|
|
Script Repository and Script
Launcher
|
This chapter covers the following topics:
The Script Repository and Script Launcher modules enable you to execute scripts that perform arbitrary management tasks on remote devices. Executing scripts on remote devices reduces the processing load on a central management station and provides a mechanism for keeping polling local.
This section details the following topics:
The Script Repository module enables you to view the scripts available on the agent to be run by the Script Launcher module. The Script Repository module also lists the languages supported by the Script Launcher module.
 |
To Access the Script Repository Module
|
| |
|
See the Sun Management Center 3.0 User's Guide for more information. The Script Repository module is available under Local Applications in the Navigator window. |
| |
2. |
Double-click Local Applications in the Navigator window. |
| |
3. |
Double-click Script Repository. |
| |
|
The Script Repository displays the following folder or group in the Viewer: |
| |
a. |
Double-click Script Information to view the Language Table and the Script
Table.
|
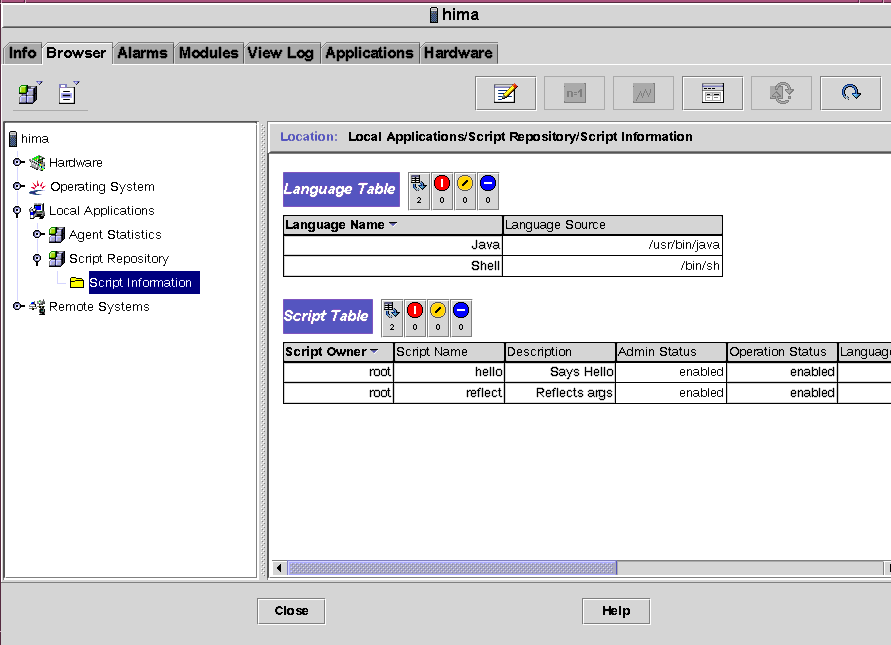
FIGURE 5-1 Script Repository Module
Script Information
- This group includes two tables:
- The Language Table, which lists the supported languages (currently, Java and shell script).
- The Script Table, which enables you to view available scripts on the agent.
Language Table
The first table in the Script Information group is the Language Table. It lists all the scripting languages supported on the agent. Each table entry has the following attributes:
- Language Name (for example, Java)
- Language Source (for example, /usr/java)
There are no commands available on this table. You cannot specify a new language or remove a language. The number of entries is fixed and is defined by the implementation of the module and the languages it supports.
