Using Java Bean Services as REST Services
Overview
Java APIs are business interfaces based on Java classes. Some specialized Java APIs whose methods must use parameters of either serializable Java Beans or simple data types such as String, Int, and so forth can be categorized as Java Bean Services.
Java Bean Services are a subtype of Java interface. You can locate them through a search by "Interface Subtype" category and "Java Bean Services" category value. Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway allows these specialized Java classes to be exposed as REST services.
Similar to PL/SQL REST services, once Java Bean Services have been successfully deployed as REST services, an integration developer can invoke the deployed REST services from client program using languages like Java, PHP, Javascript, Python, and so on.
To better understand how to use the deployed service to fetch and use application data, detailed design-time and runtime tasks are included in this chapter. For the example described in the following sections, Oracle JDeveloper 10g (10.1.3.3.0) is used to create a project with a Java class and invoke the service.
The following REST service invocation examples are included in this section:
Invoking a REST Service Using HTTP GET Method
REST Service Invocation Scenario
Consider a Java Bean service 'REST Service Locator' (oracle.apps.fnd.rep.ws.service.EbsRestLocator) as an example to explain the REST service invocation. REST Service Locator is a sample Java API that consists of methods to retrieve details about deployed Oracle E-Business Suite REST services.
A Java client is used to make HTTP GET request to the getRestInterface service operation. The getRestInterface service operation returns the details of a REST service identified by its internal name.
In this example, HTTP Basic Authentication scheme is used to provide username and password information in the HTTP request header. The user credentials are authenticated and authorized by ISG's REST Service Provider. After validation, the getRestInterface service operation executes the request for the authenticated user.
After the successful service invocation, the client will receive a REST response message with the details of the REST service whose internal name has been passed in HTTP URL at run time during service invocation.
Invoking a REST Service Using Java
Based on the REST service invocation scenario, the following tasks are included in this section:
Deploying a REST Service
Use the following steps to deploy the Java Bean Service called REST Service Locator:
-
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite as a user who has the Integration Repository Administrator role.
Select the Integrated SOA Gateway responsibility and the Integration Repository link from the navigation menu.
-
In the Integration Repository tab, click Search to access the main Search page.
-
Click Show More Search Options to display more search fields.
Enter the following key search values as the search criteria:
-
Category: Interface Subtype
-
Category Value: Java Bean Services
-
-
Click Go to execute the search.
Click the REST Service Locator interface name link to open the interface details page.
-
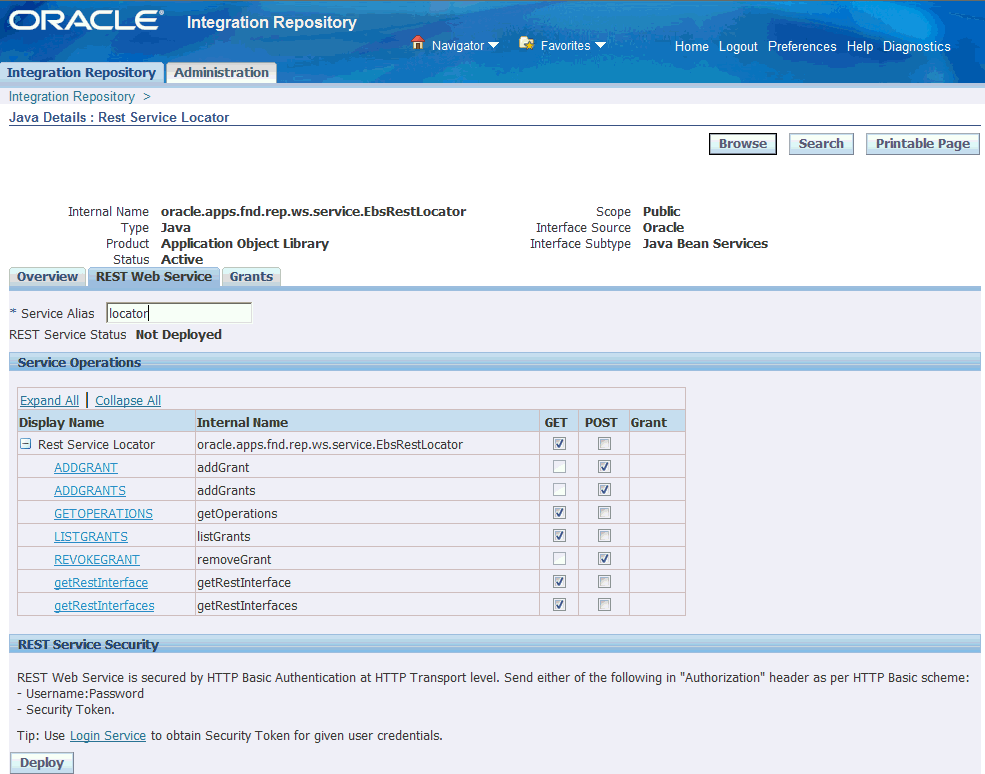
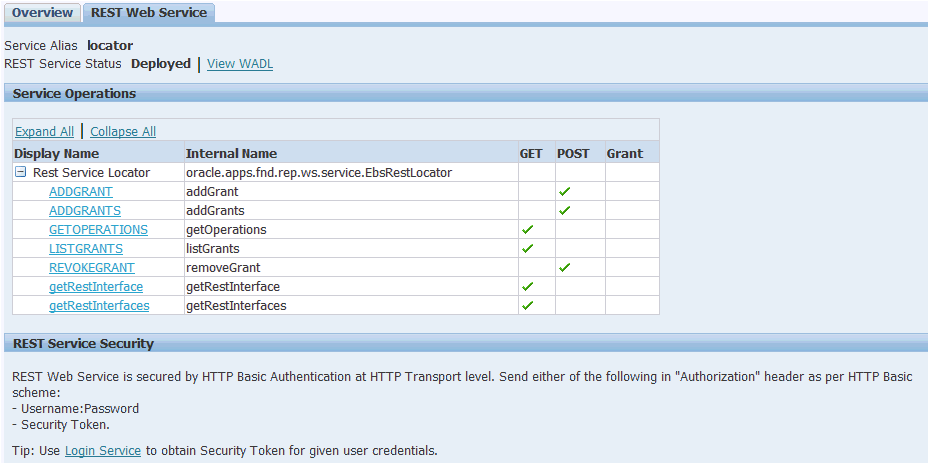
In the REST Web Service tab, enter the following information:
Interface Details Page with REST Web Service Tab to Deploy a Java REST Service
-
Service Alias: locator
The alias will be displayed as the service endpoint in the WADL and schema for the selected method or operation.
-
Select Desired Service Operations
In the Service Operations region, HTTP method check boxes are preselected.
Note that if a Java method is annotated with a specific HTTP method, then the corresponding HTTP method check box is preselected for that method. The administrator can change the HTTP method check box selection before deploying the service.
For more Java Bean Services annotation guidelines, see Annotations for Java Bean Services.
In this example, the 'getRestInterface' service operation has been annotated with the GET HTTP method; therefore, the GET check box is automatically selected.
-
-
Click Deploy to deploy the service to an Oracle E-Business Suite environment.
Once the REST service has been successfully deployed, 'Deployed' appears in the REST Service Status field along with the View WADL link. Click the View WADL link to view the deployed service WADL description.
For more information on deploying REST services, see Deploying REST Web Services, Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway Implementation Guide.
