14 Processing Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 14.1, "Understanding Foreign and Alternate Receipts Entry"
-
Section 14.3, "Entering Manual Receipts in Foreign and Alternate Currencies"
-
Section 14.4, "Processing Automatic Receipts and Automatic Debits in Foreign Currencies"
-
Section 14.5, "Generating Credit Reimbursements in Foreign Currencies"
-
Section 14.6, "Processing Accounts Receivable Drafts in Foreign Currencies"
-
Section 14.7, "Posting Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts"
14.1 Understanding Foreign and Alternate Receipts Entry
You can process receipts in a domestic, foreign, or alternate currency. Specifically, you can process a receipt in any currency and apply it to invoices in any currency if the company base currency on the receipt is the same as the domestic currency of the invoices.
For example, assume the company base currency is Canadian dollars (CAD) and you want to apply a receipt in CAD. The domestic currency of the invoices to which you want to apply the receipt is U.S. dollars (USD). The company base currency of the receipt (CAD) is different from the domestic currency of the invoices (USD); therefore the system does not accept the receipt entry.
The currencies for the invoices are:
-
Invoice Number: 221
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: None
-
Invoice Number: 223
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: CAD
In this example:
-
You cannot apply a USD receipt to the domestic amount of invoice 221 (USD).
-
You cannot apply a CAD receipt in CAD to pay the foreign amount of invoice 223 (CAD).
In both cases, the company base currency on the receipt (CAD) is different from the domestic currency of the invoices.
To complete the receipt entry, you must change the company number on the receipt to a company with a base currency of USD.
14.1.1 Programs to Enter Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts and Foreign Drafts
This table lists the programs you can use to process receipts in multiple currencies, and indicates whether the program is used for foreign currency receipts only or both foreign and alternate currency receipts:
| Program Name (Program Number) | Menu | Foreign Currency | Alternate Currency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Receipts Entry (P03B102) | G03B12 | Yes | Yes |
| Speed Receipts Entry (P03B0001) | G03B12 | Yes | No |
| Apply Receipts to Invoices (R03B50)
Note: This is the program for automatic receipts processing. |
G03B13 | Yes | No |
| Process Auto Debits (R03B571) | G03B131 | Yes | No |
| Enter Our Drafts (P03B602)
Enter Customer Drafts (P03B602) |
G03B161 | Yes | No |
|
Note: The receipt programs in the Account Receivable system do not support multicurrency intercompany settlements. If you enter a multicurrency intercompany receipt, the system issues an error message. You cannot post the entry. |
14.1.2 Understanding Domestic Currency Receipts
A domestic currency receipt is a receipt that is in the same currency as the base currency of the invoice.
In this example, the company base currency is USD. You can:
-
Apply a USD receipt to the domestic amount of invoice 221 (USD).
-
Apply a USD receipt to the domestic amount (USD) of invoice 222 (EUR).
The currencies for the invoices are:
-
Invoice Number: 221
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: None
Domestic currency of receipt: USD
-
Invoice Number: 222
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: EUR
Domestic currency of receipt: USD
The receipts, which are in the base currency of the company (USD), pay the domestic amount of the invoices, even though one of the invoices has a foreign amount (EUR).
The system does not calculate a realized gain or loss on domestic currency receipts.
14.1.3 Understanding Foreign Currency Receipts
A foreign currency receipt is a receipt that is in the foreign (transaction) currency of the invoice. You specify the foreign currency of the receipt at the time you enter the receipt. When you enter a foreign currency receipt, these criteria must be met for the system to process the receipt:
-
The foreign currency of a receipt must be the same as the transaction currency of the invoice.
-
The base currency of the receipt must be the same as the domestic (base) currency of the invoice.
-
If the bank account is a monetary account, the currency of the company to which the bank account is assigned must be the same as the base currency of the receipt and invoice; otherwise, the system issues an error message and you cannot continue entering the receipt.
When you enter a receipt in a foreign currency, the system converts the foreign currency amount to the domestic currency amount based on the exchange rate in the F0015 table or, if applicable, a spot rate entered on the receipt record.
In this example, the base currency of the receipt is USD. You can:
-
Apply a EUR receipt to the foreign amount of invoice 223 (EUR).
-
Apply a CAD receipt to the foreign amount of invoice 224 (CAD).
In both cases, the company base currency on the receipt is the same as the domestic currency of the invoices; therefore, the system enables you to apply receipts in the foreign currency.
The currencies for the invoices are:
-
Invoice Number: 223
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: EUR
Domestic currency of receipt: EUR
-
Invoice Number: 224
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: CAD
Domestic currency of receipt: CAD
The receipts, which are in the foreign currency of the invoices (EUR and CAD, respectively), pay the foreign amounts of the invoices. A realized gain or loss might be calculated if the exchange rate changes between the time the invoice was entered and the receipt is applied.
14.1.4 Understanding Alternate Currency Receipts
An alternate currency receipt is a receipt that is in a currency different from the domestic or foreign currency of the invoice to which it applies.
With alternate currency receipt processing, you can enter an invoice for a customer in one currency and receive payment in a currency that is different from the transaction currency of the invoice and the domestic currency of the company. This prevents you from having to void the original invoice and enter a new invoice that is in the same currency as the receipt.