You can modify only the Language Source field.
 |
To Change the Language Source
|
| |
1. |
Update the entry in the cell. |
| |
|
For example, if you want to change /usr/java to /usr/java1.2, enter it directly in the cell. The information that you enter here is made persistent. |
Note - If you enter an invalid path name or file name, you will receive an alarm.
| |
2. |
Click OK to acknowledge, or Cancel to cancel, your edits in the confirmation box, as shown in FIGURE 5-2. |
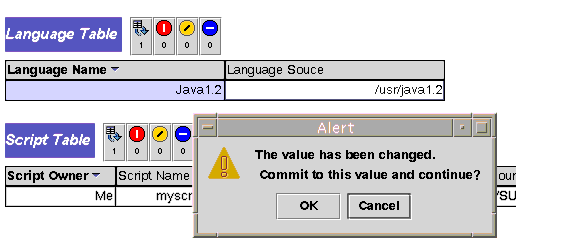
FIGURE 5-2 An Alert Box Seeking Confirmation
 |
To Detect Alarms
|
 |
SysRM generates an information (INFO) alarm if the language cannot be found at
the specified location.
|
Script Table
The Script Table lists all scripts known to the Script Launcher on the agent. Each entry in the table has the following attributes.
TABLE 5-1 Script Table Values
| Script Owner
|
The user on the agent who owns this script.
|
| Script Name
|
The script name.
|
| Description
|
A description of the purpose of the script.
|
| Admin Status
|
Enabled indicates that the owner allows the script to be used by others.
Disabled indicates that the owner does not allow the script to be used by anyone else.
|
| Operation Status
|
For example:
Enabled indicates that the script is available and can be started by a launch table entry.
Disabled indicates that the script cannot be used.
NoSuchScript indicates that the script does not exist at the specified location.
WrongLanguage indicates that the language is not known.
|
| Language
|
The language in which the script is written. This value needs to
be one of the languages listed in the "Language Table."
|
| Script Source
|
File name of the script.
|
| Default Argument
|
The default argument for this script.
|
| Script Users
|
The users who are permitted to use this script.
|
| Groups
|
The UNIX groups which are permitted to use this script.
|
Note - The only field you can modify is the Admin Status through the browser. The Admin Status is the area where you enter the desired status of your script. For example, the Admin Status can be "enabled" or "disabled." While this choice reflects your desired status, only the Operation Status reflects the actual status once the module determines that all criteria have been met and are ready.
Script Table Alarms
- An info alarm will be issued if the script is not in a supported language.
- An info alarm will be issued if the script is not accessible.
The ScriptInfo.dat File
The ScriptInfo.dat contains information about the scripts that are available to be run. You can add a new script to the ScriptInfo.dat file so that the module recognizes it. All the scripts that belong to a user must be listed in this file.
 |
To Add a New Script
|
The format of the ScriptInfo.dat file follows the standard configuration file format.
<slice>:<attribute>=<value>
|
| |
2. |
Save the new script in the ScriptInfo.dat file. |
You can access the ScriptInfo.dat file in the following directory identified by your user name.
For example:
/var/opt/SUNWsymon/SysMgmtPack/script-launcher/scripts
|
| |
3. |
Place the information in the above directory. |
If this file already contains information about a script, add your script below the current information.
An example of the ScriptInfo.dat file, with two scripts, follows:
Script1:Owner = Scott
Script1:Name = MyHello
Script1:Desc = Says Hello
Script1:Language = Java1.2
Script1:Source = Hello.class
Script1:AdminStat = 1
Script1:OperStat = 1
Script1:Users = Noble
Script1:Groups = Staff
Script2:Owner = Denise
Script2:Name = MyFile
Script2:Desc = Says Hello
Script2:Language = Java1.2
Script2:Source = Hello.class
Script2:AdminStat = 1
Script2:OperStat = 1
Script2:Users = Noble
Script2:Groups = Staff
|
Security for Script Repository
The security for Script Repository is implemented as follows:
- Only the root user can place scripts in the following directory:
/var/opt/SUNWsymon/SysMgmtPack/script-launcher/scripts
|
- Each script specifies the users and groups who are allowed to execute the script. These are specified as entries within Users and Groups in the script configuration file. In addition these fields can be modified from the console through the Script Table. Only esadm users are allowed to modify these fields.
- root cannot be in the Script Users field of the Script Table.
