| Solstice Enterprise Manager 4.1 Managing Your Network |
|
Controlling User Access
With the Security tool you can control user access to Solstice Enterprise Manager (Solstice EM) tools and managed objects. Based on the needs and responsibilities of system administrators, operators, and other users managing the components of your network, you can determine who may use any of the Solstice EM tools, and which managed objects they are allowed to access and manipulate for monitoring purposes.
This chapter comprises the following topics:
- Section 6.1 Overview
- Section 6.2 Getting Started With Security
- Section 6.3 Turning Off Access Control
- Section 6.4 Preparing for Security Control
- Section 6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools
- Section 6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects
- Section 6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility
6.1 Overview
Controlling user access to Solstice EM tools and managed objects is an option.
Without access control, anyone can access all Solstice EM tools and manipulate the managed objects. The risks of this approach can be devastating when individuals without the proper authority or expertise alter or delete important components of the Solstice EM configuration and object attributes.
By controlling user access, you can prohibit unwanted access to critical applications and network components. By controlling user access, users are allowed to access only those applications and objects they need based on their network management responsibilities and other relevant criteria.
6.1.1 Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model
The access control model used by Solstice EM is based on the X.741 Recommendation issued by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU). This model uses rules and a logic in which these rules are enforced as a mechanism to control user access.
6.1.1.1 Security Rules
The basis for denying or granting users access to tools and managed objects are security rules. Security rules are controls that identify the user groups to which access controls are to be applied, the tools or managed objects for which access is to be denied or granted, and the policy to determine if access is to be denied or granted.
As such, the tasks outlined in this chapter involve working with users, tools and managed objects, and creating security rules.
What differentiates security rules from each other is the range of access granted or denied to the user groups.
6.1.1.2 Policy for Enforcing Security Rules
Note – Security rules that deny access to tools and managed objects are always enforced before security rules that grant access.
Note – When users derive their access privileges from multiple security rules, only one of these security rules will be enforced and determine the user's access to tools and managed objects.
The preceding notes contain the two fundamental principles to remember for determining an individual user's access. The principles and the policy logic are the same for controlling user access to Solstice EM tools and managed objects. The following graphic illustrates the logic of the policy that is used.
The policy logic used to enforce the security rules is a process of elimination, done in a hierarchical manner. When multiple security rules define an individual user's access privileges, only one of these rules will determine what the user can and cannot do.
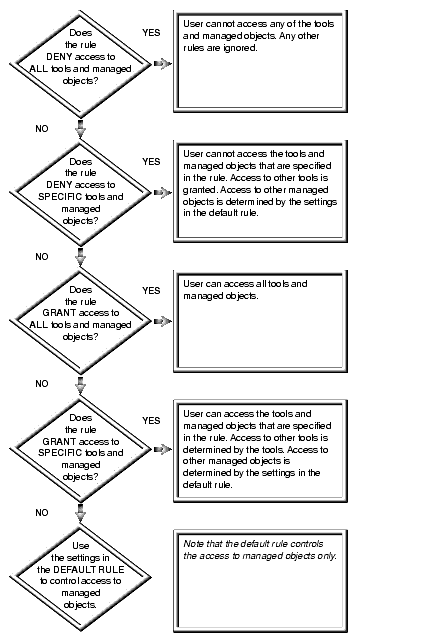
FIGURE 6-1 Solstice EM Enforcement of Security Rules6.1.1.3 About Users and Groups
In the Solstice EM control model, security rules are not set for individual users but for a group of users. This requires using existing user groups, or creating new groups and assigning individual users to such groups.
The identity of individual users and the groups to which they belong needs to be known to the MIS to which they connect. User identity is recorded in an access control list. User group data is recorded in profiles. (See Section 6.4.6 Preparing User Profiles for more information on user profiles.)
The control model used by Solstice EM allows individual users to belong to more than one group. This can result in situations where several seemingly conflicting rules control the access privileges of an individual user. In reality there is no conflict because of the policy logic in which the rules are enforced. The following scenario best illustrates the point.
Example- User John Doe is an operator monitoring alarms exclusively pertaining to routers. As such, John belongs to two user groups: the Operators group and the Routers group.
Users of the Operators group derive their privileges from one rule which denies them access to the Event Logs tool. Users of the Routers group derive their privileges from one rule which grants all users of that group access to all Solstice EM tools.
The question is: "Can John Doe start and use the Event Logs tool, say for creating or editing log files?" The answer is NO because rules that deny access are always enforced before rules that grant access. John, however, does have access to any of the other Solstice EM tools.
Tip – The preceding example illustrates the importance of ensuring that you do not assign Solstice EM users to user groups whose access to tools and managed objects would be denied due to conflicting security rules. Thorough advance planning and good record keeping should help avoid access problems.
- The Implementation Overview section in Preparing for Security Control for more information about users, groups, and profiles.
- The Implementation Overview section in Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools for more details about the type of rules to use for controlling user access to applications.
- The Implementation Overview section in Controlling Access to Managed Objects for more details about the type of rules to use for controlling user access to managed objects.
6.1.2 Predefined Groups, Security Rules, and Object Sets
The Solstice EM installation procedure provides you with a minimum of predefined privilege groups, security rules and sets of objects to get you started.
- Predefined privilege groups - Full Access, Operators, and View Only. The use of the predefined and custom-created privilege groups is required when you want to control user access to the tools, managed objects, or both.
- Predefined security rules - Full Access, DenyAccessControlObjectsChange, and View Only. Use the predefined security rules as a starting point for controlling user access to managed objects.
- Predefined object sets - DenyAccessControlObjectsChange, Connection, and View Only. Use the predefined object sets as a starting point to control user access to managed objects.
The installation procedures give you the opportunity to enable or disable (default) access control. If you choose to enable access control, you are also given the opportunity to create user profiles and to assign users to one of the three default privilege groups provided by the Solstice EM installation.
6.1.3 Implementation Schemes for Access Control
When you want to control user access, you can opt for the following schemes:
- Control user access to tools. This scheme is best suited when you are new to Solstice EM. It is also a stepping stone toward the more complex task of controlling user access to managed objects.
- Control user access to managed objects. This scheme is best accomplished after you have acquired expertise in controlling user access to Solstice EM tools and tasks.
6.1.3.1 Control User Access to Tools
This scheme enables you to specify for a group of users the tools and tasks to which they are granted and denied access. The term tool means any Solstice EM tool such as Network Views, Network Discovery, Alarms, Security, and so on, as well as any custom-developed or third party application integrated using the Solstice EM API. The term task means any application features supported by the tool, such as create, edit, delete, and so on.
For example, network administrators should be able to create log files and alter the events that are to be recorded, while operators may only need the capability to view log records. In this instance, you would grant your network administrators the privilege to start and use the Event Logs tool to create and specify the contents of log files. In contrast, operators would be denied access to the Event Logs tool but would be able to use the Log Entry tool to look at log records.
6.1.3.2 Control User Access to Managed Objects
This scheme enables you to specify the managed objects to which a group of users is granted and denied access. The term managed object, and any of its variations such as object sets, are the representations of network components such as routers, hubs, bridges, logical and hierarchical views of the network, alarms, and so on.
Assume your company has regional headquarters in Boston and San Francisco. The two regional system administrators should only be able to manage the network components pertaining to their respective areas. By controlling access to managed objects, you can create access controls that exclude the Boston system administrators from seeing and manipulating network components pertaining to the San Francisco headquarters and vice versa.
6.1.4 Implementation Plan
Implementing an access control scheme requires that you put the necessary framework in place. You need to perform a number of preparatory tasks to set the stage for setting access controls to tools only, or to tools and managed objects.
This chapter is organized according to the implementation schemes discussed in Section6.1.3 Implementation Schemes for Access Control.
- Section 6.1 Overview provides information that is pertinent to controlling user access to Solstice EM tools and managed objects.
- Section 6.4 Preparing for Security Control provides an overview and preparatory tasks that need to be performed when you want to control user access to both Solstice EM tools and managed objects.
- Section 6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools provides an overview and tasks for controlling user access to tools.
- Section 6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects provides an overview and tasks for controlling user access to managed objects.
The following table identifies the major tasks to be accomplished for each of the implementation schemes and the sections in this chapter where the information can be found.
TABLE 6-1 Implementation Schemes No access control.
All users have full and equal access to all applications and managed objects.If you chose to disable security control during the installation procedure, no other tasks need to be performed. If you chose to enable security control during the installation procedure, but do not want to implement security control after all, then turnoff access control as explained in Section6.3 Turning Off Access Control. No other access control tasks discussed in this chapter need to be performed. See Chapter 2 of the Installation Guide for more information about enabling or disabling security during installation. Tool access control If security control was disabled during the installation procedure, turn on access control as explained in Section6.4.4 Turning On Security Control. Perform the tasks as explained in Section6.4 Preparing for Security Control. Follow the directions of Section6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools. Managed object access control If you did not implement any application access controls: Turn access control on as explained in Section6.4.4 Turning On Security Control. Prepare for access control as explained in Section6.4 Preparing for Security Control. Control user access to Solstice EM tools as explained in Section6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools. Control user access to managed objects as explained in Section6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects. If you implemented access controls to tools: Control user access to managed objects as explained in Section6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects.
Each section starts with an overview that provides details about concepts and other information appropriate for the tasks to be performed.
6.1.5 Related Tasks
See chapter 5 in the Customization Guide for information on creating log files.
6.1.6 Related Files
- /opt/SUNWconn/em/build/acct/EM-config
- /opt/SUNWconn/em/build/acct/init_access_privil eges
- /opt/SUNWconn/em/build/acct/init_access_user_a pps
- /opt/SUNWconn/em/build/acct/init_user
- The em_login daemon
6.2 Getting Started With Security
All access control operations are performed in the Solstice EM Security window which is displayed when you start the Security tool.
You can start the Security tool from the following places:
- The Administration window accessible from Network Tools
- The operating system command line
- When logged in as root or users with permission to grant All Privileges start Security, they always have the right to connect to the MIS without user ID and password authentication.
- Users belonging to less privileged user groups can connect to the MIS with user ID and password authentication when security rules allow them to do so.