For example, assume that you work for a U.S. company and you enter invoices in the currency of the customer's company. The customer's company forwards invoices to their parent company for payment. The parent company uses a different currency than the customer's company and your company. With alternate currency receipt processing, you can apply the receipt in whatever currency it is submitted.
When you enter an alternate currency receipt, the currency of the company for the bank account must be the same as the base (domestic) currency of the company on the receipt. For example, a U.S. company enters an alternate currency receipt in Canadian dollars and applies it to a foreign currency invoice in Japanese yen. The base currency of the company on the receipt is USD; therefore, the currency of the company for the bank account must also be USD. If the currency of the company for the bank account is different from the base currency of the company on the receipt, you receive an error message and cannot continue entering the receipt.
Entering receipts in an alternate currency is similar to entering domestic and foreign currency receipts. Most of the processing for alternate currency receipts is based on the setup that you do before you actually enter the receipts. You activate alternate currency receipt processing in a processing option in the Standard Receipt Entry program (P03B102) and specify the currency code of the alternate currency receipt when you enter the receipt.
The Standard Receipt Entry program converts the selected invoices to the alternate currency amount so that you can apply the alternate currency receipt. To convert the invoice amount, the program uses the exchange rate between the invoice currency and the alternate currency in the F0015 table based on the general ledger date or, if applicable, a spot rate entered on the receipt record.
In this example, the company base currency is USD. You can:
-
Apply a EUR receipt to the domestic amount of invoice 225 (USD).
Note:
If an invoice is domestic-only and the receipt is not domestic, the receipt is considered an alternate currency receipt, not a foreign currency receipt. -
Apply a JPY receipt to the foreign amount of invoice 226 (CAD).
In both cases the company base currency on the receipt is the same as the domestic currency of the invoices; therefore, the system enables you to apply receipts in an alternate currency.
The currencies for the invoices are:
-
Invoice Number: 225
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: None
Alternate currency of receipt: EUR
-
Invoice Number: 226
Domestic currency of invoice: USD
Foreign currency of invoice: CAD
Domestic currency of receipt: JPY
The receipts, which are not in the foreign or domestic currency of the invoices, pay the domestic (USD) and foreign (CAD) currency amounts of the respective invoices.
A realized gain or loss might be calculated if the exchange rate changes between the time that the invoice was entered and the receipt is applied.
14.1.4.1 Example: T-Accounts for Alternate Currency Receipts
These t-accounts describe how transactions move in and out of accounts when an alternate currency receipt is involved. The t-account entries are for a foreign currency invoice (500.00 CAD), the domestic side of the invoice (313.44 USD), and an alternate currency receipt (347.33 EUR).
These exchange rates apply:
-
Exchange rate (invoice date):
1 CAD = 0.62688 USD
-
Exchange rates (receipt date):
1 CAD = 0.69466 EUR
1 EUR = 0.9024271 USD
Figure 14-1 T-accounts for revenue, trade, cash, and clearing accounts
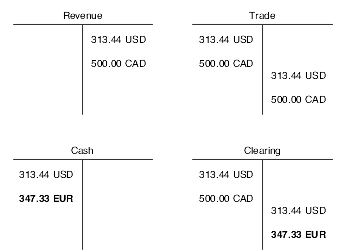
Description of ''Figure 14-1 T-accounts for revenue, trade, cash, and clearing accounts''
The alternate currency entries are EUR.
14.1.5 Understanding Multicurrency and Receipt Types
This section discusses the receipt types with special multicurrency considerations.
14.1.5.1 General Ledger Receipts
A general ledger receipt, sometimes referred to as a G-type receipt, is a miscellaneous receipt that is not applied to a customer invoice. A miscellaneous receipt could be a rebate or any other type of payment that does not affect the accounts receivable trade account.
To enter a miscellaneous receipt using the Standard Receipts Entry (P03B102) or Speed Receipts Entry (P03B0001) program, the base currency of the company associated with the general ledger account number must be the same as the base currency of the receipt. If the general ledger account is a monetary account, the currency code of the account must be the same as the transaction currency code of the receipt. If they are different, the system issues an error message Bank Account Currency Invalid when you enter the miscellaneous receipt.
14.1.5.2 Balance Forward Receipts
You can use the Speed Receipts Entry program to enter receipts in a foreign currency. You cannot use this program to enter receipts in an alternate currency.
When entering balance forward receipts in a foreign currency using the Speed Receipts Entry program, you can apply a receipt across companies if the base currency of the receipt company is the same as the base currency of the invoice company.
For example, company 70 (a CAD company) enters a foreign currency invoice in EUR. Company 75 (also a CAD company) receives payment and applies it to the invoice for company 70. In this example, the base currency of the receipt company is the same as the base currency of the invoice company.
14.1.6 Understanding Multicurrency Fields Updated During Receipt and Draft Entry
When you enter a foreign currency receipt or draft or an alternate currency receipt, the system populates one or more fields in one or more tables with the short account ID of the account associated with the AAI items involved. The system uses these account IDs to create automatic entries when you post receipts and drafts.
The fields populated during receipt and draft entry are the same with two exceptions. For draft entry, the system does not populate:
-
The GL bank account.
