Oracle Warehouse Management Crossdocking
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Crossdocking
- Planned Crossdocking
- Opportunistic Crossdocking
- Crossdocking and Change Management
- Crossdocking Exceptions
- Crossdocking Criteria
- Crossdock Execution
Overview of Crossdocking
Crossdocking is the use of inbound receipts to satisfy outbound demands. You can use crossdocking to match outbound shipments to scheduled receipts in advance. This enables you to achieve faster flow-through times and optimize warehouse resources. Oracle Warehouse Management supports two types of crossdocking, planned crossdocking and opportunistic crossdocking. Planned crossdocking matches expected receipts to a demand source, and opportunistic crossdocking matches demands to received supply.
Crossdocking occurs during a period of time known as the crossdock planning horizon. The crossdock planning horizon is the time period within which the system considers demands with a schedule shipment date for crossdocking.
The earliest crossdock time is the beginning of the crossdock planning horizon. This is the maximum time difference that a scheduled receipt can lag with respect to the scheduled shipment time. For example, if the earliest crossdock time is four hours, and a demand exists with a scheduled shipment time of 6:00 p.m., then the system does not consider material with a scheduled receipt time that is earlier than 2:00 p.m.
The latest crossdock time is the end of the crossdock planning horizon. This is the minimum time difference that a scheduled receipt can lag with respect to the scheduled shipment time. For example, if the latest crossdock time is one hour, and a demand exists with a scheduled shipment time of 6:00 p.m., then the system does not consider material with a scheduled receipt time that is later than 5:00 p.m.
The crossdock window is the difference between the earliest and latest crossdock time. For example, if the earliest crossdock time is four hours, and the latest crossdock time is one hour, then the crossdock window is three hours.
Planned Crossdocking Versus Opportunistic Crossdocking
You use planned crossdocking and opportunistic crossdocking for different scenarios. Planned crossdocking works best when you know your supply in advance. It enables you to control the throughput of your warehouse and matches known demand with expected supplies. Opportunistic crossdocking helps with uncertainties. It uses the rules engine to match newly arriving supply to existing demands. This helps in cases in which a supply or demand source is changed, modified, or cancelled.
Related Topics
Planned Crossdocking
Planned crossdocking occurs during pick release. Oracle Warehouse Management uses release sequence rules to sequence demand sources, and fulfills the demand based on the allocation method that you specify during pick release. When you run pick release, the system uses the allocation method to determine whether crossdock should be planned. If crossdock should be planned, then the system uses the crossdock criteria that you specified to determine the eligible supply. If you did not define the crossdock criteria during pick release, then the system uses the rules workbench to determine the appropriate planned crossdock criteria to use for the demand.
If the system identifies a supply source other than inventory for fulfillment, then it determines the scheduled ship time for the delivery lines, and assigns the scheduled ship date and times to delivery lines as follows:
-
If an outbound trip exists, then the system bases the departure time on the dock schedule.
-
If the sales order is associated with a delivery, then the system checks to see whether a carrier exists. If a carrier exists, then the system bases the departure dated on the carrier time and dock door appointment.
If multiple dock door appointments for the carrier exist, then the system selects the dock door and appointment that is closest to the scheduled ship date and time.
-
If the sales order has a specified ship method, then the system determines the carrier and the exact time for the carrier if the carrier has a dock door appointment for the same day. If multiple appointments exist, then the system selects the appointment that is closest to the scheduled ship time and date.
-
If none of these conditions apply, then the system uses the departure time as the scheduled ship time for the order; however, if the crossdock criteria allow scheduling flexibility, then the system assumes the order can ship anytime during the day.
To perform planned crossdocking Oracle Warehouse Management:
-
Determines supply eligibility
-
Performs pegging
-
Creates delivery
-
Links reservation to supply and demand
-
Assigns crossdock operation plan
-
Changes delivery line status to Planned for Crossdock
Supply Eligibility
The available supply sources for planned crossdocking are approved PO, ASN, internal requisition, intransit shipments, and material in receiving. You can peg material in receiving only if the material is not associated with a putaway suggestion. To peg material in receiving, you must turn off the organization parameter Pregenerate after Receipt. See Warehouse Organization Setup, Oracle Warehouse Management Implementation Guide for more information. When the system identifies the eligible supply lines, it performs the following checks:
-
The supply and demand items must be the same. You cannot use a substitute item.
