for the Certificate of Analysis (R37900) program enable you to print the preferred value on the Certificate of Analysis report. Processing options for the Test Revisions (P3701) program enable you to evaluate samples against the preferred values.
- Preferred Minimum
-
Enter the lowest value for the preferred test result. This value must be greater than or equal to the value that you enter in the Allowed Minimum field. Use the preferred minimum value to measure quality to a more precise specification than a customer requests.
Processing options for the Certificate of Analysis (R37900) program enable you to print the preferred value on the Certificate of Analysis report. Processing options for the Test Revisions (P3701) program enable you to evaluate samples against the preferred values.
- Product Code
-
Enter a UDC (98/SY) that identifies a system. Values include:
01: Address Book.
03B: Accounts Receivable.
04: Accounts Payable.
09: General Accounting.
11: Multicurrency.
- Result UOM (result unit of measure)
-
Enter a UDC (37/UM) to identify the unit of measure for a test result. Examples of units of measure include barrels, boxes, cubic yards, gallons, and hours.
- Target
-
Enter the target or preferable test result within the test results range. The system does not validate against a target value; this field is for informational purposes only.
- Test ID (test identification)
-
Enter the unique identifier for a test that you perform on an item. For example, you can enter COL for color test or CL-2 for a clarity test.
- Test Result Name
-
Enter the name for the test result.
- User Defined Codes
-
Enter a code that identifies the table that contains user-defined codes. The table is also referred to as a UDC type.
8.2 Setting Up Test Result Names
This section provides an overview of test result names setup and discusses how to set up test result names.
8.2.1 Understanding Test Result Names Setup
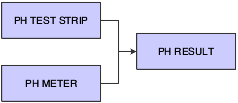
You can set up test result names to group similar tests with different test definitions (a set of test specifications). For example, you might have a pH test with a test definition that requires you to use a test strip and another pH test with a test definition that requires you to use a meter. The test definitions are different, but the result from each test is a pH result.
Test result names can help simplify inquiry, reporting, and blend rules. For example, you might want to review and compare test results for all pH tests. You can use the pH test result name to do this without inquiring on each test individually. You can also add a blend rule to the test result name instead of adding it to each test individually. For example, you add a blend rule to the pH test result name, and the system applies the blend rule to all tests that the pH test result name comprises.
This diagram illustrates how you might group pH tests:
The system stores test result names in the Test Result Name (F37013) table.
8.2.2 Forms Used to Set Up Test Result Names
8.2.3 Setting Up Test Result Names
Access the Test Result Name Revisions form.
Figure 8-2 Test Result Name Revisions form
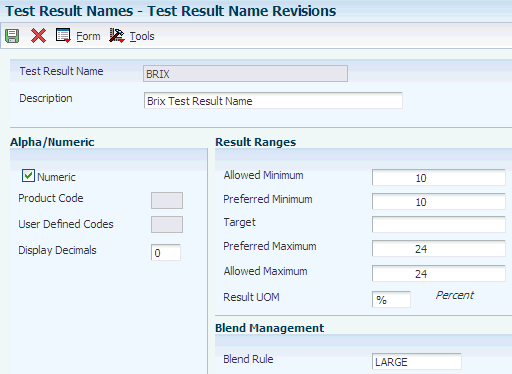
Description of "Figure 8-2 Test Result Name Revisions form"
- Blend Rule
-
Select a UDC to indicate the blending rule for results. Values are:
AVERG: Weighted average of blend lots.
EQUAL: Equal lots else blank.
LARGE: Largest value of blend lots.
LRLOT: Value from largest lot.
NOCAL: No calculation - value is blank.
SMALL: Smallest value of blend lots.
SUM: Sum values for all blend lots.
These values are stored in the QA Result Blend Rules UDC table (31BQB).
Note:
The special handling codes that are assigned to these UDC values determine which blend rules are used in the business functions. You can change the UDC values, but you cannot change the special handling codes.
8.3 Setting Up Test Conversions
This section provides an overview of test conversion setup and discusses how to set up test conversions.
8.3.1 Understanding Test Conversion Setup
You must set up test conversions for those tests for which the test definition unit of measure is different from the test result name unit of measure. For example, you perform a pH test using a test strip, and the test result is yellow. You set up test conversions to convert the value of a color to a numeric value in the system.
The system uses the converted results to display a common measurement for reports and inquiries. The system uses the converted result during blending. The types of conversions include:
-
Single value: the system converts the value that you enter to a corresponding value.
-
Range: the system converts the value that you enter to a corresponding value within a range.