The field for this account does not display during draft entry
-
The alternate currency realized gain/loss accounts and amounts and clearing accounts and amounts.
Drafts are not processed in alternate currencies; they are processed only in domestic and foreign currencies.
By understanding how the system updates the fields, you can better understand the automatic entries that the system generates during the post. This table shows the fields and tables that are updated based on the AAI that is used:
| Account | Field Updated | Table Updated | AAI Item Used | Additional Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Ledger Bank | GLBA | F03B13 | RB | If the account associated with the AAI item RB that the system uses is a monetary account, the currency of the account must be the same as the transaction currency of the receipt. |
| Accounts Receivable Trade | AID | F03B14 | RC | The system always uses the account ID of the AID field from the F03B11 invoice record that the receipt pays. Otherwise, the accounts receivable trade account used for the invoice would not be offset by the receipt. |
| Foreign Currency Realized Gain | AIDT | F03B14 | RG | None. |
| Foreign Currency Realized Loss | AIDT | F03B14 | RL | None. |
| Alternate Currency Realized Gain | AIDA | F03B14 | RY | None. |
| Alternate Currency Realized Loss | AIDA | F03B14 | RZ | None. |
| Accounts Receivable Trade for Chargebacks | AID
AIDC |
F03B11
F03B14 |
RC | If you know the invoice number to which the chargeback applies, the system creates the chargeback record in the currency of the invoice to which it applies.
If you do not know the invoice number to which the chargeback applies, you can create a stand-alone chargeback for one or more invoices. When you enter the stand-alone chargeback for multiple invoices, the system creates the chargeback records in the receipt currency. |
| Deduction Suspense | AID
DAID |
F03B11
F03B14 |
RN | If you know the invoice number to which the deduction applies, the system creates the deduction record in the currency of the invoice to which it applies.
If you do not know the invoice number to which the deduction applies, you can create a stand-alone deduction for one or more invoices. When you enter the stand-alone deduction for multiple invoices, the system creates the deduction records in the receipt currency. |
| Rounding Differences | RASI | F03B14 | R8 | The system assigns document type RR to a receipt record in the Receipts Detail table (F03B14) when the receipt is either fully applied on the foreign side but not fully applied on the domestic side, or fully unapplied on the foreign side but not fully unapplied on the domestic side. This rounding record is at the receipt level and is not associated with any particular invoice line. |
|
Note: The system does not update a field for AAI item R7 (clearing account for alternate currency receipts). The system retrieves the account that it uses to generate the automatic entries when you post the receipt. |
14.2 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section:
-
Ensure that the accounts receivable AAIs are set up for the currency and company combinations.
-
Complete the multicurrency processing options.
14.3 Entering Manual Receipts in Foreign and Alternate Currencies
This section describes how to:
-
Set multicurrency processing options for Standard Receipt Entry.
-
Enter receipts in a foreign currency.
-
Load open invoices for receipt application.
-
Select open invoices for receipt application.
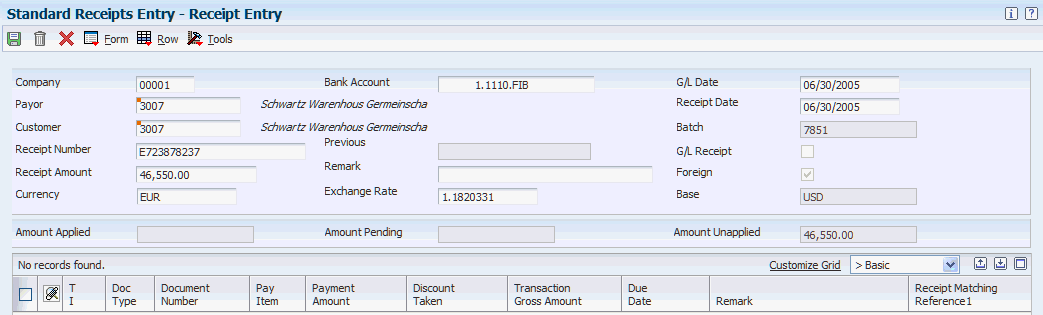
14.3.1 Forms Used to Enter Receipts in a Foreign Currency
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipt Entry | W03B102E | Manual Receipts Processing (G03B12), Standard Receipts Entry
On the Work With Customer Receipts Inquiry form, click Add. |
Enter receipts in a foreign or alternate currency. |
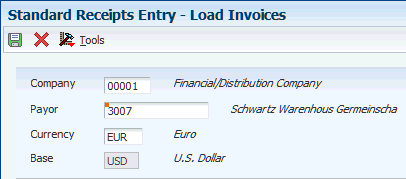
| Load Invoices | W03B102J | On the Receipt Entry form, select Load from the Form menu. Enter the values to retrieve the invoices to which the receipt applies and click OK. | Retrieve invoices and display them in the detail area of the Receipt Entry form. |
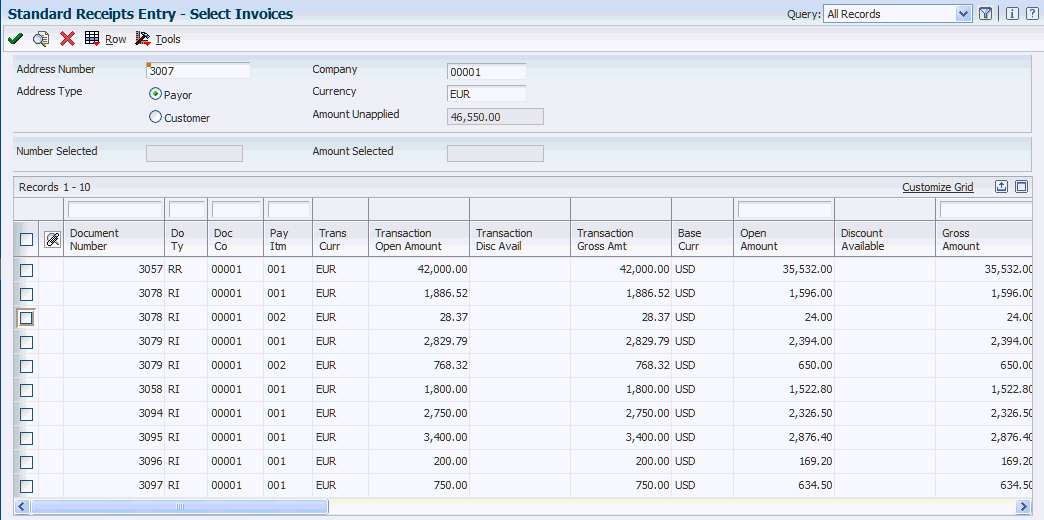
| Select Invoices | W03B102H | On the Receipts Entry form, choose Select from the Form menu. Enter the values to display the invoices, and then manually select each invoice to which the receipt applies. | Retrieve invoices and display them in the detail area of the Receipt Entry form. |