-
If a delivery line is associated with a project and task, then the system does not allow fulfillment across projects and tasks. It considers only material that belongs to the same project and task, or common stock.
Note: If the organization allows fulfillment across projects and tasks, then crossdock planning ignores the project and task information on supply and demand sources.
-
The scheduled receipt time of the supply must be within the crossdock window. The system automatically assumes that all past-due supply lines are available for crossdocking if they satisfy the past-due supply cutoff. The system assigns scheduled receipt lines a receipt date and time as follows:
-
If an inbound trip exists, then the system assigns the arrival time based on the dock appointment.
-
If an ASN exists, then the system assigns the arrival time based on the ASN.
-
If neither condition applies, then the system assigns the receipt date and time based on the PO promise date. If the crossdock criteria are flexible, then the system assumes the receipt can occur anytime during the day.
-
Pegging
After Oracle Warehouse Management creates the eligible supply list, it runs the crossdocking algorithm to perform pegging. It then selects one or more supply sources for crossdocking. If you select the prioritize document on the Crossdock Criteria window, then the system considers the document with the highest priority first.
If a demand is already pegged to a supply, then the system considers only the reserved supply for crossdocking. It uses the crossdock criteria to check whether the supply is eligible for crossdocking and whether the scheduled receipt date occurs within the crossdock window. If the supply meets the criteria, then the system considers the prior reservation and modifies the reservation record to enable crossdocking.
Reservation Linking
Oracle Warehouse Management creates a reservation that links the supply to an existing demand. For more information about reservations, see Item Reservations, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
Create Delivery
If the delivery lines are linked to a delivery or crossdock planning run, Oracle Warehouse Management does not create a delivery. If no link exists, then it merges the delivery lines with the outbound crossdock delivery if it occurs within the crossdock window. If the delivery does not occur within the crossdock window, then it creates a new delivery for the crossdocked lines.
Assign Operation Plan
After Oracle Warehouse Management creates the delivery, it assigns the appropriate operation plan to the material. For more information about operation plans see Set Up Operation Plans.
Change Delivery Line Status
After Oracle Warehouse Management pegs the supply, creates the reservation and delivery, and assigns and operation plan, it changes the status of the crossdock lines to Planned for Crossdock. It ignores these lines in future pick releases and planned crossdocking runs.
Related Topics
Opportunistic Crossdocking
Opportunistic crossdocking is supply initiated. Oracle Warehouse Management considers material in receiving to fulfill a demand if you enable Opportunistic Crossdocking on the Organization Parameters window. See Warehouse Organization Setup, Oracle Warehouse Management Implementation Guide. Oracle Warehouse Management uses the rules workbench to determine the appropriate crossdock criterion to use for supply. Depending on the eligible demand sources, crossdocking goal, and time fences that you specify in the opportunistic crossdock criteria, the system determines to which demand to crossdock the supply. It then stamps and operation plan on the material. To perform opportunistic crossdocking, the system:
-
Validates supply source
-
Determines eligibility pool
-
Performs pegging
-
Creates reservations
-
Creates delivery
Verify Supply Source Validity
The system determines the crossdock criteria for the received lines. Based on the crossdocking criteria, it determines whether you can crossdock the received material.
Determine Eligibility Pool
If you can crossdock the supply, then the system identifies the eligible delivery lines for crossdocking based on the crossdock criteria. The available demand sources are scheduled sales orders, backordered sales orders, scheduled internal orders, backordered internal orders, and backordered WIP component demand. Oracle Warehouse Management performs the following checks to determine eligible demand:
-
The delivery line item and the received line item are the same.
-
The crossdock criteria allow the demand document type.
-
If the received items are associated with a project and task, and the organization does not allow fulfillment across project and tasks, then only demand that belongs to the same project and task, or common demand, is eligible for crossdocking.
