10 Setting Up Accounts Payable for Multicurrency Processing
Before you can process accounts payable transactions in multiple currencies, you must assign currency codes to supplier records and set up currency-specific AAIs.
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 10.1, "Setting Up Supplier Records for Multicurrency Processing"
-
Section 10.3, "Setting Up Multicurrency AAIs for Accounts Payable"
10.1 Setting Up Supplier Records for Multicurrency Processing
This section provides an overview currency codes and supplier records and discusses how to:
-
Set multicurrency processing options for Supplier Master Information (P04012).
-
Assign a currency code to a supplier record.
10.1.1 Form Used to Assign Currency Codes to a Supplier Record
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Master Revision | W04012A | Multi-Currency Setup (G1141), Designate A/P Currency.
Select a supplier on the Work With Supplier Master form and select the Vouchers tab. |
Assign currency codes to a supplier record. |
10.1.2 Setting Multicurrency Processing Options for Supplier Master Information (P04012)
This section discusses processing options that are specific to multicurrency processing.
10.1.2.1 Defaults
- 2. Amount Currency Code
-
Specify the default currency code for the A/B Amount Code field. If you leave this processing option blank and the A/B Amount Code field on the Supplier Master Revision form is blank, the system uses the currency code of the company assigned to the Business Unit field on the Address Book Revision form.
The A/B Amount Code field appears on the Supplier Master Revision form only if multicurrency is activated in the General Accounting Constants program.
10.1.3 Assigning Currency Codes to a Supplier Record
Access the Supplier Master Revision form.
The currency codes that you assign on this form are stored in the Supplier Master table (F0401).
Figure 10-1 Supplier Master Revision form
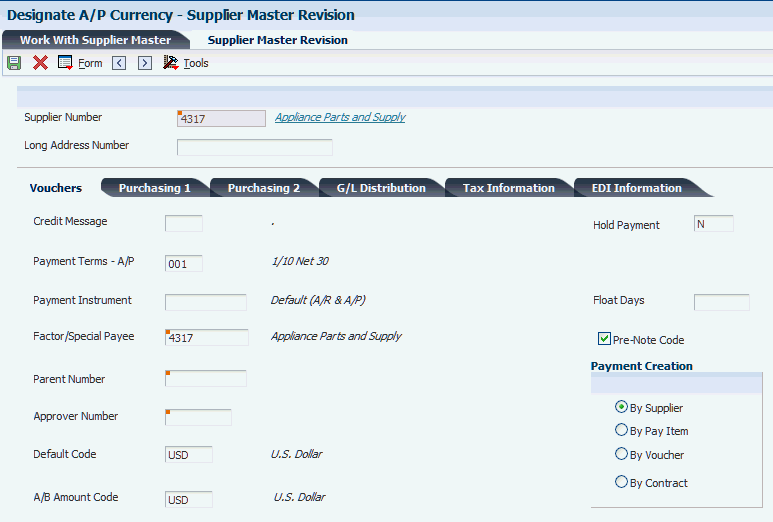
Description of ''Figure 10-1 Supplier Master Revision form''
|
Note: After you assign an address book amount code to a supplier record, do not change the currency code in the A/B Amount Code field if any the address book amount fields in the Supplier Master table (F0401) have values. If you do change the currency code, there are meaningless amounts in the F0401 table because of mixed currencies. |
- Default Code
-
Enter the code that identifies the default currency that the system assigns when you enter vouchers for the supplier. You can override this value when you enter the voucher, or you can leave this field blank and assign the currency code for each transaction.
If you leave this field blank, the system uses the currency of the company assigned to the supplier record as the default. This is the CRRP field in the F0401 table.
- A/B Amount Code
-
Enter the currency in which you track address book amounts for the supplier, including amounts vouchered this year and the prior year. The currency that you specify is used to record and store transaction history.
If you leave this field blank, the system uses the currency code specified in the Amount Currency Code processing option. If that processing option is blank, the system uses the currency code of the company assigned to the Business Unit field on the Address Book Revision form.
This is the CRCA field in the F0401 table.
10.2 Converting Supplier Master Currency Codes
This section provides overviews of supplier currency conversion and the Address Book Conversion program, and discusses how to:
-
Run the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program.