14.3.2 Setting Multicurrency Processing Options for Standard Receipt Entry (P03B102)
This section discusses the processing options that are specific to multicurrency processing.
14.3.2.1 Display
- 8. Currency
-
Specify whether to retain the currency code entered on the Receipt Entry form after you enter the receipt so that it appears on the form for subsequent receipts. Values are:
Blank: Do not the retain the currency code.
1: Retain the currency code.
- 9. Exchange Rate
-
Specify whether to retain the exchange rate entered on the Receipt Entry form after you enter the receipt so that it appears on the form for subsequent receipts. Values are:
Blank: Do not retain the exchange rate.
1: Retain the exchange rate.
14.3.2.2 Currency
- 1. Edit Effective Date
-
Specify whether the system validates the effective date that it uses to retrieve the exchange rate against the general ledger date that you enter on the receipt. Values are:
Blank: Do not validate the effective date.
1: Validate the effective date. The system issues a warning when the effective date of the exchange rate retrieved from the F0015 tables is not in the same period as the GL date on the receipt.
- 2. Alternate Currency Receipts
-
Specify whether to allow the payment of an invoice in an alternate currency (a currency other than the base or transaction currency of the invoice). Values are:
Blank: Do not allow payment in an alternate currency.
1: Allow payment in an alternate currency.
14.3.3 Entering Receipts in a Foreign Currency
Access the Receipt Entry form.
The process to enter a receipt is the same regardless of whether it is in a foreign or alternate currency. This section discusses only the multicurrency fields for entering receipts in a foreign and alternate currency.
- Currency
-
Enter the currency of the receipt. If you leave this field blank, the system uses the currency code of the address book number entered in the Payor field. If there is no currency code assigned to the payor's address book record, the system uses the currency code assigned to the company in the Company field.
- Exchange Rate
-
Displays the default exchange rate. This is the exchange rate between the receipt currency (Currency field) and the base company currency (Base field).
The system automatically retrieves the exchange rate from the F0015 table. To override the exchange rate in the F0015 table or if no exchange rate exists, enter a value in this field.
The number in this field can have a maximum of seven decimal positions. If more are entered, the system adjusts to the nearest seven decimal positions.
- Base
-
Displays the base currency code of the company that is assigned to the receipt.
- Foreign
-
Selects this check box automatically when the currency code that you enter differs from the base currency code.
14.3.4 Loading Open Invoices for Receipt Application
Access the Load Invoices form.
- Company
-
Displays the company number entered on the receipt. The system selects only invoices for the payor and company specified. To select invoices for another company, change the value of this field. To select all invoices for the payor regardless of the of the company number, enter *.
- Payor
-
Displays the payor number entered on the receipt. The system selects only invoices for the payor specified. To select invoices entered for a different payor, change the value of this field.
- Currency
-
Displays the currency code entered on the receipt. The system selects only invoices entered for the transaction currency specified. To select invoices entered in a different currency, change the value of this field. To select all invoices for the payor regardless of the currency code, enter *.
14.3.5 Selecting Open Invoices for Receipt Application
Access the Select Invoices form.
To select specific open invoices and apply them to a receipt:
-
Accept the default values in these fields or change them, if applicable:
-
Address Number
-
Company
-
Currency
-
-
Select the Type option that corresponds to the address number:
-
Payor
-
Customer
-
-
Click Find to display all open items that meet the search criteria.
-
Select the invoices to which the receipt applies by double-clicking in the Document Number field or by selecting each invoice and then clicking the Select button.
