| C H A P T E R 9 |
|
Creating Maps and Mapsets Using the SGU |
Sun MTP provides two methods for managing maps and mapsets.
For a description of the BMS macro instructions, refer to the IBM documentation.
This chapter contains the following topics:
|
Note - You cannot invoke the CSGU transaction from a 3270-type terminal or if you are using TN3270 emulation; you must be running a local client. |
|
 Type the CSGU transaction on a blank Sun MTP screen or press PF9 on the main menu of the Development System.
Type the CSGU transaction on a blank Sun MTP screen or press PF9 on the main menu of the Development System.
FIGURE 9-2 shows the SGU-Maps Maintenance screen.
FIGURE 9-1 shows a map to the functions of the SGU.

When you start the SGU, the Maps Maintenance Menu is displayed. The Maps Maintenance Menu displays only files with an .sgu extension, the Sun MTP native form of the BMS mapset. These mapset files maintain basic BMS options for the maps associated with the mapset.
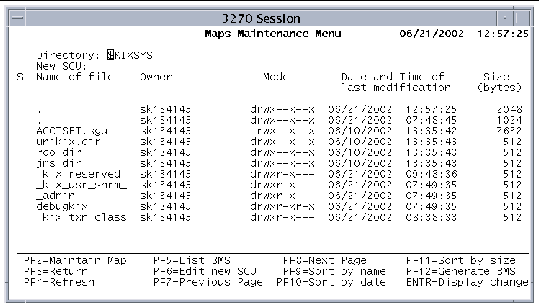
You can only modify the Directory and the New SGU fields on this screen.
The following function keys are active on the Maps Maintenance Menu screen:
|
Opens the Map Set Characteristics screen with the selected file as the work file. If no file is selected, the file that is marked by the location of the cursor is automatically selected. Use this option to modify an existing mapset or one of its maps. Mapset Characteristics describes the Map Set Characteristics screen. |
|
|
Closes the Maps Maintenance Menu and returns to the Development System main menu or a blank transaction screen. |
|
|
Refreshes the data in the file list portion of the screen after a file's attributes are modified. |
|
|
Displays the BMS Maintenance Menu, which lists files with .bms extensions. See Displaying BMS Files. |
|
|
Creates a new .sgu file with the file name specified in the New SGU field, and displays the Map Set Characteristics screen with default values. See Mapset Characteristics, for more information. If no name was entered in the New SGU field, you are prompted to type a file name. To cancel file creation, press PF3 or Enter after the error message. |
|
|
Displays the files on the previous screen. If the top of the file list is displayed, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Displays the files on the next screen. If the bottom of the file list is displayed, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by file name. |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by the file's modification date. |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by file size. |
|
|
Creates a .bms macro file from an .sgu file. This screen is described in Creating BMS Macro Instructions. |
|
|
Makes effective any changes to the Directory field. The file display area is cleared and the files in the new directory are displayed. |
|
1. On the Maps Maintenance Menu, type a name in the New SGU field and press PF6.
2. The Map Set Characteristics screen is displayed with the message New file created.
Mapset Characteristics describes this screen in detail.
3. Make any changes to the default characteristics and press Enter.
4. To define extended attributes for the mapset, press PF5 on the Map Set Characteristics screen.
Defining Extended Attributes for the Mapset describes the Extended Attribute screen. Make any changes to the default characteristics and press Enter.
5. Press PF3 to return to the Map Set Characteristics screen.
|
1. On the Map Set Characteristics screen, press PF4 to display the Map List screen.
2. On the Map List screen, press PF4 to insert a map.
See Adding Map Names to the Mapset.
After you create the map, you can:
When you select a .sgu file on the Maps Maintenance Menu and press PF2, or type the name of a New SGU and press PF6, the Map Set Characteristics screen in FIGURE 9-3 is displayed, showing the characteristics of the current mapset. Data on this screen is equivalent to that defined by the BMS DFHMSD macro instruction.
