Login Page
The Login page for SunScreen appears when the browser connects to the designated Screen. FIGURE 4-3 shows the Login page for SunScreen.
The controls on the Login page are explained in TABLE 5-1.
Table 5-1 Controls on the SunScreen Login Page
Changing the Password
During installation, a default administration user account called admin with the password admin was created. Change this password as soon as possible to assure the security of the Screen.
Do not change the administration address (le0, qe0, hme0, and the like), the administration certificate, the local certificate, or the administration-group certificate. If you change these items, you risk losing your connectivity from the Administration Station to the Screen. Reestablishing your connectivity is difficult and requires that you log into the Screen directly or use an Administration Station that is still working. It also requires exchanging encryption information
Online Documentation
You can look at the online documentation by clicking the Documentation button on the login page, as shown in FIGURE 4-3 or by clicking the Documentation button on the administration GUI navigation bar, shown in FIGURE 4-3.
SunScreen Information Page
The SunScreen Information page is the default selection in the Select Task field of the Login page. On this page you can move to the Policies List page, choose the Screen about which you want information, view the logged information about a Screen's performance, check the status of a Screen, and view the SKIP statistics, view the online documentation, and logout.
Administration GUI Navigation Bar and Buttons
The administration GUI navigation bar and navigation buttons, shown in FIGURE 5-2, appear at the top of administration GUI pages. You should use these button for moving among the pages of the administration GUI.
Figure 5-2 Administration GUI Navigation Buttons
If these buttons are missing from a page of the administration GUI, it means that you have unsaved changes from your editing session. Once you have saved your changes the buttons reappear.
TABLE 5-2 describes the administration GUI navigation buttons.
Table 5-2 Administration GUI Navigation Buttons
The Name of the Screen
You choose the name of the Screen about which you want to view the information from a choice list. The names of the screens from among which you can choose are those that are in the centralized management group or HA cluster.
The Log Browser Tabs on the Information Page
Clicking one of these tabs displays the status, logs, and the traffic and SKIP statistics.
Status Tab
The Status tab is displayed by default. The Status tab displays the information shown in FIGURE 5-3. This information is derived from the system and the configuration of the firewall when you installed the SunScreen or modified the configuration. You cannot edit any of the fields on this page.
Figure 5-3 SunScreen Information Page--Status Tab
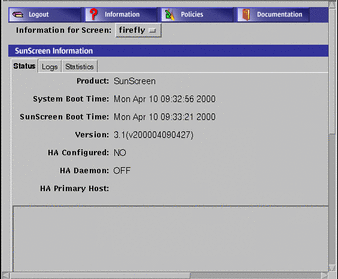
TABLE 5-3 describes the information presented on this page.
Table 5-3 Status Information|
Title |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Product |
The name of the software product. |
|
System Boot Time |
Date and time when the system was last restarted. |
|
SunScreen Boot Time |
Date and time when the system was last restarted. |
|
Version |
The release of the software that is running. |
|
HA Configured |
Whether high availability (HA) is configured (YES or NO). |
|
HA Daemon |
Whether the high availability daemon is running (OFF or ON). If the HA daemon is running, the members of the HA cluster appear in the area below along with the state of each member of the HA cluster (Active or Passive). |
|
HA Primary Host |
The name or IP address of the primary host of the high availability cluster. |
|
Host Names |
Lists the hosts configured for HA. This information appears in the area set off from the rest of the information and is updated by default every 30 seconds. You can change the update interval by changing the poll interval in the Logs tab. |
|
Status |
Shows the status of the primary and secondary HA hosts. The status is ACTIVE, PASSIVE, and NONRESPONSIVE. This information appears in the area set off from the rest of the information and is updated by default every 30 seconds. You can change the update interval by changing the poll interval in the Logs tab. |
|
Help button |
Displays the online help for this page. |
Logs Tab
The logs tab displays the Log Browser panel, as shown in FIGURE 5-4.
Figure 5-4 SunScreen Information Page--Logs Tab
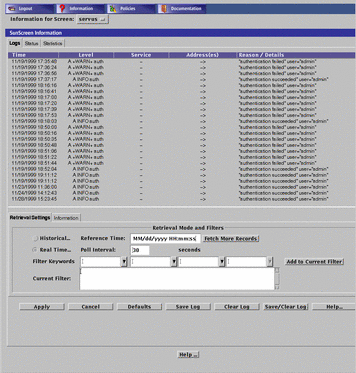
TABLE 5-4 describes the column headings for the log panel of the SunScreen Information page.