The Select button acts like a toggle, enabling you to select or deselect invoices. Alternatively, you can select Select/Deselect from the Row menu.
The system marks the invoices that you select. It keeps track of the number of invoices and the total amount of the invoices and displays that information at the bottom of the Select Invoices form.
You can change the search criteria to display more invoices, for example for another payor or for transactions in a different currency, and continue selecting the invoices to pay.
-
Click Close to display the selected invoices in the detail area of the Receipt Entry form.
The system displays open invoices in the order in which they were selected.
-
On the Receipt Entry form, apply the receipt to the selected invoices and click OK.
- Address Number
-
Displays the payor number that is entered on the receipt header. You can change this value to locate invoices for another address book number.
- Company
-
Displays the company number that is entered on the receipt header. You can change this value to search for invoices entered for a different company, or you can enter * to display all of the invoices for the address book number regardless of the company number.
- Currency
-
The system displays the currency code that is entered on the receipt header. The system uses this currency code to search for invoices that are entered with same transaction currency code and the same base currency code pair. For example, if you enter a receipt in CAD for company 00002, which is assigned a base currency of EUR, the system displays CAD in this field on the Select Invoices form, but searches only for invoices with a base currency of EUR and a transaction currency of CAD.
Note:
Be aware, the transaction currency code that displays in the grid area of the form is not the transaction currency of the invoice; it is the transaction currency code of the receipt. The system displays the transaction currency code of the invoice in the Curr Code (currency code) field. - Trans Curr (transaction currency)
-
The currency code of the receipt. The system searches for invoices entered in the currency specified in the Currency field in the header area of the Select Invoices form, and displays the transaction amounts in the currency of the receipt.
- Base Curr (base currency)
-
The base currency of the invoice and the receipt transactions. The base currency code of the transactions must be the same, or the system does not display the invoices on the form.
- Curr Code (currency code)
-
The transaction currency of the invoice. If you specify a currency code in the header of the Select Invoices form, the system displays only invoices with the same transaction currency.
14.4 Processing Automatic Receipts and Automatic Debits in Foreign Currencies
This section provides overviews of processing automatic receipts in a foreign currency and processing automatic debits in a foreign currency, lists prerequisites and discusses how to process automatic debits in a foreign currency.
14.4.1 Understanding How to Process Automatic Receipts in a Foreign Currency
You can process automatic receipts in either the domestic or the foreign currency of an invoice. To process automatic receipts in multiple currencies, you must enter the currency code, exchange rate, and currency mode in the Electronic Receipts Input table (F03B13Z1). The currency code of the receipt must reflect either the domestic or foreign currency of the invoices being paid. You cannot process automatic receipts in an alternate currency. Instead, you must enter them manually through the Standard Receipt Entry program (P03B102).
Automatic receipts processing uses these tables:
-
Electronic Receipts Input (F03B13Z1).
This table contains information that was loaded from a bank tape, and therefore contains information that was entered at the bank.
-
Receipts Header (F03B13).
The system creates records in this table when you run the Update Receipts Header program (R03B551).
-
Receipts Detail (F03B14).
The system creates unapplied cash (RU) records in this table when you run the Update Receipts Header program.
To successfully upload automatic receipt entries from an external source and process them in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, you must first create a custom program that provides proper data to fields in the F03B13Z1 table.
To successfully match and apply foreign currency receipts to invoices, define processing options for the algorithms that you use and understand what information is required by the F03B13Z1 table. You can define algorithms for Invoice Selection Match (R03B50A), Balance Forward Match (R03B50B), Known Invoice Match With Amount (R03B50D), Known Invoice Match Without Amount (R03B50E), and Combination Invoice Match (R03B50F).
14.4.1.1 Write-Off Tolerance Amounts
The write-off tolerance amounts for underpaid and overpaid invoices are based on the currency code of the receipt, and not the currency code of the invoice or company. You specify tolerance amounts in the processing options for algorithms R03B50A, R03B50D, and R03B50E. Set up a different version of the algorithm for each receipt currency, and then specify the currency code in the data selection when you process automatic receipts using the Apply Receipts to Invoices program (R03B50). By doing this, the write-off tolerance amounts is meaningful for each currency.
14.4.2 Understanding How to Process Automatic Debits in a Foreign Currency
You process automatic debits to record the withdrawal of funds from a customer's bank account. To create a batch of automatic debits in a foreign currency, specify foreign currency in the Currency Mode processing option and the currency code in the data selection of the Create Automatic Debit Batch program (R03B571). An automatic debit batch can contain only one currency.
The currency of the invoices that you process must be the same as the currency of the bank account if the GL bank account is a monetary account. For example, if you process automatic debits in a foreign currency of Canadian dollars (CAD), the currency of the GL bank account must also be CAD.
14.4.3 Prerequisites
Before you complete the task in this section:
-
Set the Currency Mode processing option to 1 to use the foreign currency of the invoice to process automatic debits.
-
Verify that the GL Bank Account processing option contains the correct bank account.
If the bank account is a monetary account, the currency of the account must be the same as the currency of the invoices.
-
Select only one currency in the data selection.
If you do not do this, the program uses the currency of the first invoice as the default foreign currency.
