Managing Security
This chapter covers the following topics:
About Security
Note: The audience for this chapter is the administrator who organizes, sets up, and maintains the master category hierarchy and Solution Security.
Overview topics in this section include:
Summary
Solution Security provides a flexible way to control the user access of solutions. Solution Security identifies which solutions in the knowledge base that users can access. Solution Security uses the following main factors to determine whether or not a user can access a solution:
-
Category Security Groups: Category Security Groups--also known as category views--provide users access to a group of solution categories. Users can access only the categories within their assigned categories and subcategories. For more information, see Category Security Groups.
-
Categories: Categories are groups of solutions by subject area. Solution categories are comparable to a folder that contains solutions. Security control at the category level, using Visibility, restricts access to all solutions and subcategories within the category. For more information, see Managing Categories.
-
Visibility: Visibility is the relative sensitivity or confidentiality of a solution. You associate visibilities with users, categories, subcategories, solutions, and statements. All of these associations impact which solutions that a user can access.
For more information, see About Visibility.
-
Read Access Controls: Users can access Oracle Knowledge Management when:
-
The user's assigned Visibility is more restrictive than the data Visibility level.
-
A category belongs to the assigned Category Security Group and the category is visible.
-
A solution belongs to an accessible category and the solution is visible.
-
A statement belongs to an accessible solution and the statement is visible.
-
-
Write Access Controls: Solution Security has the following write-access controls:
-
When submitting a solution for approval, a user can only submit to flows associated with one's own Category Security Group.
-
On top of the resource group checking, a user can only lock and update a solution if the solution is accessible and the user can see all the statements of the solution. If security setup changes and causes the loss of read-write access to locked solutions, a concurrent program can unlock the “stuck” solutions for other users to work on.
-
About Visibility
The sensitivity or visibility of a categories, solutions, and statements is a factor that determines whether or not a particular user can access a category, solution, and statement. The Visibility Level is a reflection of the confidentiality or sensitivity of the category, solution, and statement. For example, some solutions are more sensitive or confidential than others, and therefore you should allow only a specific group of users to access them. Some solutions are not so sensitive, such that you consider them to be general access solutions that customers--or possibly anyone--could have access to.
Visibility is a linear scale of designating the relative sensitivity or confidentiality of categories, solutions, and statements. You cannot create duplicate Visibility names.
High Restrictions, Limited Access
At one end of the linear scale, a Visibility Level is highly restrictive with limited access. A highly restrictive Visibility Level is for highly sensitive or highly confidential information.
Low Restrictions, Broad Access
At the other end of the linear scale, the Visibility Level has low restrictions with broad access. A Visibility Level with low restrictions is for broader, more public audiences, where the information has low sensitivity or low confidentiality.
Categories
You--the administrator--organize and create categories. When you create categories (and subcategories), you specify the Name and Visibility. When you define the categories you choose from a list of visibilities for each category. You cannot specify that a child category--a subcategory--be more visible than its parent category. Oracle Knowledge Management filters the list of available visibilities that are available for a child category according to the visibility of its parent.
For more information, see Managing Categories.
Solutions
Solution authors specify the visibility of their solutions when they create or update solutions.
Statements
Authors of statements specify the visibility of statements when they create or update them.
Organization of Visibility Levels
Visibility levels let you define how the visibilities fit together in a linear manner or scale, from low sensitivity to high sensitivity.
Visibility levels for category and solution are extensible. As an administrator, you can insert new visibility levels anywhere along the scale. At the time of implementation, you should set up visibility levels and associate them to user access.
Visibility levels for statements are not extensible. You cannot modify the seeded visibilities for statements.
Typically, high visibility categories, solutions, or statements have low sensitivity, and many people can view them. On the other hand, low visibility categories, solutions, or statements have high sensitivity, and relatively few people can view them. The highest visibility might be for external usage, and the lowest visibility might be for internal usage.
Before you assign visibility levels to categories, you must create the master category hierarchy. As you create the categories in the hierarchy, you assign the category visibility levels. When users create solutions and statements, they assign each solution and statement a visibility Level.
For more information on creating categories, see Managing Categories.
