| Solstice Enterprise Manager 4.1 Customizing Guide |
Introducing Solstice Enterprise Manager
This chapter provides introductory information designed to help you get going with Solstice Enterprise Manager (Solstice EM) software and your day-to-day network management tasks.
This chapter describes the following topics:
- Section 1.1 What is Solstice EM?
- Section 1.2 Solstice EM Features
- Section 1.3 Solstice EM Components
- Section 1.4 Basic Solstice EM Concepts
- Section 1.5 Solstice EM APIs
- Section 1.6 Related Reading
- Section 1.7 Solstice EM Tools--Complete Listings
1.1 What is Solstice EM?
Solstice EM software is a distributed, standards-based, hierarchical, object-oriented suite of enterprise-grade network management tools, and a rich set of application programming interfaces (APIs) for developing custom network management applications. That means Solstice EM is a highly flexible, totally customizable network management solution that can be scaled and configured to fit your needs. You can use any or all of the Solstice EM tools "as is," or you can combine them with your own custom applications written to the
Solstice EM API.1.1.1 What Can You Manage With Solstice EM?
Solstice EM provides tools for monitoring, evaluating, and refining your network. The management functions you can perform with Solstice EM include:
- Discovering components on your network
- Automated tools let you keep track of components as they are added or removed from your network. Support for CMIP, SNMP, and RPC agents allow you to gather information about a wide variety of network components. Component details are stored in industry-standard relational databases on one or more management information servers.
- Visualizing your network
- A powerful Network Views tool serves as the graphical command center of Solstice EM, from which you can organize and manage your network components as groups of icons in logical, hierarchical, and geographical views. You can create as many different views of your network components as you want, using whatever view is most appropriate for the task at hand. For example, you can view your network components on a cartographically accurate geographical map background--a map of the world, perhaps, or a blueprint of one of your buildings--which lets you see at a glance not only what component is reporting a fault but where that component is physically located. You can then initiate actions to correct the fault directly from the Network Views tool.
- Configuring network components
- Solstice EM object properties editors in combination with CMIP, SNMP, and RPC agents let you configure all aspects of your network components, from general network properties to detailed component data, such as individual router interfaces. Schema- and MIB-to-GDMO compilers let you customize specific object attributes.
- Detecting, tracking, and correcting network problem
- A sophisticated alarm manager and request template designer, in combination with data viewers, and logging, reporting, and graphing tools, let you gather detailed information about your network, configure and respond to alarms, and design dynamic request templates to automatically gather and respond to network and component conditions.
- Managing user access to objects and applications
- The Solstice EM Security tool lets you control user access to individual Solstice EM and custom tools, as well as to specific sets of network components.
- Customizing the Solstice EM interface
- You can tailor Solstice EM tools in a wide number of ways, from pull-down and pop-up menus, to tool palettes, to default parameters and automatic monitoring methods. You can run almost every Solstice EM component from the UNIX command line, if you want, to create script-based maintenance routines. You can even modify MIB, ASN.1, and GDMO definitions to customize settings for the types of objects you can work with in Solstice EM.
- Developing custom network management applications
- Solstice EM is a standards-based, object-oriented environment that supports the Portable Management Interface (PMI) API over Simple Network Management (SNMP), Common Management Information (CMIP), and SunNet Manager Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocols, as well as full conformance with Telecommunications Management Networks (TMN) standards.
1.1.2 Who Uses Solstice EM?
Large companies, for example, the telecommunications industry use Solstice EM to manage hundreds of thousands of network nodes, with network components ranging from mainframes, subnetworks, gateways, servers, routers, and hubs, to workstations, personal computers, and agent-enabled mobile devices. Such companies use the standard suite of Solstice EM tools alongside their own custom tools developed with the Solstice EM APIs and toolkit.
Smaller companies use Solstice EM "out of the box" to manage all their network components, knowing that Solstice EM can be scaled to meet whatever needs they have as their company grows.
Any company interested in secure, high-performance management of distributed network resources, from portable handheld devices to deskbound graphical workstations, can use Solstice EM's distributed agent-oriented technology to manage virtually any type of network component.
1.2 Solstice EM Features
Solstice EM provides the following network management features:
- Comprehensive suite of network management tools, from objects to enterprises, infrastructure to interfaces.
- Manage virtually any network-aware component, from UNIX workstations to Windows-based PCs, printers to routers, subnetworks to network interfaces.
- Graphical "point and click" CDE (Common Desktop Environment) tools and UNIX command-line interfaces allow real-time ease-of-use and script-based automation.
- Multiple concurrent users run anywhere, anytime with UNIX-based security and scalability.
- Distributed, hierarchical, ASN.1 object-oriented architecture utilizing an industry-standard SQL-compatible relational database (InformixTM by default).