The Script Launcher module enables you delegate management functions to agents. (Management functions are defined as management scripts written in a management scripting language.) The Script Launcher module is a multi-instance module. All instances of the Script Launcher module access the same Script Repository module for language and script information.
The Script Launcher module enables you to:
- Control who is allowed to read, write, and execute scripts from the Script Repository module.
- Specify arguments for management scripts.
- Initiate and terminate management scripts.
- Monitor and control running management scripts.
- View the results produced by running management scripts.
- Control who is allowed to read, write, and execute scripts.
 |
To Access the Script Launcher Module
|
| |
|
See the Sun Management Center 3.0 User's Guide for more information. The Script Repository module is available under Local Applications in the Navigator window. |
| |
2. |
Double-click Local Applications in the Navigator window. |
| |
3. |
Double-click Script Launcher. |
| |
|
The Script Launcher displays the following two folders or groups in the Viewer: |
- Launch Table
- Result Table
| |
a. |
Double-click Script Launcher to view the Launch Table and the Result Table.
|
Launch Area
- This group includes two tables:
- The Launch Table enables you to create an entry, add a row, or define a script to be launched by creating an entry.
- The Result Table enables you to view the results of running a selected script.
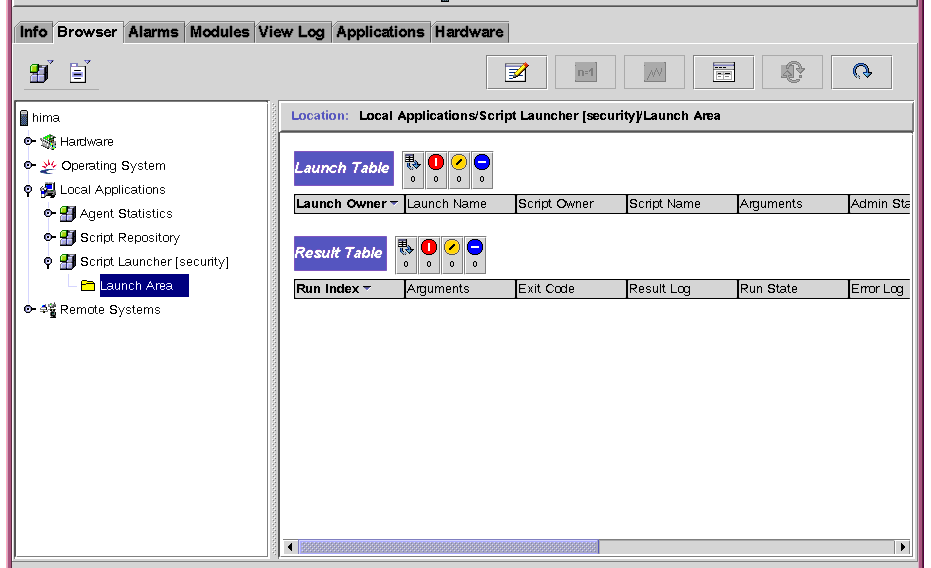
FIGURE 5-3 Script Launcher Module with the Launch Area Displayed
Launch Table
The Launch Table controls the execution of all scripts. The Launch Table describes scripts that are ready to be launched along with descriptions of their parameters. An entry in the Launch Table attaches an argument to a script.
An entry in the Launch Table also defines the owner, used to associate permissions to execute the script. Several instances of a script may be created through one single entry on this table, and several entries on this table may point to a same script on the Script Table. You can execute several identical scripts with different arguments and permissions.
Launch Table Attributes
The Launch Table has the following attributes.
