Using the -sunhpc Option
LSF Suite version 3.2.3 supports the bsub command-line option -sunhpc, which gives users special control over Sun MPI jobs. As mentioned earlier, the -sunhpc option and its arguments must be the last option on the bsub command line:
bsub [basic_options] [-sunhpc sunhpc_args] job
"Redirect stderr" through "Spawn a Job in the Stopped State" describe the -sunhpc arguments.
Redirect stderr
Use the -e argument to redirect stderr to a file named file.Rn, where file is the user-supplied name of the output file. The Rn extension is supplied automatically and indicates the rank of the process producing the stderr output.
For example, to redirect stderr to files named boston.R0, boston.R1, and so forth, enter
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 4 -q hpc -sunhpc -e boston hpc-job
Redirect stdout
Use the -o argument to redirect stdout to a file named file.Rn, where file is the user-supplied name of the output file. The Rn extension is supplied automatically and indicates the rank of the process producing the stdout output.
For example, to redirect stdout to files named boston.R0, boston.R1, and so forth, enter
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 4 -q hpc -sunhpc -o boston hpc-job
Collocate Jobs by Specifying Job ID
Use the -j argument to specify the job ID of another job with which the new job should collocate.
For example, to cause job hpc-job to be collocated with a job whose job ID is 4622, enter
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 4 -q hpc -sunhpc -j 4622 hpc-job
Use bjobs to find out the job ID of a job. See the LSF Batch User's Guide for details.
Collocate Jobs by Specifying Job Name
Use the -J argument to specify the name of another job with which the new job should collocate.
For example, to cause job hpc-job1 to be collocated with a job named hpc-job2, enter
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 4 -q hpc -sunhpc -J hpc-job2 hpc-job1
Specify the Number of Processes
Use the -n argument to specify the number of processes to run. This argument can be used in concert with the bsub -n argument to cause process wrapping to occur. Process wrapping is the term used to describe a technique for distributing multiple processes to fewer processors than there are processes. As a result, each processor has multiple processes, which are spawned in a cyclical, wrap-around, fashion.
For example, the following will distribute 48 processes across 16 processors, resulting in a 3-process wrap per processor.
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 16 -q hpc -sunhpc -n 48 hpc-job
If you specify a range of processors rather than a single quantity and a larger number of processes, the process wrapping ratio (number of processes per to processor) will depend on the number of processors that are actually allocated.
For example, the following will distribute 48 processes across at least 8 processors and possibly as many as 16.
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 8,16 -q hpc -sunhpc -n 48 hpc-job
Consequently, the process-to-processor wrapping ratio may be as high as 6:1 (48 processes across 8 processors) or as low as 3:1 (48 processes across 16 processors).
Spawn a Job in the Stopped State
Use the -s argument to cause a job to be spawned in the STOPPED state. It does this by setting the stop-on-exec flag for the spawned process. This feature can be of value in a program monitoring or debugging tool as a way of gaining control over a parallel program. See the proc(4) man page for details.
Note -
Do not use the -s argument with the Prism debugger. It would add nothing to Prism's capabilities and would be likely to interfere with Prism's control over the debugging session.
The following example shows the -s argument being used to spawn an interactive batch job in the STOPPED state.
hpc-demo% bsub -I -n 1 -q hpc -sunhpc -s hpc-job
To identify processes in the STOPPED state, issue the ps command with the -el argument:
hpc-demo% ps -el F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD 19 T 0 0 0 0 0 SY f0274e38 0 ? 0:00 sched
Here, the sched command is in the STOPPED state, as indicated by the T entry in the S (State) column.
Note that, when spawning a process in the STOPPED state, the program's name does not appear in the ps output. Instead, the stopped process is identified as a RES daemon.
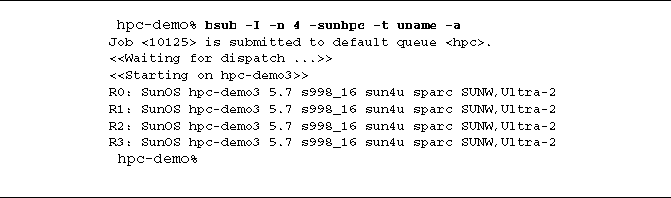
Generate Rank-Tagged Output
Use the -t argument to cause all output to be tagged with its MPI rank.
Note -
The -t argument cannot be used when output is redirected by the -e or -o options to -sunhpc.
For example, the following adds a rank-indicator prefix to each line of output.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