- Customizable interfaces and support for custom third-party applications by means of the PMI API over SNMP, CMIP, RPC, and TMN protocols.
- Development support tools are a set of API modules, object development tools, compilers, and debuggers; for developing your own custom network management applications.
- Backward-compatibility with SunNetTM Manager and Solstice Site/Domain Manager data and applications.
1.3 Solstice EM Components
Solstice EM components can be divided into two categories:
- Architecture--the structural components underlying the Solstice EM environment.
- Network Management Tools--a way to access and manipulate the Solstice EM environment and the components on your network.
These components are described in the following sections.
1.3.1 Solstice EM Architecture
The network management in the Solstice EM environment is based on the exchange of information between managers and agents. It is client/server-based, hierarchical and object-oriented environment comprising following components:
- Motif Applications--The manager applications run on the Motif enviroment. The applications can either be custom applications or Solstice EM Tools.
- JMA Server--The Java Management Adapter (JMA) provides the framework for the thin client/fat server model. JMA is not exposed to end users or developers. It is a transparent component lying between services such as the JMI and the MIS. JMA provides the infrastructure for services such as JMI API, Topology API, and Alarm API to communicate seamlessly with the MIS. It is responsible for the scheduling and synchronization of all PMI calls made by each Java API. It provides an event handling mechanism, which allows clients to register their own events and servers to forward the events to the clients.
- SEM CORBA Gateway--SEM CORBA Gateway translates CORBA manager requests in Interface Description Language (IDL) to Solstice EM Portable Management Interface (PMI) or equivalent requests. Also translates Solstice EM PMI responses to IDL or Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) responses, and PMI events to CORBA events. The SEM CORBA Gateway is designed to work with standard management reference models (such as SNMP/IP and CMIP/OSI). The interfaces defined and implemented by the SEM CORBA Gateway define the interaction between it and applications.
- Managed objects--Solstice EM is centered around the concept of managed objects. A managed object is a set of programmatic services and attributes that describes a type of managed resource. In practical terms, it means that each physical component on your network is represented by one or more objects in an MIS database (see below). When you perform an action in Solstice EM on a network component--for example, setting a configuration parameter or retrieving status information, you are actually performing that action on the managed object representing the network component.
- Every managed object has a set of characteristics, referred to as attributes, that define the kind of information the object can accept or provide, and a set of programmatic behaviors, called methods, that define what an object can do with that information. Specific values assigned to a given set of attributes are referred to as the object's properties. For example, an object attribute called IPaddress might have a value of 129.148.20.114. See Managing Your Network for more information about gathering managed object attribute data.
- Agent software--provides object-level communication methods between your network components and the rest of Solstice EM--that is, the means by which you can use Solstice EM to get and set properties on managed objects. Solstice EM supports SNMP, CMIP, and RPC agents, and includes a set of CMIP- and RPC-based SolsticeTM Enterprise Agents (SEA) that support a wide variety of managed objects, including legacy objects created in SunNet Manager and Solstice Site/Domain Manager. See Section 1.4.2 Agents and Stations for more information.
- Management Information Server (MIS)--a machine hosting an SQL database containing a Metadata Repository (MDR) and a Management Information Tree (MIT), which are used by Solstice EM to maintain information about the properties and relationships, respectively, of all managed objects on your network. An MIS daemon and a set of ancillary MIS service daemons provide MIS services on the MIS host. For data security or organizational convenience, you can use multiple MIS hosts, with one MIS database on each host. Multiple MISs can be linked so that all appear as one MIS to a given user. See Section 1.4.3 Management Information Servers for more information.
- Application programming interfaces--support communication and protocol translation between one or more MISs and Solstice EM and/or custom network management tools. See Section 1.5 Solstice EM APIsfor more information.
- Solstice EM and/or custom network management tools--the tools you use to access and manipulate the Solstice EM environment and managed objects. These tools are described in Section 1.3.2 Solstice EM Network Management Tools.
The relationships between Solstice EM architectural components are illustrated in the following figure. Explanations of basic Solstice EM network management concepts are provided in Section 1.4 Basic Solstice EM Concepts.