Table 5-4 Column Headings on the Log Panel of the SunScreen Information Page|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Time |
Indicates the time that the packet or event represented by this record was logged by the Screen. Use this time field to retrieve records in Historical mode as set in the Log Browser Tab Retrieval Setting. |
|
Level |
Indicates the type and severity level of the logged event. |
|
Service |
Indicates the network service or protocol, such as TCP, IP, NFS, Telnet, or HTTP, over which this packet was sent or to which the event is related. |
|
Address(es) |
Shows the address from which and to which a packet was sent. Arrows indicate direction. Some events that, by themselves, are not related to IP traffic will not have an address or addresses, as shown in the example. |
|
Reason/Detail |
Shows the reason a packet or event was logged or the detail regarding the logging. This information depends on the requirements of the rules within a policy. |
The logs tab also displays the Retrieval Setting tab and Information tab for the logs.
Logged packets are configured in the packet filtering rules so that a packet or an event is displayed which meets the requirements of a rule in a policy. The log has two retrieval modes: Historical and Real Time.
-
The Historical mode allows you to examine a particular segment for a particular time.
-
The Real Time mode displays information as the packets pass through the Screen while you are looking at the log.
For more information setting the values for the log browser, see the section on the "Retrieval Setting Tab" below.
Retrieval Setting Tab
FIGURE 5-5 shows the Retrieval Setting tab for the SunScreen Information page and the log browser in particular. The Filter Keywords, Add to Current Filter, and Current Filter controls are discussed in greater detail in the following section, "Setting a Log Viewing Filter."
Figure 5-5 Retrieval Setting Tab
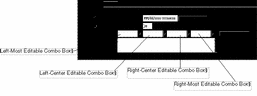
TABLE 5-5 describes the controls on the Retrieval Setting tab.
Table 5-5 Controls on the Retrieval Setting Tab
Setting a Log Viewing Filter
The Log Browser filters log events to be displayed. The language that it uses is identical to the filtering options of the logdump command in the command-line program; it is a superset of the language used by the Solaris snoop packet monitor tool.
You have full access to this language typing an arbitrary logdump expression in the Current Filter text entry box in its Retrieval Settings tab and clicking the Apply button to activate it.
In addition, the Filter Keywords controls provide the ability to create many simple filtering expressions. These controls reduce typing effort as well as serving as reminders of filtering options.
The Filter Keywords controls are used by selecting one or more operations from their choice lists or entering a target (operand) in the rightmost editable combo box. After this choosing or typing your entry, click the Add to Current Filter button to add these items to the Filter Keywords text entry box at its current insertion pointer.
The leftmost editable combo box contains the Boolean operators and, or, and not.
The left-center editable combo box provides filtering terms that are complete and restrict the type of log event displayed. TABLE 5-6 describes the terms in the left-center editable combo box.
Table 5-6 Filter Terms of the Left-Center Editable Combo Box|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
loglvl pkt |
Allows displaying network packet-type events |
|
loglvl sess |
Allows displaying network session-type events |
|
loglvl auth |
Allows displaying events related to authentication operations |
|
loglvl app |
Allows displaying events related to screen application (usually proxy) operations |
|
logapp auth |
Allows displaying events from the authentication subsystem |
|
logapp edit |
Allows displaying events related to registry or policy editing |
|
logapp ftpp |
Allows displaying events from the FTP proxy |
|
logapp log |
Allows displaying events related to the logging facilities themselves |
|
logapp httpp |
Allows displaying events from the HTTP proxy |
|
logapp smtpp |
Allows displaying events from the SMTP proxy |
|
logapp telnetp |
Allows displaying events from the Telnet proxy |
|
logsev emerg |
Allows displaying events of an emergency severity |
|
logsev alert |
Allows displaying events of an alert severity or above |
|
logsev crit |
Allows displaying events of a critical severity or above |
|
logsev err |
Allows displaying events of an erroneous severity or above |
|
logsev warn |
Allows displaying events of a warning severity or above |
|
logsev note |
Allows displaying events of a notice severity or above |
|
logsev info |
Allows displaying events of an informative severity or above (all events that are not of debug severity) |
|
logsev debug |
Allows displaying events of a debug severity or above (all events) |
The right-center editable combo box provides filtering terms most of which are incomplete and require an operand value, You type these in the rightmost editable combo box. They are added to the choice list of the rightmost editable combo box for reference so that you need not retype the value if you want to use it again. TABLE 5-7 describes the filter terms in the right-center editable combo box.