14.4.4 Forms Used to Process Receipts in a Foreign Currency
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Auto Batch Debits | W03B571A | Automatic Debiting (G03B131), Process Auto Debits | Process automatic debits in a foreign currency. |
| Add Version | W98305WH | On the Work With Auto Debit Batches form, click Add.
Enter the identifier information for the version and click OK. |
Identify and run the version to create automatic debit batches. |
14.4.5 Processing Automatic Debits in a Foreign Currency
Access the Work with Batch Versions program and select a version.
14.5 Generating Credit Reimbursements in Foreign Currencies
This section provides an overview of credit reimbursements in a foreign currency and discusses how to generate credit reimbursements in a foreign currency.
14.5.1 Understanding Credit Reimbursements in a Foreign Currency
Credit reimbursements are used to reclassify credits in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system to open vouchers in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system. When you generate credit reimbursements, the system pays open credit memos and generates vouchers to reimburse the customer.
You use the data selection to specify the records in which to create reimbursements. The system creates reimbursements only if the amount is a credit (negative). Credit reimbursements are generated based on groupings by customer, company, and currency.
14.5.1.1 Example: Data Selection for Credit Reimbursements
Assume you have these records in the Customer Ledger table (F03B11):
| Customer | Company | Currency Code | Amount | Document Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4272 | 00001 | USD | 200.00 | RI |
| 4272 | 00001 | USD | –100.00 | RM |
| 4272 | 00001 | EUR | 50.00 | RI |
| 4272 | 00001 | EUR | 100.00 | RI |
| 4272 | 00001 | EUR | –200.00 | RM |
| 4272 | 00010 | USD | 80.00 | RI |
| 4272 | 00010 | EUR | –150.00 | RM |
| 4272 | 00010 | EUR | 180.00 | RI |
You generate credit reimbursements using this data selection: customer number 4272, company 00001, and currency code EUR. The system generates one reimbursement for 50.00 EUR based on customer number 4272, company 00001, and currency EUR. The system generates a reimbursement because the overall balance of the customer's account is negative. If, however, the overall balance had been positive, the system would not generate a reimbursement.
You generate credit reimbursements using this data selection: customer number 4272 and document type RM. The system generates three reimbursements for customer 4272:
-
One for 100.00 USD based on customer number 4272, company 00001, and currency USD
-
One for 200.00 EUR based on customer number 4272, company 00001, and currency EUR
-
One for 150.00 EUR based on customer number 4272, company 00010, and currency EUR
The system does not consider the overall balance of the customer's account because you specified document type RM.
14.5.2 Generating Credit Reimbursements in a Foreign Currency
Select Period End Processing (G03B21), Generate Reimbursements.
14.6 Processing Accounts Receivable Drafts in Foreign Currencies
This section provides an overview of accounts receivable drafts in a foreign currency.
14.6.1 Understanding Accounts Receivable Drafts in a Foreign Currency
In most countries, a draft is a promise to pay a debt. Many areas of the world use draft processing, although it might be referred to as something other than draft processing. For example, in Asia Pacific, the draft process is commonly used for post-dated checks. In the U.S., it is used for credit card payments.
You can process drafts in a foreign currency if the transaction currency of the invoice is the same currency as the draft. The transaction currency of an invoice determines the currency that is used throughout the draft process. If the transaction currency of an invoice is foreign, you must print, remit, and collect it as a draft in a foreign currency. For this reason, you cannot process drafts in an alternate currency.
Depending on whether a foreign currency draft must be accepted by the customer, you can process drafts either manually or automatically.
14.6.1.1 Manual Receipt Drafts in a Foreign Currency
Manual drafts are also called customer acceptance drafts because the customer must accept them before they can be remitted to the bank.
When you enter a manual draft on the Draft Entry form, the currency must match the transaction currency of the invoice. If the transaction currency is foreign, the system selects the Foreign check box on the Draft Entry form. The Draft Entry form is similar to the Receipt Entry form.
14.6.1.2 Automatic Receipt Drafts in a Foreign Currency
Automatic drafts are also called pre-authorized drafts because they do not require customer acceptance. You and the customer agree in advance that the customer will pay with a draft.
You create automatic drafts by running the A/R Batch Draft Creation program (R03B671). When you create automatic drafts, the system processes them in the transaction currency of the invoice. If the transaction currency is foreign, the system processes the draft in the foreign currency.
14.6.1.3 Foreign Currency Drafts with Contingent Liability
You remit drafts to the bank so that it can collect funds from the customer's bank. If you request an advance from a bank before the actual due date of the draft, some countries require that you recognize a contingent liability.
Before you remit a foreign currency draft with contingent liability, run the Draft Remittance program (R03B672). Set the processing options under the G/L Remittance form as follows:
-
AAI for Draft GL Account. Set to 2 (contingent) to create journal entries for a contingent liability.
-
Exchange Rate Override. Enter an override exchange rate, if applicable.
If you leave this field blank, the system retrieves the exchange rate from the F0015 table.
If you remit drafts in more than one currency, the system prints a report with an * in the Due Date Total and Customer Total columns. When you approve and post the remittance batch, the system creates journal entries for foreign currency gains and losses.
Unlike domestic currency drafts with contingent liability, the system records gains and losses during the draft remittance process for foreign currency drafts with contingent liability. (For foreign currency drafts without contingent liability, the system records gains and losses during the collection process.)