Creating a Security Grant
After deploying the REST Service Locator as a REST service, the integration administrator can create a security grant to authorize the service or method access privileges to a specific user, a user group, or all users.
Use the following steps to create a security grant:
-
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite as a user who has the Integration Repository Administrator role. Select the Integrated SOA Gateway responsibility and the Integration Repository link from the navigation menu.
-
Perform a search to locate the REST Service Locator service the administrator just deployed earlier.
-
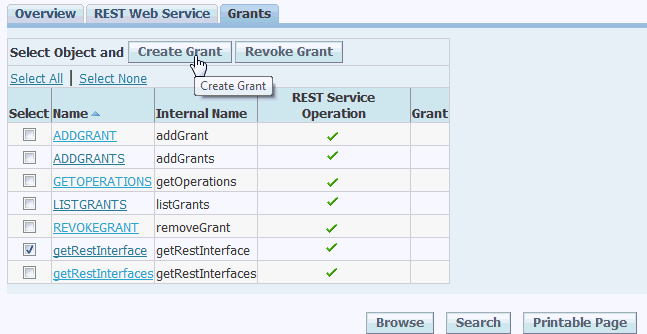
In the interface details page of the selected custom Java Bean Services, click the Grants tab.
-
Select the
getRestInterfacemethod check box and then click Create Grant.Interface Details Page with Grants Tab
-
In the Create Grants page, select "All Users" as the Grantee Type.
Note: In this example, the
getRestInterfaceservice operation is granted to all users. In actual implementation, you should define strict security rules. Create grant to a user or more appropriately to a group of users defined by roles and responsibilities.Create Grants Page
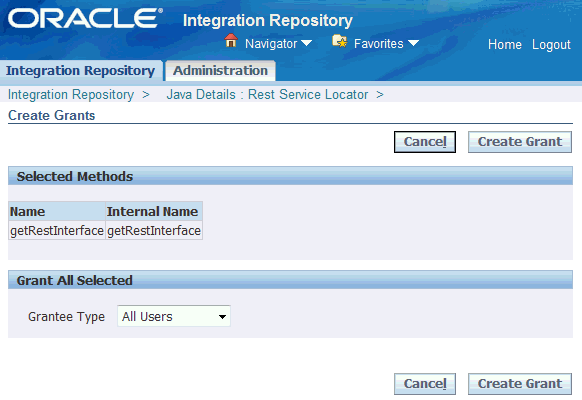
Click Create Grant. This grants the selected method access privilege to all Oracle E-Business Suite users.
Recording Resource Information from Deployed WADL
To obtain service resource information from the deployed WADL for the REST Service Locator service, an integration developer clicks the View WADL link in the REST Web Service tab.
REST Web Service Tab with Deployed "View WADL" Link
The following WADL description appears:
<xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<application name="EbsRestLocator" targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/soaprovider/pojo/ebsrestlocator/"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/soaprovider/pojo/ebsrestlocator/"
xmlns="http://wadl.dev.java.net/2009/02" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:tns1="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/addgrant/"
xmlns:tns2="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/addgrants/"
xmlns:tns3="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/getoperations/"
xmlns:tns4="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/getrestinterface/"
xmlns:tns5="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/getrestinterfaces/"
xmlns:tns6="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/locatorsvc/removegrant/">
<grammars>
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=addgrant.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=addgrants.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=getoperations.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=getrestinterface.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=getrestinterfaces.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/servicelocator/?XSD=removegrant.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
</grammars>
<resources base="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/locator/">
<resource path="addGrant/">
/
...
</resource path>
...
<resource path="/getRestInterface/{irepClassName}/">
<param name="irepClassName" style="template" required="true" type="xsd:string" />
<method id="getRestInterface" name="GET">
<request>
<param name="ctx_responsibility" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_respapplication" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_securitygroup" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_nlslanguage" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_orgid" type="xsd:int" style="query" required="false" />
</request>
<response>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns4:getRestInterface_Output" />
<representation mediaType="application/json" type="tns4:getRestInterface_Output" />
</response>
</method>
</resource>
<resource path="removeGrant/">
/
...
</resource path>
</application>
Copy or record the following information which will be used later when defining a Java client:
-
<resources base>="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/locator/">This information
http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/locator/will be used later in Java client program as baseUrl. -
<resource path>="/getRestInterface/{irepClassName}/">This information
/getRestInterface/{irepClassName}/will be used later to form the later part of the service URL. The input{irepClassName}is a path variable, and it will be replaced with the internal name of an interface.
Creating a Project with a Java Class
This section describes how to create a project with a Java class that will be used to invoke the REST Service Locator service.
To create a project and a Java class:
-
Open Oracle JDeveloper.
-
From the main menu, choose File > New.
In the New Gallery window, expand the General category and select 'Applications'. In the Items list, select Custom Application.
Click OK. The "Create Custom Application - Name your application" page is displayed.
-
Enter an appropriate name for the application in the Application Name field, for example ISGJavaRESTProject. Click Next.
-
The "Create Custom Application - Name your project" page is displayed. Enter an appropriate name for the project in the Project Name field, for example ISGJavaRESTClient.
In the Project Features tab, select 'Java' from the Available list. Move the selected feature from the "Available" window to the "Selected" window using the right arrow button.
Click Next.
-
Click Finish in the Configure Java Settings dialog box.
The newly created project should be visible in the Projects workspace.
-
Select and right-click on the project name you just created in the Application Navigator and choose New from the drop-down selection menu.
-
In the New Gallery window, expand the General category and select 'Java'. In the Items list, select Class. Click OK.
-
In the Create Java Class dialog, change the default class name to 'RestInvocationGETMethod'. Accept all other defaults and click OK.
-
The new class opens automatically in the source editor, displaying the skeleton class definition.
Replace the skeleton class definition with the following Java code:
package isgrestget; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URL; import com.sun.jersey.core.util.Base64; public class RestInvocationGETMethod { /** * This Method invokes the a rest service using HTTP GET Method with path parameter in URL */ public static void invokeREST(String svcUrlStr,String username,String passwd,String pathParam) throws IOException { String getURL = svcUrlStr + "/" + pathParam; URL url = new URL(getURL); //Obtaining connection to invoke the service HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); String auth = username + ":" + passwd; byte[] bytes = Base64.encode(auth); String authStr = new String(bytes); //Setting Http header values conn.setRequestMethod("GET"); conn.setRequestProperty("Authorization", "Basic " + authStr); conn.setRequestProperty("Accept", "application/json"); conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Language", "en-US"); conn.setUseCaches(false); conn.setDoInput(true); conn.setDoOutput(true); conn.connect(); System.out.println("\n 'GET' request sent to URL : " + url); System.out.println("\n Response code - " + conn.getResponseCode()); //Get Response String response = null; try { response = readHttpResponse(conn); } finally { if (conn != null) conn.disconnect(); } //Show Response System.out.println("Response is : \n" + response); } /** * This method reads response sent by the server and returns it in a string representation. */ private static String readHttpResponse(HttpURLConnection conn) { InputStream is = null; BufferedReader rd = null; StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer(); try { if (conn.getResponseCode() >= 400) { is = conn.getErrorStream(); } else { is = conn.getInputStream(); } rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); String line; while ((line = rd.readLine()) != null) { response.append(line); response.append('\n'); } } catch (IOException ioe) { response.append(ioe.getMessage()); } finally { if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (Exception e) { } } if (rd != null) { try { rd.close(); } catch (Exception e) { } } } return (response.toString()); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String baseUrl = "http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/locator"; String svcUrlStr1 = baseUrl + "/getRestInterface"; //Invoke REST service invokeREST(svcUrlStr1, "<EBS_username>", "<password>", "PLSQL:FND_PROFILE"); } }Please note that resource information recorded earlier from the deployed WADL is now placed in the
baseUrlandsvcUrlStr1elements. PLSQL:FND_PROFILE is the interface internal name and that it is assumed to be deployed in the instance.Note: Use https (instead of http) in the
baseUrlif your Oracle E-Business Suite instance is running on the SSL-enabled environment. Additionally, you need to import the SSL certificate into your client JVM's keystore. -
Replace
<hostname>:<port>,<EBS_username>, and<password>with the actual values in the code. -
Save your work by selecting File > Save All.