The range must be numeric.
-
Formula: the system uses a formula to convert the value (for example, to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius).
These tables illustrate the conversion:
| Test Definition | Result Name | Conversion ID | Test Result | Converted Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH test strip | pH | Test strip to meter | Yellow | 4.0 |
| pH meter | pH | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Conversion ID | From Value | Converted Value |
|---|---|---|
| Test strip to meter | Yellow | 4.0 |
| Test strip to meter | Green | 7.0 |
The system stores test conversions in the Test Result Conversions (F37014) and Test Result Conversion Tables (F37015) tables.
8.3.2 Forms Used to Set Up Test Conversions
8.3.3 Setting Up Test Conversions
Access the Conversion Table Revisions form.
Figure 8-3 Conversion Table Revisions form
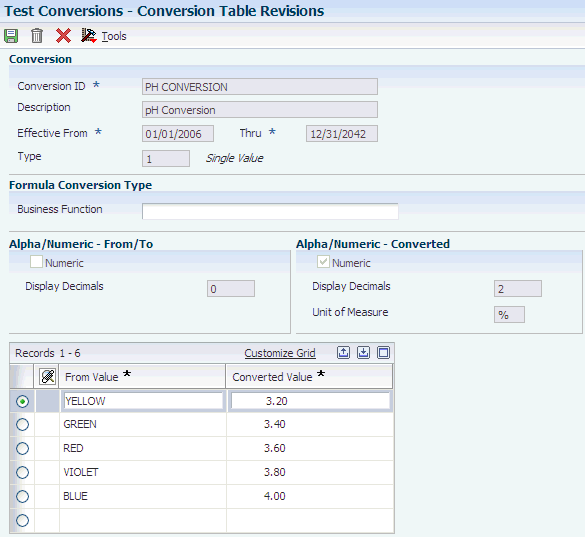
Description of "Figure 8-3 Conversion Table Revisions form"
- Type
-
Enter a UDC (37/CT) that identifies the type of conversion. For example, enter 1 for a single value and 2 for a range of values.
- Business Function
-
Enter the name of the custom business function that contains the calculation. Use the source file, Quality Result Conversion Template (B31B9050), as a template to create custom functions.
- From Value
-
Enter a result that the system uses for the conversion.
- To Value
-
Enter the end value in a range. For example, if 1 to 10 is the range, enter 10 in this field.
- Converted Value
-
Enter the conversion value for a single value or range of values.
8.4 Setting Up Test Definitions and Result Durations
This section provides an overview of test definitions and result durations setup and discusses how to set up test definitions and result durations.
8.4.1 Understanding Test Definitions and Result Durations Setup
You must set up test definitions and result durations in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Quality Management system for the quality tests that you perform on a blend lot. For example, before you can enter test data for a pH test, you must set up an acceptable quantity, and percentage and result ranges for the test.
You can enter sample information, such as number and size of samples, how many tests the sample has to pass, sampling method, and sampling container.
You can also define a change threshold that enables you to compare previous and current test results and to evaluate the significance of the changes.
8.4.2 Prerequisite
If you want to use sample management, set up sample containers for use in quality testing.
8.4.3 Forms Used to Set Up Test Definitions and Result Durations
8.4.4 Setting Up Test Definitions and Result Durations
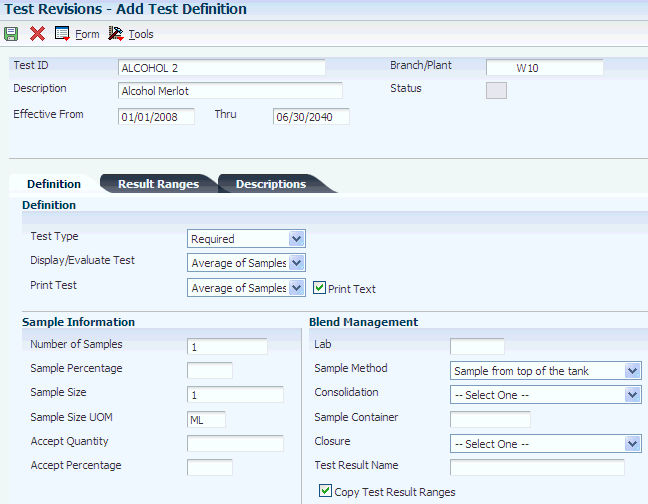
Access the Add Test Definition form.
8.4.4.1 Definition Tab
Select the Definition tab.
- Test Type
-
You can classify a test as required, optional, or guaranteed, but for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Blend Management, the system does not validate or use these settings.