TABLE 5-2 Launch Table Attributes
| Owner
|
The manager who owns this entry.
|
| Name
|
The name of the entry. This should be unique for each row in the launch table.
|
| Script Owner
|
In combination with the script name, it identifies the script.
|
| Script Name
|
In combination with the script owner, it identifies the script.
|
| Arguments
|
Arguments to be supplied to the script.
|
| Admin Status
|
The value of this object indicates the desired status of this launch table entry, which can be either "enabled" or "disabled."
|
| Operation Status
|
The value of this object indicates the actual status of this launch table entry, which can be either "enabled" or "disabled."
|
| Max Running
|
The maximum number of concurrently running scripts that may be invoked from this entry. The default value is 3. This field can be modified by directly writing into the field.
|
| Max Completed
|
The default value is 3. The maximum number of finished scripts invoked from this entry in the "Launch Table" allowed to be retained in the "Result Table."
|
| Life Time
|
The default maximum amount of time a script launched from this entry may run. The default value is 86,400 seconds (1day).
|
| Expire Time
|
The default maximum amount of time information about a script launched from this entry is kept in the "Result Table" after the script has completed execution.
|
Result Table
The Result Table lists all scripts that are currently running or have recently terminated.
This table contains information on the following types:
- When the script started and finished execution
- The reason the scripts finished executing
- The result of the script, the remaining time the script is allowed to run
Every row in the Result Table contains the arguments passed during script invocation, the results produced by the script, and the script exit code. The Result Table also provides information about the current run state, and start and end timestamps.
The Result Table has the following attributes.
TABLE 5-3 Result Table Attributes
| Run Index
|
The locally arbitrary, but unique identifier associated with this running or finished script is obtained by prepending launchName with an increasing integer starting from 0.
|
| Argument
|
The argument supplied to the script when it started.
|
| Start Time
|
The date and time when the execution started.
|
| End Time
|
The date and time when the execution terminated.
|
| Life Time
|
How long the script can execute. If the script has not terminated when this time has expired, the script is killed automatically.
|
| Expire Time
|
How long this row can exist in the "Result Table" after the script has terminated. This is the value of "Expire Time" field of Launch Table when the script was launched. A script entry will be removed from Result table when "Expire Time" seconds are past since the script comes to "Not Running" state.
|
| Exit Code
|
The reason why a script finished execution.
Possible values are:
None: Script is still in "initializing" or "Running" state.
Halted: Script has been aborted.
Successful: Script finished executing successfully
Failed: Script finished execution with an error.
|
| Result
|
The path to the log file.
|
| Run State
|
The script execution status. Possible values are:
Initializing: The script is initializing
Running: The script is running.
Not Running: Note that the script could be in this state because of successful completion, failing, or aborting. The exact reason why the script is "Not Running" is reflected in "Exit Code" field.
|
| Error
|
The path to the log file.
|
Viewing Results
You can either view the results of running the scripts in the Show Result Table or you can view the entries in the Result Log.
 |
To View the Results from the Result Table
|
| |
1. |
Right-click on a running script entry in the Result Table. |
| |
2. |
Select View the Result Log to view the result log file corresponding to the selected running script in a new window. |
| |
|
The Probe Viewer displays the result of the log. |
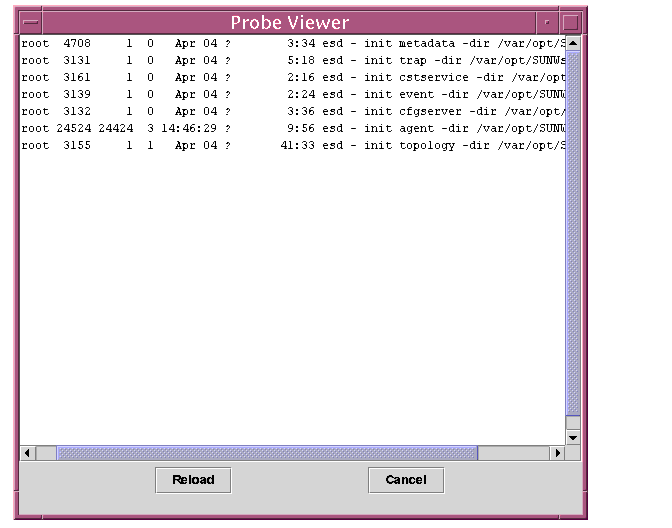
FIGURE 5-4 Sample Log Content
Result Table Alarms
An information (info) alarm is generated if a running script is aborted.