-
Set processing options for Address Book Conversion - F0401 (R890401E).
10.2.1 Understanding Supplier Currency Conversion
You might have to convert supplier currency codes and address book amounts for any number of reasons, including:
-
The suppliers want to receive payments in a different currency.
-
You want to submit payments to the suppliers in a different currency.
-
You want to view supplier address book (statistical) amounts in a different currency.
For example, assume several Japanese suppliers requested that you begin submitting their payments in Canadian dollars (CAD). You can run the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program (R890401E) to convert the supplier currency code for those specific suppliers from Japanese yen (JPY) to CAD.
The Address Book Conversion - F0401 program converts these currency code and amount fields in the F0401 table at the same time or independently of one another:
-
Default Code (CRRP).
To comply with multiple requests from suppliers who want to receive payments in a different currency, run this program to convert the default currency code for those suppliers. Alternatively, if you have just a few currency codes to convert, you can change them manually on the Supplier Master Revision form.
-
A/B Amount Code (CRCA).
To view address book balance amounts for suppliers in a different currency, run this program to convert the address book currency code and these amounts in the F0401 table:
-
Statistical amounts (year-to-date voucher amounts, prior-year voucher amounts, and so on). Statistical amounts appear on the Additional Supplier Information form, which can be accessed from the Supplier Master Revision form.
-
Limit amounts (minimum and maximum purchase order amounts). Limit amounts appear in the Purchasing 2 section of the Supplier Master Revision form.
-
10.2.2 Understanding the Address Book Conversion Program
The use the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program to convert default currency codes, address book currency codes and amounts, or both for multiple suppliers. To do so, you must specify this information in the processing options for Address Book Conversion - F0401 program:
-
Exchange rate date to use to convert address book amounts.
-
Currency code to use to convert address book currency code and amounts. The system updates the A/B Amount Code (CRCA) field in the F0401 table.
-
Currency code to use to convert default currency codes. The system updates the Currency Code field (CRRP) in the F0401 table.
You can set up different versions of the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program. if you want to convert different currency codes for specific suppliers. For example, you might set up one version of the program to convert default currency codes only, another version to convert address book currency codes and amounts only, and still another to convert both.
Use the data selection to select only those suppliers that you want to convert to another currency. If you do not specify their address book numbers, the conversion program converts all suppliers. To convert amounts for all suppliers assigned a certain category code, specify the category code.
10.2.2.1 Exceptions Report
When you run the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program, the system prints an exceptions report. Review the report for any of these messages, and rerun the conversion program if necessary:
-
No processing errors.
The conversion program updates the F0401 table if you set the processing option to update address book balances.
-
Currency exchange rate not found.
The currency code that you are converting to is not set up in the exchange rate table, or the exchange rate or effective date is not set up for the currency code.
-
Invalid currency entered.
The currency code that you entered in either or both of the currency processing options is not valid.
-
Update error - record locked or not found.
The supplier master record is in use.
10.2.2.2 Example: Converting Supplier Amounts from U.S. Dollars to Canadian Dollars
This example shows supplier address book amounts before and after converting from U.S. dollars (USD) to Canadian dollars (CAD).
10.2.2.3 Before Converting Supplier Currency Codes
The Default Code and A/B Amount Code fields on the supplier master record are USD.
You set the processing options for the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program as follows:
-
Address book and amounts currency = CAD
-
Default currency code = blank
-
Minimum order and maximum order values = 50
The exchange rate in the F0015 table is 1 USD = 1.59190 CAD.