If the mapset exists, the current characteristics are displayed. If you are defining a new mapset, BMS default characteristics are displayed and this message is displayed in the response area of the screen:

These function keys are active on the Map Set Characteristics screen:
|
Writes data to disk. This saves the current mapset characteristics, mapset, map and field data to the disk under the file name identified by the current working SGU mapset file. You must press PF2 when you finish editing to save the SGU editing session. |
|
|
Returns to the Maps Maintenance Menu. If you modified data but did not write it to disk, this message is displayed: SGU File has been modified ...press PF3 to quit or PF2 to save. |
|
|
Displays a list of map names currently defined for the mapset. The functions available on this screen are described in Adding Map Names to the Mapset. |
|
|
Displays the extended attributes for this mapset. These attributes are the default for all maps defined in this mapset. |
|
|
Modifies mapset characteristics. Data is validated. If valid, the new information is accepted and this message is displayed: Invalid data is highlighted. The cursor is positioned over the first invalid field and this message is displayed: |
The following table lists the data fields on the Map Set Characteristics screen and acceptable values. These fields are validated when you press Enter on the Map Set Characteristics screen.
The SGU supports most options for the BMS DFHMSD, DFHMDI and DFHMDF macro instructions. However, the Sun MTP BMS Assembler and the Sun MTP runtime module can support only a subset of these options. See Supported BMS Functions for a list of the supported options.
|
Type of output to be produced by the assembler after the BMS macro is uploaded to the mainframe. D: Generate a symbolic description map. &: Generate a symbolic description map or a physical map, depending on the JCL. |
|
|
Storage area tags to generate. Applies only to a symbolic description map. I: Generate input field names only. |
|
|
Indicates the format of the symbolic description map to be generated. Applies only to a symbolic description map. C: Generate a COBOL-compatible storage area with appropriate data names. K: Generate a C structure header file describing the storage area. P: Generate a PL/I-compatible storage area with appropriate data names. A: Generate an Assembler-compatible storage area with appropriate data names. This option is not currently supported. |
|
|
Determines whether or not a start printer command is sent to the printer by a BMS output mapping operation. |
|
|
Indicates whether each map in a symbolic description map is to occupy a different storage area or whether all maps are to occupy the same storage area. Auto storage and base name are mutually exclusive. Applies only to a symbolic description map. A: Auto storage. Each map within the set is to occupy a separate storage area. blank: All maps within the set occupy the same storage area. |
|
|
Indicates the line length for the printer. Only the default option is supported for standard printers. All options are supported for 3270-type devices. D: Default printer line length is determined by the settings at the printer. |
|
|
Uses the same storage base for symbolic description maps as multiple map sets. The base name can contain one to eight characters; the first character must be alphabetic. If the name is left blank, each mapset defined by a program starts at a unique storage base. |
|
|
Specifies whether or not a map sent to the terminal frees the keyboard after the map is sent. If not set, this field defaults to the input inhibited status. Y: Turn off input inhibited status - frees the keyboard after the map is sent. N: Turn on input inhibited status - does not free the keyboard after the map is sent. |
|
|
Default value that all maps and fields are set to within the mapset. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for validation attributes; otherwise, it does not support them. Y: Any data field with this option set must be completely filled in with data. If the cursor is moved from this field and the field is not completely filled with data, the inhibit input condition is raised. |
|
|
Specifies whether or not a map sent to the terminal sounds the audible alarm after the map displays. |
|
|
Specifies the default value that all maps and fields are set to within the mapset. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for validation attributes but does not support them. Y: Data must be entered into any field when this flag is set. If the cursor is moved from the field and no data was entered, the inhibit input condition is raised. |
|
|
Specifies whether or not a map that is sent to the terminal resets all Modified Data Tags (MDTs) before the map displays on the terminal. |
|
|
Type of terminal that the physical map is to support. Enter any 6-character code into this field. If this field is equal to 3270-2, the name of the file created when the BMS is assembled has an M appended, assuming the suffix parameter described in Map set suffix is not set. |
|
|
Format/interpretation of data sent/received by the BMS processor. |
|
|
One-character suffix to be added to the end of the mapset name; or it can be left blank. This suffix is used to distinguish between maps of different sizes or languages. |
|
|
Specifies whether or not to include a 12-byte TIOA prefix when generating the symbolic description map. |
|
|
Code that CICS uses to determine the logical device mnemonic to use for a BMS output operation. Used only for TCAM and VTAM-supported 3600 terminals and batch logical units. Any 2-character code can be entered in this field, or it can be left blank. |
|
|
Indicates whether or not outboard formatting is supported by the physical mapset. This option is not supported. |
|
|
Identifies the repeating symbol. The repeating symbol is recognized as an alphanumeric, unprotected field when setting default values to fields. See Field Attribute Defaults. |
|
|
Identifies the repeating symbol. The repeating symbol is recognized as a numeric, unprotected field when setting default values to fields. See Field Attribute Defaults. |
|
|
Identifies the repeating symbol. The repeating symbol is recognized as having a hexadecimal initial value when setting default values to fields. See Field Attribute Defaults. |
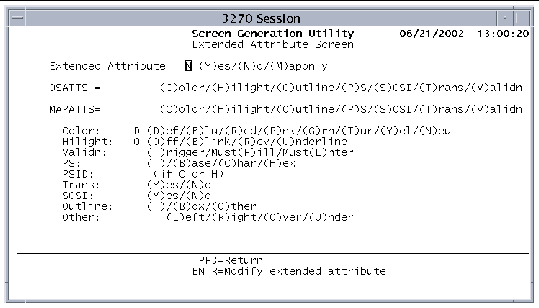
The Extended Attribute Screen defines extended attributes for the mapset.