-
Add required library for JSON format:
Use the following steps to add the required library file to the project properties.
-
Select and right-click on the project name you just created earlier to open a selection menu.
-
Select Project Properties from the menu.
The Default Properties dialog box opens.
-
Select Libraries and Classpath, and click Add Library. The Add Library dialog box opens.
-
In the Add Library dialog box, select the Project folder and then click New.
The Create Library dialog box opens.
-
In the Library Name field, enter 'Jersey-bundle_1.0.0.0_1-1-5-1.jar'.
Click Add Entry. The Select Path Entry dialog box appears.
-
In the Select Path Entry dialog box, locate and select the 'Jersey-bundle_1.0.0.0_1-1-5-1.jar' file that you have downloaded. This adds it to the Classpath.
Click OK. The 'Jersey-bundle_1.0.0.0_1-1-5-1.jar' is now added to the Project folder.
-
The Project Properties dialog box appears. Click OK. This project is now set up with the required library.
-
Invoking a REST Service Using a Java Class
After creating a project with a Java class RestInvocationGETMethod.java, you need to compile and execute the process to invoke the REST service.
Use the following steps to compile and run the Java class:
-
In the Application Navigator, right-click on the
RestInvocationGETMethod.javaJava class you just created at the design time. Select Make from the menu. -
Right-click on the
RestInvocationGETMethod.javaJava class. Select Run from the menu.
Monitor this process and check for successful compilation in the Log window. Verify that the execution is successful in the Log window.
Request Header Information
In this example, getRestInterface Java method is exposed as a REST service operation with the GET method. There is no input payload for the GET method. The path variable {irepClassName} is replaced with actual value "PLSQL:FND_PROFILE" sent as part of the HTTP URL shown below when the getRestInterface REST service operation is invoked.
URL = http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/locator/getRestInterface/PLSQL:FND_PROFILE
Note: For GET requests, JSON is the default output response format. Use Accept header application/xml to receive response in XML format. If Content-Type header is sent in a GET HTTP request, it will be ignored.
Request Headers
Authorization: Basic xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Accept: application/json
Content-Language: en-US
Viewing Output Message
When the REST service is successfully invoked, the following output in JSON format appears in the Log window:
{
"OutputParameters" : {
"EbsRestServiceBean" : [ {
"alternateAlias" : "plsql/PLSQL:FND_PROFILE",
"serviceAlias" : "profile",
"serviceName" : "PLSQL:FND_PROFILE",
"wadlUrl" : "http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/profile?WADL"
} ],
"ControlBean" : [ {
"fields" : "",
"filter" : "",
"limit" : "",
"offset" : ""
} ]
}
}
Notice that the service information identified by its internal name PLSQL:FND_PROFILE is returned. For example, the WADL URL, service name, and service alias are included as part of the response message.
Annotating and Invoking a Custom Java Bean Service
Since not all Java APIs registered in the Integration Repository can be exposed as REST services, only some specialized Java APIs described earlier with proper annotation can be exposed as REST services. To better understand how to annotate those specialized Java APIs as Java Bean Services, and how to invoke Java Bean Services with REST service security, this section describes the entire process from annotating a custom Java API to invoking the service using the HTTP GET method.
REST Service Invocation Scenario
This example uses a custom Java API called Employee Service (oracle.apps.per.sample.service.EmployeeInfo) to explain the entire annotation and upload processes as well as the service invocation. There are two invocation scenarios. One scenario is to get employee details, and the other one is to get direct reports for the logged in user.
To get employee details, an HTML page with Javascript is used to make an HTTP GET request to the getPersonInfo service operation contained in the custom API. An employee ID is provided at run time for the service to retrieve the associated employee name and the employee's manager name. After the successful service invocation, the employee details corresponding to the employee ID are displayed in the HTML page.
To get direct reports for the logged in user, a different HTML page with Javascript is used in this scenario to make an HTTP GET request to the getDirectReports service operation. The logged in user credentials are provided when the getDirectReports service operation is invoked. After the successful service invocation, the logged in user's subordinates or the user's direct reports are displayed in the HTML page with the requested number of records shown in each page.
High Level Process Flow for Creating Custom Java Bean Services
To develop custom Java Bean Services, an integration repository developer needs to create and annotate the custom Java APIs based on the Integration Repository Annotation Standards for Java Bean Services. After the interface creation, an integration repository administrator needs to validate the annotated APIs. If no error occurs during the validation, the administrator will then upload the custom APIs to Oracle Integration Repository where they can be published as REST services through Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway.
For annotation information, see: Annotations for Java Bean Services.
Annotating and Invoking a Custom Java Bean Service from HTML Pages with Javascript
Based on the REST service invocation scenario, the following tasks are included in this section:
-
Parsing and Uploading the Annotated Custom Java Bean Service to the Integration Repository
-
Invoking a Custom REST Service from HTML Pages with Javascript
Creating and Compiling Custom Java APIs
This section describes how to create and annotate a custom Java Bean Service called Employee Information (oracle.apps.per.sample.service.EmployeeInfo).
Guidelines for Developing Custom Java APIs
During the planning stage, use the following guidelines to plan and develop the custom Java APIs that will be exposed as REST services through Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway:
-
Develop a Java class whose public methods provide business functionality. Business logic should be embedded into these public methods.
-
The custom Java APIs and method names will be used in Web service URL. Therefore, ensure to provide friendly names.
-
If you need initialized Oracle E-Business Suite Context within the Java method, ensure the following:
-
Use ISG Context (IContext) to get handle to runtime information.
For example,
IContext ctx = ContextManager.getContext(); -
Retrieve fully initialized Oracle E-Business Suite WebAppsContext based on the request header / security token.
For example,
WebAppsContext wctx = (WebAppsContext) ctx.getExternalContext();WebAppsContextmay be used later for application specific validation, such as fine grained access control.
-
-
You may use the Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway database connections within the Java APIs.
For example,
conn = DBConnectionManager.getConnection(); -
Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway provides a standard exception handling from the infrastructure. Ensure that the Java APIs throw or rethrow a throwable exception whenever an error condition occurs.
-
-
If above Java methods require complex data objects to be exchanged as input and output parameters, then develop Java Beans.
Java Beans should:
-
Implement
java.io.Serializable. -
Have no-argument constructor.
-
Have accessor methods, following 'get' and 'set' naming convention, for private attributes.
-
Creating Custom Java APIs
In this example, you need a service that will return the details of a specific person in the hierarchy of the logged in user, as well as return all the reports of the logged in user.