10.2.2.4 After Converting Supplier Currency Codes
After you run the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program, the address book amounts for the supplier are in CAD; however, their payments remain in USD, as shown in this table:
| F0401 Field | Description | Before Conversion | After Conversion | Rounded From |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A6CRRP | Currency Code - A/P | USD | USD | Not applicable |
| A6CRCA | Currency Code - A/B | USD | CAD | Not applicable |
| A6AYPD | Amount Vouchered Year-to-Date | 157,500.00 USD | 250,724.25 CAD | Not applicable |
| A6APPD | Amount Vouchered Prior Year End | 138,000.00 USD | 219,682.20 CAD | Not applicable |
| A6ABAM | Address Book Amount | Not used | Not used | Not applicable |
| A6ABA1 | Address Book Amount | Not used | Not used | Not applicable |
| A6APRC | Open Order Amount | 3,000.00 USD | 4,775.70 CAD | Not applicable |
| A6MINO | Minimum Order Value | 15,000.00 USD | 23,900.00 CAD | 23,878.50 CAD |
| A6MAXO | Maximum Order Value | 30,000.00 USD | 15,350.00 CAD | 47,757.00 CAD |
|
Important: The field A6ABAM stores a user-defined fixed amount and the field A6ABA1 is not functional in the F0401 table. If you use either of these fields, be aware that the conversion program converts the amounts, regardless of whether they are monetary amounts. |
10.2.2.5 Example: Converting Parent/Child Structure with Different Currencies
If you have a parent/child structure with different default and address book currency codes, you can use the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program to convert the parent independently from its children or vice versa. With this flexibility, you can continue to track address book amounts in the currency of the parent company while issuing invoices or submitting payments to some of its subsidiaries in another currency. This flexibility also enables you to convert address book amounts at the subsidiary level, to convert the currencies of a parent and its children at the same time, and so on.
10.2.2.6 Before Converting Currency Codes
This table shows a parent/child relationship with different currencies before the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program has been run to convert customer currency codes:
| Relationship | Address Book Currency | Default Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Parent | JPY | JPY |
| Child 1 | JPY | USD |
| Child 2 | JPY | GBP |
| Child 3 | JPY | EUR |
Child 1 and Child 3 have requested that you issue their invoices in CAD. You run the Address Book Conversion - F0401 program to convert their default currency from USD and euro (EUR), respectively, to CAD.
|
Note: You can convert the currency codes of a parent and its children at the same time, if applicable. |
10.2.2.7 After Converting Currency Codes
This table shows the results after running the Address Book Conversion - F0401 conversion program:
| Relationship | Address Book Currency | Default Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Parent | JPY | JPY |
| Child 1 | JPY | CAD |
| Child 2 | JPY | GBP |
| Child 3 | JPY | CAD |
This example shows that you can track address book amounts in the currency of the parent company (JPY) while issuing invoices to its subsidiaries in different currencies (CAD and GBP).
10.2.3 Running the Address Book Conversion - F0401 Program
The Address Book Conversion - F0401 program is not set up on a menu.
Access the Batch Versions form and enter the program number R890401E in the Batch Application field.
10.2.4 Setting Processing Options for Address Book Conversion - F0401 (R890401E)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
10.2.4.1 Update
- 1. Update Supplier Master Balances
-
Specify whether to update the statistical information for the supplier master record, such as the vouchered year-to-date and vouchered prior year. Values are:
Blank: Do not update the statistical information.
1: Update the statistical information.
- 2. Exchange Rate Date
-
Specify the date to use to retrieve the exchange rate from the F0015 table. If you leave this processing option blank, the system uses today's date to retrieve the exchange rate.
10.2.4.2 Currency
- 3. Address Book Currency Code
-
Specify the currency code to use to update the A/B Amount Code field on the Supplier Master Revision form. If you leave this processing option blank, the system does not update the field.
- 4. Currency Code
-
Specify the currency code to use to update the Default Code field on the Supplier Master Revision form. If you leave this processing option blank, the system does not update the field.
10.2.4.3 Rounding
- 5. Rounding Factor
-
Specify the factor by which to round amounts for each of these fields:
-
Minimum Order Value
-
Maximum Order Value
For example, if you enter 100, the system rounds the amount to the nearest 100, if you enter 50, the system rounds to the nearest 50, and so on.
-
10.3 Setting Up Multicurrency AAIs for Accounts Payable
This chapter provides an overview of the multicurrency AAIs for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable and discusses how to:
-
Set up AAIs for payable bank accounts.
-
Set up AAIs for payable trade accounts.
-
Set up AAIs for unrealized gains and losses on foreign currency vouchers.
-
Set up AAIs for realized gains and losses on foreign currency payments.