1. Press PF5 on the Map Set Characteristics screen.
The following figure shows the Extended Attribute Screen.
|
Note - Sun MTP reserves space in the maps for all extended attributes, but supports only the Color and Hilight extended attributes. |
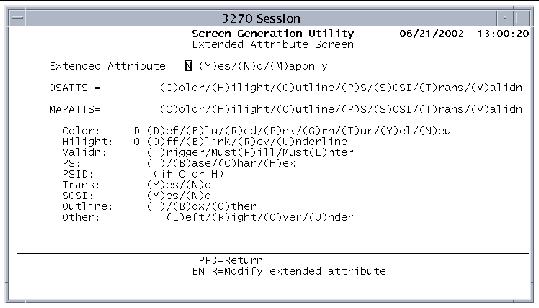
2. Specify the extended attributes.
3. Press Enter to confirm the changes.
The following table describes the fields on the Extended Attribute screen and their options.
|
Even though extended attributes can be specified for the mapset, only those attributes described in Extended Attributes are displayed. N: Do not use extended attributes or indicates that they are specified by the DSATTS and MAPATTS fields. Y: Use extended attributes in both the physical and symbolic description mapset. Setting this field to Y is equivalent to specifying: DSATTS=(COLOR,HILIGHT,VALIDN,PS) MAPATTS=(COLOR,HILIGHT,VALIDN,PS) M: Use extended attributes in the physical mapset only. Setting this field to M is equivalent to specifying: |
|
|
Exact attributes to use in the symbolic description map. A string of up to seven characters can be specified. Each character stands for a specific extended attribute. If an attribute is specified in this field, it should also be displayed in the MAPATTS field. |
|
|
Exact attributes to use in the mapset. A string of up to seven characters can be specified. Each character stands for a specific extended attribute. |
|
|
Extended attribute color default to assign to maps and fields defined within the mapset. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for color attributes to be assigned and provides support on certain devices. See Extended Attributes for more information. |
|
|
Default highlighting attribute to assign to maps and fields defined within the mapset. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for highlight attributes. The hilight attribute is supported for various devices. See Extended Attributes for more information. |
|
|
Indicates whether to use programmed symbols. C: Use a programmed symbol set and specify the programmed symbol identifier by a single character. H: Use a programmed symbol set and specify the programmed symbol identifier by two hexadecimal characters. |
|
|
Programmed symbol set identifier depending on the PS operand specified. |
|
|
Field can contain both EBCDIC and DBCS data. The DBCS data is indicated by a shift out (SO) character at the start of the data and a shift in (SI) character at the end of the DBCS data. |
|
|
Draw a box around a field or to draw lines above, below or to the left or right of the field. |
|
|
Field is enabled only if the Outline option is set to O. L: Draw a line to the left of the field. R: Draw a line to the right of the field. |
The Map List screen enables you to add, modify, and delete map names from the mapset. It lists the map names defined for the mapset. If you are adding a map to a new mapset, no map names are listed on this screen. If you are modifying a mapset, the screen can list up to 170 map names.