Oracle Knowledge Management includes:
-
Seeded visibility levels of Internal and External.
-
End-dated visibility levels of Limited and Restricted to accommodate backward compatibility. However, new installations include only the seeded Internal and External visibility levels.
As the administrator, you need to assign visibility levels for user access. When the user logs on, Oracle Knowledge Management allows the user to access all the solutions that are at the assigned visibility Level up to the most visible level. You can define and configure user access levels at any time. Oracle Knowledge Management provides the seeded solution access levels of Internal and External for new installations.
If you are upgrading from an earlier version of Oracle Knowledge Management, you can add Restricted and Limited access levels to maintain backward compatibility. You would normally perform that setup during implementation.
Category Security Groups
In addition to Visibility assignments to categories, solutions, and statements, you associate Category Security Groups (category views) with categories and responsibilities. Category Security Groups are the means of partitioning the full set of solutions so one set of users can see only one set of categories, while another set of users can see another set of categories.
When a user logs on, Oracle Knowledge Management determines in real time the user's responsibility and therefore the category view.
The assignments of Visibility and Category Security Groups determine which categories that the user has access to, such as for searching or browsing, creating solutions, and drilling down to statement details.
Depending on a user's access, the categories within their Category Security Group (category view) appear. Even though a user has a particular category view, the user might not see all the categories if that user has a low sensitivity visibility assignment, but within that category, there are highly sensitive categories, for example. This means that two users who have access to the same category view can see different categories depending on the visibility of those categories and their user access.
Solution Security Filtering Hierarchy
Solution Security evaluates the Category Security Groups (category views) and the Visibility Levels of categories, solutions, and statements to determine what the user can have access to. Solution Security uses the following filtering sequence:
-
Category Security Groups are the first level of filtering. This occurs when a user logs on to or accesses Oracle Knowledge Management.
-
Category visibilities are the second level of filtering. A user can only access the categories within his access level. If there are solutions that are within the user's Visibility Level, but are in a category the user cannot access, the user cannot successfully search for, browse, or view those solutions. Within a category, the user has access only to the solutions and statements within his Visibility Level.
Statement Filtering and Category Security Groups
There is no direct connection between statements and category groups. Statement filtering is by statement Visibility and then indirectly through the solution to which the statement belongs, and then the category group to which the solution belongs.
About Associating Solutions and Categories
Because you can associate solutions with multiple categories, solutions can also belong to more than one Category Security Group.
Other solutions might re-use the statements from other published solutions. For maintenance purposes, only solutions that belong to the same Category Security Group can re-use the statements that are within the same Category Security Group.
When knowledge workers search for statements, the system filters their results by whether or not the statement belongs in the same Category Security Group and also the Visibility Level of the statement itself.
Solution Security Relationships
The following topics describe and show the relationships among various components of Solution Security:
-
Relationships Between Visibility Levels and Users, Categories, Solutions, and Statements
-
Relationships Between Categories, Visibility, and Category Security Groups
-
Relationships Between Responsibilities and Category Security Groups and User Access
Relationships Between Visibility Levels and Users, Categories, Solutions, and Statements
Visibility Levels are on a linear scale. At one end of the scale, the visibility is very restrictive--such as Internal. At the other end of the scale, the visibility is open or less restrictive--such as External.
Category, Solution, and Statement Visibility Levels
Categories, solutions, and statements all have a Visibility attribute. Whereas the Visibility Levels for solutions and categories are extensible, the Visibility Levels for statements are not extensible. The seeded Visibility Levels for statements are Internal and External. You cannot create or delete Visibility Levels for statements. The seeded Visibility Levels for categories and solutions are Internal and External. You can create or delete additional Visibility Levels for categories and solutions.
For more information, see also Set Up and Maintain Visibility Levels.
You assign users Visibility Levels by way of two profile options: one for statements and one for categories and solutions. The assignment of Visibility Levels to a user means that the user can see any solution, category, or statement that has that Visibility Level or a less restrictive level.