To Use Security
1. Start Security in one of the following ways:
- From the Network Tools window, click Administration, and then click Security.
- From an operating system prompt, enter the following command:
- em_accessmgr (to connect to a local MIS server)
- or
- em_accessmgr [-help] [-host hostname] &
- For example: em_accessmgr -host omega to connect to the MIS on the server omega and start the Security tool.
- The Security window is displayed.
2. Perform any of the tasks discussed in this chapter.3. Click File->Exit when you are finished.See Also Section 6.8.1.1 The em_accessmgr Command for more information about the command options.
6.3 Turning Off Access Control
When you turn off access control, you are giving all Solstice EM users complete access to applications, managed objects, and the operations for manipulating the objects. Any Solstice EM user can add and remove applications, add and remove managed objects, and change object attributes.
Turning off access control can be done either during or after the installation procedure. If you turned off access control during installation, no further tasks need to be performed. You can always turn on access control later when you want to control user access.
In the event access control had previously been turned on, either during installation or at a later point in time, you can override it by disabling access control. If you do, any security rules that were put in place before disabling access control will no longer control the users' actions.
Turning off access control requires you to disable access control.

To Turn Off Access Control
1. Start the Security tool in one of the following ways:
- From the Administration window, click Security.
- From the command line, execute the following command line at an operating system prompt:
- em_accessmgr
- or
- em_accessmgr -host MIS_Server_Name
2. In the Security window, click Actions->Security Defaults to display the Defaults dialog.3. Verify that the Security option at the top of the dialog is "Off."4. Click OK.6.4 Preparing for Security Control
As explained in Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model, individual users derive their access privileges from security rules that are applied to the privilege group to which they belong. The chapter overview also explained that users can belong to more than one group. In such event, users derive their access privileges from all the groups to which they belong.
Whether you want to control user access to Solstice EM tools and tasks only, or also to managed objects, you need to perform a number of preparatory tasks to ensure the necessary framework is in place. The section Getting Ready for Security Control in this chapter takes you through the tasks in the sequence that they need to be performed.
6.4.1 About Users, Granting All Privileges, and Root
All Solstice EM users must have UNIX accounts which you create using the UNIX administration tools available for this purpose, such as admintool from Solaris. In addition, the identity of the users must be recorded in an access control list. This is done by using Solstice EM. Solstice EM makes a distinction between users who are logged in as root, users who can grant all privileges, and regular users.
Users who are logged in as root or users who can grant all privileges always enjoy the following access privileges:
- Full access to all the Solstice EM tools, managed objects, and the em_accesscmd utility, even if they belong to a group controlled by restrictive rules.
- Create and modify Solstice EM user information and group profiles.
- Access to remote MIS servers.
Users not logged in as root or who cannot grant All Privileges in Security tool cannot change security access controls. However, they can access tools and manipulate managed objects based only on their access privileges to tools and managed objects.
6.4.2 About Privilege Groups
Solstice EM privilege groups--also referred as groups--are a collection of Solstice EM users having the same security privileges. Solstice EM privilege groups have no relationship to UNIX user groups. Privilege groups can have one or more members. There is no limit to the number of users you can assign to a group. Also, users can belong to more than one group.
Security rules are set for the groups. When users belong to several privilege groups, they derive their security privileges from all the rules that control the groups to which they belong. As such, users may have seemingly contradictory privileges. Refer to Section6.1.1 Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model for more information about how Solstice EM determines user access.
Group details such as membership, tools, and/or managed objects that group members can access based on the access privileges, are recorded in profiles. These profiles are represented as objects in the management information base.
A Solstice EM installation provides the following predefined groups.
6.4.3 Getting Ready for Security Control
Getting ready for security control requires you to carry out several preparatory tasks. The following outlines the tasks to be performed if you want to control user access to either Solstice EM tools or to managed objects.
- Log in as root or as super user, create UNIX accounts for all Solstice EM users.
- If not enabled during installation, turn on access control.
- Follow the instructions in Turning On Security Control.
- If multiple management information servers are used, prepare for remote connections to the MIS.
- Follow the instructions in Preparing for Remote Connections to the MIS.
- Prepare user profiles, if you did not do so during the installation. If you did and need not add any other profiles, skip this step. If you prepared some user profiles during installation, but need to add more, then execute this step.
- Follow the instructions in Preparing User Profiles.
- Note that at this stage of preparing user profiles you cannot yet specify group membership. You will be able to assign users to groups when you prepare the group profiles.
- If specific users need the ability to grant all privileges, follow the instructions in Granting Security Privileges.
- Prepare group profiles.
- Follow the instructions of Preparing Group Profiles.
At this stage you will be able to complete the user profile by assigning group membership.
Note that group profiles will be completed with information about the list of tools, and the rules for controlling user access to tools, when you perform the tasks described in Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools.
Similarly, the group profiles will be completed with information about the managed objects, and the rules for controlling user access to the objects, when you perform the tasks described in Controlling Access to Managed Objects.
6.4.4 Turning On Security Control
When you enable access control, you can grant or deny user access to the tool itself and to the operations that can be performed with these tools. Regarding access to managed objects, you can determine which users have access to which objects, and the operations they can perform on these objects.
Turning on access control requires you to do the following:
- Enable the Security option
- Edit the security controls in the Solstice EM configuration file
- Restart the MIS