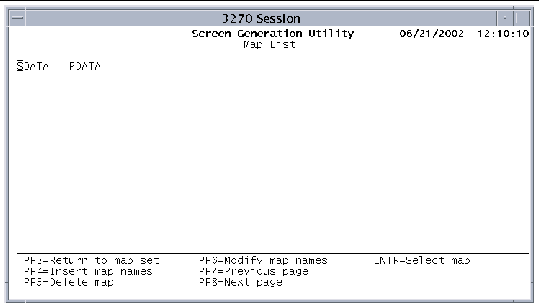
The following function keys are active on the Map List screen:
|
Displays the Map Insert screen, which enables you to insert map names in the list. New names are inserted in front of the map name where the cursor is positioned. |
|
|
Marks a map for deletion and invokes the Map Delete Confirmation screen, shown in FIGURE 9-14. To delete a map name from the mapset, place the cursor on the map name and press PF5. See Deleting a Map. |
|
|
Modifies currently defined map names. Map names are validated to ensure that they are unique. |
|
|
Displays the previous page of map names. If this is the first page of map names, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Displays the next page of map names. If this is the last page of map names, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Returns to the Map Characteristics screen (see Customizing Map Characteristics). The map name to be processed is the one shown at the current cursor position. |
1. Press PF4 on the Map List screen.
The blank Map List screen is displayed.
2. Type the name of the new map.
You can define up to 255 maps for any one mapset. Any map takes on the characteristics of the current mapset. You can override any of these characteristics for individual maps. The next section describes how to customize the characteristics of an individual map.
3. Press Enter to add the map.
The Map Characteristics screen enables you to customize the characteristics of a single map.
|
1. On the Map List screen, position the cursor on the name of the map you want to customize and press Enter.
The Map Characteristics screen shown in FIGURE 9-6 is displayed.
Data on the Map Characteristics screen is equivalent to what is defined by the BMS DFHMDI macro instruction.
If the map was previously defined, its characteristics are displayed. If the map was just inserted into the mapset, the default characteristics are displayed.
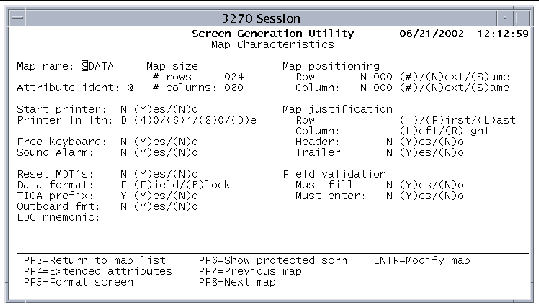
2. Change the values on the screen according to your requirements.
See TABLE 9-3.
3. Press Enter to modify the map.
The following function keys are active on the Map Characteristics screen:
|
Displays the Format screen. This is a full-screen display that contains the current definition of a map. Use this function to define the screen layout. See Formatting a Screen. |
|
|
Displays a full-screen version of the map as it appears to the end user, complete with protected, unprotected, numeric and highlighted fields. You can test the data entry fields by typing in sample data. The data is not saved. |
|
|
Displays the previous map in the mapset. If this is the first map of the mapset, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Displays the next map in the mapset. If this is the last map of the mapset, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Modifies map characteristics. Data on the screen is validated. If valid, the new information is accepted and this message is displayed: If any data does not pass the validation tests, the invalid fields are highlighted and the cursor is on the first invalid field. If any errors are detected, this message is displayed: |
The following table lists the data fields on the Map Characteristics screen and acceptable values. These fields are validated when you press Enter on the Map Characteristics screen.
The Map Size # rows and # columns fields of the Map Characteristics screen are handled in a special way when modified. These fields determine the maximum size of the data input screen to be formatted.
For example, if # rows is 2 and # columns is 80, then only two lines of the screen allow any data to be defined during the screen formatting process. If # rows is 24 and # columns is 80, then the entire screen can be formatted. If # rows is 10 and # columns is 80, only the area in the first 10 lines can contain format data.
If the screen is already formatted and you modify these fields, the screen format is affected. For example, if the number of columns in the previous example is decreased from 80 to 40, all fields defined past column 40 are dropped. Any fields that started before column 40 and ended after column 40 are truncated to column 40.
|
1. On the Map Characteristics screen, press PF4 to display the map's Extended Attribute screen.
See FIGURE 9-7.
|
Note - This is the same screen that is displayed if you press PF5 on the Map Set Characteristics screen shown in FIGURE 9-5. |
See TABLE 9-4 for a description of each attribute field.