Note: If the organization allows fulfillment across project and task, then Oracle Warehouse Management ignores the project and task on supply and demand sources for crossdocking.
-
The scheduled ship time for the delivery lines must occur within the supply crossdock window. The system automatically considers all backordered lines with a past-due scheduled ship date for crossdocking if you enable opportunistic crossdocking for backordered lines. Oracle Warehouse Management uses the following guidelines to assign delivery lines a scheduled ship date and time:
-
If an outbound trip exists, then the system determines the arrival time based on the dock schedule. If a trip has a dock appointment, then the system uses the schedule shipment date as the earliest appointment time for the appointment window.
-
If a sales order is associated with a delivery, then the system checks to see whether it has an associated ship method or carrier. The system uses the ship method to determine the carrier, and the exact time for the carrier if the carrier has a dock appointment on the same day. If multiple dock appointments exist, then the system selects the dock appointment that is closest to the scheduled ship date and time.
-
If none of the preceding exists, then the system uses the arrival time as the scheduled ship time on the order.
-
Pegging
After the system creates a list of eligible delivery lines, then the crossdocking algorithm performs pegging and selects one more demands sources for crossdocking. If you select the Document Priority check box, then the system considers the document type with the highest demand first.
Reservation Linking
Oracle Warehouse Management creates a reservation that links the demand to incoming supply. For more information about reservations, see Item Reservations, Oracle Inventory User's Guide.
Create Delivery
The system merges the delivery lines with an existing delivery if the outbound delivery is within the crossdock window. If no delivery is within the crossdock window, then the system creates a new delivery for the crossdocked items.
Opportunistic Crossdock Receipt Validations
Crossdocking execution performs the following validations upon receipt:
-
Verifies whether supply source is already planned for crossdocking: If the supply source is already planned for crossdocking and has a valid demand source, then the system chooses an operation plan for the item.
-
Supply source is ineligible for crossdocking or crossdocking is not allowed: If the supply source is ineligible, or crossdocking is not allowed for the organization, then the system directs you to put away the material.
-
Supply source is reserved to a demand source and opportunistic crossdocking is enabled: The system uses the crossdock criteria to validate the supply and demand sources. If both are eligible for crossdocking, then the system identifies the received material for crossdocking, and assigns an operation plan.
-
Supply source is not reserved and opportunistic crossdocking is enabled: The system uses the crossdocking criteria to validate the supply source. If the supply source can be crossdocked, then the system identifies the appropriate demand source. The system then uses the crossdocking algorithm to identify the exact demand source.
Related Topics
Crossdocking and Change Management
You can make changes to supply and demand sources after the system links the supply and demand. The following tables display the changes the system makes if you modify supply and demand sources.
| Status | Negative Change to Demand Source | Positive Change to Demand Source | Change in Schedule of Demand Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Receipt | This triggers a change to the reservation quantity. The system changes the reservation quantity to meet the new demand. If multiple supply sources are linked to multiple reservations, then the system first consumes the latest supply source. |
The additional quantity becomes available for crossdocking with a different delivery line status. | This does not change the reservation quantity or existing crossdock link. If you enable exception management, then the system creates an exception if the changes in the schedule jeopardize crossdocking feasibility. |
| After Receipt and During Execution | Not Allowed | The additional quantity becomes available for crossdocking with a different delivery line status. | This does not change the reservation quantity or existing crossdock link. If you enable exception management, then the system creates an exception if the changes in the schedule jeopardize crossdocking feasibility. |
| After Pick Confirm | Not Allowed | The additional quantity becomes available for crossdocking with a different delivery line status. | This does not change the reservation quantity or existing crossdock link. If you enable exception management, then the system creates an exception if the changes in the schedule jeopardize crossdocking feasibility. |
