Chapter 1 Introduction to Performance Reporting Manager
This chapter discusses the following topics:
About Performance Reporting Manager
Performance Reporting Manager is an add-on product to Sun Management Center that enables you to create reports detailing the status of your machines. Performance data is gathered by the history logging capability that is part of Sun Management Center. Performance reports generated with Performance Reporting Manager use the data collected in this manner.
The product includes 16 standard reports for which the report options are predefined. History logging of the data properties used in standard reports is automatically started by the software. You can also create your own custom reports by selecting options from the report templates that are provided. Performance Reporting Manager can generate the following types of reports:
-
Performance
-
Hardware system
-
Hardware configuration
-
Software packages and patches
-
Alarms
-
System uptime
To use Performance Reporting Manager, the first step is to install and set up the add-on software. For information about the installation and setup of Performance Reporting Manager, see Chapter 2, Performance Reporting Manager Installation and Setup. For additional information about installing Sun Management Center software, see the Sun Management Center 3.6 Installation and Configuration Guide.
You can generate any of the standard reports included with the software after the Performance Reporting Manager software is installed and set up. For more information about standard reports, see Chapter 3, Standard Reports.
You can also create your own custom reports. You select the format for your report from the available report formats given. Performance Reporting Manager includes several format options for viewing reports. For information about creating custom report requests, see Chapter 4, Custom Reports.
Reports can provide information about one host, all hosts, or a set of hosts that you designate. In general, data is collected on the agent machines. The data is then transferred to a database on the server machine. You can request a report for any agent machine for which data has been collected. A host must be in the Sun Management Center server context to be included in a report. For more information about how the data in reports is collected, see Data Collection Process.
The host name in a report usually refers to the agent machine. One exception is in the case of alarm reports. Alarms resulting from an agent machine that is down or is otherwise not responding will list the name of the server machine.
Any standard or custom report can be scheduled to generate automatically at a regular interval. Additionally, you can save reports in other file formats either for viewing in a web browser, or for using tools to analyze data. For more information regarding these report options, see Chapter 5, Report Options.
Performance Reporting Manager automatically logs a number of data properties. These properties are predefined for you. For more information regarding this feature, and for other reference information, see Appendix A, Reference Information.
For information about the installation and setup of Performance Reporting Manager using the command line, see Appendix B, Installing Using the Command Line. For additional information about installing Sun Management Center software using the command line, see the Sun Management Center 3.6 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Data Collection Process
Before installing and using the software to generate reports, you should have an understanding of how data collection occurs. The Performance Reporting Manager add-on product uses the history logging capability for agent machines that is provided by the Sun Management Center software. A data collection service is created on the server layer. The following types of data are collected:
-
Hardware system data
-
Hardware configuration data
-
Software package data
-
Software patch data
-
Performance data
-
System uptime data
The data is logged on the agent machines. The data collection service on the server layer collects this data from the agent machines and then stores it. The data returned in reports comes from the data stored on the server or stored on the agent machine.
Raw Data
Raw data is the term given to data that is logged in the history log files located on the agent machines. The ability to log raw data is a feature of the Sun Management Center base product. This data can be logged either on a single machine or on a group of machines by using the grouping capability. If you use the grouping capability, the data is logged at the time interval that you specify. For more information about the grouping capability, see Data Properties, and Chapter 13, Managing Group-related Jobs, in Sun Management Center 3.6 User’s Guide.
Raw data is retained on the agent machine for eight days. This limit is necessary because the total volume of raw data is very large. Data is purged after eight days. For example, on the ninth day, the first day of raw data is purged from the agent machine. At any given time on the agent machine, the last eight days of raw data is available. Before this data is purged, summary records are preserved.
Roll-up Process
Before raw data is purged, the data is summarized or “rolled-up” at predefined intervals. Roll-up data is the term given to the data that has been summarized. Before any raw data is purged, the minimum, maximum, and average values are calculated. These values can be preserved in several ways.
Hourly data is data that is summarized or rolled-up every hour. The raw data for each hour is processed to create a summary record for that hour. For example, if raw data is logged every five minutes, a total of twelve raw records are available in one hour. When data is rolled-up after one hour, the twelve raw records are processed to find the minimum, maximum, and average values during that hour. One summary record is generated for the twelve raw records. The hourly data is first computed on the agent machine. The data is then brought over to the server machine, where the data is added to the database.
The daily, weekly, and monthly values are calculated in a similar manner. The maximum, minimum, and average values are also calculated for each period, and the data is added to the database.
Data is retained in the following manner:
-
Hourly data is kept for 7 days.
-
Daily data is kept for 5 weeks.
-
Weekly data is kept for 12 months.
-
Monthly data is kept for 24 months.