To Turn On Security Control
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Security Defaults to display the Defaults dialog.2. Enable or disable access control:
- To enable access control, verify that the Security option at the top of the dialog is On (default).
- To disable access control, verify that the option is Off.
3. Click OK.4. Edit the assignments for the following access control variables in the $EM_HOME/build/acct/EM-config configuration file:
- EM_ACCESS_PASSWORD CONTROL
- EM_ACCESS_CONNECTION CONTROL
- EM_ACCESS_BACKWARD_COMPATIBILITY
5. For each of these variables, use TRUE to enable and FALSE to disable the variable.The following is an example of access control settings in an EM-config file.
- The two TRUE statements indicate that access to Solstice EM will be controlled and that and user password will be required and verified. the FALSE statement indicates that objects created using Solstice EM V2.1 will not be accessible. See the Developing Applications guide for details concerning this configuration file.
6. Restart the MIS after turning on Security by executing this command at an UNIX system prompt:
- em_services -reload
6.4.5 Preparing for Remote Connections to the MIS
To connect to a remote MIS server, the following must be set up:
- The names of the systems connecting to the MIS server must be added to the list of trusted hosts on the system where the MIS resides.
- If the users connecting to the MIS need the capability to set and change object attributes or access controls, you must enable the "Grant All Privileges" option for each of these users.
When users connect to a remote MIS server, the machine from which they are connecting must be recognized as a trusted host by the server on which the MIS resides. For example, when John Doe connects from the machines called alpha, beta, and gamma, to a remote MIS server called omega, then the systems alpha, beta, and gamma must be known as a trusted host to establish a connection to omega. You accomplish this by adding the names of the alpha, beta, and gamma systems to the list of trusted hosts in the Security Defaults dialog on the omega server.
With an established trusted host relationship, users can connect to a remote MIS but cannot make any changes. To connect to a remote MIS with the intention of changing object attributes, or application access, or both, users must be able to grant all privileges, or be able to log in as root. See Granting Security Privileges for step-by-step instructions.

To Allow Connections to a Remote MIS Server
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Security Defaults to display the Defaults dialog.2. Next to Trusted Hosts at the bottom of the dialog, type the name of the MIS server and click Add.
- Repeat this step for every MIS server to which the users who can grant all privileges should be able to connect to.
3. Click OK.

To Prevent Connections to a Remote MIS Server
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Security Defaults to display the Defaults dialog.2. Select the MIS server from the list of trusted hosts and click Delete.
- Repeat this step for every MIS server to which users who can grant all privileges should no longer be able to connect to.
3. Click OK.6.4.6 Preparing User Profiles
When access control is turned on, Solstice EM requires that the identity of users be known to the management information server. User profile information is recorded in a Solstice EM access control list. In addition to the profile information, Solstice EM requires that all users have UNIX accounts.
Note – It is imperative that the UNIX accounts be created before you create the user profiles. Failing to do so will result in your inability to prepare user profiles and an error message will be displayed.
When access control is turned off, UNIX accounts are still needed but no Solstice EM user profiles need to be created.
To prepare user profiles you will need the following information:
- User ID of the user's UNIX account.
- The individual's first and last names.
- Whether the user will be able to grant all privileges. See Section6.4 Preparing for Security Control and Section6.4.7 Granting Security Privileges for more information.
User profiles are prepared using either the Security tool or the command line. Using the Security tool, you create new user profiles in one of the following two ways:
- Completing the User Create dialog
- Duplicating an existing user profile
For preparing user profiles from the command line, see Section6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility.

To Prepare User Profiles
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Create to display the Create dialog.2. On the Identity tab, in User Login, type the user ID.
- For example: jdoe. The user ID must be a valid login ID for the host on which the current MIS is running. What you type in this field is what is listed in the User Login column in the Security window.
3. In Full Name, type the user's first and last names.4. For users who will be entrusted with security management, click Grant All Privileges.
- See Section6.4.7 Granting Security Privileges for more information on the privileges associated with the option of Granting All Privileges.
5. Click Apply to continue adding other users, or click OK when you have finished.The user ID is immediately added to the list of users and groups, and an empty user profile object for that individual is added to the MIS.
Group membership cannot be assigned until group profiles have been prepared. Once group profiles have been prepared, you can assign group membership.

To Prepare User Profiles by Duplication
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to list the existing users.2. Select the user whose profile you want to use for creating a new one.3. Click Actions->Duplicate to display the Duplicate dialog.4. On the Identity tab, type the user login for the user profile you want to create.5. Enter the user's first and last names.6. Click any of the other tabs and update the information as necessary.7. Click OK.6.4.7 Granting Security Privileges
When access control is turned on, users who can grant all privileges--regardless of the groups to which they belong--are automatically granted update privileges to controlled applications and managed objects.
The option Granting All Privileges enables any user to use all Solstice EM tools, to manipulate and update managed objects and access privileges to which they normally do not have access. Users who can grant all privileges may update user records and group profiles except their own, change security rules, change access controls to applications, and update object attributes.
The privilege of granting all privileges can be given to any user when you prepare the user's profile or later as the need arises.
Note – Note that users who are member of the Full Access group do not automatically have the ability to grant all privileges.

To Grant Security Privileges
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to display all Solstice EM users.2. Click the user record to select it and then click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected user.3. Click Grant All Privileges.
- When selected, the option displays a check mark.
4. Click OK.6.4.8 Preparing Group Profiles
When access control is turned on, group identities, just like user identities, need to be recorded in profiles that are stored in the management information database as objects. Group profiles also identify the security rules that determine whether or not the group members are granted or denied access to the specified tools and the managed objects.
To prepare group profiles you need to have the following information on hand:
- The name to be given to the group
- The IDs of the users who will become members of the group
Group profiles will be completed when you carry out the task for controlling user access to applications and managed objects.
Group profiles are created using the Solstice EM graphical user interface or from the command line. Using the graphical user interface, you create group profiles in one of the following two ways:
- Completing the Group Create dialog
- Duplicating an existing group profile
For preparing group profiles from the command line, see Section6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility.
Tip – Use the Full Access users group (or any other existing group) as the basis for creating (by duplication) group profiles for new users groups; then, modify the access controls for the newly created group as needed.

To Prepare Group Profiles by Duplication
1. In the Security window, select the Privilege Groups tab to display the list of existing privilege groups.2. Select the group you want to use as the basis for creating a new privilege group.3. Click Actions->Duplicate to display the Group Duplicate dialog.
- This dialog is identical to the Create Privilege Group dialog. A duplicate of that group is created and the group information is loaded into the dialog.
4. On the Identity tab, type the name of the new privilege group5. Type a group description.6. Move from tab to tab and modify the existing group information to meet the requirements for the new group.7. Click OK.