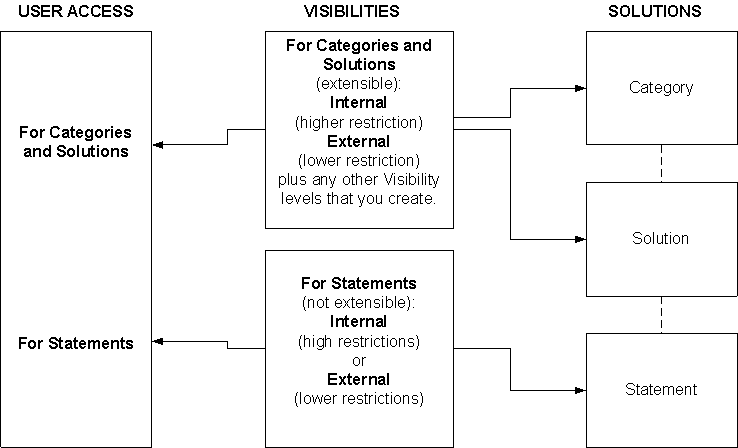
The following diagram shows the relationships between Visibility and:
-
Users
-
Categories, Solutions, and Statements
Visibility with Users, Categories, Solutions, and Statements
Relationships Between Categories, Visibility, and Category Security Groups
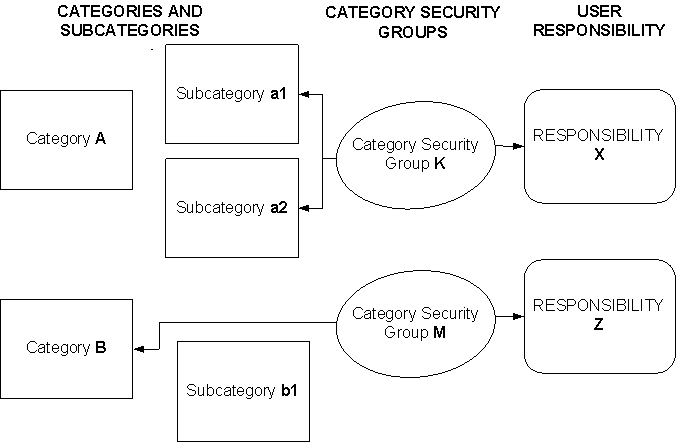
The following diagram shows the relationships between categories and Category Security Groups (category views):
-
An association between Category Security Group K and Subcategories a1, and a2, but not category A. A user with Security Group K sees only subcategories a1 and a2.
-
An association between Category Security Group M and category B. A user with Category Security Group M access sees category B and all subordinate categories that branch from category B, such as subcategory b1.
Note: Oracle Knowledge Management always displays the highest node in the category hierarchy that you have selected. For example, if you first associate subcategory b1 to Category Security Group M, and then you associate parent category B to Category Security Group M, then parent category B replaces subcategory b1 in the display of categories.
Categories and Category Security Groups
Relationships Between Responsibilities and Category Security Groups and User Access
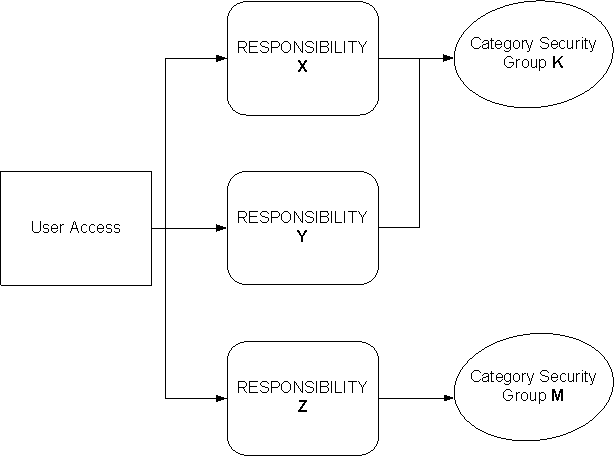
The following diagram shows relationships between Responsibilities and:
-
Category Security Groups: You can associate a Category Security Group to one or more Responsibilities. However, you can associate only one Category Security Group to a Responsibility. The following figure shows that both Responsibilities X and Y have an association with Category Security Group K, but each Responsibility has only one association with a Category Security Group.