To achieve this goal, create the following Java files:
-
A Java class
EmployeeInfo.javacontains the following three methods. Based on the scenarios, they are read-only methods and we will map each Java method to HTTP GET verb.-
getAllReports- This method returns an array of all reports of the requesting user. -
getDirectReports- This method returns a list of direct reports of the requesting user. -
getPersonInfo- This method returns the person details for a specific person Id.This method requires a key identifier parameter for "Person Id". Therefore,
personIdwill be annotated askey_param.... * @param personId Person Identifier * @rep:paraminfo {@rep:required} {@rep:key_param} ...
-
-
A Java class
PerServiceException.javathat extends SOAException in Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway. -
A Java Bean
PersonBean.javato capture person information.
To create and compile custom Java APIs:
Use the following steps to create and compile custom Java APIs:
-
Create the first Java class called
PersonBean.javawith the following Java code:This Java class extends
java.lang.Ojbect.package oracle.apps.per.sample.beans; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; public class PersonBean implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private int personId; private String firstName; private String lastName; private String salutaion; private String fullName; private String nameSuffix; private String emailAddress; private String employeeNumber; private String workPhone; private Date startDate; private int reportingLevel; private int supervisorPersonId; private String supervisorEmployeeNumber; private String supervisorFullName; private String reportingHierarchy; public void setPersonId(int personId) { this.personId = personId; } public int getPersonId() { return personId; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setSalutaion(String salutaion) { this.salutaion = salutaion; } public String getSalutaion() { return salutaion; } public void setFullName(String fullName) { this.fullName = fullName; } public String getFullName() { return fullName; } public void setEmailAddress(String emailAddress) { this.emailAddress = emailAddress; } public String getEmailAddress() { return emailAddress; } public void setEmployeeNumber(String employeeNumber) { this.employeeNumber = employeeNumber; } public String getEmployeeNumber() { return employeeNumber; } public void setStartDate(Date startDate) { this.startDate = startDate; } public Date getStartDate() { return startDate; } public void setNameSuffix(String nameSuffix) { this.nameSuffix = nameSuffix; } public String getNameSuffix() { return nameSuffix; } public void setWorkPhone(String workPhone) { this.workPhone = workPhone; } public String getWorkPhone() { return workPhone; } public void setReportingLevel(int reportingLevel) { this.reportingLevel = reportingLevel; } public int getReportingLevel() { return reportingLevel; } public void setSupervisorPersonId(int supervisorPersonId) { this.supervisorPersonId = supervisorPersonId; } public int getSupervisorPersonId() { return supervisorPersonId; } public void setSupervisorEmployeeNumber(String supervisorEmployeeNumber) { this.supervisorEmployeeNumber = supervisorEmployeeNumber; } public String getSupervisorEmployeeNumber() { return supervisorEmployeeNumber; } public void setSupervisorFullName(String supervisorFullName) { this.supervisorFullName = supervisorFullName; } public String getSupervisorFullName() { return supervisorFullName; } public void setReportingHierarchy(String reportingHierarchy) { this.reportingHierarchy = reportingHierarchy; } public String getReportingHierarchy() { return reportingHierarchy; } } -
Create the second Java class called
PerServiceException.javawith the following Java code:This Java class extends
java.lang.Ojbect.package oracle.apps.per.sample.common; import oracle.apps.fnd.soa.util.SOAException; public class PerServiceException extends SOAException { public PerServiceException(String message) { super(message); } public PerServiceException(Throwable t) { super(t); } public PerServiceException(String message, Throwable t) { super(message, t); } public PerServiceException(String errorCode, String message, Throwable t) { super(errorCode, message, t); } } -
Create the third Java class called
EmployeeInfo.javawith the following Java code:This Java class extends
java.lang.Ojbect.package oracle.apps.per.sample.service; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import oracle.apps.fnd.common.WebAppsContext; import oracle.apps.fnd.isg.common.IContext; import oracle.apps.fnd.isg.common.mgr.ContextManager; import oracle.apps.fnd.isg.common.mgr.DBConnectionManager; import oracle.apps.per.sample.beans.PersonBean; import oracle.apps.per.sample.common.PerServiceException; import oracle.jdbc.OraclePreparedStatement; import oracle.jdbc.OracleResultSet; /** * A sample class to demonstrate how Java API can use the ISG REST framework. This class provides * methods to retrieve list of direct reports, all reports of a person. It also has methods to * retrieve personal details and accrual balance of a person. * @rep:scope public * @rep:product PER * @rep:displayname Employee Information * @rep:category IREP_CLASS_SUBTYPE JAVA_BEAN_SERVICES */ public class EmployeeInfo { public EmployeeInfo() { super(); } /** * This method returns a list of direct reports of the requesting user. * * @return List of person records who are direct reports * @rep:paraminfo {@rep:innertype oracle.apps.per.sample.beans.PersonBean} * @rep:scope public * @rep:displayname Get Direct Reports * @rep:httpverb get * @rep:category BUSINESS_ENTITY sample */ // Demonstration of list return type public List<PersonBean> getDirectReports() throws PerServiceException { // Get the ISG context, which has runtime information IContext ctx = ContextManager.getContext(); // Retrieve fully initialized webappscontext, as per the request header / security token WebAppsContext wctx = (WebAppsContext) ctx.getExternalContext(); // Use webappscontext for apps specific validation e.g. fine grained access control etc. int userId = wctx.getUserId(); String userName = wctx.getUserName().toUpperCase(); // Here we intend to filter based on the specific user who is invoking the service String filter = " AND LEVEL = 2 START WITH USER_NAME = :1"; List<PersonBean> personList = null; try { Map<Integer, PersonBean> map = makeBean(filter, userName); if (map != null) personList = new ArrayList<PersonBean>(map.values()); } catch (SQLException sqle) { throw new PerServiceException("SQL error while getting the all reports", sqle); } return(personList); } /** * This method returns an array of all reports of the requesting user. * * @return Array of person records who are reporting into the requesting user's organization hierarchy * @rep:scope public * @rep:displayname Get All Reports * @rep:httpverb get * @rep:category BUSINESS_ENTITY sample */ // Demonstration of array return type public PersonBean[] getAllReports() throws PerServiceException { // Get the ISG context, which has runtime information IContext ctx = ContextManager.getContext(); // Retrieve fully initialized webappscontext, as per the request header / security token WebAppsContext wctx = (WebAppsContext) ctx.getExternalContext(); // Use webappscontext for apps specific validation e.g. fine grained access