-
Set up AAIs for realized gains and losses on alternate currency payments.
-
Set up AAIs for the clearing account for alternate currency payments.
10.3.1 Understanding Multicurrency AAIs for Accounts Payable
You set up AAI items to calculate currency gains and losses. The system uses these AAIs to distribute the gain or loss to the correct general ledger account. The potential for a currency gain or loss is due to exchange rate fluctuations that occur between either:
-
The time a voucher is entered and payment is issued (realized gain/loss).
-
The time a voucher is entered and the end of a period if the voucher is still open (unrealized gain/loss).
For payments and open vouchers in a foreign currency, the gain or loss is calculated between the domestic and foreign currencies. For payments in an alternate currency, the gain or loss is calculated between the domestic, foreign, and alternate currencies.
You also set up AAI items to define trade accounts for foreign currency vouchers and bank accounts for foreign and alternate currency payments.
Some AAI items have a suffix of xxx to accommodate a three-character currency code. You use the xxx suffix to set up multiple currency-specific AAI items for each company. If you do not specify a currency code (that is, leave it blank), the system uses the currency code of the company as the default.
10.3.2 Setting Up AAIs for Payable Bank Accounts
AAI item PB (payable bank) specifies the default bank account that the system assigns if you do not assign a bank account when you enter a voucher. The bank account can be either a monetary account, which has a currency designation or a non-monetary account, which has no currency designation. The system credits the bank account for the amount entered on the payment The account must include a business unit.
The sequence in which the system searches for AAI item PB is:
-
PBxxx. The system uses PBxxx that is associated with the company entered on the voucher, where xxx is the transaction currency of the voucher.
-
PBxxx. The system uses PBxxx for company 00000, where xxx is the transaction currency of the voucher.
-
PBxxxx. The system uses PBxxxx that is associated with the company entered on the voucher, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PBxxxx. The system uses PBxxxx for company 00000, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PB. The system uses PB that is associated with the company entered on the voucher.
-
PB. The system uses PB for company 00000.
If you do not assign a bank account when you enter a voucher, the system assigns a GL bank account with which to pay the voucher based on AAI item PB. The bank account can be either a monetary account, which has a currency designation or a non-monetary account, which has no currency designation. A currency code assigned to a bank account designates it as a monetary account and foreign currency vouchers can be paid only in that currency.
Different currency conditions apply depending on whether the bank account is monetary or non-monetary.
10.3.2.1 Monetary Bank Account
If you enter a foreign currency voucher and you or the system assigns a monetary bank account, the bank account currency must be the same as the transaction currency of the voucher and the base currency of the company associated with the bank account must be the same as the base (domestic) currency of the voucher.
For example, assume the company base currency is U.S. dollars (USD). You enter a foreign currency voucher in the euro (EUR). The monetary bank account associated with the payment must also have a currency of EUR.
You can change the bank account to any monetary bank account if both of these criteria apply:
-
The currency of the monetary bank account is the same as the transaction currency of the voucher.
-
The base currency of the company associated with the bank account is the same as the base (domestic) currency of the voucher.
The system validates for both of these criteria.
|
Note: When you enter a manual payment for a foreign currency voucher, you cannot override the default bank account with a bank account that is in the domestic (base) currency of the voucher. You receive an error message Currency Code Invalid for Bank Account.Similarly, if you create a payment group and enter an override bank account (in the processing options) with the same currency as the domestic voucher and set the payment currency to the domestic voucher currency, the system does not include the voucher in the payment group. Again, the bank account currency must be the same as the transaction currency of the voucher and the base currency of the company associated with the bank account must be same as the base (domestic) currency of the voucher. |
10.3.2.2 Non-Monetary Bank Account
If you enter a foreign currency voucher and you or the system assigns a non-monetary bank account, the bank account currency must be the same as the base currency of the voucher.
For example, assume the company base currency is USD. You enter a foreign currency voucher in EUR. The bank account associated with the voucher must have a currency of USD.
You can change the bank account to any non-monetary bank account that has the same domestic currency as the voucher company. You can then pay any foreign currency voucher from that bank account, provided it is in the transaction currency of the voucher.