Depending upon the time range specified in a report request, the most granular data is returned in a report. For example, if the specified date range is seven days, then hourly data is returned. If the specified date range is beyond the last seven days but within the last five weeks, then daily data is returned.
Data for Reports
Data polling starts after the Performance Reporting Manager software is installed and set up, and once the server is started. The Sun Management Center server starts polling the agent machines every hour to collect the data logged on those machines. Logged data is available for reports at the following intervals:
-
Hardware system data – 90 minutes after the server is started.
-
Patch and package data – 30 minutes after the server is started.
-
Hardware configuration data – 90 minutes after the server is started.
-
Uptime Status Reports, Percentage Uptime (Total) Reports, and Total Uptime (Total) Reports – 90 minutes after the agent is added to the topology of the Sun Management Center server.
-
Percentage Uptime (Detailed) and Total Uptime (Detailed) reports – 1 day after the server is started.
Data on the agent machines is collected at different times. Data is logged on an agent machine after the following time intervals:
-
Hardware system and hardware configuration data – Every 12 hours.
-
Patch and package data – Every 12 hours.
-
Performance data – According to the logging interval specified in the Property Logging Setting dialog box. This data is stored in the history log files.
-
Process data – Every 15 minutes.
The data collection service on the server layer collects the data in the following manner:
-
Data is collected from agent machines that are in the current server context and have the Performance Reporting Manager software installed. The agent machine must be in the server's topology.
-
Roll-up data for performance is collected every hour.
Report Manager
The Report Manager GUI is linked to the Sun Management Center JavaTM console only, and is opened from the Tools menu. You manage all report activity through the Report Manager GUI. For example, from Report Manager you can generate a report, create a new custom report, or schedule a report to generate at regular intervals.
For more information, see Report Manager GUI.
Report Requests
You can either use any of the standard reports included with Performance Reporting Manager, or create your own custom system management reports. For all standard reports, the report specifications and report format are already predefined and saved for your repeated use.
A custom report enables you to specify the content you want included in your reports, as well as the report output format. The saved report specifications are called a report request. The report request is based on one of several report templates. A report request is used to generate either a standard or a custom report. The report request is also used to schedule reports to run regularly.
For more information about using standard report requests, see Chapter 3, Standard Reports. For more information about creating custom report requests, see Chapter 4, Custom Reports.
Categories and Subcategories
The reports in the Report Manager GUI are organized by category and subcategory name. The left pane of Report Manager displays a hierarchy view that shows all the reports by name, both for standard and custom reports.
The first level of the hierarchy contains the category names. The second level of the hierarchy contains the subcategory names. The report requests themselves are found at the third level of the hierarchy. All standard reports are organized in the hierarchy view under predefined categories and subcategories.
You can place any type of custom report under the category or subcategory of your choosing. This ability enables you to control the organization of your reports.
Performance Reporting Manager has the following predefined categories and subcategories:
-
Alarm
-
Alarms
-
-
Hardware
-
System
-
Configuration
-
-
Performance
-
CPU
-
Swap
-
Memory
-
-
Software
-
Packages
-
Patches
-
-
System Uptime
-
Uptime Status
-
Percentage Uptime
-
Total Uptime
-
Output Format Options for Reports
Performance Reporting Manager provides the following possible output formats for its reports:
-
Tabular
-
Line graph
-
Bar chart
-
Stacked Bar Chart
-
Pie chart
-
Area Chart
-
Stacked Area Chart
-
Comma- or Tab-Separated Text
All format options are not available for every report. The type of report determines the format options available. Certain formats do not make sense for particular reports, so these formats are not always given as an option. When creating a custom report request, you choose from the available format options given at that time.
Once a report request is saved, an icon depicting the report format option appears in the hierarchy view in the Report Manager GUI. Each icon is representative of the format chosen for the report. A lock symbol is added to the icon when the request is for a standard report that comes with Performance Reporting Manager. Standard reports have predefined reporting options that you cannot change.
Tabular Report
The tabular report option returns data in table format. The distinctive icon for the tabular option is a table. The table icon is a grid with rows and columns. The cells of the table contain the numerical values for the data properties specified in the report request. You change the column sizing by dragging either edge of the column heading. If the title to a column heading appears truncated or is followed by several dots, you might want to resize the column in order to view all information. Tabular reports can be sorted by clicking on a column, except for performance reports. Performance reports are presorted according to the time field.
When the Real Time range is selected, you can update the information by clicking the Refresh button located at the right top of the table. The new data is added to the top of the table.
Line Graph Report
The line graph report option returns data as graphs with line plots. The line graph icon is a graph with a climbing, jagged line. The number of graphs contained in each report depends on the Graph Orientation option selected in the report request.
When the Real Time range is selected for a report, the graph refreshes according to the refresh interval of the properties being logged. For Real Time reports, only the last hour of data is visible on the graph at any point in time.
