Setting up a Dial-up Link Configuration
In this example, the workstation is running Solstice X.25 so that it can dial into the PSDN. A modem provides the connection to the PSDN.
Figure 8-13 Setting up a Dial-up Link Configuration
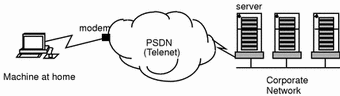
As there is a server on the corporate network that is attached to the same PSDN, the workstation can access the server, for example, by making a PAD call. From there, it can rlogin to other machines on the corporate network. Alternatively, the server could be configured to act as an IP router, giving direct access to the whole network. To configure a machine to use a dial-up connection:
-
Create a link to the PSDN.
-
Configure the logical channel ranges.
-
Specify that V25bis calling procedures are to be used.
-
Set the idle disconnect timer to a reasonable value.
-
Configure X.32 authentication procedures.
-
Add the telephone number of the point of connection to the network (in this case a modem) to the X.25 Routing table.
Note -
Before configuring Solstice X.25 9.2, you must configure your modem to operate in V.25bis mode--refer to your modem manufacturer's documentation for instructions that apply to your particular modem.
Configuring the WAN Link to the PSDN
First configure the link between the server and the PSDN. In the example this is the onboard serial port connected to the modem.
-
Edit Link 0, the default WAN link.
Click on the entry for Link 0 in the scrolling list, then click on Modify Link.
-
Change the other values as shown in the snapshot below.
Refer to "x25tool Overview" for help if you do not know how to change values:
Figure 8-14 Modifying a WAN Link Configuration
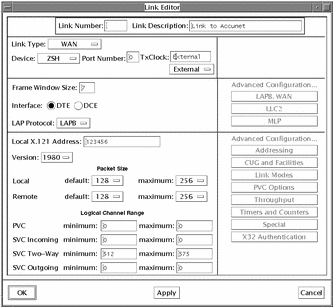
-
Click on Apply to update the configuration.
Configuring the Idle Disconnect
You will need to set the Idle Disconnect. This is the period of time, in tenths of a second, that the link will remain idle before closing down.
-
From the Link Editor, select Timers and Counters.
The Timers and Counters button is located under Advanced Parameters.
-
Set the Idle Disconnect.
Set a value (in tenths of a second) that is high enough to allow for lost traffic and retries, but low enough that you are not constantly paying for an idle link.
-
Click on OK to update the configuration and return to the Link Editor.
-
Click on OK to update the configuration and exit the Link Editor.
Configuring Parameters
Once you have created the link, you need to specify that V25 calling procedures are to be used, and set the idle disconnect to a reasonable value.
Configuring V.25bis Calling Procedures
V.25bis calling procedures are used to control the modem for a dial-up link. You must specify that V.25bis calling procedures are to be used. The parameters you need are located in the LAPB and WAN Parameters window. To configure the parameters:
-
Display the LAPB and WAN Parameters window.
In the Link Editor, click on the LAPB,WAN button, which is located under Advanced Configuration. The LAPB and WAN Parameters window appears.
-
Choose V25 Calling procedures.
Pull down the Calling Procedure menu and choose V25.
-
Set the V25 Call Request Timer.
This determines the length of time, in tenths of a second, that your machine will continue trying to connect to the remote network before timing out. If your modem supports call fail indications, set the V25 Call request timer to 0. Check with your modem supplier to find out if this is the case.
Configuring X.32 Authentication Procedures
Next you need to configure the X.32 authentication procedures. These are used on dial-up links by most PSDNs, to prevent people without permission from dialing in. To configure X.32 authentication:
-
Set Enable X.32 Authentication to Yes.
You can choose to carry out X.32 authentication at link level or a packet level. When connecting to a PSDN, use link level as this means the authentication is carried out by the network. Packet level is appropriate when connecting with another machine (back to back, for example) when you want the machine and not the network to do the authentication. Both the Identity and the Signature can be any hexadecimal string, up to 32 characters long, not containing whitespace.
-
Click on OK to exit the LAPB and WAN parameters window.
-
Save the configuration.
This makes sure your changes will be used when you start X.25. From the x25tool main menu select File => Save, and save the changes to the current configuration. Or you can select File => Save As, to save the changes in a different configuration.
Configuring the X.25 Routing Table
The final step in configuring a dial-up machine is to add the telephone number for the network point of connection to the X.25 routing parameters table so that it is mapped to the X.121 address of the machine you want to be able to access. In the example, this is a host on the remote network that is configured to act as an IP router, providing access to the remainder of the network.
To display the X.25 Routing table, in the x25tool window, pull down the Services menu and click on Routing. The X.25 Routing parameters table applies across all links. To configure:
-
Click on Add, then select Top.
When the window first appears, the parameters are all grayed out. Clicking on Add, Top creates a new template entry and specifies that the entry will go at the top of the list.
-
Select the Route Type.
The example uses a route to an individual host, so choose X.121 Host.
-
Enter the number of the link that reaches this destination.
This is the number you assigned to the link when you created it. In the example this is link 0.
-
Enter the address of the server on the corporate network that also has a connection to the X.25 PSDN.
-
Enter the Telephone Number used to reach this destination.
In a dial-up configuration, this is the address of your point of attachment to the X.25 PSDN, in most cases a modem.
-
Enter a comment (optional).
You could identify the destination that this link reaches, for example.
-
Save your changes.
Pull down the File menu and choose the Save option.
The completed Routing window for this example looks like this:
Figure 8-15 Routing Parameters Window
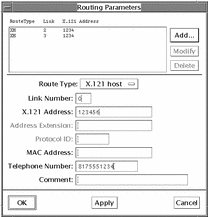
This configuration creates a mapping between the telephone number and the X.121 address of the remote host. When the machine has traffic for the remote host, it knows to dial into the X.25 PSDN. The traffic will then be routed to the remote machine.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