control etc. int userId = wctx.getUserId(); String userName = wctx.getUserName().toUpperCase(); // Here we intend to filter based on the specific user who is invoking the service String filter = " START WITH USER_NAME = :1 "; PersonBean[] array = null; try { Map<Integer, PersonBean> map = makeBean(filter, userName); if (map != null) array = map.values().toArray(new PersonBean[map.size()]); } catch (SQLException sqle) { throw new PerServiceException("SQL error while getting the direct reports", sqle); } return(array); } /** * This method returns the person details for a specific person id. Throws error if the person * is not in requesting user's org hierarchy. * * @return Details of a person in the logged on user's org hierarchy. * @param personId Person Identifier * @rep:paraminfo {@rep:required} {@rep:key_param} * @rep:scope public * @rep:displayname Get Person Details * @rep:httpverb get * @rep:category BUSINESS_ENTITY sample */ // Demonstration of simple navigation using path param public PersonBean getPersonInfo(int personId) throws PerServiceException { // Get the ISG context, which has runtime information IContext ctx = ContextManager.getContext(); // Retrieve fully initialized webappscontext, as per the request header / security token WebAppsContext wctx = (WebAppsContext) ctx.getExternalContext(); // Use webappscontext for apps specific validation e.g. fine grained access control etc. int userId = wctx.getUserId(); String userName = wctx.getUserName().toUpperCase(); String filter = " START WITH USER_NAME = :1 "; Map<Integer, PersonBean> map = null; try { map = makeBean(filter, userName); } catch (SQLException sqle) { throw new PerServiceException("SQL error while getting the direct reports", sqle); } if (map == null) throw new PerServiceException(PerServiceException.AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE, "No org hierarchy found for user - " + userName, null); boolean doesExist = map.containsKey(personId); if (!doesExist) throw new PerServiceException(PerServiceException.AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE, "The given person " + personId + " either does not exist or does not belong to the current user's - " + userName + " hierarchy", null); PersonBean bean = map.get(personId); return(bean); } /************************* private members ****************************/ private Map<Integer, PersonBean> makeBean(String sqlFilter, String userName) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; OraclePreparedStatement stmt = null; OracleResultSet rs = null; HashMap<Integer, PersonBean> personMap = new HashMap<Integer, PersonBean>(); IContext ctx = ContextManager.getContext(); try { String sql = GET_PERSON_INFO1 + sqlFilter; // preferred way of obtaining connection, rather than from WebAppsContext conn = DBConnectionManager.getConnection(); stmt = (OraclePreparedStatement) conn.prepareStatement(sql); stmt.setString(1, userName); rs = (OracleResultSet) stmt.executeQuery(); while (rs != null && rs.next()) { int personId = rs.getInt(1); String firstName = rs.getString(2); String lastName = rs.getString(3); String title = rs.getString(4); String fullName = rs.getString(5); String nameSuffix = rs.getString(6); String empNumber = rs.getString(7); String emailAddr = rs.getString(8); String workPhone = rs.getString(9); int supervisorId = rs.getInt(10); java.util.Date startDate = rs.getDate(12); int level = rs.getInt(16); String supervisorName = rs.getString(17); String supervisorEmpNumber = rs.getString(18); String reporting = rs.getString(19); // Do any data validation / transformation if necessary, here PersonBean personBean = new PersonBean(); // Set the information into the serializable bean personBean.setPersonId(personId); personBean.setFirstName(firstName); personBean.setLastName(lastName); personBean.setSalutaion(title); personBean.setFullName(fullName); personBean.setNameSuffix(nameSuffix); personBean.setEmployeeNumber(empNumber); personBean.setEmailAddress(emailAddr); personBean.setWorkPhone(workPhone); personBean.setSupervisorPersonId(supervisorId); personBean.setStartDate(startDate); personBean.setReportingLevel(level); personBean.setSupervisorFullName(supervisorName); personBean.setSupervisorEmployeeNumber(supervisorEmpNumber); personBean.setReportingHierarchy(reporting); personMap.put(personId, personBean); } } finally { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (Exception e) {}; rs = null; } if (stmt != null) { try { stmt.close(); } catch (Exception e) {}; stmt = null; } // preferred way of closing the connection DBConnectionManager.closeConnection(conn); } return(personMap); } private static final String GET_PERSON_INFO1 = "SELECT DISTINCT E.PERSON_ID, E.FIRST_NAME, E.LAST_NAME, E.TITLE, E.FULL_NAME, E.SUFFIX,\n" + "E.EMPLOYEE_NUMBER, E.EMAIL_ADDRESS, E.WORK_TELEPHONE, E.SUPERVISOR_ID,\n" + "E.SUPERVISOR_ASSIGNMENT_ID, E.EFFECTIVE_START_DATE, E.EFFECTIVE_END_DATE,\n" + "E.USER_ID, E.USER_NAME, LEVEL, PRIOR E.FULL_NAME, PRIOR E.EMPLOYEE_NUMBER,\n" + "SYS_CONNECT_BY_PATH(E.FULL_NAME, '/')\n" + "FROM\n" + "(SELECT PPF.PERSON_ID,\n" + "PPF.FIRST_NAME,\n" + "PPF.LAST_NAME,\n" + "PPF.TITLE,\n" + "PPF.FULL_NAME,\n" + "PPF.SUFFIX,\n" + "PPF.EMPLOYEE_NUMBER,\n" + "PPF.EMAIL_ADDRESS,\n" + "PPF.WORK_TELEPHONE,\n" + "PAF.SUPERVISOR_ID,\n" + "PAF.SUPERVISOR_ASSIGNMENT_ID,\n" + "GREATEST(PPF.EFFECTIVE_START_DATE, PAF.EFFECTIVE_START_DATE) EFFECTIVE_START_DATE, \n" + "LEAST(PPF.EFFECTIVE_END_DATE, PAF.EFFECTIVE_END_DATE) EFFECTIVE_END_DATE,\n" + "FUR.USER_ID,\n" + "FUR.USER_NAME\n" + "FROM FND_USER FUR, PER_ALL_PEOPLE_F PPF,\n" + "PER_ALL_ASSIGNMENTS_F PAF\n" + "WHERE PPF.PERSON_ID = PAF.PERSON_ID (+)\n" + "AND PPF.BUSINESS_GROUP_ID = PAF.BUSINESS_GROUP_ID (+)\n" + "AND (SYSDATE BETWEEN PPF.EFFECTIVE_START_DATE\n" + "AND PPF.EFFECTIVE_END_DATE\n" + "AND SYSDATE BETWEEN PAF.EFFECTIVE_START_DATE\n" + "AND PAF.EFFECTIVE_END_DATE)\n" + "AND FUR.EMPLOYEE_ID = PPF.PERSON_ID\n" + ") E\n" + "CONNECT BY SUPERVISOR_ID = PRIOR PERSON_ID"; } -
Place these Java class files in the respective folders in the
JAVA_TOPdirectory. -
Navigate to the respective folders in
JAVA_TOPand execute the corresponding commands to compile Java class files:java PersonBean.java java PerServiceException.java java EmployeeInfo.java
The corresponding
.classfiles will be created in the respective folders in theJAVA_TOPdirectory. -
Stop and restart Oracle E-Business Suite application server.
Parsing and Uploading the Annotated Custom Java Bean Service to the Integration Repository
Once the custom Java classes have been successfully deployed to a target instance, the integration repository administrator needs to validate the annotated custom interface definition Employee Information against the annotation standards for Java Bean Services using Integration Repository Parser. During the validation, if no error occurs, an iLDT file will be generated. The administrator will then upload the generated iLDT file to Oracle Integration Repository.
Perform the following steps to parse and upload the annotated custom interface definition Employee Information to Oracle Integration Repository:
-
Source the environment in the run file system and set CLASSPATH to include all libraries and JAR files used by the custom Java API.
-
Ensure the annotated custom interface definition and related Java classes are located in the target instance.
