Chapter 2 Using Sun Management Center Administrative Domains
A Sun Management Center administrative domain is an arbitrary collection of resources that can include a complete site, individual buildings, hosts, networks, subnets, links, and so on. The organization of an administrative domain collection is in a hierarchy.
Note –
In this document, administrative domain refers to a Sun Management Center administrative domain. This term should not be confused with other uses of the term domain related to other Sun products or documentation.
This chapter describes the following topics:
Administrative Domains Concepts
Sun Management Center software can monitor a multitude of hosts. To enable you to perform your monitoring tasks in an efficient manner, Sun Management Center software organizes hosts into groups. The largest, highest-level grouping is an administrative domain. An administrative domain is an arbitrary grouping of hosts, subnets, networks, buildings, and so on.
You can create one or more administrative domains. Each administrative domain consists of one or more members that are arranged in a hierarchy. For example, you might decide that an administrative domain consists of all the hosts in one building. Or, you might decide that an administrative domain consists of all the hosts in a campus. Note the following characteristics that apply to domains.
-
Each domain name must be unique.
-
Domain names cannot be changed.
-
Users who belong to the group esdomadm can create administrative domains, create groups within administrative domains, and perform similar tasks. For more information about security, see Chapter 18, Sun Management Center Security.
For example, you might set up three administrative domains, one for production, one for testing, and one for integration testing. Alternatively you might set up domains that are based on hardware platform, such as a domain for x86 machines and a domain for Sun Blade 1000s. If you set up a domain for each hardware platform, you might also set up a group within that domain for the machines of that hardware platform with a specific patch applied
Tip –
Spend some time planning how you want to organize your hosts into different administrative domains.
Decide whether you need additional groups below the administrative domain to organize your hosts. For example, if there are several hundred hosts, placing your hosts individually in one administrative domain is impractical.
You might decide to break the administrative domain into a set of smaller groups, for example, campuses. The Headquarters administrative domain might consist of several campus locations. Each of these campus locations might be broken into smaller groups, for example, buildings. Similarly, each building might be broken into smaller groups, such as networks, subnets, and groups. Finally, each group contains individual hosts.
In this particular example, the hierarchical order, from highest level to lowest level, is as follows:
-
Administrative domain
-
Campus
-
Building
-
Network
-
Subnet
-
Group
-
Individual host
For detailed information about creating administrative domains, see To Create Administrative Domains.
The home domain is the administrative domain that is displayed when you log into a specific server.
Starting Sun Management Center Software
The Sun Management Center server software automatically starts upon completion of installation and when the server system reboots. You use a console to access the server.
 To Start Sun Management Center
To Start Sun Management Center
-
To start the Sun Management Center console, type the following command:
% installed-root-directory/sbin/es-start -c
where the default installed root directory is /opt/SUNWsymon.
The login screen appears.
Note –You can also access some Sun Management Center features from a browser. For more information, see Chapter 15, Managing Objects Using the Web Console.
-
Type a valid user name, password, and server host name in the appropriate fields.
The user account must be listed in the /var/opt/SUNWsymon/cfg/esusers file on the Sun Management Center server.
Tip –To change the server port number or the communications security level for this console session, click Options.
-
Press the Return key, or click the Login button.
The Set Home Domain window appears if you have not previously logged in to this server or if you have not set a home domain. The home domain is the administrative domain that is displayed when you log in to a specific server. This dialog box appears each time you start the console until you set a home domain.
During installation, a default administrative domain that is named Default Domain is created for you. The Default Domain initially consists of one object, your server host. To use the default administrative domain, select Default Domain and click the Go To button. For information about setting the home domain, see To Set the Home Administrative Domain.
At this time, you might want to populate your administrative domain or perform other tasks.
-
To create objects in your administrative domain, see Populating Administrative Domains.
-
To explore the main console window, see Chapter 5, Managing Objects in Sun Management Center.
-
To explore monitoring features, see Chapter 8, Monitoring Data Properties.
-
To create additional administrative domains, see To Create Administrative Domains.
-
 To Close a Session of Sun Management Center
To Close a Session of Sun Management Center
Choose Close from the File menu in the main console window.
The console appears so that you can login again.
 To Set the Home Administrative Domain
To Set the Home Administrative Domain
-
To access the Set Home Domain window, choose Set Home Domain from the File menu in the main console window.
Tip –The Set Home Domain window appears automatically if you have not previously logged in to this server or if you have not set a home domain.
-
In the Set Home Domain window, select the name of the administrative domain that you want to set as your home domain.
The selected administrative domain is highlighted.
-
Click the Set Home button.
You see the following message at the bottom of the Set Home Domain dialog box.
Setting Home Domain...Please wait
When the home domain has been set, the message changes.