To Prepare Group Profiles
1. In the Security window, select the Privilege Groups tab.2. Click Actions->Create to display the Create Group dialog.3. On the Identity tab, in Privilege Group Name, type the group's name.4. Type a group description.
- For example, if the group will contain the names of operators monitoring the routers in your network, "Router Operators" might be a suitable name.
5. On the Members tab, specify the group members as follows:
- Select one or more users from the Managed Users list on the left and click Add.
- To select all users, click Select All and then click Add.
The rest of the group profile will be completed when you carry out the tasks outlined in Section6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools and Section6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects.
6.4.9 Saving and Reusing Profiles
After defining profiles for the Solstice EM users and groups, you may want to save the profile information to a file of your choice. This file can then be loaded back into the system after an upgrade or a re-installation of Solstice EM.
When importing a file, the file to be imported must have been created using the Export command. The imported access information is created in the current MIS. This information is appended to any pre-existing information. No information is removed.

To Save Profiles
1. In the Security window, click File->Export to display the Export dialog.2. Select one of the following options:
- All Access Control Objects - Select this option to save the access control data of all users, groups, and trusted hosts, applications, targets, rules, and security default information for the current MIS.
- Users, Groups, Trusted Hosts, and Application List - Choose this option to save information for the current MIS.
- Targets, Rules, and Security Defaults - Select this option to save control access data information for the current MIS.
3. In File Name, type a directory path name and file name for saving the profiles.
- If you do not know the directory path name, click Browse to select a directory path name. Use the * wildcard and click Filter to filter the contents of the selected directory. For example, /home/user1/EM_EXPORTS/* will display the contents of this directory; from this list, select the file to which the data should be saved. If the file does not exist, type a file name.
4. Click OK.

To Reuse Saved Profiles
1. In the Security window, click File->Import to display a standard Select File dialog.2. Enter the directory path and file name, or click Browse to search for and select an existing profile file.3. Click OK.6.4.10 Printing Profiles
You can print the list of Solstice EM users and groups in two formats:
- Text format - Prints the existing user groups and their members in plain ASCII format.
- Table format - Creates an encapsulated PostScript file of the table listing the user groups in the Security window.

To Print Profiles
1. In the Security window, click File->Print to display the Print dialog.2. Select Print to File or Printer as print destination.
- If you select Print to File, click the [...] button to display a file selection dialog from which you select the profile to be printed.
3. Select either Text or Table format.4. Click Print.6.4.11 Searching for Users and Groups
Solstice EM provides a search mechanism for finding existing Solstice EM users and groups based on search criteria that you specify.

To Search for Users and Groups
1. In the Security window, click Action->Find to display the Find dialog.2. Select User or Privilege Group from the Find options.3. Select the type of match.4. Specify whether or not to use case sensitivity when searching.5. (Optional) Enter the search string.6. Click Find to start searching.7. Click Close to exit.6.4.12 Maintaining User Profiles
Maintaining user profiles includes the following activities:
- Modifying the profile properties of existing users
- Assigning users to other groups
- Deleting user profiles
The above tasks can be performed using the Security tool as explained below, or from the command line as explained in Section6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility.

To Update User Profiles
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to display the existing users.2. Select the user from the list, and click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected user.3. Move from tab to tab and enter your changes.4. Click Apply to change and keep the dialog open, or click OK to change and exit.

To Assign Users to Other User Groups
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to list the existing users.2. Select the user from the list and click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected user.
- Alternatively, double-click on the user's name.
3. Select the Privilege Groups tab.4. To add the user to another privilege group, select the privilege group from the list on the left and click Add.5. If necessary, to remove the user from a privilege group to which the user currently belongs, select the privilege group from the list on the right and click Remove.6. Click Apply or OK.

To Delete User Profiles
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to list all existing users.2. Select the name of the user to be deleted.3. Select Actions->Delete.4. Click OK.6.4.13 Maintaining Group Profiles
Maintaining group profiles includes the following activities:
- Updating the properties of groups, such as the changing the group's members, the group's privileges to applications and database objects
- Deleting groups
The above tasks can be performed using the Security tool as explained below, or from the command line as explained in Section6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility.

To Update Group Profiles
1. In the Security window, click the Privilege Groups tab to list the existing groups.2. Select the privilege group whose profile is to be updated and click
Actions->Properties to display the Group Properties dialog.
- Alternatively, double-click the privilege group.
- The dialog is identical to the Group Create dialog.
3. Moving from tab to tab, update the group's properties as necessary.4. Click OK.

To Delete Group Profiles
Caution – Deleting groups by deleting group profiles irrevocably and immediately removes the corresponding group profile objects from the MIS.
1. In the Security window, click the Privilege Groups tab to list the existing groups.2. Select the privilege group you want to delete and click Actions -> Delete.6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools
This section of the guide discusses the tasks you need to perform to control user access to Solstice EM tools.
The tasks involved in controlling access to tools are easy to accomplish. As such, controlling user access to Solstice EM tools can be considered a stepping stone toward building the expertise you need to control user access to managed objects.
Note – Before you carry out any of the tasks outlined in this section of the chapter, you must have accomplished all the required preparatory tasks outlined in Section6.4 Preparing for Security Control.
6.5.1 Implementation Overview
This overview expands the concepts introduced in the chapter overview and discusses them in more detail.
This Implementation Overview provides more details about the following:
- Definition of Solstice EM tools and tasks
- Security rules for controlling access to tools
- Guidelines for controlling access to tools
6.5.1.1 About Solstice EM Tools and Tasks
Solstice EM enables you to control access at the tool level and at the task level.
As used in this guide, tool means any Solstice EM tool and any custom-developed application developed using the Solstice EM API; tasks mean any of the tool features supported by the tool, such as edit, create, delete, and so on.
Before you can proceed with setting access controls, all tools must be placed under Solstice EM Security control.
6.5.1.2 Security Rules for Controlling Access to Tools
As explained in Overview, security rules are at the heart of Solstice EM for controlling user access. User access to tools can be controlled by creating security rules that deny or grant access in the following ways:
- Deny members of identified groups access to all Solstice EM tools - Use this type of rule when you want to exclude specific users from accessing any Solstice EM and all of the Solstice EM tools. When no specific groups are identified, the rule applies to all groups.
- Deny members of identified groups access to specific Solstice EM tools - Use this type of rule when you want to ensure that specific users do not have the capability to run specific tools. For example, denying operators the right to create log files using Solstice EM's Event Logs tool.
- Deny members of identified groups the ability to perform specific tasks when using Solstice EM tools - This type of rule allows specific users to run the tools but they are denied access to specific tool features, such as the edit or delete function provided by the tool. For example, allowing operators to view log records using Solstice EM's Log Entries tool, but denying them the capabilities of editing the log records in the log file, or deleting them using the Log Entries tool edit and delete functions.
The logic used for controlling user access is explained in Section6.1.1 Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model.
Access to the tool is enforced by the tool itself. The MIS only stores the list of features that can be accessed for each application.
6.5.2 Getting Ready to Control Access to Solstice EM Tools
The tasks in this section need to be carried out if you want to control user access to Solstice EM tools and tasks. The following outline is a high-level overview of the tasks to be performed.
- Make sure you have accomplished all preparatory tasks.
- If necessary, add custom-developed applications to Solstice EM.
- Follow the instructions in Section6.5.3 Placing Tools Under Security Control.
- Define the privileges for accessing tools and tasks.
- Follow the instructions in Section6.5.5 Granting and Denying Access to Tools and Tasks.
6.5.3 Placing Tools Under Security Control
Before you can specify access controls to applications and tasks, you must ensure that any custom-developed applications for which you want to control user access are under Solstice EM control.
If you plan on controlling user access at the task level for custom-developed applications, you will need to obtain the following:
- The name of the application's executable(s).
- The exact name of the application tasks to which access will be controlled. The task name must be the name recognized by the application. For example, if you want to control user access to the delete function of the XYZ application, you need to know that the developer named that function "XYZDelete."
Once the tools are added to Solstice EM, tasks supported by the tools appear as a list of options from which you make your selections.