All options specified on this screen override options that were specified for the mapset.
3. Press Enter to modify the map.
|
Even though extended attributes can be specified for the map, only those attributes described in Extended Attributes are displayed. N: Extended attributes are not supported or they are specified by the DSATTS and MAPATTS fields. Y: Extended attributes are supported for the physical map and symbolic description map. Setting this field to Y is equivalent to specifying: DSATTS=(COLOR,HILIGHT,VALIDN,PS) MAPATTS=(COLOR,HILIGHT,VALIDN,PS) M: Extended attributes are used in the physical map only. Setting this field to M is equivalent to specifying: |
|
|
Exact attributes to use in the symbolic description map. Specify a string up to seven characters. Each character stands for a specific extended attribute. If an attribute is specified in this field, it should also be displayed in the MAPATTS field. |
|
|
Exact attributes to use in the map. Specify a string up to seven characters. Each character stands for a specific extended attribute. |
|
|
Extended attribute color default to assign to map and fields defined within the map. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for the assignment of color attributes and provides support on certain devices. See Extended Attributes for more information. |
|
|
Default highlighting attribute to assign to the map and fields defined within the map. Sun MTP reserves space in the symbolic map for highlight attributes. The hilight attribute is supported for various devices. See Extended Attributes. |
|
|
Indicates whether to use programmed symbols. C: Use a programmed symbol set. The programmed symbol identifier is specified using a single character. H: Use a programmed symbol set. The programmed symbol identifier is specified using two hexadecimal characters. |
|
|
Programmed symbol set identifier depending on the PS operand specified. |
|
|
Indicates whether the background of the field is transparent or opaque. |
|
|
Field can contain both EBCDIC and DBCS data. The DBCS data is indicated by a shift out (SO) character at the start of the data and a shift in (SI) character at the end of the DBCS data. |
|
|
Draw a box around a field or to draw lines above, below or to the left or right of the field. |
|
|
Field is enabled if the Outline option is an O. L: Draw a line to the left of the field. R: Draw a line to the right of the field. |
The Format screen function enables you to design maps by typing data onto the screen. Press PF5 on the Map Characteristics screen to open the format function.
If the screen was formatted, current format data is displayed. If you are formatting the screen for the first time, the screen is blank. You can define up to 1,023 fields for each map in a mapset.
All cursor controls on the keyboard function normally. Map attributes currently assigned apply when formatting the screen. This means that if you specified a map size smaller than a full screen on the Map Characteristics screen, only that portion of the screen accepts keyboard input. The remainder of the screen is protected and does not allow any data entry.
The physical terminal used to format a screen must be at least as large as the screen itself. For example, a Model 5 terminal can be used to format either Model 2 or Model 5 screens, but not Model 4 screens.
Although they are not listed on the blank format screen, the following function keys are active during the screen formatting process:
|
Opens the Help screen described in To Display the Formatting Help Screen. |
|
|
Shifts the line left or right n characters. See To Shift a Line to the Right or Left. |
|
|
Shifts the screen left or right n characters. This function is similar to the Shift Line function. The active keys on this screen are: |
|
|
Moves or copies the current line. See To Move or Copy the Current Line. |
|
|
Deletes or inserts n characters. See To Delete or Insert Characters. |
|
|
Deletes or inserts n lines. This function is similar to the Delete/Insert Characters function. The active keys on this screen are:
|
|
|
Centers all fields on the current line. The number of blank characters before the first field and the number of blank characters after the last field are evenly distributed to both the left and right margins. If the number of blank characters is not evenly divisible by 2, the extra blank character is added to the right. |
|
|
Accepts the Format screen data and displays the Field Characteristics screen. You must press Enter to save any screen format data. If you change the format of the screen and press PF3 without first pressing Enter, the changes are lost. |
|
 Press PF1 on the Format screen to display the Help screen.
Press PF1 on the Format screen to display the Help screen.
Press PF3 to return to the Format screen.
This screen explains the function of each PF key, the Enter key, and describes how to identify the current character, current line, and current field.

An attribute identifier is a unique character that identifies the beginning of a field. It immediately precedes a data field and occupies that physical location on the screen. It is also used as an aid in the automatic assignment of attributes to the field. Attribute identifiers are defined when you assign characteristics to a map. The default attribute identifier is @. See Customizing Map Characteristics.