 |
To View the Result Table Log File From the Command Line
|
| |
1. |
Go to the following directory:
/var/opt/SUNWsymon/SysMgmtPack/script-launcher/scripts/<UserName>/logs
|
|
The results of the scripts are saved in log files. The log files are saved in the above location. The log file name will carry the particular running instance so that the current log file can be identified when a user runs the same script several times.
| |
2. |
Open the file at the command line and view the results. |
Security for the Script Launcher
The security for Script Launcher is implemented as follows:
- root cannot be part of the LaunchOwner field of the Launch Table. In such cases, if you want the root of a machine to run scripts as a super-user, create a new user on the machine and use that user name to run the scripts.
- The launchOwner must be a part of new esscrusers group on the server. Only esscrusers can create rows or make changes in the Launch Table.
- The Launch Owner, or launchOwner, must be a valid user on the agent machine, which means the user must either be a local user or someone added through a service such as NIS on the agent. Scripts are run with the launch owner's permissions.
Available Commands
The following commands are available from the Script Launcher.
 |
To Add a New Entry to the Launch Table
|
| |
1. |
Right-click the Launch Table header. |
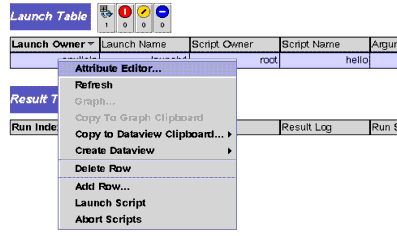
FIGURE 5-5 Commands available at the row level
| |
|
Fill in all the required parameters. |
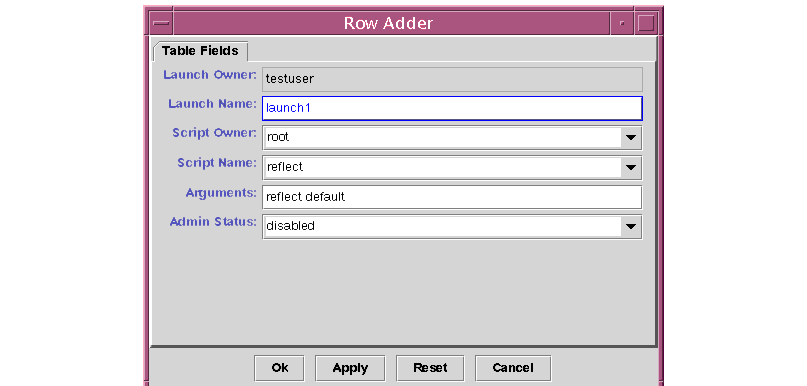
FIGURE 5-6 The Row Adder
The Script Owner and Script Name values point to the script that should be started from this launch button.
 |
To Delete an Entry in the Launch Table
|
 |
Select Delete Row and proceed to delete the row.
|
 |
To Launch An Instance of the Script
|
 |
Select Launch Script.
|
| |
|
An instance of the launch will be launched. |
 |
To Abort Scripts
|
 |
Select Abort Scripts to abort all the scripts launched from this row.
|
From the Result Table
 |
To View the Result Log
|
| |
1. |
Right click on the row for which you want the results from the Result Table window. |
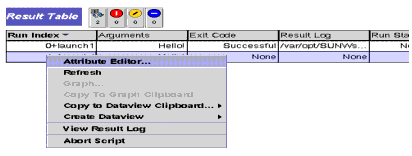
FIGURE 5-7 View result Log Command
| |
2. |
Select View Result Log. |
| |
|
SysRM displays the results in a corresponding window. |
FIGURE 5-8 Sample Log Content
| |
3. |
View the result log file that contains results of the selected running script. |
 |
To Abort a Script
|
 |
Select Abort Script.
|
- The script instance corresponding to that row will be aborted.





Copyright © 2001 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.