To Place Tools Under Security Control
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Applications List to display the Applications dialog.2. Click Add to display the Application Create dialog.3. In Application Name, type the name of the application to be added.
- You can choose either the name of the executable or the commercial name.
4. In Description, type a description of the application.5. (Optional) At the bottom of the dialog, type the description for the Application Task.
- Enter the description for an application task before adding the task name to the list. For example, if the task is delete, type: Delete.
- Attempting to add a description to an existing task results in a duplicate task name displaying in the list. If you have done this, delete the undescribed task name from the list, leaving only the described version of the task.
6. Still at the bottom of the dialog, enter the application task.
- For example, if the name of the task is "XYZDelete", then type: XYZDelete. If the application developer named the task "XYZ-delete", then type: XYZ-delete. The syntax of the task must match the task name as defined by the application developer.
- Note the Task and Description list display table in the center of the Application Add dialog. This is a display/selection list only. To add a task to this list, enter the task name in the Application Task field below the table, and then click Add. The feature name must be the name recognized by the application (for example, the Viewer application task "Move Object" is listed as "MoveObject").
7. Click Apply.8. Keep adding tool tasks and descriptions until you have added all the features to be controlled.9. Click OK when you are finished.

To Place Tools Under Security Control by Duplication
1. In the Security window, click View->Privilege Components->Applications List to display the Applications dialog.2. Select the application you want to use for creating a new one, and click Duplicate to display the Application Duplicate dialog.3. Enter the application name.4. Change the application's description.5. Make any necessary modifications as follows:
- To delete a feature from the list, select it and then click Delete.
- To modify a feature description or name, first delete the existing feature from the list, and then re-add it with the new description.
6. Click Apply for each change.7. Click OK when you are finished.6.5.4 Removing Tools From Security Control
When specific tools are no longer to be used under Solstice EM, you should remove them. Removing tools from Solstice EM control results in deleting the objects which represent these tools in the MIS.
If the tool to be removed is a custom-developed application for which you had specified access controls at the task level, removing it will result in losing task information which may have been time consuming to collect.
You cannot restore a tool that was removed. If the application is a Solstice EM tool, your only option is to reinstall Solstice EM. If the tool to be removed is a custom-developed application, you will need to add it again under Solstice EM as explained in Section6.5.3 Placing Tools Under Security Control.

To Remove Tools From Security Control
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Applications List to display the Applications dialog.2. Select the tool name from the list and click Delete.3. Click Close.6.5.5 Granting and Denying Access to Tools and Tasks
After making sure that all applications are under Solstice EM control, you can proceed by specifying the rules that will determine the group access privileges to tools and tool tasks.
You both grant or deny access at the tool level and at the task level at the same time.

To Grant and Deny Access to Tools and Tasks
1. In the Security window, click the Privilege Groups tab.2. Select the group and click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected group.3. On the Tasks tab, select Task Access by Application and click Edit to display the Edit Task Access By Application dialog.4. In Application Names, select the application.
- Solstice EM tools are listed by the names of their executables. For example, the Security tool is listed as em_accessmgr.
5. Specify the level of access by selecting No Access, Full Access or Specify Tasks.
- No Access - Denies the members of the group any access to the tool. Users will not be able to start and run the tool.
- Full Access - Grants the members of the group complete access to the tool and its tasks. Users will be able to start and run the tool and perform all tasks supported by the tool.
- Specify Task - Grants the members of the group access to the tool but denies and grants access to specific tool tasks. Users will be able to start and run the tool. If, for example, you denied access to the Delete task, users will not be able to perform any delete operations.
6. If you selected Specify Tasks, select the tasks from the list of available tasks.
- The list of tasks available for selection is determined by the selected application.
7. Click Apply to continue, or click Close when you have finished to return to the Properties dialog.8. Click OK.The group profile data in the MIB is updated to include the rules that determine access to the tools and tasks.
6.5.6 Viewing Tool Access Privileges
When security control is enabled, individual Solstice EM users can view the privileges that control their access to tools and tasks.

To View Tool Access Privileges
1. In the Security window, click the Users tab to list the users.2. Select a user.3. Click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected user.4. Click the Tasks tab to view access privileges information.
- The information shown is for viewing only and cannot be changed. See Section 6.5.5 Granting and Denying Access to Tools and Tasks for instructions on granting and denying access to tools.
5. Click Cancel to close the dialog.6.5.7 Updating Tool Access Privileges
Organizational or other changes affecting the Solstice EM configuration may require you to update the access controls to tools and tasks.
Note – To make any changes, you must either be a user who can grant all privileges, or be logged in as root. If necessary, follow the instructions in Section6.4.7 Granting Security Privileges before making any of the desired changes. You cannot change your own privileges; to do so, log in as root.

To Update Tool Access Privileges
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Applications List to display the Applications dialog.2. Select the application you want to modify and click Edit to display the Applications Edit dialog.3. Enter your changes.
- To change the tool name or tool task, click in the Description field box and type your changes.
- To delete a task from the list, select it and click Delete.
- To modify a task description or task name, type the new task description or task name.
4. Click OK.6.6 Controlling Access to Managed Objects
This section of the guide discusses the tasks you need to accomplish to control user access to managed objects.
The tasks involved in controlling access to managed objects are complex and require a solid understanding of the Solstice EM configuration as well as experience in controlling user access to Solstice EM tools. As such, controlling user access to managed objects should only be considered after you have acquired expertise in controlling user access to Solstice EM tools and tasks.
Note – Before you carry out any of the tasks outlined in this section of the chapter, you must have accomplished all the required preparatory tasks outlined in Section6.4 Preparing for Security Control and the tasks outlined in Section6.5 Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools.
6.6.1 Implementation Overview
This overview expands the concepts introduced in the chapter overview and discusses them in more detail to successfully set up security controls to managed objects.
This Implementation Overview provides more details about the following:
- Security rules for controlling access to managed objects
- Definition of object sets
- Guidelines for controlling access to managed objects
6.6.1.1 Security Rules for Controlling Access to Managed Objects
As explained in Section6.1 Overview, security rules are the foundation for controlling user access.
User access to managed objects can be controlled by creating rules that deny or grant access in the following ways:
- Deny members of specific groups access to all managed objects - Use this type of rule when you want to exclude the members of specific groups from accessing all objects in the MIS. When no specific groups are identified, the rule applies to all groups. This rule is sometimes referred to as the global deny rule.
- Deny members of specific groups access to specific managed objects - Use this type of rule when you want to exclude the members of specific groups from accessing specific objects. For example, members of the "Routers Operators" group should not have any access to managed objects representing bridges which are monitored by members of the "Bridge Operators" group. This rule is sometimes referred to as the item deny rule.
- Grant members of specific groups access to all managed objects - Use this type of rule when you want to ensure that all members of specific groups have access to all the managed objects. For example, members of the "SysAdmin" group should have access to all managed objects in the MIS. This rule is sometimes referred to as the global grant rule.
- Grant members of specific groups access to specific managed objects - Use this type of rule when you want to ensure that all members of specific groups have access to specific managed objects. For example, members of the "Boston SysAdmin" group have access to all objects representing the Boston network components in the management information database. This rule is sometimes referred to as the item grant rule.
- Grant and/or deny members of all groups access to managed objects - When none of the above rules apply, Solstice EM will use this type of rule--sometimes referred to as the default rule--to determine user access as follows:
- To managed objects that are not included in a list of managed objects to which access is either specifically granted or denied.
- To managed objects where there are no rules that specifically deny or grant user groups access to managed objects.
- For example, user Jane Smith is a member of the "Router Operator" group whose access privileges are defined by a rule that grants the group members access to managed objects of the router type in the MIS.
In addition, there are no rules that specifically deny the group members access to objects of a type other than router.
Jane Smith's access to managed objects that are not of the router type, will be determined by the default rule settings.The logic used for controlling user access is explained in Section6.1.1 Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model.
The installation provides you with the following predefined security rules.
The MIS enforces the access control policy as defined by the security rules.
Before you proceed in setting access controls to managed objects, you must have completed all preparatory tasks as explained in Preparing for Security Control and Controlling Access to Solstice EM Tools.
6.6.1.2 Understanding Object Sets
An object set is a group of managed objects protected by the same access rule. Object sets identify managed objects within the security domain. An object set can be one or more of the following:
- Any managed object type or class
- One or more specific instances of an object.
- All objects below that object in the Management Information Tree (MIT)
- One or more subtrees below an object, including or not including the object itself
- One or more attributes of an object
The following are some examples of object sets:
- All Solstice EM log files, except AlarmLog
- topoNodes contained in the 129.146.0.0 network
- "Set" operations on objects of the type "router"
A default Solstice EM installation provides the following predefined object sets.
See Section6.8.1.4 More About Object Sets for more information.
6.6.2 Getting Ready to Control Access to Managed Objects
The tasks in this section of the chapter need to be carried out if you want to control user access to managed objects. The following outline is a high-level overview of the tasks to be performed.
- Make sure you have accomplished all preparatory tasks.
- If you are not already controlling user access to Solstice EM tools, define access controls to Solstice EM tools.
- Define the object sets.
- Follow the instructions in Section6.6.3 Defining Object Sets.
- Define the security rules for the object sets.
- Follow the instructions in Section6.6.4 Defining Security Rules for Object Sets.
- Assign the objects sets and rules to the appropriate groups.
- Follow the instructions in Section6.6.5 Assigning Objects and Security Rules to Groups.
6.6.3 Defining Object Sets
Note – To define object sets, you must be logged in as root or a user with "grant all" privileges.
To complete the tasks pertaining to specifying object sets, you will need to have the following information on hand:
- The object class of the objects
- The name of the object instance in the MIS
- The access scope in the topology
- Target filters
- Available CMIS filter(s)
- The operations that can be performed on the objects
Using the graphical user interface, you add sets of objects in one of the following ways:
- Using the Object Set Create dialog
- Duplicating an existing definition