| Status | Negative Change to Supply Source | Positive Change to Supply Source | Change to Supply Source Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Receipt | Changes the reservation quantity. The system splits the delivery line and the balance quantity is in the Ready to Release status so the system can use other sources to fulfill the remaining demand. If you enable exception management, then the system creates an exception and notifies the planner to take corrective action. |
The additional quantity becomes available for crossdocking and the system leaves the reservation links intact. | This does not change the reservation quantity or the existing reservation link between supply and demand. If you enable exception management, then the system creates an exception and notifies the planner to take corrective action. |
| After Receipt and Before Load | This occurs if negative corrections or returns exists, or if the material fails inspection. The system splits the delivery line originally in the Crossdock Status, and the remaining quantity is in the Ready to Release status and the system terminates the operation plan. | The available quantity becomes available for crossdock, and the system does not change the existing reservation link. The system terminates the existing operation plan because the material must be deconsolidated. |
N/A |
| After Receipt and Load, but Before Drop | Positive or negative corrections and inspections cannot be carried out for a loaded LPN. | Positive or negative corrections and inspections cannot be carried out for a loaded LPN. | N/A |
| After drop | Positive or negative corrections and inspections cannot be carried out for a dropped LPN. | Positive or negative corrections and inspections cannot be carried out for a dropped LPN. | N/A |
| After staging | You cannot make corrections to a staged LPN. | You cannot make corrections to a staged LPN. | N/A |
| Status | Negative Change in Reservation Quantity | Positive Change in Reservation Quantity | Cancellation of Reservation |
| Before Receipt | The system splits the delivery line and the balance quantity is in the Ready to Release status. | The system verifies the supply or demand source is not over-reserved | The delivery line is changed to ready to release. |
| After Receipt but Before Load | The system splits the delivery line and the balance quantity is in the Ready to Release status. The system asks you to deconsolidate at the next drop and assigns a new operation plan to the items no longer needed for crossdock. |
The system verifies the supply or demand source is not over-reserved The system asks you to deconsolidate at the next drop and assigns a new operation plan to the items no longer needed for crossdock. |
The system removes crossdock tasks and determines a new operation plan. The delivery lines revert to the ready to release. |
| After Receipt After Load and Before Drop | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| After Receipt and After Drop | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| After Crossdock | No changes to reservations are allowed. | No changes to reservations are allowed. | No changes to reservations are allowed. |
Negative Changes to Supply After Receipt
Change management performs the following actions if negative changes occur to supply after receipt:
-
Negative correction from receiving: A negative correction splits the reservation.
-
Negative correction from inventory: The system reduces the reservation record, and does not create a reservation record for the corrected quantity.
-
Returns: The system deletes the reservation for the returned quantity.
-
Inspection rejection: The system splits the reservation quantity, and changes the reservation line status of the rejected quantity.
Crossdocking Exceptions
Crossdocking exceptions can occur if:
-
The supply source is delayed and the document is not modified
-
The supply source is delayed and the document is modified
-
The supply source is canceled or reduced
-
The supply source fails inspection
-
The material is not available for crossdocking
The system generates the following types of crossdocking exceptions:
Note: Time initiated exceptions are more severe than schedule initiated exceptions.
-
Time-initiated exceptions
-
Schedule initiated exceptions
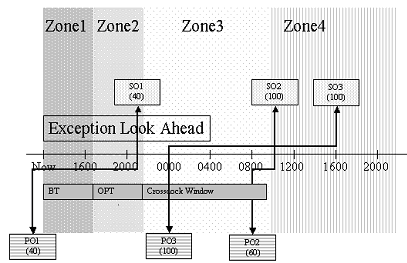
Oracle Warehouse Management uses a concurrent program to check for exceptions and assign an exception code to each exception. It uses the parameter Look-Ahead Time to check whether incoming supply is available for crossdocking. The concurrent program checks for all supply scheduled to arrive in the warehouse within the exception look-ahead time window. It considers the past-due supply and assumes the supply-scheduled receipt date and time is the current system date and time. It uses the supply source and the crossdocking reservation and determines the corresponding demand source. The concurrent program divides the future time window for the supply into four zones. The concurrent program uses these zones to categorize the different exception types.
If crossdocked demand lies in zone one, then the remaining time for crossdocking is less than the order processing time. The system cannot perform a crossdock and records an error. If the supply source is late, then the system records a late exception. If the supply is not late, then the system records a schedule exception.