-
User Access: You can assign as many Responsibilities as you want to a user, but there is only one single active Responsibility at a time for a given user. When the user logs on, the user selects which Responsibility to activate among all the Responsibilities assigned to him or her. Through the profile option setup, you can assign one set of Visibility Level values per Responsibility. For example, if the user has two Responsibilities X and Y, it is possible to assign the user:
-
External statements and external solutions and categories for Responsibility X.
-
Internal statements and internal solutions and categories for Responsibility Y.
-
Responsibilities with Category Security Groups and User Access
About Changing Security Settings
Changes to the Security settings--for example, adding or removing categories from Category Security Groups or adding a new Visibility Level--impact the index that Oracle Knowledge Management uses for searches. For example, if you assign a category that has a lot of subcategories and solutions to a Category Security Group, a user who belongs to that Category Security Group can access a lot of data. When these changes occur, the user cannot search for it immediately. Only after the background concurrent requests complete their tasks can the user search for the data.
Set Up and Maintain Visibility Levels
When you can create a new Visibility Level, you must decide where it fits in the hierarchy of other Visibility Levels. You must plan your Visibility Levels in a linear manner in terms of sensitivity, from low sensitivity with high access to high sensitivity with low or restricted access.
In its simplest form, you might have only two Visibility Levels:
Internal: For more sensitive material that should be available only internally to your company and your employees.
External: For less sensitive material that is available to customers or the public.
Navigation
Setup > Security > Visibility Levels
Notes
-
When you create new Visibility Levels, you place the new Visibility Level above or below existing Visibility Levels.
-
You cannot create duplicate Visibility Level names.
-
After you create Visibility Levels, you assign Visibility Levels to users, categories, solutions, and statements.
Set Up and Maintain Category Security Groups
Topics in this section include:
About Category Security Groups
Category Security Groups are defined views of categories that determine whether or not a particular user can access a category, solution, and statement. Category Security Groups are subsets of the master category hierarchy and represent subject areas. After you--the administrator--define the master category hierarchy, you must also define the views--the Category Security Groups--of the master category hierarchy.
You associate Category Security Groups with:
-
Categories and subcategories: To indicate which categories and subcategories that a user can view. When you create Category Security Groups, you specify which categories to include.
For more information, see Create a Category Security Group.
-
Responsibilities: To indicate which users can see which categories. You can associate a Category Security Group to one or more Responsibilities, but you can associate only one Category Security Group to a Responsibility. When you define Responsibilities, you associate a Category Security Groups with them. The Responsibility with which a user logs on to the module determines which Category Security Group to use for accessing the knowledge base.
About Category Setup
You set up a master category hierarchy at the time of implementation. The definition of categories and the master hierarchy need to be flexible enough to represent subject areas, products, structure of the company, and so on. Typically, you maintain and modify the master category hierarchy over time. You can add, edit and delete categories as required.
For more information, see Managing Categories.
About Organizing Category Security Groups
After creating the master category, you--the administrator--define Category Security Groups, which are category views that users have of the knowledge base. Category Security Groups are subsets of the master category hierarchy. Although the master category hierarchy includes a root Home category, you cannot include the root Home category in your Category Security Group. Instead, each Category Security Group has becomes its own virtual Home, which varies according to the selected categories.
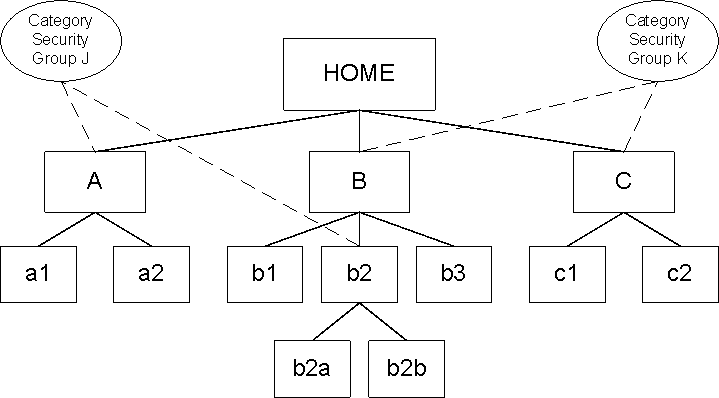
The following figure shows a sample layout of a master category hierarchy with two Category Security Group views, J and K.