To Define Object Sets
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Sets to display the Object Sets dialog.2. Click Create to display the Object Set Create dialog.
- The Object Sets Create dialog is organized in the following two groups: Objects and Operations.
3. In Object Set Name, enter a name for the object set as you want to see it listed in the Object Sets dialog.4. Specify the types of objects to be included in the object set as follows:
- Click Types, select an object type from the list, click Add, and then click Close.
- Alternatively, type in the name of the object type in the text field next to the Types button.
5. Specify object instances to be included in the object set as follows:
- Click Instances, select an object instance from the list, click Add, and then click Close.
- Alternatively, type in the name of the object instance in the text field next to the Instances button.
- The Object Instances do not bear any relationship to the Object Types.
6. Specify the Scope (Base Object).
- Click the scope selection box to display the available options. If you select either Base to the Nth Level or Nth Level, you must also specify the level in the number field next to the selection list. Use the up and down arrows to select the correct level.
7. (Optional) Define a CMIS filter by clicking Filter to display the CMIS Filter dialog.
- Using the CMIS Filter dialog, you can create and save a new CMIS filter definition, or load an existing filter. See CMIS Scoping and Filtering in the Developing Applications guide for more information.
8. On the Operations Group tab, select either All Operations, or select the operations individually.9. (Optional) Create a CMIS filter by clicking Event Discriminator to display the CMIS Filter dialog.10. Click OK.

To Define Object Sets by Duplication
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Sets to display the Object Sets dialog.2. Select an object set in the list and click Duplicate to display the Object Sets Duplicate dialog.3. Enter the name of the new object set.4. Make any other changes as necessary.5. Click OK.

To Create CMIS Filters
1. In the Security window, click Object->Object Sets to display the Object Sets [Create] dialog.
- See CMIS Scoping and Filtering in the Developing Applications guide for more information.
2. Click Filter to display the CMIS Filter dialog.3. Enter the filter definition as follows:
- Click Item to display the CMIS Filter Item dialog.
- Select the Operator for the item.
- Type the Attribute ID.
- Click Search to display the CMIS Filter Item Search dialog.
- Type the Attribute Value.
- Add the item to the CMIS filter definition.
- Click OK to add the item to the filter definition and return to the CMIS Filter dialog.
4. (Optional) Click Save to name and save the filter.5. Click OK.6.6.4 Defining Security Rules for Object Sets
When you do not want to give all users the same level of access to managed objects, you can use the predefined rules and add your own. With security rules you can refine user access to the object level and exclude specific users from accessing designated objects.
Note – Individual users derive their privileges from the group to which they belong. Security rules only apply to users belonging to user groups. Users who do not belong to any groups (an unlikely event) derive their access privileges from the default rule.
As explained in Section6.6.1.1 Security Rules for Controlling Access to Managed Objects you can control user access in the following ways.
Using the Object Access Rule dialog:
- Deny groups access to all sets of objects.
- Deny groups access to specific objects.
- Grant groups access to all sets of objects.
- Deny groups access to specific sets of objects.
Using the Defaults dialog specify access defaults applicable to all users when no other access rule prevails.
Detailed steps for creating these security rules are provided in the following sections.
If necessary, see Section6.1.1 Understanding the Solstice EM Access Control Model for information about security rules and the logic used for enforcing them.

To Deny Groups Access to All Sets of Objects
- This type of rule is also referred to as the global deny rule.
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Object Access Rule dialog.2. Click Create to display the Object Access Rule Create dialog.3. In Rule Name, type the name of the custom access rule.4. In Privilege Groups Using Rule, click Edit List to display the Edit Privilege Groups List dialog.5. Select one, several, or all user groups listed in All Groups and click Add.6. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.7. Do not specify any sets of objects.8. Select one of the three Deny options.9. When finished creating rules, click OK, otherwise click Apply.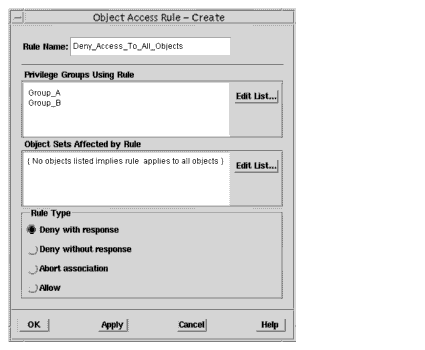
FIGURE 6-2 Rule Denying Group Access to All ObjectsFIGURE 6-2 Illustrates a rule that denies the members of the groups "Group_A" and "Group_B" access to all objects. When users attempt to access the objects, an informational message will be displayed.