If crossdocked demand lies within zone two, the remaining crossdock time is more than the order processing time, but less than the order processing time + buffer time. Though the system can still perform crossdocking, you may need to manually expedite the supply. In this case, the system records a warning exception code. If the supply source is past due, then the system records a late exception. If the supply is not late, then it records a schedule exception.
If crossdocked demand lies within zone three, the remaining crossdock time is more than the order processing time + buffer time, but less than the order processing time + buffer time + crossdock window. This implies that crossdocking is possible without manual expedite, and the system does not record an exception.
If crossdocked demand lies within zone four, the remaining crossdock time is more than the order processing time + buffer time + crossdock window. Though crossdocking is possible, an unnecessary wait time is required for the inbound material before you can ship the order; therefore, the system records a scheduled exception with the code warning.
The following table shows the exception codes:
| Exception Code | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LE | Error | Late Exception |
| LW | Warning | Late Exception |
| SE | Error | Schedule Exception |
| SW | Warning | Schedule Exception |
Time Initiated Exceptions
A concurrent program tracks crossdocked receipts and generates exceptions. The concurrent program checks for all past-due supply, and determines whether the material will arrive in time. A late exception occurs when incoming supply does not arrive on schedule. The system generates a warning if the time remaining for the planned crossdock is more than the buffer time, but less than the latest crossdock time. It generates an error exception if the time remaining to fulfill is greater than the buffer time.
Schedule Initiated Exception
The system generates a system exception if the crossdock window is violated. A schedule exception occurs if the time remaining to fulfill the demand is more than the buffer time + order processing time + Crossdock window.
Exceptions Corrective Action
Once the system records a crossdocking exception, it triggers one of the following corrective actions:
-
Reschedule supply and demand: To change the supply and demand, you change either the document, or the dock door appointment.
-
Delete reservation: You can manually delete the reservation and sever the link between the supply and demand.
Crossdocking Criteria
You use the Crossdock Criteria window to determine the eligible supply and demand sources for crossdocking. After you create a crossdock criterion, you enable it in the rules workbench.
To Create a Crossdock Criterion
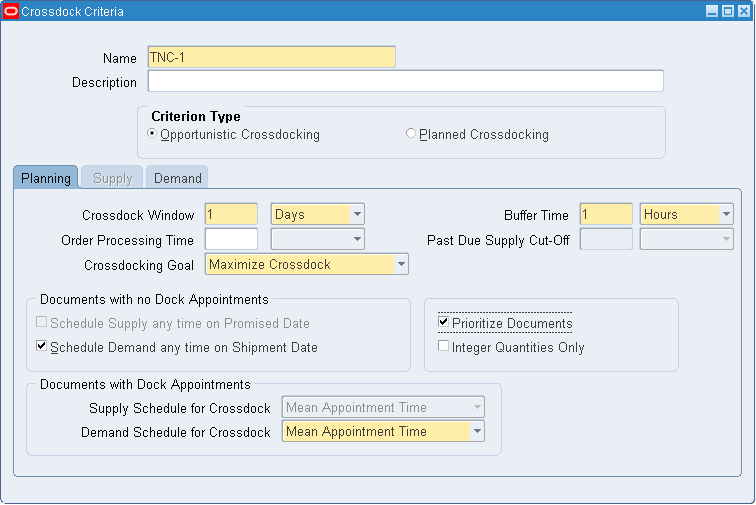
-
Navigate to the Crossdock Criteria window.
-
Enter a name and a description for the crossdock criteria.
-
Select the Criterion Type. Planned crossdocking attempts to select a supply from among eligible supply sources and matches it to a given demand source. Opportunistic crossdocking selects from eligible demand sources, and matches it to a given supply source. See Overview of Crossdocking for more information about opportunistic and planned crossdocking.
-
Enter the time bucket for which the system considers documents for crossdocking. You can enter a crossdock window in days, hours, or minutes.
-
Enter the Order Processing Time. This is the time required to process the order. If you do not enter a value in this field, then the system automatically assumes the value is zero. You can enter an order processing time in hours, days, or minutes.