14.6.1.4 Foreign Currency Drafts and Processing Options
Review this table for information about processing options specific to foreign currency draft processing:
| A/R Draft Processing Program | Multicurrency Processing Options |
|---|---|
| Enter Our Drafts (P03B602)
Enter Customer Drafts (P03B602) |
On the Display tab, set the Currency Code processing option to retain the currency code entered on the Draft Entry form after you accept a draft.
On the Display tab, set the Exchange Rate processing option to retain the exchange rate entered on the Draft Entry form after you accept a draft. On the Currency tab, set the Edit Effective Date processing option to validate the effective date used to retrieve the exchange rate against the general ledger date entered on the draft. |
| Invoice Print with Draft (R03B5051) | On the Currency tab, set the Print Currency processing option to print invoices with foreign currency amounts and currency codes. |
| Draft Collection with Status Update (R03B680) | On the Exchange Rate tab, specify a spot rate in the Exchange Rate Override processing option or leave the field blank to retrieve the rate from the F0015 table.
This exchange rate is used for drafts that pay foreign invoices, regardless of the invoice currency, and applies only to drafts remitted without contingent liability. |
| Draft Remittance (R03B672) | On the G/L Remittance tab, specify a spot rate in the Exchange Rate Override processing option or leave the field blank to retrieve the rate from the F0015 table.
This exchange rate is used to create journal entries for a contingent liability and applies only to drafts remitted with contingent liability. |
14.7 Posting Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts
This section provides an overview of the post process for foreign and alternate currency receipts and discusses how to post foreign and alternate currency receipts.
14.7.1 Understanding the Post Process for Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts
After you process foreign and alternate currency receipts, you must post them.
When you post foreign and alternate currency receipts, the pre-post for the Receipt Post program retrieves the accounts receivable offset method from the Accounts Receivable Constants program (P0000). If the offset method is B (batch), the system verifies that there are no foreign or alternate currency receipts in the batch. If there is at least one foreign or alternate currency receipt, the pre-post changes the accounts receivable offset method for the batch to S (pay item) and continues processing. The pre-post does this because you cannot post using offset method B if one or more receipts in a batch are in a foreign or alternate currency.
The Receipt Post program performs the tasks described in this table, regardless of whether you use multicurrency processing. For information specific to posting receipts in a multicurrency environment, review the Multicurrency Considerations column in this table:
| Task Performed by Receipt Post | Multicurrency Considerations |
|---|---|
| Selects unposted receipt transactions from the Receipts Header (F03B13) and Receipts Detail (F03B14) tables. | None. |
| Verifies that the batch has an approved status. | None. |
| Creates entries to debit the appropriate bank account for the receipt amount in the Account Ledger table (F0911). | Creates entries in the foreign currency (CA) ledger to debit the appropriate bank account for the foreign currency receipt amount in the F0911 table. |
| Creates automatic offset entries to credit the accounts receivable trade account for the receipt amount in the F0911 table. | Creates automatic offset entries to credit the accounts receivable trade account for the AA (domestic) and CA ledgers in the F0911 table. |
| Creates automatic entries for discounts, write-offs, chargebacks, and deduction accounts. | Creates automatic entries for discounts, write-off, chargebacks, and deduction accounts in the CA ledger for the foreign currency amount. |
| Currency gains and losses do not apply to non-multicurrency environments. | Creates automatic entries for foreign currency and alternate currency gains and losses. |
| Slight rounding differences do not apply to non-multicurrency environments. | Creates journal entries for slight rounding differences, if applicable. |
| Detailed currency restatement does not apply to non-multicurrency environments. | Updates the alternate currency ledger (XA) and, if applicable, the YA and ZA ledgers and produces a separate post report if you enter a version of the Detailed Currency Restatement program (R11411) in the processing options. |
| Updates balances in the F0902 table. | None. |
| Updates the posted status to P (posted) in the F0911 table. | None. |
| Updates the posted status to D (posted) in the F03B13 and F03B14 tables. | None. |
| Updates the posted status to D (posted) in the Batch Control Records table (F0011). | None. |
14.7.1.1 Posting Receipts to Monetary Bank Accounts
To post multicurrency receipts to monetary bank accounts, the system requires that certain criteria are met. Monetary bank accounts are accounts that are assigned a specific currency code. To successfully post receipts to a monetary bank account, the transaction currency of the receipt must be the same as the currency of the bank account.
If the general ledger bank account of a receipt is a monetary account, the system posts a receipt if these criteria are met:
-
The currency of the receipt is the same as the transaction currency of the invoice.
The system does not post a receipt if the receipt is applied to the domestic side of a foreign currency invoice. For example, the transaction currency of an invoice is U.S. dollars (USD) and the domestic currency is EUR. You receive a payment in the domestic currency of the invoice (EUR) and enter the receipt for a monetary bank account (EUR). When you post the receipt, you receive an error message because the currency of the invoice (USD) and the currency of the bank account (EUR) are different.
-
The currency of the receipt is the same as the currency of the general ledger bank account.