To Deny Groups Access to Specific Sets of Objects
- This type of rule is also referred to as the item deny rule.
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Object Access Rule dialog.2. Click Create to display the Object Access Rule Create dialog.3. In Rule Name, type the name of the custom access rule.4. In Privilege Groups Using Rule, click Edit Group List to display the Edit Privilege Groups List dialog.5. Select one, several, or all user groups listed in All Groups and click Add.6. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.7. In Objects Sets Affected By Rule, click Edit List to display the Edit Object Sets List dialog.8. In All Object Sets, select the objects to which access is to be denied and click Add.9. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.10. Select one of the three Deny options.11. When finished creating rules, click OK, otherwise click Apply.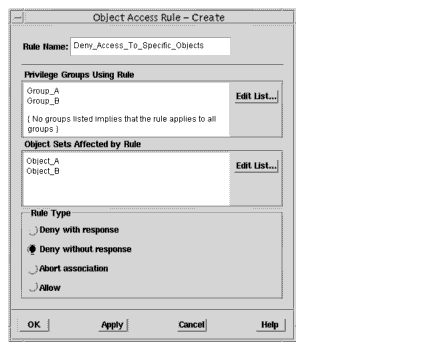
FIGURE 6-3 Rule Denying Group Access to Specific Objects
- FIGURE 6-3 Illustrates a rule that denies the members of the groups "Group_A" and "Group_B" access to the objects "Object_A" and "Oject_B". When attempting to access these two objects, no informational message will be displayed.

To Grant Groups Access to All Sets of Objects
- This type of rule is sometimes referred to as the global grant rule.
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Object Access Rule dialog.2. Click Create to display the Object Access Rule Create dialog.3. In Rule Name, enter the name of the custom access rule.4. In Privilege Groups Using Rule, click Edit Group List to display the Edit Privilege Groups List dialog.5. Select one, several, or all user groups listed in All Groups and click Add.6. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.7. In Objects Sets Affected By Rule, click Edit List to display the Edit Object Sets List dialog.8. Click Select All and then click Add.9. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.10. Select Allow.11. When finished creating rules, click OK, otherwise click Apply.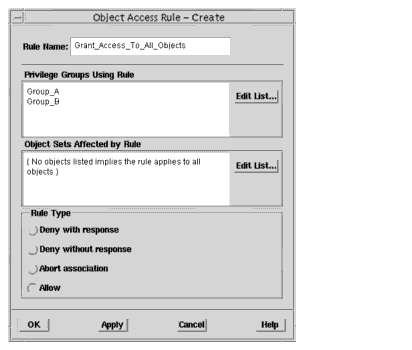
FIGURE 6-4 Rule Granting Access to All Objects
- FIGURE 6-4 Illustrates a rule that grants the members of the groups "Group_A" and "Group_B" access to all objects.

To Grant Groups Access to Specific Sets of Objects
- This type of rule is sometimes referred to as the item grant rule.
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Object Access Rule dialog.2. Click Create to display the Object Access Rule Create dialog.3. In Rule Name, type the name of the custom access rule.4. In Privilege Groups Using Rule, click Edit Group List to display the Edit Privilege Groups List dialog.5. Select one, several, or all user groups listed in All Groups and click Add.6. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.7. Click Edit Target List to display the Edit Targets List dialog.8. In All Object Sets, select the objects to which access is to be granted and click Add.9. Click OK to return to the Rule Create dialog.10. Select Allow.11. When finished creating rules, click OK, otherwise click Apply.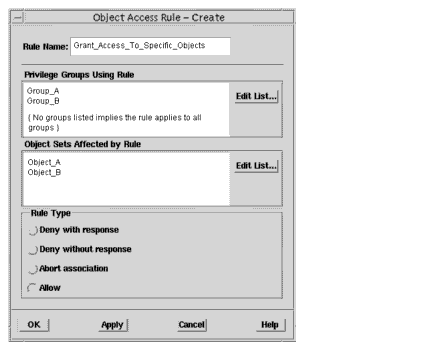
FIGURE 6-5 Rule Granting Access to Specific Objects
- FIGURE 6-5 Illustrates a rule that grants the members of the groups "Group_A" and "Group_B" access to the objects "Object_A" and "Object_B".

To Create Security Rules by Duplication
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Object Access Rules dialog.2. Select the rule to duplicate and click Duplicate to display the Object Access Rule Duplicate dialog.3. In Name, type the name of the new custom access rule.4. (Optional) Enter your modifications.5. Click OK.

To Specify Default User Access
- This type of rule is sometimes referred to as the default rule.
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Security Defaults to display the Defaults dialog.2. Verify that Security is turned on.3. Define the access defaults for each operation type.4. Choose the desired access level for the logging of security and audit events.5. If users will access remote MIS servers, add the names of these servers and click Add.6. Click OK.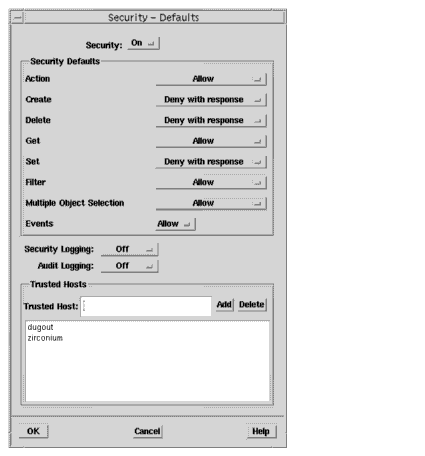
FIGURE 6-6 Default RuleFIGURE 6-6 Illustrates the default rule that applies to groups in the absence of any other security rules, and to users who do not belong to any groups.
As shown, users are allowed to do the following:
- From the Action setting - Request an agent to invoke a specific behavior that is supported by the managed object that receives the request.
- From the Get setting - Request information from an agent.
- From the Filter setting - Request an agent to perform a test on a managed object before carrying out a request.
- From the Events setting - To request an agent to send event report messages.
- From the Multiple Object Selection - Request an agent to send a single request to several managed objects.
- Users logging in from the dugout and zirconium systems can, for example, connect to the server on which the MIS resides.
- Users are not allowed to do the following:
- From the Create setting - Request an agent to create a managed object.
- From the Delete setting - Request an agent to delete one or more managed objects.
- From the Set setting - Request an agent to change attribute values of a managed object.
- From the Security Logging setting - Request an agent to generate service or mechanism violation notifications or events to allow the logging of all security violations.
- From the Audit Logging setting - Request an agent to generate Service Report notifications or events to log all authorized access to management information at the object level.
6.6.5 Assigning Objects and Security Rules to Groups
After you have defined object sets and created security rules, you are ready to assign these objects and rules to the appropriate user groups.

To Assign Objects and Security Rules to Groups
1. In the Security window, click the Privilege Groups tab.2. Select the group and click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected group.3. On the Object Access Rules tab, specify the group's security rules as follows:
- From the All Rules list, select one, several or all security rules that will apply to the group and its members, and then click Add.
4. On the Database Objects tab, specify the managed objects accessible to the group folder as follows:
- From the All Database Object list, select one, several or all database objects, and then click Add. The selected objects are listed in Group Database Objects on the right.
5. Click OK.6. Repeat steps 2 to 5 for every group until you are finished.The group profiles in the MIS are automatically updated with the object sets and security rules.
6.6.6 Viewing Access Privileges to Managed Objects
Individual Solstice EM users can view the privileges that control their access to managed objects.
Users whose access to managed objects is controlled view their privileges as follows:
- On the Access Rules tab of the Properties dialog, when rules that deny or grant access to managed objects are put in place.
- In the Defaults dialog, when rules that deny or grant access to managed objects have not been put in place, or for any managed objects not governed by any grant or deny rules.
Users who do not belong to any groups view their access privileges to managed objects in the Defaults dialog.