-
Enter a Buffer Time. This is the time required to safely fulfill an order. The system uses the order processing time and the buffer time to trigger exceptions. The system does not consider supply and demand that occur within the buffer zone for crossdocking. If you do not enter a value in this field, then the system automatically assumes the value is zero. You can enter a buffer time in hours, days or minutes.
-
Enter a Past Due Supply Cut-Off. This is the offset time the system uses to determine the past due supply cut off time fence. This parameter is used for planned crossdocking. The system does not consider any supply that occurs beyond this time fence for crossdocking.
The following demand exists for which crossdocking needs to be planned at 8:00 a.m. The order processing time is two hours, the buffer time is one hour, and the crossdock window is four hours. Shipment 1 has a shipment time of 3:00 p.m. and Shipment 2 has a scheduled ship time of 4:00 p.m. The time fences for the demand sources are:
Demand Order Processing Time Buffer Time Crossdock Window Past Due Supply Cut-Off Shipment 1 3:00 p.m. - 1:00 p.m. 1:00 p.m. - 12:00 p.m. 12:00 p.m. - 8:00 a.m. 8:00 a.m. - 7:00 a.m. Shipment 2 4:00 p.m. - 2:00 p.m. 2:00 p.m. - 1:00 p.m. 1:00 p.m. - 9:00 a.m. 8:00 a.m. - 7:00 a.m. For Shipment 1, the system considers supply sources with a scheduled receipt time later than 12:00 p.m. or earlier than 8:00 a.m. ineligible for crossdocking. The system automatically excludes any supply more than one hour late from crossdock planning.
-
Enter the Crossdocking Goal. You can choose to maximize crossdock, minimize wait, or create custom crossdocking logic.
-
Check Prioritize Documents if you want the rules engine to consider document priority during crossdocking.
-
Check the Integer Quantities only check box. You use this option if your receiving Unit of measure is different from the demand unit of measure, and you want to ensure that you crossdock the received units as a whole.
-
Check the Schedule Demand anytime on Shipment Date check box if the demand does not have a dock door appointment. This enables the system to assume the sales order is scheduled anytime during a one-day window.
-
Check the Schedule Supply anytime on Promise Date check box if an inbound dock schedule does not exist for incoming supply. This enables the system to assume the purchase order is scheduled anytime during one-day window.
Note: This parameter is available only for planned crossdocking.
-
For documents with dock door appointments, select the demand and supply schedule for crossdock. The choices are:
-
Earliest Appointment Time: If an appointment is from 2:00 p.m. to 4:00 p.m., the system recognizes 2:00 p.m. as the scheduled receipt or shipment time for crossdock.
-
Mean Appointment Time: If an appointment is from 2:00 p.m. to 4:00 p.m., the system recognizes 3:00 p.m. as the scheduled receipt or shipment time for crossdock.
-
Latest Appointment Time: If an appointment is from 2:00 p.m. to 4:00 p.m., the system recognizes 4:00 p.m. as the scheduled receipt or shipment time for crossdock.
-
-
Select the Supply tab to enter supply sources for planned crossdocking, or select the Demand tab to enter demand sources for opportunistic crossdocking.
