19 Rating by Date and Time with Pipeline Manager
This chapter describes how to set up time models for the Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) Pipeline Manager.
For information about Pipeline Manager, see "About Pipeline Rating" in BRM Configuring Pipeline Rating and Discounting.
About Rating by Date and Time with Pipeline Manager
A time model defines a combination of time periods. Each time period covers a specific time range for one or more days.
You use time models and time periods to charge different prices for the same service depending on the day and time.
Each time period contains the following information:
-
Day code: The day or days the time period covers. For example, Weekdays (Mon.-Fri.).
-
Time interval: The time range the time period covers for the day code. For example, 08:00-17:00 Peak Time.
Important:
A time model must cover all the days of the week. Within a time model, although you can create multiple day codes, you cannot use the same day in multiple day codes.For example, one time model contains these time periods and is associated with a price model that charges for GSM telephony service as shown in Table 19-1:
Table 19-1 Rating by Date and Time
| Time Period | Day Code and Time Interval | Charge from Price Model (Euro Cents per Minute) |
|---|---|---|
|
WEEKPEAK - Weekdays Peak |
Weekdays (Mon.-Fri.) 08:00 - 17:00 |
.15 |
|
WEEKOFF1 - Weekdays Off-Peak 1 |
Weekdays (Mon.-Fri.) 17:00 - 22:00 |
.12 |
|
WEEKOFF2 - Weekdays Off-Peak 2 |
Weekdays (Mon.-Fri.) 22:00 - 08:00 |
.10 |
|
WENDOFF - Weekend Off-Peak |
Weekends (Sat., Sun., Holidays) 00:00-24:00 |
.09 |
Figure 19-1 shows a map from Pricing Center showing the time model in graphic form:
Figure 19-1 Example Time Model in Pricing Center
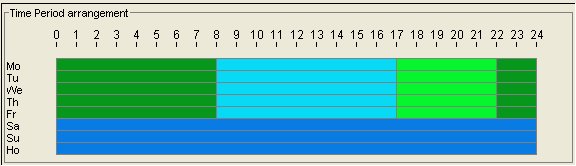
Description of ''Figure 19-1 Example Time Model in Pricing Center''
Note:
Holidays are not treated as normal days, so you can add holidays to a time period without conflicting with any other days.You include time models and time periods in rate plan configurations, which specify a price model for a rate plan version. When a call is rated, the time model and time period, with the service code and impact category, determine the charge.
See "About Pipeline Rate Plan Configurations".
About Holiday Calendars
A holiday calendar is a set of dates that you designate as holidays. Each date can either be a specific date valid only in one year, such as May 11, 2003 for Mother's Day in the US, or a recurring date valid each year, such as January 1 for New Year's Day.
You include a calendar in a rate plan. The rating module uses the calendar to determine if a date in an event detail record (EDR) is a holiday. You can include the same calendar in multiple rate plans, but you can also create different calendars for different rate plans.
Configuring Date and Time Rating
To configure date and time rating, do the following:
-
Create time models in Pricing Center and link them to rate plan configurations.
-
Create holiday calendars in Pricing Center and link them to rate plans. See "Creating Holiday Calendars".
-
Configure the DAT_TimeModel and DAT_Calendar modules.
Note:
When you update time model and calendar data, you must use the Reload semaphore to reload data into the DAT_TimeModel and DAT_Calendar modules. See "Reloading Data into a Pipeline Manager Module" in BRM System Administrator's Guide.
Creating Holiday Calendars
To charge special rates for a holiday, do the following in Pricing Center:
-
Create a holiday calendar, including each holiday you want to include in a given rate plan.
-
Include the holiday calendar in a rate plan.
-
Define a day code that includes Holiday.
For example, the time period in Figure 19-2 includes Holiday in its day code:
Figure 19-2 Defining a Day Code Including Holiday
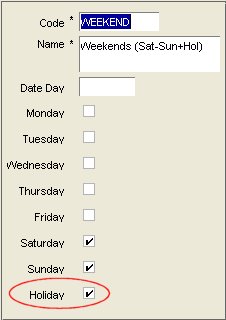
Description of ''Figure 19-2 Defining a Day Code Including Holiday''
-
Add the day code to a time period when defining a time model.
-
Include the time model in a rate plan configuration that is part of the same rate plan that includes the holiday calendar.
For more information, see Pricing Center Help.
About Special Day Rates
Use special day rates to create special rates for specific times or days, independent of time models. You can create two types of special day rates:
-
Global: Special day rates that apply to all accounts in your system. See "About Global Special Day Rates" and "Setting Up Global Special Day Rates".
-
Account-specific: Special day rates that apply only to one or more specific accounts in your system. You must create an extended rating attribute (ERA) for each account in Customer Center for this type of special day rate.
See "Setting Up Account-Specific Special Day Rates".
Important:
When you create a special day discount, such as a birthday discount, any usage that begins on the discounted day and continues into the next, non-discounted day is fully discounted. Discounting does not split the charge packet at midnight but applies the discount for the entire call. For example, a customer receives a discount for 10% off on all birthday calls. On his birthday, the customer makes a 40 minute call that starts at 11:50 p.m. and ends on 12:30 a.m. the next day. The entire 40 minutes is discounted 10%.
About Global Special Day Rates
You can adjust charges for all accounts in your system based on the following:
-
A specific date (for example, January 1, or a range of dates, for example April 1 through April 15)
-
One or more days of the week (for example Sunday, or Tuesday and Thursday)
-
A time period for the specified days
-
A time period for all days
You can adjust charges in the following ways:
-
A fixed amount (for example, reduce the charge by 1 dollar)
-
A percentage discount (for example, reduce the charge by 10%)
-
An absolute value (for example, replace the charge with 1 dollar)
This functionality is performed by the FCT_Dayrate module. To adjust the rate, the module finds EDRs that match the date and time, adjusts the charge, and overwrites the amount in the EDR.
For example, if you offer a 20% New Year's Day discount, the FCT_Dayrate module finds EDRs for calls made on January 1, calculates a 20% discount, and overwrites the charge in the EDR.
Special day charge adjustments are calculated after main rating. Therefore, rates based on time models are applied first, then adjusted separately by the special day rate.
Setting Up Global Special Day Rates
To set up special day rates that apply to all accounts, do the following:
-
Define special day rates in Pricing Center.
-
Configure the FCT_Dayrate module to calculate charges for date-based rates.
-
Configure the DAT_Dayrate module that stores the data used by the FCT_Dayrate module.
Note:
When you update special day rate data, you must use the Reload semaphore to reload data into the DAT_Dayratemodule.
Setting Up Account-Specific Special Day Rates
Important:
This procedure requires that you have the GSM Manager Customer Center Extension installed.To set up special day rates for a single account or group of accounts:
-
In Customer Center, open an account and create an ERA for the special day.
On the Promotion tab, select Special Day and enter the name BIRTHDAY and a date. For example, when creating a special day rate for a birthday, enter the date of the subscriber's birthday.
-
In Pricing Center, create a usage type that corresponds to the special day.
For example, for a birthday special rate, you might create a usage type with a code of BIRTH.
-
In Pricing Center, include the usage you defined in a discount model.
You specify the usage type as part of the discount master. The discount model also specifies the amount of the discount for this rate.
-
Configure the IRL_UsageType iRule to map this usage type to EDR data.
For example, for the usage type BIRTH, add a line similar to the following to the IRL_UsageType.data file:
N;N;.;.;.;.;.;.;.;.;.;.;Y;.;.;BIRTH
For more information on using the IRL_UsageType iRule, see "Configuring the IRL_UsageType iRule for ERAs".