Each line graph report has several viewing options. For example, you can use the Zoom button to view finer, more granular data for any point on a line. The Alarms button enables you to obtain the alarm detail for any host included in the report. The Processes button similarly enables you to obtain the top ten CPU processes and the top ten memory processes for any host in the report. For more information, see Line Graph Report Viewing Options.
The following figure shows a sample of a line graph report.
Figure 1–1 Sample Line Graph from a Standard Performance Report
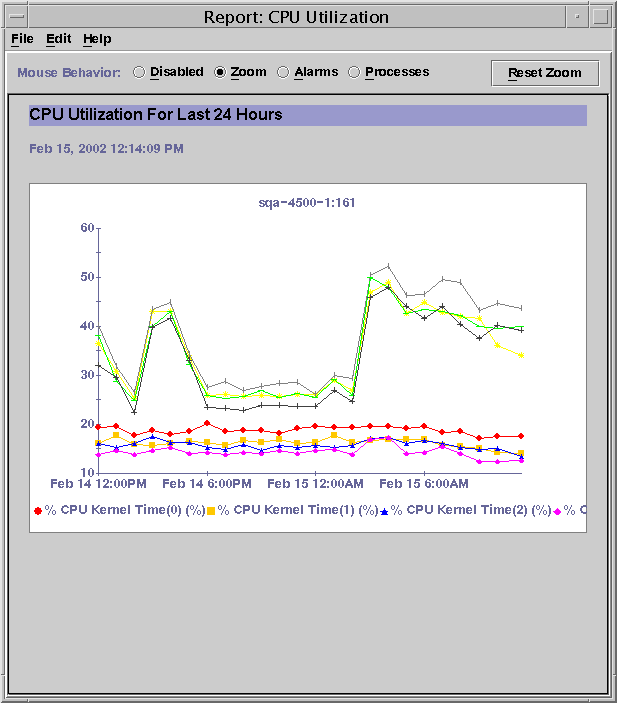
Bar Chart Report
The bar chart report option returns data as one or more graphs with bar lines. The bar chart icon is a graph that contains three vertical bars. The number of graphs contained in each bar chart report is controlled by the Graph Orientation option selected in the report request. This format enables you to create a report that provides a visual comparison of data values.
Each bar chart graph has the same viewing options as the line graph report option. See Line Graph Report.
Stacked Bar Area Chart Report
This report is similar to the stacked area chart report, except the data is displayed in a series of stacked bars instead of graphs. The distinctive icon for this report is two bar graphs. For more detail, see Stacked Area Chart Report.
Pie Chart Report
The number of pie chart reports returned depends upon whether the data property hostname is included in the report request. The report returns data as one pie chart per host if hostname is specified in the report request. If the data property hostname is not specified in the report request, only one pie chart is generated in the report. The following types of reports have the pie chart option: summary reports for system, package, patch or alarm; percent uptime (detailed and total); total uptime (detailed and total). The pie chart icon is a circle with a single line that depicts the radius.
For more information about the selection of data properties in a report request, see Data Properties.
Area Chart Report
The area chart report option returns data for each report property as a separate shaded area in a graph. The distinctive icon for this report is a shaded graph. The number of shaded graphs returned in the report depends upon the Graph Orientation option selected in the report request. If multiple properties are displayed in a report, each area will be distinguished by a different color. The legend at the bottom of the report identifies each color to the corresponding property.
When multiple properties are requested in the report, data can be hidden in this view if one shaded graph overlays another graph. This type of report is good for determining trends, but might not provide the detail required for analysis because certain properties might be obscured in the overlay. If you require all requested properties to show individually, requesting a stacked area chart report or a stacked bar area chart might be a solution.
Stacked Area Chart Report
The stacked area chart report returns data for each property as a separate shaded area in a graph, similar to the area chart report. But unlike the area chart report, data is not hidden when shaded area charts overlay each other. Instead, each property requested in the report has its own color-shaded graph. These graphs are stacked against each other. The legend at the bottom of the report associates each color with the corresponding property. The distinctive icon for this report is two shaded reports overlaid, or stacked upon each other.
This type of report is good for analysis of system status because all the requested properties are displayed. If the requested number of properties is high, however, this type of report can yield a busy-looking report. If you require only a visual representation of overall trends, you might want to request an area chart report instead.
Comma- or Tab-Separated Text Report
This report returns data in a comma- or tab-separated text file, according to the selection made. The distinctive icon for this report is a text file. A file with data in text format can be used with other tools to analyze the data, for example, a spreadsheet program.
If you used previous versions of Performance Reporting Manager, this type of report could only be generated after a graphical report was requested. This step is no longer required and you can request a comma- or tab-separated text report directly.
This type of report can also be scheduled and viewed as a web browser report. For more information, see Scheduling Reports and Options for Viewing Report Output.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