The attribute identifier character you select must not appear anywhere on the formatted screen as a literal constant.
FIGURE 9-9 shows a formatted screen with the @ character as the attribute identifier. To display a formatted screen, first select a map from the Map List screen. When the Map Characteristics screen is displayed, press PF5. There are 26 fields defined in this example.
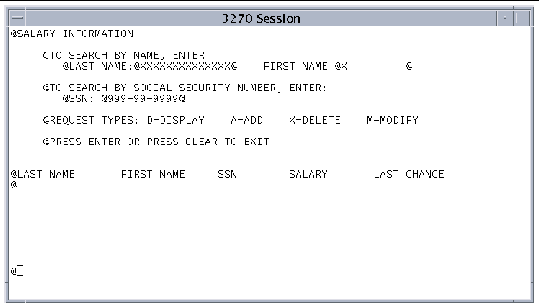
If an attribute identifier immediately follows another or is the last character of a line, an error message is displayed when you press Enter. An attribute identifier can be the last character of a line if the map is the full width of the terminal and the field wraps to the next line.
Moving an attribute identifier on the screen using the keyboard insert and delete keys can affect the previously assigned field characteristic as follows:
Do not modify any field characteristics until the screen format is satisfactory.
To move a field and retain its modified values, use the function keys described in Formatting a Screen.
When you define a new field, you can either assign attributes manually or have the SGU assign attributes automatically. If you assign attributes manually, the attributes for old fields do not change. To implement automatic assignment of new field attributes, use the Default field ident field on the Map Set Characteristics screen. If all the characters you enter in a field on the Format screen match one of the three characters defined in the Default field ident field, then the field's attributes are set as follows.
You can define one default field identifier to any one mapset. Unless they are explicitly changed, the Default field ident characters are:
All the characters match the default alphanumeric field ident
All the characters match the default numeric field ident
All the characters match the default hex field ident
|
1. Press PF4 on the Format screen to display the Shift Line screen shown in FIGURE 9-10.
2. Specify the number of characters to shift.
4. Press PF3 to return to the Format screen.
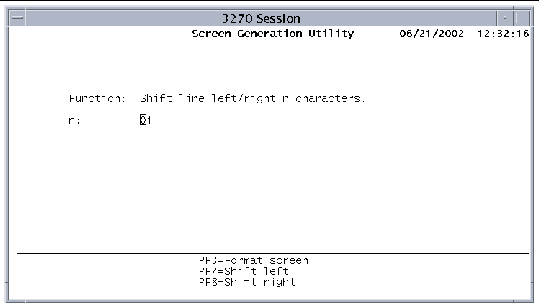
The following function keys are active on the Shift Line screen:
|
1. Press PF6 on the Format screen to display the following screen.
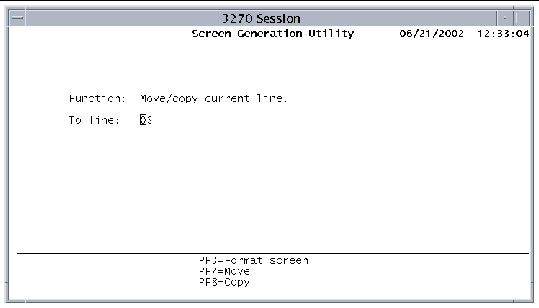
2. In the To line field, type the line, relative to the beginning of the map, to which you are moving the selected line.
This is not necessarily the line where it is displayed on the format screen. When the Move/Copy screen is first displayed, the To line field contains the line number of the line being moved.
4. Press PF3 to return to the Format screen.
The following function keys are active on the screen:
|
1. Press PF7 on the Format screen to display the following screen.
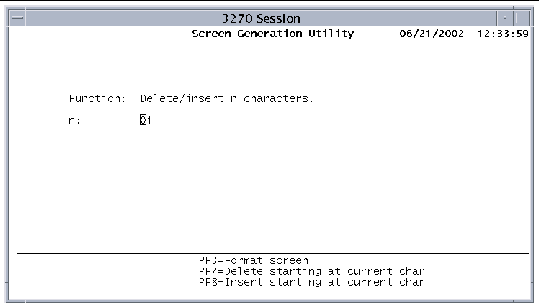
2. Type the number of characters to delete or insert beginning with the character specified by the cursor location on the Format screen.