- Display/Evaluate Test
-
All Samples: Display all occurrences of a test when using result inquiry programs. To provide for the entry of result values, all occurrences of a test appear on the Test Results Revisions form. The system uses all result values to determine whether a lot passes or fails.
Average of Samples: Display only the average result record when using result inquiry programs. All occurrences of a test appear on the Test Results Revisions form. The system uses only the average test result to determine whether a lot passes or fails.
Last Sample: Display the last occurrence of a test when using result inquiry programs. The last occurrence is the test result that was last entered on the Test Results Revisions form. The system uses only the last test result to determine whether a lot passes or fails.
No Display in Test Results: Do not display tests when using the Test Results Revisions or result inquiry programs. This value is allowed only for tests of type G (guaranteed).
- Print Test
-
All Samples: Print all occurrences of a test on the Certificate of Analysis.
Average of Samples: Print only the average test result record when printing the Certificate of Analysis.
Last Sample: Print the last occurrence of a test when printing the Certificate of Analysis. The last occurrence is the test results record that was entered last using the Test Results Revisions program.
No Print on COA: Do not print on the Certificate of Analysis.
- Print Text
-
Select to print the generic text associated with this test from the Test Results Revisions program on the Certificate of Analysis. Clear this field and the system does not print any generic text associated with this test from the Test Results Revisions program on the Certificate of Analysis.
- Number of Samples
-
Enter the number of samples to take for the test.
- Sample Percentage
-
Enter the percentage of an order quantity, which determines the number of samples to create in the Test Results Revisions program.
For example, if the sample percentage is 50 percent and the order quantity is 10, then the system creates five samples in the Test Results Revisions program. Use either this field or the Number of Samples field to control how many samples to create. You can use this field only with the order mode of the Test Results Revisions program. If the sample percentage is 100 percent, then you must test every unit in the order. Do not enter values in the Accept Percentage or Accept Quantity fields because all units on the order must pass for the lot to pass.
- Sample Size
-
Enter the quantity of one sample to take for the test. The system does not use this field; it is for information only.
- Sample Size UOM (sample size unit of measure)
-
Enter an identifying value for the unit of measure for a sample that you test. Examples of units of measure include barrels, gallons, hours, and cubic yards.
- Accept Quantity
-
Leave blank to accept the percentage or enter 1 to display or evaluate.
This value indicates the quantity of tests that must pass for the test sample to pass quality control. The system evaluates this value when the sample percentage is not equal to 100. To use this accept quantity value, you must complete these fields on the Test Definitions form accordingly.
- Accept Percentage
-
Leave blank to accept the percentage or enter 1 to display or evaluate.
This value indicates the percentage of tests that must pass for the sample to pass quality control. The system evaluates this value when the sample percentage is not equal to 100. To use the accept percentage value, you must complete the fields on the Test Definitions form accordingly.
- Lab
-
Specify the lab where the test is performed. This is the default lab for this test when you create quality test operations.
- Sample Method
-
Specify what method should be used to take samples for this test. For example, you can indicate that samples should be taken from the top of the tank. Sample methods are set up in the Sample Method UDC table (37/SM).
- Consolidation
-
Specify whether you want to allow samples to be consolidated automatically when they are created. If consolidation is permitted, you can indicate whether the consolidation is for reuse in another test, or cumulative so that it can be collected in the same container. Values are:
Cumulative: The sample quantity can be added to a common sample that is used in multiple tests.
Non-Cumulative: The sample is available only for a specific test and cannot be combined with other samples.
Reuse: The sample quantity can be reused for another test.
- Sample Container
-
Enter the sample container in which to store the sample. You set up sample containers in the Sample Container program (P3705). If you do not enter a sample container here, the system uses the default sample container from the winery constants. If you do not associate a sample container with the winery constants nor enter a sample container here, the system creates samples without containers.
- Closure
-
Specify the device that should be used to close the sample container. For example, the sample container might be corked or have a wax seal. You can set up closure devices in the Sample Closure UDC table (37/CL).
- Test Result Name
-
Enter the test result name that you want to associate with the test definition.
- Copy Test Result Ranges
-
Select to copy test result ranges automatically when you change the test result name. If you leave this option blank, the system retains the existing test result ranges even when you change the test result name.
8.4.4.2 Result Ranges Tab
Select the Result Ranges tab.