-
Execute the Integration Repository Parser using the following command to validate the annotated custom interface definition against the annotation standards:
$IAS_ORACLE_HOME/perl/bin/perl $FND_TOP/bin/irep_parser.pl -g -v -username=sysadmin per:patch/115/java:EmployeeInfo.java:12.1=EmployeeInfo.javaIntegration Repository Parser Command Process and Validation
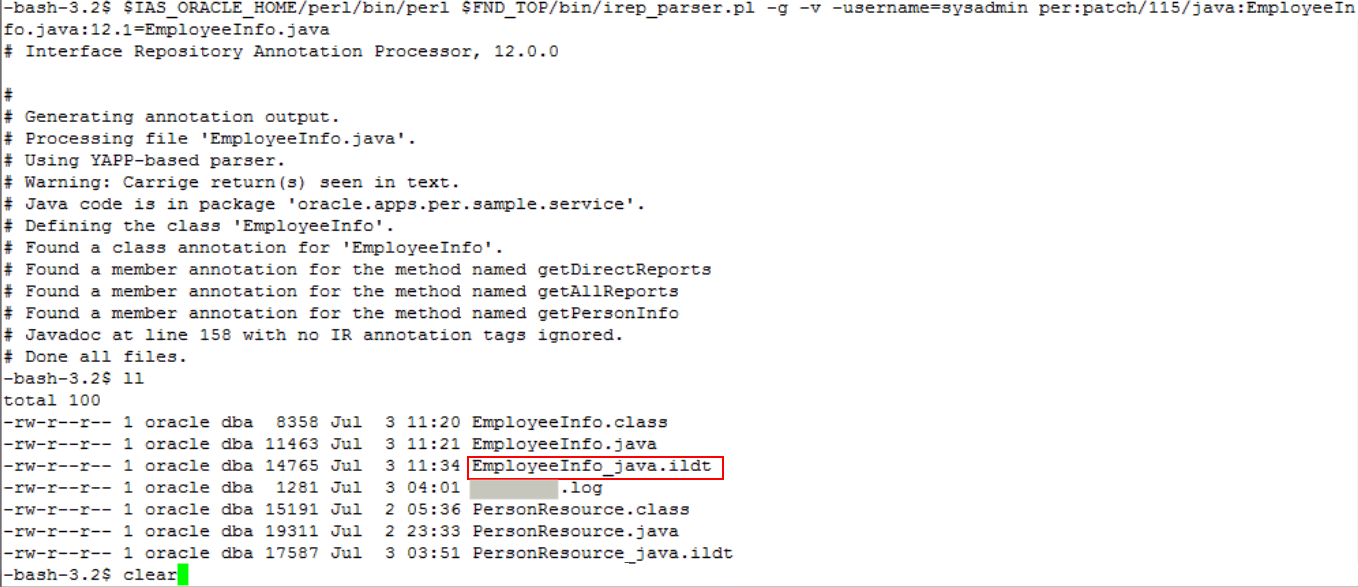
Notice that the
EmployeeInfo_java.ildtfile is successfully generated after the validation. -
Upload the generated
EmployeeInfo_Java.ildtfile to the Integration Repository by using the following FNDLOAD command:$FND_TOP/bin/FNDLOAD apps/password@TWO_TASK 0 Y UPLOAD $FND_TOP/patch/115/import/wfirep.lct EmployeeInfo_java.ildt
-
Verify the generated log file to view the upload details.
Upload Details in the Log File
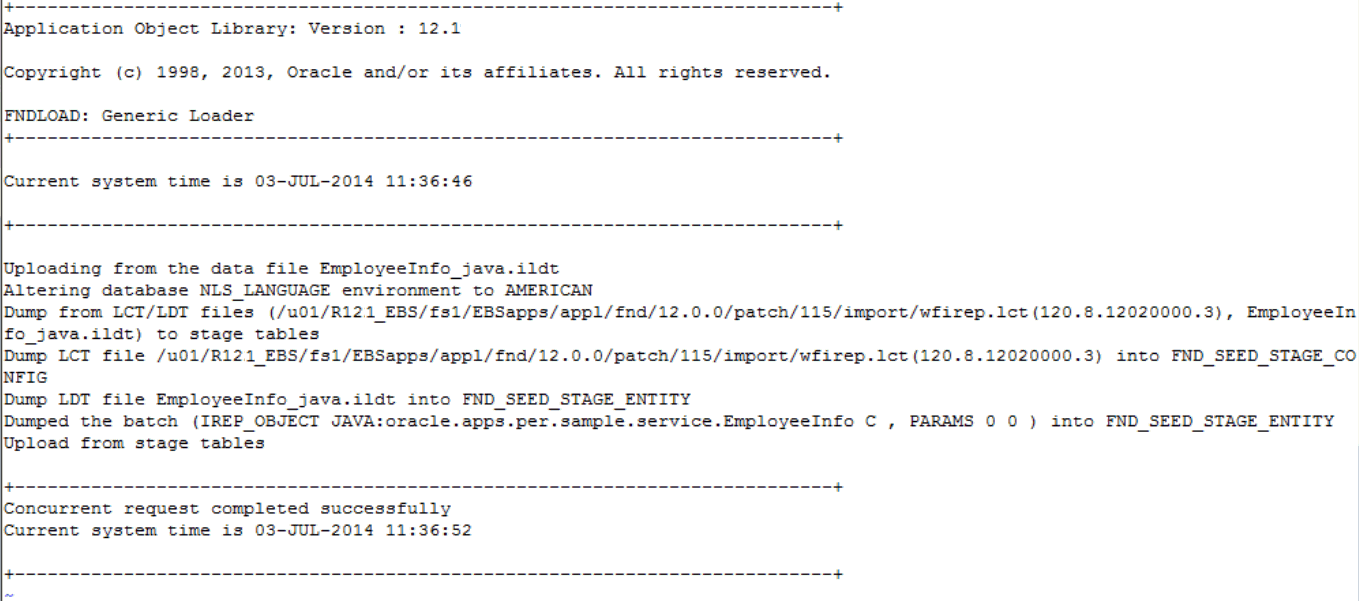
Notice that the upload process has been completed successfully.
-
Search the uploaded custom Java Service Beans interface "Employee Information" from the Integration Repository.
Click the Employee Information name link to open the interface details page.
Deploying a Custom Java Bean Service
Use the following steps to deploy the custom interface as a REST service:
-
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite as a user who has the Integration Repository Administrator role.
Select the Integrated SOA Gateway responsibility and the Integration Repository link from the navigation menu.
-
In the Integration Repository tab, click Search to access the main Search page.
-
Click Show More Search Options to display more search fields.
Select 'Custom' in the Interface Source field.
-
Click Go to execute the search.
Click the "Employee Information" interface name link to open the interface details page.
-
In the REST Web Service tab, enter the following information:
-
Service Alias: empinfo
The alias will be displayed as the service endpoint in the WADL and schema for the selected method or operation.
-
Select the POST check box for the Get Person Details Java method. Leave the rest of preselected check boxes unchanged.
-
-
Click Deploy to deploy the service to an Oracle E-Business Suite environment.
Once the REST service has been successfully deployed, 'Deployed' appears in the REST Service Status field along with the View WADL link. Click the View WADL link to view the deployed service WADL description.
For more information on deploying REST services, see Deploying REST Web Services, Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway Implementation Guide.
Creating a Security Grant
After deploying the custom interface "Employee Information" as a REST service, the integration repository administrator can create a security grant to authorize the service access privileges to all users.
Use the following steps to create a security grant:
-
Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite as a user who has the Integration Repository Administrator role. Select the Integrated SOA Gateway responsibility and the Integration Repository link from the navigation menu.
-
Perform a search to locate the "Employee Information" service the administrator just deployed earlier.
-
Select the "Employee Information" name link from the search result table to display the interface details page. Click the Grants tab.
-
Select the Employee Information service and then click Create Grant.
-
In the Create Grants page, select "All Users" as the Grantee Type.
Note: In this example, the
Employee Informationservice is granted to all users. In actual implementation, you should define strict security rules. Create grant to a user or more appropriately to a group of users defined by roles and responsibilities.Click Create Grant. This grants the selected service access privilege to all Oracle E-Business Suite users.