Home domain successfully set.
Your default administrative domain is set as your home domain. Information about the home domain appears in the main console window. For more information, see Administrative Domains Concepts.
Tip –Click the Go To button to use an administrative domain without setting the domain as the home domain. The selected administrative domain appears in the main console window. In this case, your home domain is not set, and the Set Home Domain window appears the next time that you start the console.
-
Click the Close button.
The selected home domain appears in the main console window.
Creating Administrative Domains
Use the Domain Manager window to create Sun Management Center administrative domains.
 To Create Administrative Domains
To Create Administrative Domains
-
Choose Domain Manager from the File menu in the main console window.
The Domain Manager appears.
-
In the Domain Manager, click the Add button.
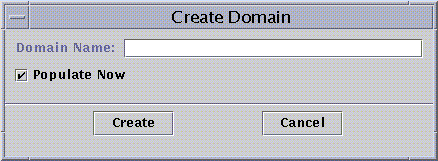
The Create Domain dialog box appears, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 2–1 Create Domain Dialog Box
-
Type the name of the new administrative domain in the Domain Name field.
-
If you do not want your administrative domain to be populated now, deselect the Populate Now check box.
The default choice is for Sun Management Center software to display a dialog box that enables you to start the Discovery Manager immediately after creating an administrative domain. For more information about the Discovery Manager, see Chapter 4, Adding Objects to the Topology Database Using the Discovery Manager.
-
To create the new administrative domain, click the Create button.
To close the window without creating the administrative domain, click the Cancel button.
If you do not have the proper security permissions to create an administrative domain, an error message is displayed. See Chapter 18, Sun Management Center Security for more information about security.
Populating Administrative Domains
Once you have created your administrative domains, you can begin to populate these administrative domains and their subordinate groups.
Note –
To populate an administrative domain, you must have esdomadm privileges. See Sun Management Center Groups for more information.
To add hosts and other resources to an administrative domain collection, use one of these methods:
-
Populate with the Discovery Manager
The Discovery Manager is the default method for populating a newly created administrative domain. Discovery Manager searches the network for resources. The search can be time-consuming, but you can shorten the search by setting limits. See Chapter 4, Adding Objects to the Topology Database Using the Discovery Manager for more information.
-
Populate with the Discovery Manager at scheduled intervals by using the Scheduling feature
The scheduling feature enables you to search periodically for new managed objects on the network. You can set the search to occur hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly. See Making and Modifying Discover Requests for more information.
-
Manually populate with the Create an Object menu option
To add objects individually, use the Create an Object option. This option is useful for adding a small number of known resources. For example, if you have installed a new host, you can use Create an Object to add the host to the local administrative domain immediately. See Chapter 3, Manually Adding Objects to the Topology Database for more information.
Managing Administrative Domains
Once you have created Sun Management Center administrative domains, you can manage those domains.
 To View Information About an Administrative Domain
To View Information About an Administrative Domain
You can list administrative domains through the Domain Manager window or the Sun Management Center main console window.
-
Access the Domain Manager from the main console window in one of the following ways:
-
Choose Domain Manager from the File menu.
-
Click the Sun Management Center Administrative Domains pull-down menu.
The current list of administrative domains is displayed.
-
-
Select the administrative domain that you want to view.
The main console window displays the selected administrative domain. The Sun Management Center Administrative Domains button changes to display the name of the administrative domain that you selected.
 To Set Security for an Administrative Domain
To Set Security for an Administrative Domain
The administrative domain Attribute Editor provides additional information about the selected administrative domain and about the rules that govern its behavior. Use the Attribute Editor to edit security information for the administrative domain.
Note –
Each Attribute Editor displays one or more tab buttons depending on the type of selected object.
-
Access the Attribute Editor in either of the following ways:
-
From the hierarchy view in the main console window, press mouse button 3 on the administrative domain icon. Then, choose Attribute Editor from the pop-up menu.
-
From the main console window, choose Domain Manager from the File menu. Then, choose an administrative domain and click the Security button.
-
-
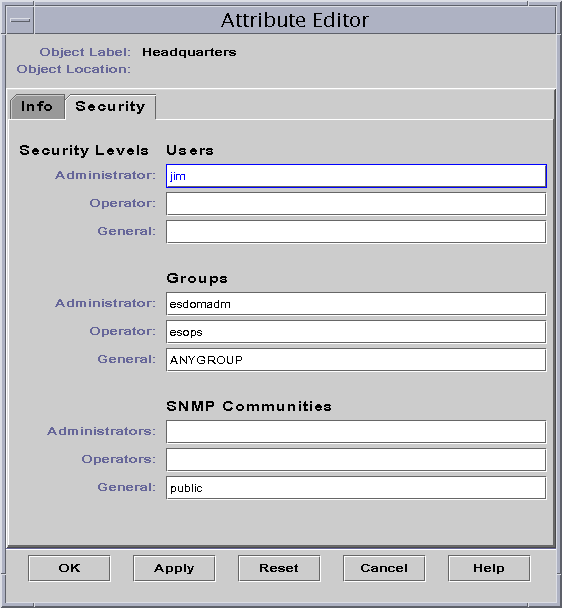
If not already selected, click the Security tab in the Attribute Editor window.