To View Privileges to Managed Objects
1. In the Security window, click the Groups tab.2. Select the user or the group whose properties are to be viewed.3. Click Actions->Properties to display the Properties dialog for the selected group.4. Click the Object Access Rules tab to view the list of rules that control the group's access to managed objects.5. Click the Database Object tab to view the managed objects subject to access control.6. Click OK if changes were made, otherwise click Cancel.

To View Privileges From the Default Rule
1. In the Security window, click View->Security Defaults to display the Default dialog.2. Click Cancel when you are finished.6.6.7 Maintaining Object Sets
Maintaining object sets includes the following activities:
- Updating object sets
- Deleting object sets
The dialogs for creating and updating object sets are identical, except for their titles. As such, the procedures for creating and modifying objects are very similar.
Caution – Security does not display warning messages when you delete object sets. Deleting object sets removes the instances representing the object sets from the MIS immediately and irrevocably.
To make any changes you must be a user who can grant all privileges, or be logged in as root.

To Update Object Sets
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Sets to display the Object Sets dialog.2. Select an object set in the list and click Edit to display the Object Sets (Edit) dialog.3. Enter your changes.4. Click OK.

To Delete Object Sets
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Sets to display the Object Sets dialog.2. Continue as follows:
- To delete an object set listed in the Object Sets dialog, select it and click Delete.
- To delete object types and instances associated with a selected object set, click Edit to display the Target Edit dialog.
3. Working in the Object Set Edit dialog, continue as follows:
- To delete an object type, select it in the Objects list and click Delete.
- To delete an object instance, select it in the Instances list and click Delete.
4. Click OK.6.6.8 Maintaining Object Privileges
Maintaining privileges for managed objects includes the following activities:
- Updating security rules
- Deleting security rules
The dialogs for creating and updating privileges are identical, except for their titles. As such, the procedures for creating and modifying custom security rules are very similar.

To Update Object Privileges
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Rules dialog.2. Select a rule from the list and click Edit to display the Object Access Rule Edit dialog.3. Make the necessary changes.4. Click OK.

To Delete Object Privileges
1. In the Security window, click Actions->Privilege Components->Object Access Rules to display the Rules dialog.2. Select the rule to delete and click Delete.3. Click Close.6.6.9 Importing/Exporting Access Control Objects
Use previously configured access control files and parameters for the following:
- Importing object files
- Exporting object files

To Import Access Control Objects
1. In the Security Window, click File->Import to display the Import dialog.2. Enter the filename to import.3. Click OK.

To Export Access Control Objects
1. From the Security Window, click File->Export to display the Export dialog.2. Choose from the following export options:
3. Enter a filename in the field to export a file.4. Click OK.6.7 Using the em_accesscmd Utility
A number of tasks pertaining to access control can be performed from the command line. This is particularly useful when you want to automate security tasks by loading existing files.
Solstice EM provides the em_accesscmd utility for the purpose of performing the most important security tasks.
Instructions for the following tasks are provided in this section:
- Creating user profiles
- Creating group profiles
- Assigning users to groups
- Deleting user profiles
- Deleting group profiles
- Adding applications under Solstice EM control
- Assigning user access to application features
- Exporting files
For a complete list of em_accesscmd commands see Section 6.8.1.3 The em_accesscmd Commands

To Create User Profiles
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command at a system prompt:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Enter the following command:
- createUser login_name "full_name"
- For example: createUser jdoe "Jane Doe"

To Create Group Profiles
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Create the user group by entering the following command:
- createGroup group_name "group_description"
- For example: createGroup OmegaSysAdmins "System Administrations of host omega"

To Assign Users to Other Groups
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Add the user to another group by executing the following command:
- addMembers "group_name" login_name
- For example, to add Jane Doe to the Operators group, enter: addMembers "Operators" jdoe
3. If necessary, remove the user from another user group by executing the following command:
- removeMembers "group_name" login_name
- For example: removeMembers "Operators" jdoe

To Delete User Profiles
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Delete the user by executing the following command:
- deleteUser login_name
- For example: deleteUser jdoe

To Delete Group Profiles
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
- See The em_accessmgr Command for more information.
2. Delete the privilege group by executing the following command:
- deleteGroup "group_name"
- For example: deleteGroup "Boston_SysAdmins"

To Place Tools under Solstice EM Control
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Add the application by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- createApplication "app_name" "app_description"
- For example: createApplication "Wizbang" "Monitor Wiz"

To Specify Tool Tasks
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Specify a tool task by executing the following command:
- createFeature "app_name" "task_name" "task_description"
- For example: createFeature "Wizbang" "feature_add" "Add Wizbang objects"

To Assign Tool Tasks to a Group
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- #em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Assign a tool task to a group by executing the following command:
- assignAppFeatures "privilege_group_name" "app_name" ["task_name"] "<task_description>"
- For example: assignAppFeatures "BostonAdmins" "Wizbang" "feature_add" "Add Wizbang objects to Boston network views"

To get a list of Authorized Tasks for a User
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Get the list by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- getAuthFeatures login_name [ "app_name"+ ] ]
- For example: getAuthFeatures jdoe "Wizbang"

To Get a List of Authorized Tools for a User
1. Start the em_accesscmd utility by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname]
2. Get the list by executing the following command from a system prompt:
- getAuthApps [login_name]
- For example: getAuthApps jdoe

To Export Access Control Objects
1. In the Administration window, click Security to start the Security tool.2. Click File->Export to use the Export dialog.3. Select from the following options:
4. Enter a file name to export.5. Click OK.6.8 Reference
This section provides reference information about command-line options for security operations.
For detailed information about dialogs, menus, and other user interface elements, refer to the Solstice EM Online Help. To access Online Help, click the Help button on any dialog box or select options from the Help menu located in the upper right corner of each Solstice EM tool window.
6.8.1 Command-Line Options
Reference information is available for the following:
6.8.1.1 The em_accessmgr Command
The em_accessmgr command is the executable to start the Security tool.
em_accessmgr [-help] [-host hostname]
For example: em_accessmgr -host omega. This command connects to the MIS on the server omega and starts the Security application.
6.8.1.2 The em_accesscmd Utility
The em_accesscmd utility is the command-line interface for creating security access profiles for users, privilege groups, and tools. You enter this command and its parameters to create users, user groups, assign users to user groups, add applications, specify access controls for tool tasks, and so on.
When adding third-party applications to Solstice EM, you first must use em_accesscmd to define the application in the MIS. Once the application is defined, you can use either em_accesscmd or the Security tool to create access control objects and assign user access privileges.
The em_accesscmd command uses the following syntax:
em_accesscmd [-help] [-host hostname] [-import filename]
[-exportall/-exportapp/-export filename].
6.8.1.3 The em_accesscmd Commands
After you start Security from the command line, you can use any of the commands documented in the following table. You can call these commands either from a file to be imported with the -import option, or directly on the em_accesscmd command line.
- No quotes are required for the login_name option or the :ALL option. Quotes are required for all other options.
- The + character following an option means you can enter multiple instances of that option. The delimiter is a space.
6.8.1.4 More About Object Sets
The following table provides detailed descriptions about object sets.
6.8.2 More About the Solstice EM-config Configuration File
When turning on security for the purpose of controlling user access, the assignments for the access control variables in the #EM_HOME/build/acct/EM-config configuration file needs to be edited. The following table describes the variables.
- You can also modify the access control variables in the /var/opt/SUNWconn/em/conf/EM-config configuration file. When you run em_services -r, your changes will not be saved, and the access control settings revert to the assignments in $EM_HOME/build/acct/EM-config.
- See the Developing C++ Applications guide for details concerning this configuration file.
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. |
Doc Set | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |