| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Technical Overview |
1. Messaging Systems: An Introduction
Configuring Physical Destinations
Authentication and Authorization
Java ES Monitoring Framework Support
Supporting a Development Environment
Supporting a Production Environment
A. Message Queue Implementation of Optional JMS Functionality
This section describes the tools you use to configure and manageMessage Queue broker services. The tools fall into two categories:
The following illustration shows the administration tools provided by Message Queue for configuring and managing broker services.
Figure 3-4 Message Queue Administration Tools
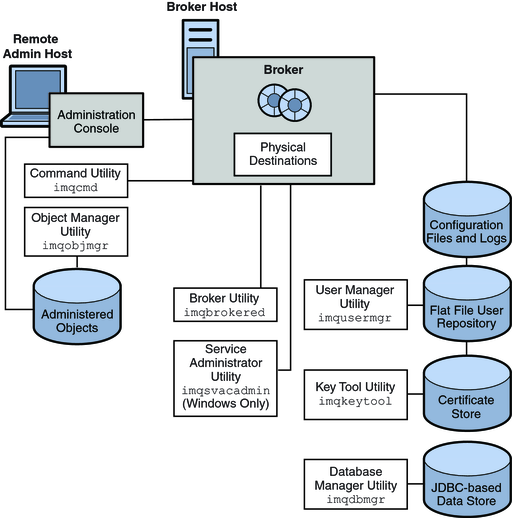
The administration tools include the following command line interfaces:
Broker utility (imqbrokerd). Used to start a broker. You can use options to the imqbrokerd command to specify whether brokers should be connected in a broker cluster and to specify additional startup configuration information.
Command utility (imqcmd). Used after starting a broker to manage broker resources, such as connection services, connections, durable subscriptions, transactions, physical destinations, and so forth.
Object Manager utility (imqobjmgr). Used to create, list, update, and delete administered objects in a JNDI object store.
User Manager utility (imqusermgr). Used to populate a file-based user repository for user authentication and authorization.
Database Manager utility (imqdbmgr). Used to create and manage a JDBC-based persistent data store. (The built-in file store requires no external management.)
Key Tool utility (imqkeytool). Used to generate self-signed broker certificates needed for SSL authentication.
Service Administrator utility (imqsvcadmin). Used to install, query, and remove a broker as a Windows service.
In addition to the command line utilities shown in Figure 3-4,Message Queue administration tools also include the GUI-based Administration Console. The Administration Console combines some of the capabilities of the Command utility (imqcmd) and the Object Manager utility (imqobjmgr). You can use it to do the following:
Manage a broker, its connection services, and other resources.
Create, update, and delete physical destinations.
Connect to a JNDI object store, add administered objects to the store, and manage them.
To serve customers who need a standard programmatic means to monitor and access the broker, Message Queue also supports the Java Management Extensions (JMX) architecture, which allows a Java application to manage broker resources programmatically.
Resources include everything that you can manipulate using the Command utility (imqcmd) and the Message Queue Admin Console: the broker, connection services, connections, destinations, durable subscribers, transactions, and so on.
Management includes the ability to dynamically configure and monitor resources, and the ability to obtain notifications about state changes and error conditions.
The JMX specification defines an architecture for the instrumentation and programmatic management of distributed resources. This architecture is based on the notion of a managed bean, or MBean: a Java object, similar to a JavaBean, representing a resource to be managed. Message Queue MBeans are associated with individual resources such as connection services, connections, or destinations, or with whole categories of resources, such as the set of all destinations on a broker. There are separate configuration MBeans and monitor MBeans for setting a resource’s configuration properties and monitoring its runtime state.
Java applications access MBeans through remote method invocation (RMI) protocols. The MBeans are hosted by an MBean server in the broker, which functions as an MBean container. The MBean server is accessed by means of a RMI connector, which is used to obtain an MBean server connection, which, in turn, provides access to the individual MBeans.
The JMX specification defines an architecture that enables the programmatic management of any distributed resource. This architecture is defined by design patterns, APIs, and various services.
JMX-based administration provides dynamic, fine grained, programmatic access to the broker. You can use this kind of administration in a number of ways.
You can include JMX code in your JMS client application to monitor application performance and, based on the results, to reconfigure the Message Queue resources you use to improve performance.
You can write JMX client applications that monitor the broker to identify use patterns and performance problems, and you can use the JMX API to reconfigure the broker to optimize performance.
You can write a JMX client application to automate regular maintenance tasks, rolling upgrades, and so on.
You can write a JMX client application that constitutes your own version of the Command utility (imqcmd), and you can use it instead of imqcmd.
You can use the standard Java Monitoring and Management Console (jconsole) that provides standard web browser access to the broker's MBeans.
JMX is the Java standard for building management applications and is widely used for managing Java EE infrastructure. If your Message Queue client is a part of a larger Java EE deployment, JMX support allows you to use a standard programmatic management framework throughout your Java EE application. Message Queue is based on the JMX 1.2 specification, which is part of JDK 1.5.
To manage a Message Queue broker using the JMX architecture, see Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Developer’s Guide for JMX Clients. For information on JMX infrastructure and configuring the broker's JMX support, see Appendix D, JMX Support, in Oracle GlassFish Server Message Queue 4.5 Administration Guide.