Recording Resource Information from Deployed WADL
To obtain service resource information from the deployed WADL for the custom Employee Information service, click the View WADL link in the REST Web Service tab.
The following WADL description appears:
<xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<application name="EmployeeInfo" targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/per/soaprovider/pojo/employeeinfo/"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/per/soaprovider/pojo/employeeinfo/"
xmlns="http://wadl.dev.java.net/2009/02" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:tns1="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/empinfo/getallreports/"
xmlns:tns2="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/empinfo/getdirectreports/"
xmlns:tns3="http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/rest/empinfo/getpersoninfo/">
<grammars>
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/?XSD=getallreports.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/?XSD=getdirectreports.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
<include href="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/?XSD=getpersoninfo.xsd" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" />
</grammars>
<resources base="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/">
<resource path="/getAllReports/">
<method id="getAllReports" name="GET">
<request>
<param name="ctx_responsibility" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_respapplication" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_securitygroup" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_nlslanguage" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_orgid" type="xsd:int" style="query" required="false" />
</request>
<response>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns1:getAllReports_Output" />
<representation mediaType="application/json" type="tns1:getAllReports_Output" />
</response>
</method>
</resource>
<resource path="/getDirectReports/">
<method id="getDirectReports" name="GET">
<request>
<param name="ctx_responsibility" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_respapplication" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_securitygroup" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_nlslanguage" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_orgid" type="xsd:int" style="query" required="false" />
</request>
<response>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns2:getDirectReports_Output" />
<representation mediaType="application/json" type="tns2:getDirectReports_Output" />
</response>
</method>
</resource>
<resource path="="/getPersonInfo/ {personId}/">
<param name="personId" style="template" required="true" type="xsd:int" />
<method id="getPersonInfo" name="GET">
<request>
<param name="ctx_responsibility" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_respapplication" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_securitygroup" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_nlslanguage" type="xsd:string" style="query" required="false" />
<param name="ctx_orgid" type="xsd:int" style="query" required="false" />
</request>
<response>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Output" />
<representation mediaType="application/json" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Output" />
</response>
</method>
</resource>
<resource path="/getPersonInfo/">
<method id="getPersonInfo" name="POST">
<request>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Input" />
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Output" />
</request>
<response>
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Input" />
<representation mediaType="application/xml" type="tns3:getPersonInfo_Output" /> </response>
</method>
</resource>
</resource path>
</application>
Copy or record the following information which will be used later when defining a Java client:
-
<resources base>="http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/">This information
http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfowill be used later in Java client program as baseUrl. -
<resource path>="/getPersonInfo/{personId}/">This information
/getPersonInfo/{personId}/will be used later to form the later part of the service URL.Note that {personId} is a path variable defined using the
<param>tag. It will be replaced with actual value (employee ID 13137 in this example) at run time when the HTTP GET method is invoked. -
<resource path="/getDirectReports/">This information
/getDirectReports/will be used later to form the later part of the service URL.
Invoking a Custom REST Service from HTML Using Javascript
This example contains two invocation scenarios:
-
Get employee personal information by invoking the
getPersonInfoREST service operation -
Get direct reports for the logged in user by invoking the
getDirectReportsREST service operation with pagination control parameter
Scenario 1: Get Employee Personal Information
Use the following steps to invoke the deployed the getPersonInfo REST service operation:
-
Create an HTML file using any text editor with the following content:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <title>Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway - REST Services Sample</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <style> table,th,td { border:1px solid black; border-collapse:collapse; } th,td { padding:5px; } </style <script language="javascript"> function getEmpDetails() { var xmlhttp; if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { var det = eval( "(" + xmlhttp.responseText + ")"); document.getElementById('div1').innerHTML=det.OutputParameters.PersonBean[0].fullName; document.getElementById('div2').innerHTML=det.OutputParameters.PersonBean[0].supervisorFullName; } } var empno = document.getElementById("empno"); var url = "http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/getPersonInfo/" + empno.value; xmlhttp.open('GET',url,true,"cbrown", password); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <center><h1>Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway - REST Services Sample</h1> <h2>Path Parameter Example</h2> </center> <h3>This example demonstrates the use of Path Parameters in REST Service URL. ISG REST Service expects personId as input. personId was annotated as key_param. Hence, it can be sent as part of GET request URL. This example does not set Accept header in HTTP Request. REST Service returns response in JSON format (JSON is default message format).<br><br> Enter employee id and click Get Details button. ISG REST Service will be invoked. Employee Name and his / her Manager's Name will be displayed.<br> </h3> <center><table> <tr> <td>Enter Employee ID</td> <td><input type="text" id="empno" size="10"/> <input type="button" value="Get Details" onclick="getEmpDetails()"/> </tr> <tr> <td>Employee Name</td> <td><div id="div1/></div></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Manager Name</td> <td><div id="div1/></div></td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>This invocation scenario uses path parameter {personId} to obtain the employee ID at run time. The
getPersonInfoservice operation is then invoked through the HTTP GET request.<resource path="="getPersonInfo/{personId}/"> <param name="personId" style="template" required="true" type="xsd:int"/> <method id="getPersonInfo" name="GET">The path parameter {personId} was annotated earlier in
@rep:key_paramand can be sent as a GET request URL.This example does not set the
Acceptheader in the GET request. The REST service returns a response message in the default JSON format. -
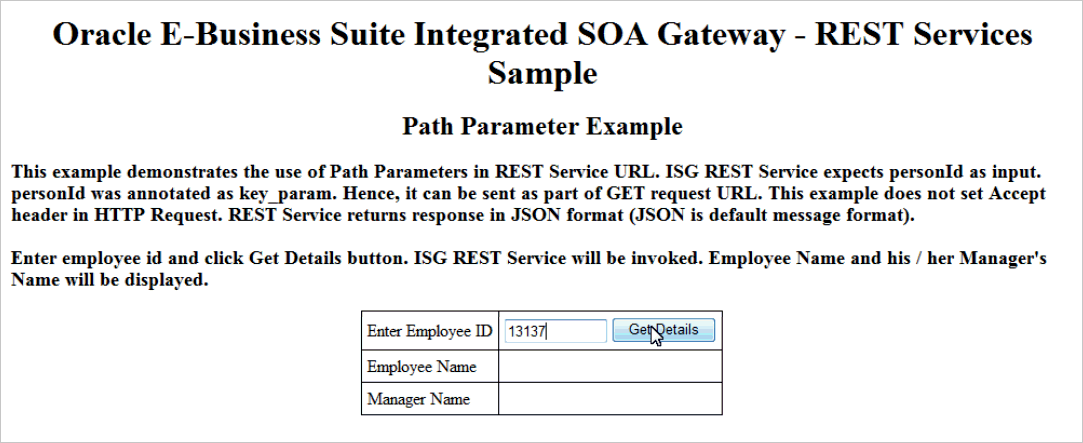
View the HTML page in a browser window.
