| Oracle® Real-Time Decisions Base Application Decision Management Applications User's Guide Release 3.1 Part Number E19024-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Real-Time Decisions Base Application Decision Management Applications User's Guide Release 3.1 Part Number E19024-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter introduces Oracle RTD Decision Management and Oracle RTD Decision Management applications in general.
This chapter contains the following topics:
The heart of Oracle RTD is a decisioning process framework that takes into account the overall performance goals with which an organization is trying to optimize, the performance metrics that measure those goals, the action required to score each of the available choices, and a weighting of those scores based on segments of the population.
The following shows an overview of how the elements feed into the general Oracle RTD decisioning process:
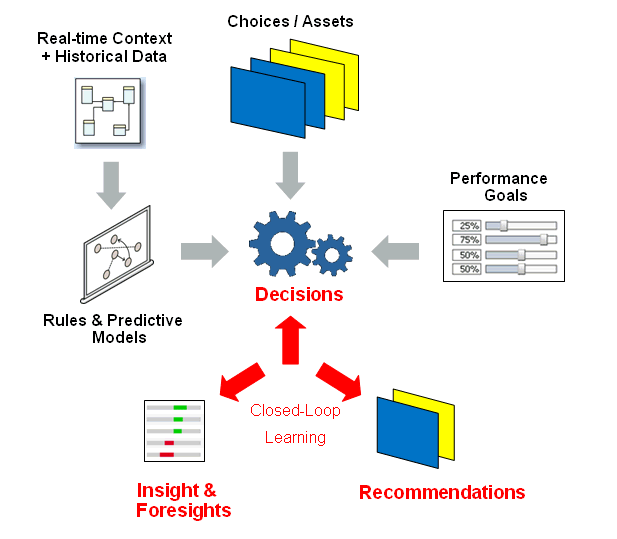
Any business organization can use Oracle RTD to decide which are the best products to offer to their customers, based on intelligence collected from previous campaigns and how that can be applied for different customer segments and in different demographics.
Marketing organizations, for example, could have a variety of different campaigns and offers within these campaigns. The choices are then - which campaign to recommend, and which offer within each campaign? The Oracle RTD decisioning process uses its built-in intelligence to make the best choices for the marketing recommendations.
Oracle RTD Decision Management extends the Oracle RTD decisioning process framework, by extending the scope of the decision framework itself and also by providing an application development environment for creating business user friendly applications for managing the lifecycle choices available for recommendation.
This section contains the following topics:
Oracle RTD Decision Management applications enable business users to easily create, update, and delete the choices that they want to be made available for Oracle RTD choice recommendations in their business processes.
The Decision Management components released with Oracle RTD Base Application are as follows:
An Oracle RTD Decision Management general purpose application infrastructure that enables you to build and use your own Oracle RTD Decision Management applications.
The framework consists of:
Decision Designer
Decision Designer is the combination of design tools built on top of the Oracle JDeveloper platform and includes the metadata files that you use to create the Oracle RTD Decision Management application. In addition to the metadata configured in Decision Designer, each Oracle RTD Decision Management application also includes an Inline Service that is deployed through the Oracle RTD platform component Decision Studio.
With Decision Designer, you generate web-based enterprise applications for business users to manage their choices in external choice repositories as referential business data. Access control to the choices can be configured to enable multi-user concurrent update mode or to restrict access to specific job role users in your business departments.
For details of how to set up Oracle RTD Decision Management applications, see Oracle Real-Time Decisions Base Application Decision Management Installation and Configuration Guide.
Decision Manager
Decision Manager is an end-user oriented web tool that allows business users to control and manage their choices in the external choice repositories.
The Decision Manager interface, as set up in the Oracle RTD Decision Management application, is configured specifically to each organization's own types of choices.
Business users can read, create, update and delete choices and choice rules. When these choices are fed back to the external choice repositories, they then become available to the other applications and transactions that use Oracle RTD for choice recommendations.
Decision Manager also enables users to access select Decision Center analytic reports on their choices directly from the Decision Manager interface.
For more details of how to use general Decision Manager features and options, see Appendix A, "Decision Manager User Interface Reference."