If the current cursor position is within an existing field when you are deleting characters, the field length is reduced by the number of characters specified. All fields to the right of the current cursor position are moved left by the number of characters specified. If the number of characters to be deleted includes part of the next field, that field is deleted. Any initial value associated with a deleted field is left on the screen; however, it is no longer associated with any field.
Characters are inserted in front of the character where the cursor is located on the Format screen. If the current cursor position is within an existing field, the field length is expanded by the number of characters inserted. All fields to the right of the current cursor position are moved right by the number of characters specified. If a field is repositioned past the right margin in the process, it is deleted from the map.
4. Press PF3 to return to the Format screen.
Any previously modified field attributes are maintained. See Attribute Identifiers.
The position of the cursor is important during the screen formatting process. The field on which the cursor is placed is the first one displayed on the Field Characteristics screen when you press the Enter key. When you return to the Format screen, the cursor is displayed on the Attribute Identifier of the last field you viewed on the Field Characteristics screen. You can modify specific fields by switching back and forth between the Format screen and the Field Characteristics screen.
1. Press Enter on the Format screen to open the Field Characteristics screen shown in FIGURE 9-13.
Data on this screen is equivalent to data that can be defined by the BMS DFHMDF macro instruction.
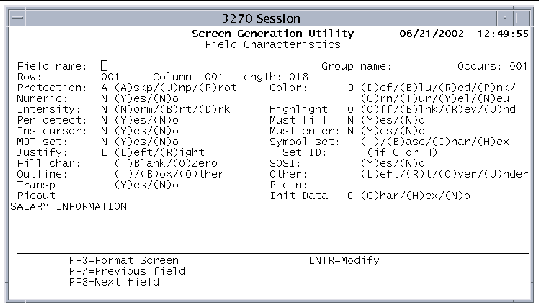
See TABLE 9-5 for a list of fields and their values.
3. When you are done, press Enter to modify the fields.
4. Press PF3 to return to the Format screen.
The following function keys are active on the Field Characteristics screen:
The following table lists the data fields on the Field Characteristics screen and their acceptable values. These fields are validated when you press Enter. See Extended Attributes for information about the supported extended attributes.
|
1. Press the PF5 key on the Map List screen to mark the selected map for deletion.
The screen shown in FIGURE 9-14 is displayed and the marked map is highlighted in bold.
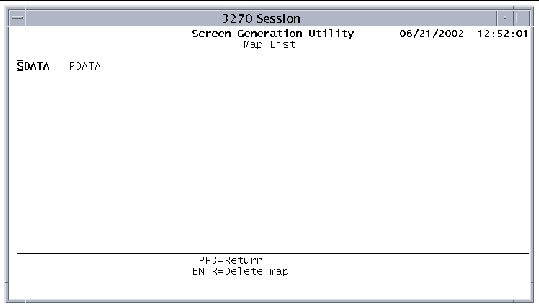
2. Press Enter to delete the map.
There is no confirmation prompt.
After you create the .sgu file, you must create a macro instructions file (a .bms file) that can be assembled by the Sun MTP BMS Assembler or exported to an IBM CICS system for assembly. The assembled file contains macros that create the physical map used during program execution and the symbolic map that is copied into an application program.
|
1. On the Maps Maintenance Menu, select an .sgu file and press PF12.
2. When the screen shown in FIGURE 9-15 is displayed, modify the values as needed.
The SGU map set Filename and Environment fields default to the .sgu file you selected on the Maps Maintenance Menu. The BMS macro Filename and Environment fields default to the file name and directory of the .sgu file.
When you generate the BMS file, the quote character set in the Quote/Apost field is used to enclose strings. Using QUOTE in this field will enclose strings in double quotation marks ("). Using APOST will enclose strings in apostrophes (').
 [ D ]
[ D ]
3. Press Enter to generate the BMS macro instructions.
4. Press PF3 to return to the Maps Maintenance Menu.
When you start the SGU, the Maps Maintenance Menu shown in FIGURE 9-2 is displayed.
|
 Press PF5 on the Maps Maintenance Menu.
Press PF5 on the Maps Maintenance Menu.
The BMS Maintenance Menu, which shows files with a .bms extension, is displayed.
 [ D ]
[ D ]
|
1. In the Directory field, type the name of the directory containing the .bms files you want to display; up to 50 characters.