Figure 8-5 Add Test Definition: Result Ranges tab
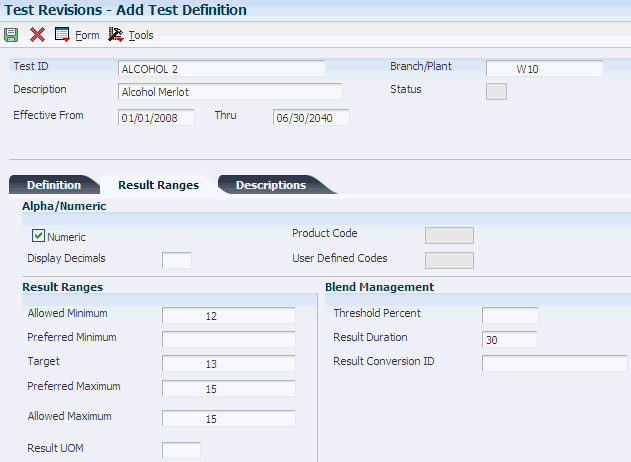
Description of "Figure 8-5 Add Test Definition: Result Ranges tab"
When you enter a test result name on the Definition tab, the system retrieves the result ranges that you set up for the test result name and displays the values on this tab.
- Change Threshold Percent
-
Specify a variation percentage between previous and current test results that you consider permissible. When you enter test results, the system uses this value to validate the test results.
You can set up change thresholds only for numeric results. If you attempt to enter a change threshold percentage for a nonnumeric result, the system issues an error message.
- Result Duration
-
Enter the number of days that the test result is valid. The system uses this value to determine the result expiration date.
8.4.4.3 Descriptions Tab
Select the Descriptions tab.
Under the Category Codes heading, categorize tests into groups for reporting purposes.
- ASTM Reference (American Society of Testing Material reference)
-
Identifies a recommended testing procedure of the American Society of Testing Material.
- Test Method
-
Enter a description of how to run a quality test. The test method is useful to both the company's quality control department and the customers. For example:
Test: Viscosity
Method: RVF #4 @10RPM
Text: Run the viscosity test on an RVF viscometer with a number 4 spindle at 10 revolutions per minute.
- Property
-
Enter the item attribute that is being tested.
- Test Duration
-
Enter the number of days it takes to complete a test.
8.5 Setting Up Test Equipment
This section provides an overview of test equipment setup and discusses how to set up test equipment.
8.5.1 Understanding Test Equipment Setup
You can set up the equipment that you plan to use for quality tests in order for the system to associate the test equipment with an operation. For example, if you use a meter to perform a pH test, you enter the data about the meter in the system. This data is only for informational purposes. You can then attach this equipment to a test definition. The system stores equipment data in the Test Equipment (F37011) table.
8.5.2 Form Used to Set Up Test Equipment
8.6 Setting Up Test Consumables
This section provides an overview of test consumables setup and discusses how to set up test consumables.
8.6.1 Understanding Test Consumables Setup
You set up the testing consumables that you plan to use for quality tests. For example, if you use litmus paper or latex gloves when performing a pH test, you must set up these consumable items in the system. You can then attach these consumables to a test definition. This setup enables the system to relieve inventory for the consumables when you close a blend operation. The system stores the information for these items in the Test Consumables (F37012) table.
8.6.2 Form Used to Set Up Test Consumables
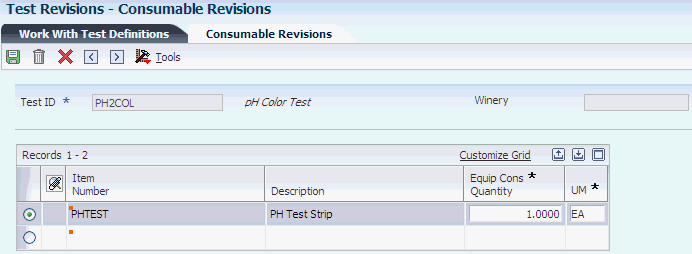
8.6.3 Setting Up Test Consumables
Access the Consumable Revisions form.
- Item Number
-
Enter an identifier for the item. The system assigns this number to an item. It can be in short, long, or third-item number format.
- Equip Cons Quantity (equipment consumable quantity)
-
Enter a value for the quantity of the item that a piece of equipment consumes during its operational use.
- UOM (unit of measure)
-
Enter a UDC (00/UM) to identify the unit of measure that the system uses to express the quantity of an item. For example, enter EA for each or KG for kilogram.
8.7 Setting Up Test Panels
This section provides an overview of test panel setup and discusses how to set up test panels.