10.3.3 Setting Up AAIs for Payable Trade Accounts
AAI item PC defines the default trade account that serves as a holding or clearing account until vouchers are paid. The system assigns the default trade account if you do not specify a different trade account using the G/L Offset field when you enter the voucher. The trade account can be specific to a supplier so that when you enter a voucher, the system uses the value of the G/L Offset field from the supplier master record.
The system uses the account number assigned to AAI item PC to create a debit in the trade account for the amount of the voucher. The account number must include a business unit. No special multicurrency considerations exist for this AAI item. Unlike other AAIs, you cannot assign a currency code xxx to AAI item PC.
The sequence in which the system searches for AAI item PC is:
-
PCxxxx. The system uses PCxxxx that is associated with the company entered on the voucher, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PCxxxx. The system uses PCxxxx for company 00000, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PC. The system uses PC that is associated with the company entered on the voucher.
-
PC. The system uses PC for company 00000.
10.3.4 Setting Up AAIs for Unrealized Gain and Losses on Foreign Currency Vouchers
If you want the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system to automatically calculate unrealized gains and losses, you must set up AAIs. These AAI items define the accounts that the system uses for unrealized gains and losses on foreign currency vouchers that are open at the end of a period:
When you run the A/P Unrealized Gain/Loss Report (R04425), the system uses the account number assigned to PV and PW to create foreign currency unrealized gains and losses on open vouchers and the account number assigned to PR to create foreign currency unrealized gain or loss offsets. To create an unrealized gain or loss amount, the system compares the amount of the original voucher to the amount of the open voucher (which is revalued based on the exchange rate at the end of the period) and creates a gain or loss for the difference.
The hierarchy for AAI items PV, PW, and PR is the same. This example shows the sequence in which the system searches for AAI item PV:
-
PVxxx. The system uses PVxxx that is associated with the company entered on the voucher, where xxx is the transaction currency of the voucher.
-
PVxxx. The system uses PVxxx for company 00000, where xxx is the transaction currency of the voucher.
-
PVxxxx. The system uses PVxxxx that is associated with the company entered on the voucher, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PVxxxx. The system uses PVxxxx for company 00000, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher.
-
PV. The system uses PV that is associated with the company entered on the voucher.
-
PV. The system uses PV for company 00000.
10.3.5 Setting Up AAIs for Realized Gains and Losses on Foreign Currency Payments
These AAI items define the accounts that the system uses for realized gains and losses on foreign currency payments:
The system creates a gain or loss entry when a payment is posted the system and uses the account number assigned to PG and PL to create foreign currency gain and loss amounts. To create a gain or loss amount, the system multiplies the voucher amount by the difference in the exchange rate between the original voucher and the foreign currency payment.
The hierarchy for AAI items PG and PL is the same. This example shows the sequence in which the system searches for AAI item PG:
-
PGxxx. The system uses PGxxx that is associated with the company entered on the payment, where xxx is the transaction currency of the payment.
-
PGxxx. The system uses PGxxx for company 00000, where xxx is the transaction currency of the payment.
-
PGxxxx. The system uses PGxxxx for company 00000, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher that is paid.
-
PG. The system uses PG that is associated with the company entered on the payment.
-
PG. The system uses PG for company 00000.
10.3.6 Setting Up AAIs for Realized Gains and Losses on Alternate Currency Payments
The gains and losses for alternate currency payments are recorded separately from standard gains and losses and are handled by using different accounts and AAIs. These AAI items define the accounts that the system uses for realized gains and losses on alternate currency payments:
The system creates a gain or loss entry when the payment is post and uses the account number assigned to AAI items PY and PZ to create alternate currency gains and losses as follows:
-
Creates an entry in the gain account if the amount derived by converting from an alternate currency directly to a domestic currency is greater than the amount derived by converting from an alternate currency to a foreign currency to a domestic currency.
-
Creates an entry in the loss account if the amount derived by converting from an alternate currency directly to a domestic currency is less than the amount derived by converting from an alternate currency to a foreign currency to a domestic currency.
The hierarchy for AAI items PY and PZ is the same. This example shows the sequence in which the system searches for AAI item PY:
-
PYxxx. The system uses PYxxx that is associated with the company entered on the payment, where xxx is the transaction currency of the payment.
