| Logical Domains (LDoms) MIB 1.0.1 Administration Guide |
| C H A P T E R 1 |
The Logical Domains (LDoms) Management Information Base (MIB) enables third party system management applications to perform remote monitoring and starting and stopping logical domains using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
The LDoms MIB software runs on the control domain only, and only one instance of the LDoms MIB can be run. You must use Solaris 10 11/06 at a minimum, and the Logical Domains 1.0.1 software at a minimum.
The LDoms MIB package (SUNWldmib.v) contains the following software components:
SUN-LDOM-MIB.mib – An SNMP MIB in the form of a text file that defines the objects in the LDoms MIB.
ldomMIB.so – An SMA extension module in the form of a shared library that enables the SMA to respond to requests for information specified in the LDoms MIB. This module also generates traps.
FIGURE 1-1 shows the interaction between the LDoms MIB, the SMA, the LDoms Manager, and a third party system management application.
FIGURE 1-1 LDoms MIB Interaction With SMA, LDoms Manager, and Third Party System Management Application
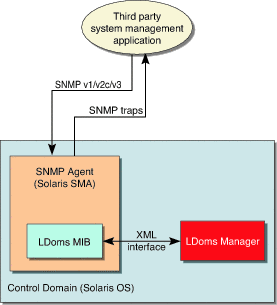
The SNMP agent listens on the standard SNMP port (161) for requests from a third party system management application to get or set data offered by the LDoms MIB The SNMP agent can also emit traps to the configured system management application using the standard port for SNMP notifications (162). The LDoms MIB is exported by the Solaris OS default System Management Agent (SMA) on the control domain.
The SMA supports the get, set, and trap functions of SNMP versions v1, v2c, and v3. Most LDoms MIB objects are read-only for monitoring purposes, but starting and stopping a logical domain is supported using a write of the ldomAdminState property of the ldomTable. See TABLE 4-1 for more information about this property and table.
A logical domain is a container that consists of a set of virtual resources for a guest operating system. The Logical Domains Manager provides the command-line interface (CLI) for creating, configuring, and managing the logical domains.
The Logical Domains Manager and the LDoms MIB support the following virtual resources:
The Logical Domains Manager exports an XML-based control interface to the LDoms MIB. The LDoms MIB parses the XML interface and populates the MIB. The LDoms MIB provides support only for the control domain.
The LDoms Manager 1.0.1 software does not provide event information when there is a change in a logical domain’s state, such as add, remove, start, or stop. So the LDoms MIB polls the Logical Domains Manager periodically for updates or status change and issues SNMP traps to the system management applications.
If the LDoms MIB can no longer allocate a needed resource, it returns a general error to the system management application through the SNMP agent. The SNMP delivery mechanism for traps does not provide confirmation. No specific state or checkpointing is implemented in the LDoms MIB. The SMA with the LDoms MIB is started and monitored by the init process and the Service Management Facility (SMF). When the SMA fails and exits, the SMF restarts the process automatically. Once restarted, the new process dynamically restarts the LDoms MIB module.
SNMP-managed objects are organized into a tree-like hierarchy. An object identifier (OID) consists of a series of integers based on the nodes in the tree, separated by dots. Each managed object has a numerical OID and an associated textual name. The LDoms MIB is registered as the ldom (205) branch under:
iso(1).org(3).dod(6).internet(1).private(4).enterprises(1). sun(42).products(2)
FIGURE 1-2 shows the major subtrees under the LDoms MIB.

Copyright © 2007, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.