8.7.1 Understanding Test Panel Setup
After you define tests, you can set up test panels for the quality tests that you perform. You use test panels to group routine tests. For example, if you routinely perform a pH test and an alcohol test, you can create a test panel for these tests. You can enter one or more test panels for a configured operation.
For each panel, you can define:
-
Name.
-
Description.
-
The tests to include in the panel.
The system stores the information for these items in the Specifications Definitions Master (F3702) and Specifications Detail (F37021) tables.
8.7.2 Forms Used to Set Up Test Panels
8.7.3 Setting Up Test Panels
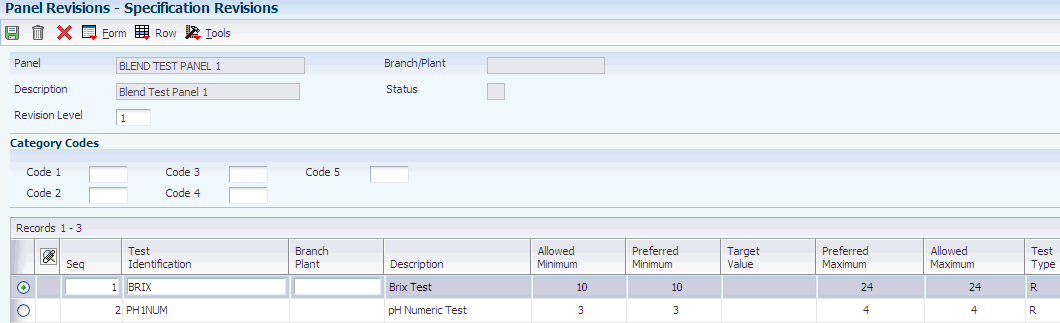
Access the Specification Revisions form.
- Panel ID (panel identification)
-
Enter the unique identification for a set of tests that you perform (for example, fermentation tests).
- Revision Level
-
Displays an alphanumeric character that represents the number of revisions to a panel. To avoid overlapping revisions, the system verifies that the start dates of revisions are greater than the end dates of other revisions.
- Status
-
Enter a UDC (00/WS) to indicate the approval status.
- Code 1, Code 2, Code 3, Code 4, and Code 5
-
Complete any of these fields to categorize tests into groups.
- Seq (sequence)
-
Enter a number that is used d to determine the sort order of tests.
- Test Identification
-
Use this field (as well as the Seq field) to group the tests within a panel.
8.8 Setting Up Sample Containers
This section provides an overview of sample containers and discusses how to set up sample containers.
8.8.1 Understanding Sample Containers
When you take samples of a blend product to test the result of a blend operation, for example, an additive operation, you can use sample containers that you set up in the system. You can associate a sample container with the test definition or you can set up a default sample container in the winery constants. If the test definition does not include a sample container, the system uses the default container from the winery constants. If you have not set up a default sample container, the system creates samples without containers.
You set up sample containers using the Sample Container program (P3705).
If you try to enter a sample transaction with a sample container that has not been set up in the Sample Container table (F3705), the system issue an error. For sample containers that are set up, but do not specify capacity and unit of measure, the system issues an error as well.
8.8.2 Form Used to Set Up Sample Containers
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Add Sample Container | W3705B | Quality Management Setup (G31B41), Sample Containers
Click Add on the View Sample Containers form. |
Set up sample containers. |
8.8.3 Setting Up Sample Containers
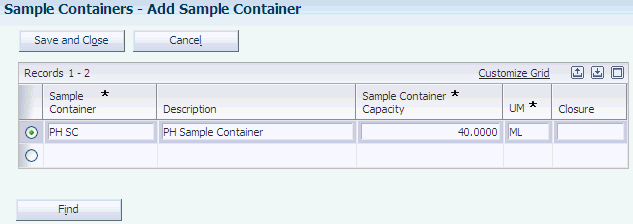
Access the Add Sample Container form.
|
Note: If you access this form to edit an existing sample container, the form title is Edit Sample Containers. |
- Sample Container
-
Select a value from the Sample Container UDC table (31B/CR) table to define what type of sample container you want to set up.
- Sample Container Capacity
-
Specify the capacity of the sample container. The system uses this value to determine how many containers are needed for a sample. For example, if a container holds 500 milliliters and you create a sample for 1000 milliliters, the system indicates that two containers are needed to collect the sample.
- UM (unit of measure)
-
Specify the unit of measure that you use to indicate the capacity of the sample container.
- Closure
-
Select a value from the Sample Closure UDC table (31B/CL) to indicate the method and material that is used to close the sample container. For example, the sample container might be corked or closed with a wax seal.