Table 5-7 Filter Terms in the Right-Center Editable Combo Box|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logwhy reason# |
Restricts display to packets that have the given logging reason why code (See Appendix D, Error Messages, TABLE 11-16 |
|
logiface iface |
Restricts display to packets that arrived on the interface named iface |
|
host hostname |
Restricts display to events either from or to hostname |
|
dst hostname |
Restricts display to events destined for hostname |
|
src hostname |
Restricts display to events origination from hostname |
|
port hostname |
Restricts display to events related to the service svcname |
|
dstport hostname |
Restricts display to events targeted to the service svcname |
|
srcport svcname |
Restricts display to events originating from the service svcname |
|
net netaddr |
Restricts display to events either from or to the network whose number is netaddr |
|
gateway gwyaddr |
Restricts display to packets that used gwyaddr as a gateway |
|
udp |
Restricts display to events related to the UDP transport protocol |
|
tcp |
Restricts display to events related to the TCP transport protocol |
|
icmp |
Restricts display to packets of the ICMP control protocol |
|
rpc |
Restricts display to packets of the RPC protocol |
|
etheraddr etheraddr |
Restricts display to packets that have arrived from this Ethernet address |
The terms in italics are variables for which you must supply a value or values in the when you choose this term from the choice list. The values for the variable are as follow:
-
reason # The reason number is shown in TABLE 11-16 in Appendix D, Error Messages.
-
hostname can be:
-
svcname can be:
-
A numeric TCP or UDP port number (for example, 23 for Telnet)
-
A numeric TCP or UDP port number range (for example, 6000. .6023 for X windows)
-
A service name known to the screen's naming service (for example, domain found in /etc/services)
-
-
iface can be:
-
The name of an interface (for example hme0)
-
-
netaddr can be:
-
The IP network number (for example 199.12.200)
-
-
gwyaddr can be:
-
The name of an Ethernet address (link-layer address gateway through which packets are flowing)
-
-
etheraddr can be:
-
The 6-octet Ethernet address (for example 8:0:20:A0:EE:E4)
-
The Information Tab
The log-browser Information tab on the Screen Information page and shown in FIGURE 5-6, provides the statistics for the current log.
Figure 5-6 Information Tab
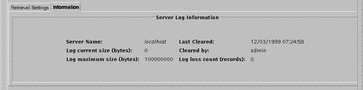
TABLE 5-8 describes the fields on the Information tab. You cannot edit the fields on this page.
Table 5-8 Fields on the Information Tab|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Server Name field |
Indicates the name of the Screen to which the Log Browser is connected. |
|
Log current size field (bytes) |
Indicates the current size of the log file in bytes on the server. |
|
Log maximum size filed (bytes) |
Indicates the maximum size of the log file in bytes on the server. |
|
Last Cleared field |
Indicates the date and time the log file was last cleared. |
|
Cleared By field |
Identifies the login name of the administrator who last cleared the log file. |
|
Log loss count (records) field |
Indicates the number of log records that have been thrown away since the last "clear" operation. Log records are lost if the log grows beyond its maximum size or if the file system on which the log is written fills before that maximum is reached. Packets that cannot be logged because the traffic load exceeds the logger's ability to store entries are not counted. |
Statistics Tab
The Statistics tab, shown in FIGURE 5-7, provides information on traffic and key statistics. Traffic statistics include data such as input and output, passed or failed, logged, and bad packets for packets received over the active interfaces. The Statistics tab is updated according to the setting in the Real Time Poll Interval field on the Retrieval Setting tab of the Logs Tab.
Figure 5-7 SunScreen Information Page--Statistics Tab
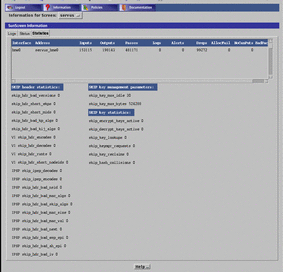
The Traffic Statistics panel (top) displays traffic statistics for each interface on the Screen. TABLE 5-9 describes the fields on the Traffic Statistics panel of the Statistics tab. The values displayed in these fields cannot be modified.