-
PYxxx. The system uses PYxxx for company 00000, where xxx is the transaction currency of the payment.
-
PYxxxx. The system uses PYxxxx that is associated with the company entered on the payment, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher that is paid.
-
PYxxxx. The system uses PYxxxx for company 00000, where xxxx is the GL offset on the voucher that is paid.
-
PY. The system uses PY that is associated with the company entered on the payment.
-
PY. The system uses PY for company 00000.
10.3.7 Setting Up AAIs for the Clearing Account for Alternate Currency Payments
AAI item P7 defines the alternate currency clearing account used when you post alternate currency payments. The alternate currency clearing account tracks the conversion from the payment amount to the original voucher amount and provides an audit trail of the offset amounts for:
-
The original foreign currency voucher and the domestic side of the foreign currency voucher.
-
The alternate currency payment and the domestic side of the alternate currency payment.
The clearing account must be in the same company as the bank account from which the payment is made. It must include a business unit and cannot be a monetary (currency-specific) account. The alternate currency clearing account balances on the domestic side, but not on the foreign side. This is because the foreign side contains different currencies, which never balances.
The sequence in which the system searches for AAI item P7 is:
-
The system uses P7 that is associated with the company entered on the payment.
-
The system uses P7 for company 00000.
These t-accounts show entries for a foreign currency voucher (CAD), the domestic side of the voucher (USD), and an alternate currency payment (EUR).
Figure 10-2 T-accounts with an alternate currency payment

Description of ''Figure 10-2 T-accounts with an alternate currency payment''
10.4 Setting Up Payment Translation Codes
The system provides payment translation codes in UDC table 98/CT for writing payments in multiple currencies. The system uses payment translation codes, which are hard-coded, to translate numbers into words using the appropriate language and decimal positions when you write payments.
Review this form for examples of payment translation codes:
Figure 10-3 Work With User-Defined Codes form
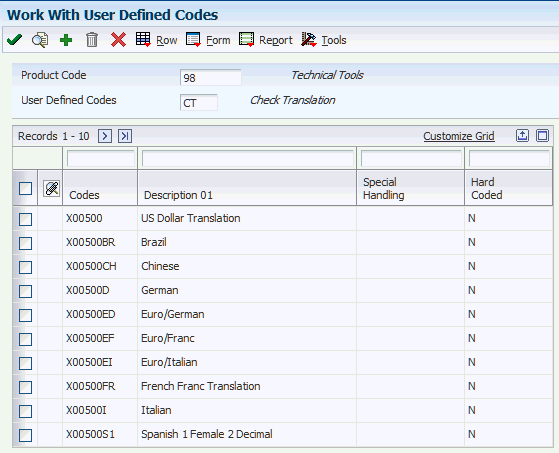
Description of ''Figure 10-3 Work With User-Defined Codes form''
10.5 (MEX) Setting Up Payment Translation Codes
This section provides an overview of how to print currency descriptions and discusses how to set processing options for Convert Numeric values to words - Spanish- (P00500S2).
10.5.1 Understanding How to Print Currency Descriptions
You can set up the X00500S2 - Spanish (male) translation routine to print the description, or name, of the currency after the amount. For example, you can set up this translation routine to print the word Pesos after the amount.
To set up this translation routine to print currency descriptions, you set up the processing options on the Convert Numeric values to words - Spanish program (P00500S2). To print currency descriptions, you must specify both the singular and plural versions of the currency description in the processing options. If you leave the processing options blank, the name of the currency does not print after the amount.
In addition, if you leave these processing options blank, the conjunction "con" prints between the whole number amount (peso) and the centavos. If you complete the processing options, the word "con" is omitted.
Specify X00500S2 as the translation routine in the processing options of the payment format program that you are using, for example, R04572.
See Entering Manual Foreign and Alternate Currency Payments.
10.5.2 Setting Processing Options for Convert Numeric Values to Words - Spanish (P00500S2)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
10.5.2.1 Printing
- 1. Currency Description Singular Form and 2. Currency Description Plural Form
-
Specify the singular form and plural form of the currency description.