The system does not post a receipt if the receipt and bank account currencies are different. For example, the transaction currency of an invoice is Canadian dollars (CAD). You receive a payment in the transaction currency of the invoice (CAD) and enter the receipt for a monetary bank account (USD). When you post the receipt, you receive an error message because the currency of the receipt (CAD) and the currency of the bank account (USD) are different.
If the post fails, the system sends an error message Account Currency Code Invalid to the work center. To correct the error, you must change the bank account of the receipt to a non-monetary account and run the post again.
14.7.1.2 Slight Rounding Differences Recorded by the Receipt Post
When you post foreign or alternate currency receipts, the system might create automatic entries for slight rounding differences. These slight rounding differences are created when a foreign or alternate currency receipt is applied to an invoice and the domestic amount of the invoice is different from the domestic amount of the receipt. The rounding difference, which is immaterial, is recorded in a rounding account as directed by AAI item R8.
Typically, rounding differences occur on transactions that involve multiple invoices and one receipt, or multiple receipts and one invoice. For these transactions, a rounding difference might occur when the system converts amounts between a foreign and a domestic currency, or an alternate and domestic currency.
To record the rounding differences, the system creates an automatic entry in the rounding account when you post the receipt. The rounding difference is associated with the receipt, not the invoice. If you adjust a receipt and the adjustment affects an existing rounding amount, the system creates a new rounding record. It does not change the original record.
14.7.1.3 Example: Slight Rounding Differences Recorded by the Receipt Post
In this example, a slight rounding difference is recorded on a foreign currency receipt. The exchange rate is 1 CAD = 0.73429 EUR.
A French company enters three foreign currency invoices for 1,250.00 CAD each (917.86 EUR each). The company receives payment for 3,750.00 CAD (2,753.59 EUR). When the company applies the domestic receipt amount (2,753.59) to the domestic invoices (917.86 × 3 = 2,753.58 EUR), the system records a slight rounding difference of + 0.01 EUR.
14.7.1.4 Multicurrency Journal Entries Created by the Receipt and Draft Post
When you post non-currency specific receipts, the system creates detailed or summarized journal entries in the Account Ledger table (F0911) based on the journal entry creation method specified in a processing option for the Standard Receipt Entry program (P03B102).However, when you post foreign and alternate currency receipts, the post program creates detailed journal entries regardless of the journal entry creation method specified in the Standard Receipts Entry program. The post does not create summarized amounts if multicurrency processing is activated in the General Accounting Constants program (P0000).
The journal entries created by the receipt post are the same as those created by the draft post.
14.7.1.5 Multicurrency Automatic Entries Created by the Receipt and Draft Post
When you post foreign currency receipts and drafts and alternate currency receipts, the system creates automatic entries (document type AE) in the F0911 table.
Unlike other post programs outside of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system, the receipt and draft post programs create automatic entries based on the account associated with an account ID at the time the receipt or draft is entered instead of the account associated with an AAI item at the time the receipt or draft is posted. The exception to this is automatic entries created for the alternate currency clearing account during the receipt post.
The automatic entries created by the receipt and draft post are the same with one exception. The draft post does not create alternate currency realized gains, losses, and clearing account amounts because drafts can be processed only in domestic and foreign currencies.
The receipt and draft post creates automatic entries in the F0911 table for these accounts:
| Account | Description |
|---|---|
| GL Bank | The post program locates the short account ID in the GL Bank Account field (GLBA) on the receipt or draft record and creates an automatic entry for the corresponding bank account. |
| Realized Gains and Losses | The post program locates the short account ID in the:
The post then creates an automatic entry for the corresponding gain or loss account. For foreign currency receipts, the post program creates an additional record with an amount in the Gain/Loss Amount field (AGL) in the F03B14 table. You can review this record in the Universal Table Browser (UTB). For alternate currency receipts, the post program creates an additional record with an amount in the Alternate Currency Gain/Loss Amount (AGLA) field in the F03B14 table. You can review this record in the UTB. The post program does not create automatic entries for gains and losses on write-off amounts. |
| Clearing | For alternate currency receipts only. The receipt post program uses AAI item R7 to create automatic entries for the alternate currency clearing account, if applicable.
The system locates the account using this hierarchy:
|
| Chargebacks | The post program locates the short account ID in the Chargeback Account ID (AIDC) field on the receipt record and creates an automatic entry for the corresponding chargeback account. |
| Deduction Suspense | The post program locates the short account ID in the Deduction Account ID field (DAID) on the receipt record and creates an automatic entry for the corresponding deductions account. |
| Rounding Differences | The post program locates the short account ID in the Rounding (RASI) field on the receipt record and creates an automatic entry for the corresponding rounding account.
The post program also creates an additional record (document type RR) with an amount in the Rounding Amount (RAMT) field in the F03B14 table. You can review this record in UTB. |
14.7.2 Posting Foreign and Alternate Currency Receipts
Depending on whether you are posting manual receipts, automatic receipts, or automatic debits, use one of these navigations:
Select Manual Receipts Processing (G03B12), Post Receipts to G/L.
Select Automated Receipts Processing (G03B13), Post Receipts to G/L.
Select Automatic Debiting (G03B131), Post Auto Debits to G/L.
You can also post receipts and automatic debits from the Receipts Journal Review or Auto Debits Journal Review program by selecting a batch, and then selecting Post by Batch from the Row menu.