For example, Category Security Group J contains parent categories A and b2. Users whose Responsibility is associated with Category Security Group J can see only those categories and subcategories of A and b2, which includes a1, a2, b2a, and b2b. These same users cannot see categories B, b1, b3, or anything in category C.
Similarly, Category Security Group K contains categories B and C. Users whose Responsibility is associated with Category Security Group K can see only those categories and subcategories of B and C, but nothing in category A.
Category Security Group Views of the Master Category Hierarchy
Create a Category Security Group
The following procedures describe to create a new category security group. You can also Update a Category Security Group and Delete a Category Security Group.
Prerequisites
You have set up categories.
Navigation
Setup > Security > Category Groups
Steps
-
Click Create Group.
-
Enter Name (required) and Description (optional).
-
Click the Related Categories tab.
-
To associate categories with the Category Security Group, click the Include Category button.
-
Expand the navigation tree, select the check box of each category or subcategory that you want to apply to the Category Security Group.
You can select one or more categories and subcategories. If you want to specify all subcategories of a category, then select only the parent category. If you want to specify only specific subcategories but not the parent category or other subcategories, then expand the parent category and select only specific subcategories.
-
Click the Apply button.
-
To add related authoring flows, click the Related Flows tab.
-
Click the Include Authoring Flows button.
For more information about authoring flows, see Managing Authoring Flows.
-
Select one or more authoring flows that you want to associate with the Category Security Group.
-
Click the Apply button.
Update a Category Security Group
After you have created a Category Security Group, you can update it to change the name, description, related category, or authoring flow.
Navigation
Setup > Security > Category Groups
Steps
-
The Category Security Groups page displays a list of Category Security Groups.
-
On the row of the Category Security Group that you want to update, click the Update icon.
The Update Category Security Group page appears.
-
To remove a category, click the Remove icon.
-
To add related categories, click the Include Category button.
-
Expand the navigation tree, select the check box of each category or subcategory that you want to apply to the Category Security Group.
For more information, see Steps 4 and 5 in Create a Category Security Group.
-
To update related authoring flows, click the Related Flows tab.
-
To remove an authoring flow, click the Remove icon on the row that lists the flow.
-
To add authoring flows, click the Include Authoring Flows button.
The Include: Authoring Flows page appears.
For more information about authoring flows, see Managing Authoring Flows.
-
Select one or more authoring flows that you want to associate with the Category Security Group.
-
Click the Apply button.
Delete a Category Security Group
You (the administrator) can remove a Category Security Group only if no authoring flows or categories are associated with the Category Security Group. Removing a Category Security Group does not affect the categories within the group. That is, removing a Category Security Group does not remove any categories. However, if you have associated any categories with the Category Security Group, you must disassociate them from the Category Security Group.
Also, when you remove a Category Security Group, the Responsibility that you had associated with the Category Security Group no longer applies to that Category Security Group. When anyone with that formerly associated Responsibility attempt to log on to Oracle Knowledge Management, an error message appears.
The following procedures describe how to:
-
Disassociate categories from a Category Security Group.
-
Delete a Category Security Group.
Navigation
Setup > Security > Category Groups
Steps
The Category Security Groups page displays a list of Category Security Groups.
-
On the row of the Category Security Group that you want to update, click the Update icon.
The Update Category Security Group page appears.
-
On each row where a category appears, click the Remove icon.
The category disappears. You must remove every category before you can delete the Category Security Group.
-
After you have removed all categories from the list, click the Apply button.
The Category Security Groups page appears.
-
On the row that lists the flow that you want to delete, click the Delete icon.
A confirmation messages asks you to if you are sure that you want to delete the Category Security Group.
-
Click the Yes button.
Note: If you had associated the deleted Category Security Group with a Responsibility, those users with that Responsibility will receive an error message when they try to log on. You should consider assigning another Category Security Group with that Responsibility.