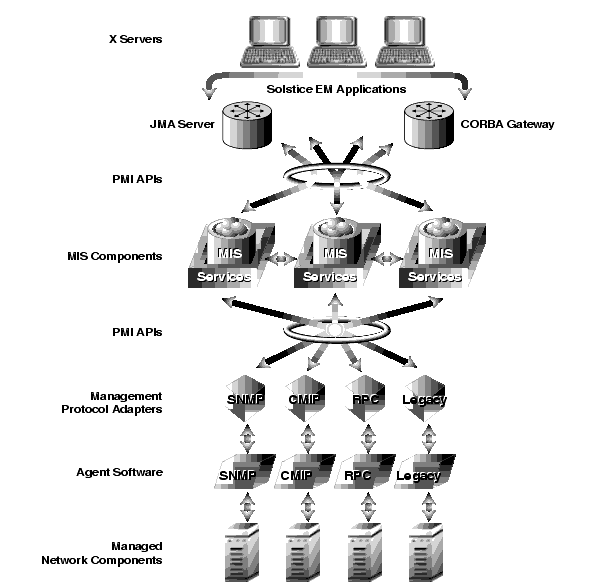
FIGURE 1-1 Solstice EM Architecture Overview1.3.2 Solstice EM Network Management Tools
Solstice EM network management tools can be divided into three general categories:
- General management--tools for day-to-day network management tasks--these are the tools you will use most often.
- MIS--tools and services for running and managing MIS servers and databases; once MIS services have been started on one or more MIS hosts, you will use these tools for occasional MIS database maintenance chores.
- Application customization and development--tools for customizing the Solstice EM environment and creating custom management applications.
The following table briefly describes the common Solstice EM tools you are likely to use most often. The tools in the table are divided into two categories: general network management tools, those you will use on a day-to-day basis, and administration. A quick-reference table describing all of the Solstice EM tools is provided in Section 1.7 Solstice EM Tools--Complete Listings
TABLE 1-1 Common Solstice EM Tools General Management Tools Alarms Configure, view, and respond to alarms posted against managed objects. Managing Your Network Data Collections Create data requests to collect performance data about selected managed objects. Managing Your Network Grapher Graph data from several Solstice EM tools. Managing Your Network Event Logs View and manage logs and log objects. Managing Your Network Network Discovery Automatically detect components on your network and populate the MIS with managed objects representing those components; a monitor function dynamically updates the MIS as components are added and removed from your network. Managing Your Network Network Tools Customizable window providing access to Solstice EM and other tools; you can add and remove Solstice EM tools, third-party tools, or your own tools to this window; provides a handy starting point for Solstice EM. Managing Your Network Network Views Graphical tool for visualizing, organizing, and managing your network; most other Solstice EM tools can be run directly from Network Views; provides a convenient, customizable, point-and-click way to view and respond to alarms, and configure object properties. Views of your network can be superimposed over cartographically accurate map backgrounds, making it easy to determine the physical location of network components and faults. Managing Your Network Object Properties View, create, and modify managed objects and object properties; commonly invoked from Network Views. Managing Your Network RPC/CMIP Data Get, set, view, and modify properties for CMIP- and RPC-managed objects. Managing Your Network Administration Tools Administration Customizable window providing access to Solstice EM administration tools. This Guide Advanced Requests Create Nerve Center request templates; used by Solstice EM to poll for object properties or receive notifications from managed object agents, and then generate responses based on the data received. This Guide Automatic Management Configure the MIS to launch and stop event requests automatically. Managing Your Network DB Backup/Restore Back up and restore MIS databases. This Guide MIS Manager Configure MIS communications and parameters. This Guide Object Editor View, create, and delete managed object attributes directly in the MIS. This Guide Security Manage user access to network management tools and managed objects. Managing Your Network SNMP MIB Browser View attributes and modify SNMP attribute values for SNMP MIBs. Managing Your Network Topology Import/Export Import or export an ASCII version of all or part of a MIS database; useful for recreating or transferring an MIS topology on another host. This Guide
1.4 Basic Solstice EM Concepts
Before you start using Solstice EM to manage the components on your network, it is useful to review some basic network management concepts as they relate to Solstice EM.
The concepts explained in this section are:
- Network Management Software-page 1-9
- Agents and Stations-page 1-9
- Management Information Servers-page 1-11
- Network Management Protocols-page 1-16
1.4.1 Network Management Software
In the context of Solstice EM, network management software refers to one or more software tools, like the Solstice EM suite, that:
- Provide user interfaces through which network management tasks can be performed.
- Issue requests to network devices--to ask a given device to take some action, typically to provide some specific information to the manager.
- Receive responses to requests.
- Receive unsolicited information (notifications) from network components concerning component status, such as problems, abnormalities, and changes in the environment.
The Solstice EM tools function as network management software for various network management functions. For example, the Solstice EM Alarms tool lets you create and manage alarms for monitoring component status.
1.4.2 Agents and Stations
Rather than communicating directly with network components, Solstice EM communicates through software agents (middlemen) that are specifically configured to understand the particular kinds of information and settings a given network component can receive or provide.