A specific Oracle RTD Decision Management application, Oracle RTD for Marketing Optimization - with its associated Inline Service - oriented to marketing organizations. This application is also referred to as RTD for Marketing Optimization.
The RTD for Marketing Optimization application serves as an application for any marketing organization that is interested in managing their marketing objects of interest as shown in Section 1.2.2, "Inter-Choice Relationships."
For details of how to install and configure RTD for Marketing Optimization, see Oracle Real-Time Decisions Base Application Decision Management Installation and Configuration Guide.
For details of how to use RTD for Marketing Optimization, see Section 2.2, "Using Oracle RTD for Marketing Optimization."
This key decision framework enhancement introduces the ability to define explicit relationships between choices beyond hierarchical relationships. This enables related choices to be actioned and processed together in a way that supports customer workflow operations and procedures.
For example, a marketing organization could have planned their marketing campaigns to be publicized on a variety of external media outlets, and have a number of possible choices to make as to what to recommend, to whom, and how. The choices could be categorized under the general headings of campaigns, offers, channels, placements, and so on. These types of choices could be treated as independent, standalone categories, but that could lead to marketing opportunities being lost due to missing connections between objects during the business intelligence gathering process.
Oracle RTD Decision Management enables relationships to be defined between the choice categories, as shown in the following marketing organization example (the basis for the Oracle RTD Decision Management application that is released with Oracle RTD Base Application):
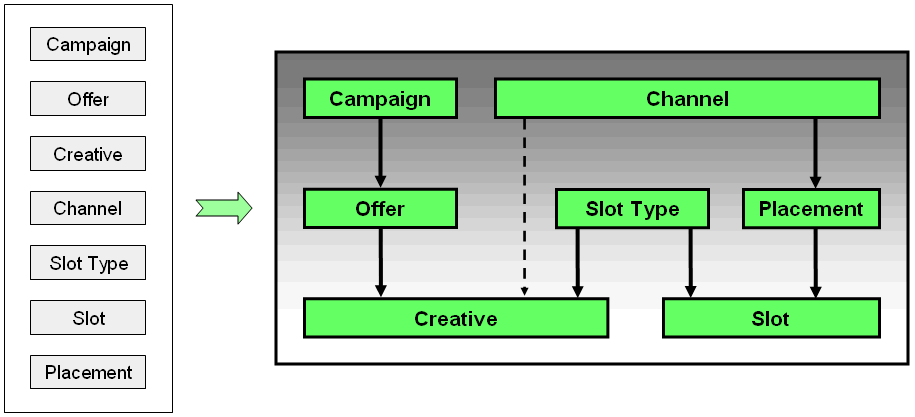
The inter-related objects shown on the right-hand side of the diagram represent and reflect the following real-world relationships:
Each campaign consists of zero, one, or more offers
Each offer must belong to exactly one campaign
Each offer consists of zero, one, or more creatives
A creative can be thought of as specific content used to deliver an offer. For example, text content and image content could be two types of creative for the same offer.
Each channel can have many potential ways (placements) to show an offer on a web page, each of which can break down into slots on the page
Slots must be of a particular slot type
Each channel can be related to zero, one, or more creatives
Each creative must belong to exactly one offer and must be associated with exactly one slot type
Each creative may be associated with one (and only one) channel, but does not have to be (creatives are also related to channels through their slot types, slots, and placements, when it is decided how the creatives will appear through their channels)
The benefits of inter-choice relationships come into play in the decisioning process as follows:
Enhanced rule evaluation - how choice eligibility is determined
For example, for a creative in a campaign, if the campaign is deemed ineligible for a particular customer, the creative will become ineligible for this customer due to the propagation of eligibility defined at the campaign-creative relationship level
Enhanced event propagation - how the success and failure of recommendations are fed back into the Oracle RTD predictive models
For example, if Oracle RTD recommends a creative, and the creative was presented to the customer, this presentation event will be recorded:
For that particular creative in the predictive model associated with creatives
For the offer and campaign in which the creative was presented, in the predictive models associated with offers and campaigns