The security information appears in the Attribute Editor window, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 2–2 Attribute Editor for an Administrative Domain
-
Type the names of user and administrator groups in the appropriate fields.
See Chapter 18, Sun Management Center Security for more information about users and groups.
-
To accept your changes and close the Attribute Editor window, click the OK button.
 To Delete an Administrative Domain
To Delete an Administrative Domain
When you delete an administrative domain, you also delete all the members of that administrative domain.
-
In the Domain Manager window, select the name of the administrative domain that you want to delete.
Note –To delete an administrative domain, you must have the appropriate security permission. For more information about Sun Management Center security, see Chapter 18, Sun Management Center Security.
-
Click the Delete button.
The Confirm Domain Deletion dialog box is displayed.
There are two versions of the Domain Deletion dialog box. One version is for any administrative domain. The other version is for the administrative domain that you are currently viewing.
-
To verify that you want to delete the selected administrative domain, click the Delete button.
The Confirm Domain Deletion dialog box displays the following message.
Deleting domain...Please wait.
When the administrative domain has been successfully deleted, the dialog box is removed and the Domain Manager updates the list of administrative domains.
-
To close the Domain Manager window, click the Close button.
Monitoring Remote Administrative Domains
Remote administrative domains are Sun Management Center administrative domains that are created in a different Sun Management Center server context. See Server Context for a description of server context.
If you are interested in an object in a different server context, you can still monitor the remote resource. To monitor the remote resource, reference the remote administrative domain in your local administrative domain. To manage the remote resource, log out of your current Sun Management Center server context and log into the remote server context. You can manage monitored properties on a resource only if the agent is managed by the server to which your console is connected. By default, Sun Management Center security gives you “read-only” privileges for remote administrative domains. For more information about security, see Chapter 18, Sun Management Center Security.
Note –
You can reference a remote administrative domain to monitor resources in that administrative domain. You cannot manage monitored properties on a remote resource.
For example, your current Sun Management Center server context might be based in the Headquarters administrative domain. A second, remote Sun Management Center server context might be based in Regional Office 1. When workers are absent from Regional Office 1, you can monitor the regional office administrative domains from Headquarters by referencing these remote administrative domains in the Headquarters server context. If an emergency occurs, administrators in Headquarters can notify a Regional Office 1 administrator immediately.
Note –
Remote administrative domains enable you to monitor critical resources continuously.
Figure 2–3 illustrates how remote monitoring works. Administrative Domain A monitors objects 1 and 2, which are assigned to Domain A. Administrative Domain A remotely monitors objects 3 and 4, which are assigned to Domain B. Note that administrative Domain A cannot monitor objects 3 or 4 without going through remote administrative Domain B.
Figure 2–3 Remote Administrative Domain
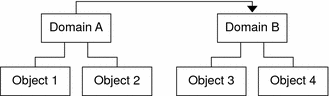
Do not create an administrative domain that refers to itself. For example, do not create an administrative domain A that references another administrative domain B which in turn, contains a reference to administrative domain A.
If two administrative domains must monitor each other, avoid creating a circular domain reference. Instead, create a domain member, for example a group, under Domains A and B as shown in the following figure.
Figure 2–4 Setting Up Successful Cross-Monitoring for Remote Administrative Domains
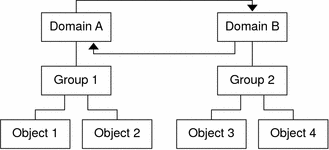
Now when making a remote reference, Domain A can reference Group 2 under Domain B, while Domain B can reference Group 1 under Domain A.
 To View Information From a Remote Administrative
Domain
To View Information From a Remote Administrative
Domain
-
In the main console window, choose Remote Domain Manager from the File menu.
The Remote Domain Manager dialog box is displayed.
-
Type the name of the remote server in the Host field.
-
If applicable, type the port number for the remote Topology manager in the Port field
By default, the Topology manager is installed on the server on port 164.
-
Click the List Domains button.
A list of administrative domains on the remote server is displayed.
-
Select the administrative domain that you want to reference.
The selected administrative domain is highlighted.
-
Click the Reference button.
The selected administrative domain is created as a reference administrative domain in the currently selected administrative domain in the main console window.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