The first element in the directory can be an environment variable, which can be followed by other subdirectories separated by slashes.
2. Press Enter to accept the change.
The file list changes to show the .bms files in the directory you specified.
The following function keys are active on the BMS Maintenance Menu:
|
Closes the BMS Maintenance Menu and returns to the Development System main menu or a blank transaction screen. |
|
|
Executes the kixed shell script with the selected file as the work file. If no file is selected, the file that is marked by the location of the cursor is used. By default, the vi editor is called. |
|
|
Refreshes the data in the file list portion of the screen. After a file is modified, press this key to display any changes. |
|
|
Displays the Maps Maintenance Menu. The Maps Maintenance Menu is described in Maps Maintenance Menu. |
|
|
Assembles selected files into physical maps. These physical maps have an extension of .map. See Assembling a BMS Map. |
|
|
Displays the previous page of files. If this is the first page, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Displays the next page of files. If this is the last page, this message is displayed: |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by file name. |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by the files' date of modification. |
|
|
Redisplays the contents of the directory, sorted by file size. |
|
|
Creates an .sgu file from a .bms file. See Creating an .sgu Mapset File. |
|
|
Makes effective any changes to the directory field. The file display area is cleared and the files in the new directory are displayed. |
You must assemble a .bms file before you can use it in your programs. An assembled file has a .map extension. Sun MTP provides two methods for assembling maps:
|
1. On the Maps Maintenance Menu, press PF5 to open the BMS Maintenance Menu.
 [ D ]
[ D ]
2. Select a .bms file and press PF6.
3. When the screen shown in FIGURE 9-18 is displayed:
a. Modify the Output filename and Output Environment fields, if needed.
They default to the values on BMS Maintenance Menu.
b. If you want the assembler to generate a COBOL copybook, a C header file, or a PL/I include file, mark that option with a Y.
The appropriate member is created based on the value of LANG in the .bms file.
c. If you want the assembler to generate a listing file, mark that option with a Y.
d. Press Enter to accept the changes before assembling.
If you do not want to assemble the file, press PF3 to return to the BMS Maintenance Menu.

4. Press PF4 to generate the .map file.
A screen is displayed with the results of the assembly. If you generated a list file, it is also displayed.

5. To save this temporary listing file, type:
The file is saved to the directory specified in the Output Environment field.
If you do not want to save the file, type :q to close this screen and return to the BMS Maintenance Menu.
|
 Type the kixbms command with the appropriate options using the .bms file as input.
Type the kixbms command with the appropriate options using the .bms file as input.
For a description of all the options, refer to the Sun Mainframe Transaction Processing Software Reference Guide.
Example: Assemble a COBOL map and generate a COBOL copybook. The copybook is created if LANG=COBOL in the .bms file. The output file is automatically named SB001.map.
Example: Assemble a C map named JB045A and generate a C header file. The header file is created if LANG=C in the .bms file. You must specify the -o option and map name if you are using a different name for the .map file.
You can create an .sgu file from a .bms file. This is useful for maintaining BMS source code imported from an IBM CICS system. There are two methods for creating an .sgu file:
|
1. On the BMS Maintenance Menu, select a file and press PF12.
2. When the screen shown in FIGURE 9-20 is displayed, change any field as needed:
a. The name of the input file is displayed in the BMS macro field.
It defaults to the file selected on the BMS Maintenance Menu. This file contains BMS macro instructions.
b. The file to be created is displayed in the SGU map set field, which defaults to the name of the BMS macro file selected for processing.
c. The Environment fields default to the directory specified on the BMS Maintenance Menu.
d. When you generate the .sgu file, the quote character set in the Quote/Apost field is used to enclose strings.

3. Press Enter to create the .sgu file.
Sun MTP displays a screen with the results of the assembly.
If you do not want to create the file, press PF3 to return to the BMS Maintenance Menu.
4. Type :q to close this screen and return to the BMS Maintenance Menu.
|
 Use the kixbms utility with the-s option to create an .sgu file from a .bms file.
Use the kixbms utility with the-s option to create an .sgu file from a .bms file.
Example: Generate an .sgu file from the TB012.bms file. The output file is automatically named TB012.sgu.
Example: Generate an .sgu file named TB012A from the TB012.bms file. You must specify the -o option to change the name of the output file.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.