HTML Page to Invoke a REST Service for Path Parameter Example
-
Enter an Employee ID (path parameter
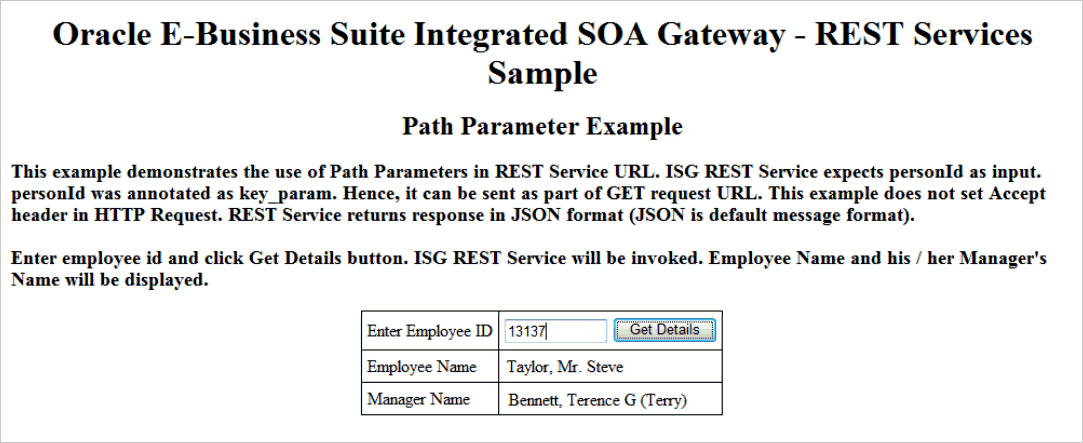
{personId}), such as 13137, in the HTML page and click Get Details. This invokes thegetPersonInfoREST service operation and returns the associated employee's name and his or her manager's name.In this example, Taylor, Mr. Steve who has the employee ID 13137 is displayed as the Employee Name; Bennett, Terrence G (Terry) who is Taylor's manager is displayed as Manager Name.
Note: Employee details in this example represent a fictitious sample (based upon made up data used in the Oracle Demo Vision instance). Any similarity to actual persons, living or dead, is purely coincidental and not intended in any manner.
HTML Page with Employee Personal Information
Scenario 2: Get Direct Reports for the Logged in User
Use the following steps to invoke the deployed the getDirectReports REST service operation:
-
Create an HTML file using any text editor with the following content:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <title>Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway - REST Services Sample</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <style> table,th,td { border:1px solid black; border-collapse:collapse; } th,td { padding:5px; } </style <script language="javascript"> function getPrev() { offset = parseInt(offset) - 3; getDirectReports(offset); } function getNext() { offset = parseInt(offset) + 3; getDirectReports(offset); } function getDirectReports(offsetP) { var xmlhttp; if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else {// code for IE6, IE5 xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xmlhttp.onreadystatechange=function() { if (xmlhttp.readyState==4 && xmlhttp.status==200) { xmlDoc=xmlhttp.responseXML; txt=""; retRows=0; x=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("PersonBean"); if (x.length > 0) { txt = "<br><table border = \"1\"><tr><th>Employee Id</th><th>Employee Name</th></tr>"; } else { txt = "No records to display"; } for (i=0;i<3;i++) { txt = txt + "<tr><td>" + xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("personId")[i].firstChild.nodeValue + "+ xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("personId")[i].firstChild.nodeValue + "</td>"; txt = txt + "<td>" + xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("fullName")[i].firstChild.nodeValue + " + xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("fullName")[i].firstChild.nodeValue + "</td></tr>"; } if (x.length > 0) { txt = txt + "</table><br>"; } y=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ControlBean"); rOffset = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("offset")[0].firstChild.nodeValue; rFrom = 1 + parseInt(rOffset); rTo = 3 + parseInt(rOffset); txt = txt + "Displaying " + rFrom; txt = txt + " to " + rTo + " records.<br>"; document.getElementById("div1").innerHTML=txt; if(offsetP > 2) { document.getElementById("div2").innerHTML="<input type=\"button\" value=\"Previous\" onclick=\"getPrev()\"/>"; } else { document.getElementById("div2").innerHTML=""; } if(x.length == 4) { document.getElementById("div3").innerHTML="<input type=\"button\" value=\"Next\" onclick=\"getNext()\"/>"; } else { document.getElementById("div3").innerHTML=""; } } } var url = "http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/getDirectReports/?ctx_orgid=204&limit=4&offset" + offsetP; xmlhttp.open('GET',url,true); xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/xml"); xmlhttp.send(); } </script> </head> <body> <center><h1>Oracle E-Business Suite Integrated SOA Gateway - REST Services Sample</h1> <h2>Pagination Control Parameters Example</h2> </center> <h3>This example demonstrates the use of Pagination Control Parameters. When you click Get Directs button, ISG REST Service will be invoked. Provide EBS username and password. On successful invocation, the first 3 direct reports (employees) of the logged in user will be displayed. Next and Previous buttons will be displayed based on the number of records. </h3> <center> <input type="button" value="Get Directs" onclick="getDirectReports(0)"/> <div id="div1/></div> <div id="div2/></div> <div id="div3/></div> </center> <script type="text/javascript"><!-- offset=0; //--></script> </body> </html>This invocation scenario uses pagination control parameter offset defined in the Javascript to limit the number of records returned at run time and for pagination when
getDirectReportsservice operation is invoked through HTTP GET request.<script language="javascript"> ... var url = "http://<hostname>:<port>/webservices/rest/empinfo/getDirectReports/?ctx_orgid=204&limit=4&offset" + offsetP; xmlhttp.open('GET',url,true); xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/xml"); xmlhttp.send(); } </script>This example sets the
Acceptheader in the GET request. The REST service returns a response message in XML format. -
View the HTML page in a browser window.
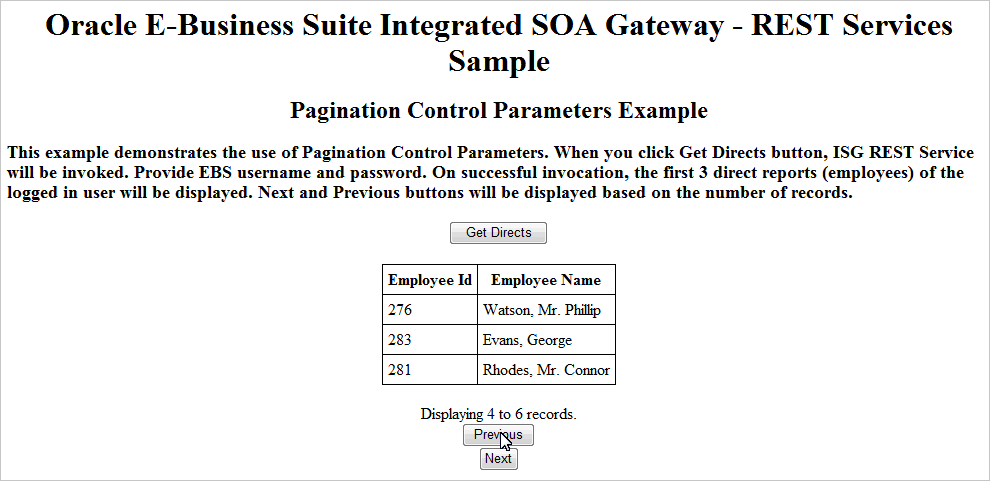
HTML Page to Invoke a REST Service for Pagination Control Parameters Example
-
Click Get Directs in the HTML page. This invokes the
getPersonInfoREST service operation. A pop-up window appears requiring you to enter the username and password.After you entered the username and password and clicked OK, the service returns the first 3 direct reports (employees) of the user you just entered in the table. Click Next to display the next 3 records retrieved from the direct reports list. Click Previous to display the last 3 records from the current direct reports list.
HTML Page with Direct Reports Shown as the Results