Table 5-9 Controls on the Traffic Statistics Panel of the Statistics Page|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Interface field |
Name of the interface. |
|
Address field |
Address of the interface. |
|
Inputs field |
Total number of packets seen on that network interface. This number includes packets processed by the Screen and intranet traffic. Because this counter records more than just the number of packets through the interface, the number can be much higher than the sum of the numbers in the Passes and Drops fields, which record the number of packets passed and dropped. |
|
Outputs field |
Total number of packets passed from other interfaces on the Screen and sent out over this interface. |
|
Passes field |
Number of packets received from another interface, matched to an ALLOW rule exactly, and sent out over the designated interface. |
|
Logs field |
Number of packets that have been logged by the Screen according to the actions in the active configuration. |
|
Alerts field |
Number of SNMP alerts generated because of the traffic on this network interface. |
|
Drops field |
Number of packets that have been dropped, either as a result of exactly matching a DENY rule or as a result of not matching any rule and being dropped as the default action of the Screen's interface. |
|
AllocFail field |
Error counter for packets lost because of the lack of resources. |
|
NoCanPuts field |
Error counter for packets lost because of the lack of stream flow control. |
|
BadPackets field |
Error counter for packets lost because of errors. |
The SKIP Statistics panel shows the SKIP statistics for the SunScreen. TABLE 5-10 describes the fields on the SKIP Statistics panel of the Statistics page. The values displayed in these fields cannot be modified.
Table 5-10 Controls on the SKIP Statistics Panel of the Statistics Tab|
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
|
skip_hdr_bad_versions field |
Total number of SKIP headers with invalid protocol versions. |
|
skip_hdr_short_ekps field |
Number of SKIP headers with short encrypted packet fields. |
|
skip_hdr_short_mids field |
Number of SKIP headers with short MID fields. |
|
skip_hdr_bad_kp_algs field |
Number of SKIP headers with unknown cryptographic algorithms. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_encodes field |
Number of SKIP V1 headers encoded. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_decodes field |
Number of SKIP V1 headers decoded. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_runts field |
Number of SKIP V1 headers with short packets. |
|
V1 skip_hdr_short_nodeids field |
Number of SKIP V1 headers with short node identifiers. |
|
IPSP skip_ipsp_decodes field |
Number of SKIP V2 headers decoded. |
|
IPSP skip_ipsp_encodes field |
Number of SKIP V2 headers encoded. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_nsid field |
Number of headers with a bad V2 name space identifier. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_algs field |
Number of headers with unknown or bad authentication algorithms. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_size field |
The number of headers with an authentication error in the MAC size. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_mac_val field |
The number of headers with an authentication error in the MAC value. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_next field |
Number of headers with a bad Next Protocol field. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_esp_spi field |
Number of headers with a bad V2 SPI field. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_ah_spi field |
Number of headers with a bad V2 AH SPI field. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_iv field |
Number of headers with a bad V2 initialization vector. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_short_r_mkeyid field |
Number of headers with a short V2 receiver key identifier. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_short_s_mkeyid field |
Number of headers with a short V2 sender key identifier. |
|
IPSP skip_hdr_bad_bad_r_mkeyid field |
Number of headers with a bad V2 receiver key identifier. |
|
skip_key_max_idle field |
Time, in seconds, until an unused key is reclaimed. |
|
skip_key_max_bytes field |
Maximum number of bytes to encrypt before discarding a key. |
|
skip_encrypt_keys_active field |
Number of encryption keys in the cache. |
|
skip_decrypt_keys_active field |
Number of decryption keys in the cache. |
|
skip_key_lookups field |
Total number of key cache lookups. |
|
skip_keymgr_requests field |
Total number of key cache misses (key not found). |
|
skip_key-reclaims field |
Total number of key entries reclaimed. |
|
skip_hash_collisions field |
Total number of table collisions. |
The Action Buttons
FIGURE 5-8 shows the action buttons for the SunScreen Information Page. Use these buttons to control the various actions on the log.
Figure 5-8 Action Buttons on the SunScreen Information Page
TABLE 5-11 describes the action buttons on the SunScreen Information Page.
Table 5-11 Action Buttons on the SunScreen Information Page
Help System
The Help button displays context-sensitive help for the page on which you are. It brings up a new browser window, which you can quit to return to your page or you can move it aside and keep it open for quick reference.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