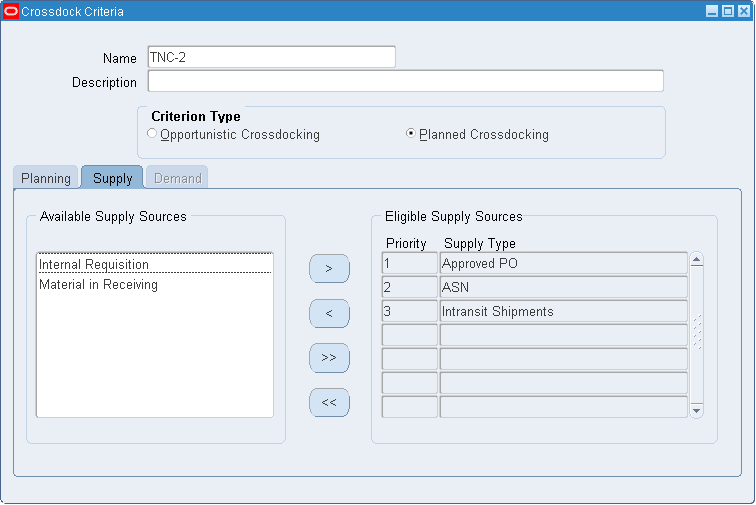
To Enter Supply Sources
-
Select an available supply source for planned crossdocking from the Available Supply Sources region. Click the greater than button to make the supply source eligible. You can click the button with two greater than symbols to make all supply sources eligible for planned crossdocking. The available supply sources are:
-
Approved PO
-
ASN
-
Internal Requisition
-
Intransit Shipments
-
Material in Receiving
-
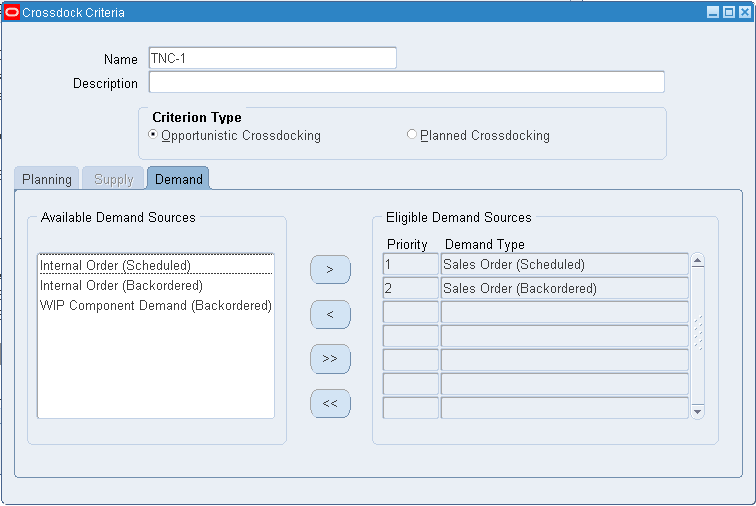
To Enter Demand Sources
-
Select an available demand source for opportunistic crossdocking from the available Demand Sources region. Click the greater than button to make the demand source eligible. You can click the button with two greater than symbols to make all demand sources eligible for crossdocking. The available demand sources are:
-
Sales Order (Scheduled)
-
Sales Order (Backordered)
-
Internal Order (Scheduled)
-
Internal Order (Backordered)
-
WIP Component Demand (Backordered)
-
-
After you enter the supply or demand source information, save your work.
Related Topics
Describing the Rules Workbench
Crossdock Execution
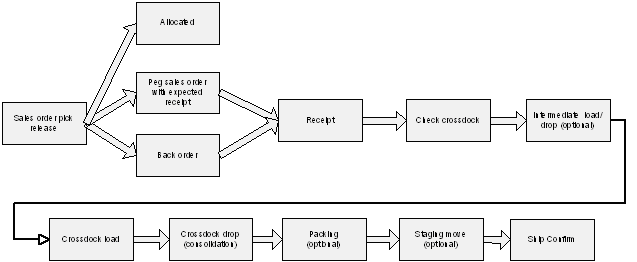
Crossdock execution occurs after you identify supply and demand. Oracle Warehouse Management uses a predefined crossdocking operation plan to stage the material to an outbound staging lane. You can perform intermediate loads and drops if you define them in the operation plan before you drop the material in outbound staging. The crossdock drop follows the seeded outbound operation plans, and either drops the material at a staging lane, or consolidates the material in a consolidation location. For more information about setting up operation plans, see Setup Operation Plans. You can optionally perform a staging move to move material between the consolidation location and the staging lane, or between staging lanes. The following figure depicts the crossdock execution flow.
To determine staging lanes for material, the system uses the following criteria:
-
If any line of the same delivery exists in a staging lane, then the system directs you to drop the current crossdock in to the same staging lane. If the delivery is spread across multiple staging lanes, then the system suggests that you drop the material in the last dropped staging lane.
-
If any pending tasks remain for the same delivery drop, then the system suggests the same staging location for both the pending tasks, and the crossdock line.
-
If dock door appointments exist for the delivery, then the system suggests the staging lane for the dock door that is associated with the delivery.