In network management jargon, a station is a network management software component that communicates with one or more agents. In the case of Solstice EM, the station component is the MIS (see Section 1.4.3 Management Information Servers). Consider the example, as illustrated in FIGURE 1-1, a Solstice EM tool sends a request to an agent via the MIS and a Management Protocol Adapter (MPA). The agent, in turn, passes that request to the network component. On the return trip, the component's response is passed first to the agent, then to the MIS by means of the MPA, and then finally back to the Solstice EM tool. Solstice EM handles the translation between various agent protocols transparently; for most management tasks, users do not need to know what type of agent is associated with a given network component.
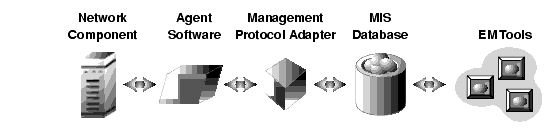
FIGURE 1-2 Agent Communications OverviewEvery network component managed by Solstice EM has an associated software agent. In some cases, the agent software is embedded in the component; for example, burned into a component's ROM. In most cases, however, the agent software resides on a host machine to which the component is connected, and provides services for a related set of components.
Solstice EM is based on the ISO-standard agent/station network management model. The strength of this model is that your network management software does not need to maintain configuration information for every network component available on the market. As new types of components are added or upgraded on your network, the agent software that travels with a given component is able to communicate the new configuration information to the management software.
Solstice EM supports the following common agent protocols:
- CMIP--Common Management Information Protocol
- SNMP--Simple Network Management Protocol
- RPC--SunNet Manager Remote Procedure Call
Solstice EM also provides full conformance with Telecommunications Management Networks (TMN) standards. See Section 1.4.4 Network Management Protocols for more information about network protocols supported by Solstice EM.
Note – Solstice EM installation includes by default a set of Solstice Enterprise Agents (SEA), which allow you to communicate with components configured for legacy SunNet/Site/Domain Manager environments. Other agents may be installed as well, depending on your package options. Refer to the Installation Guide for complete information.
1.4.3 Management Information Servers
In the Solstice EM environment, a Management Information Server (MIS) is a machine hosting an object-oriented SQL database containing information about every component on your network that is managed by Solstice EM. In this model, physical network components are represented as managed objects in an MIS database (see FIGURE 1-3).
In general terms, the MIS provides the following services:
- Access control
- Requests
- Connections
- Events and alarms
- Logging
- Object management
Functionally, the resources on an MIS can be divided into four general categories:
- An MIS database containing information about the components on your network.
- An MIS Nerve Center that provides the logic and methods to actually do something with the information in the MIS; the Nerve Center is the source of requests and responses based on network conditions.
- Portable Management Interface (PMI) APIs and Management Protocol Adapters (MPAs).
- A set of ancillary MIS services that make the information in the MIS database available to network management applications and software agents.
For data security or logical convenience, you can use multiple MIS databases, with one MIS database on each host. Multiple MIS databases can be linked so that all appear as one database to a given user.
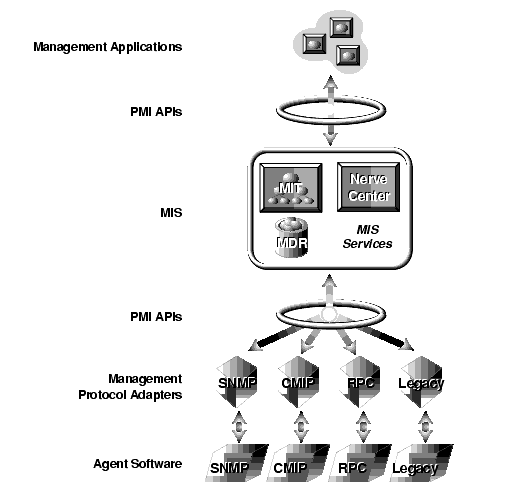
FIGURE 1-3 Overview of Management Information Servers1.4.3.1 More About MIS Databases
A Solstice EM MIS database comprises two primary components:
- Metadata Repository (MDR)--maintains information about managed object attributes and properties; the specific configuration settings used by network components. This data encompasses everything from the syntax required to refer to an attribute to the composition of an object package. The language used to describe network components is the Guidelines for the Definition of Managed Objects (GDMO), outlined in the ITU X.722 ISO/IEC 10165-4 standard. The MIS allows for dynamic updates to the MDR.
- Management Information Tree (MIT)--a tree-like, hierarchical representation of the relationships between network components. For example, a network might have subnetwork branches, from which routers, switches, and hubs are parents to gateways, workstations, and printers. The MIS supports dynamic creation, maintenance, and deletion of objects in the MIT.
1.4.3.2 More About the MIS Nerve Center
The MIS Nerve Center provides the logic and methods to interrogate agent software for information about network components, receive notifications from agents, and initiate actions based on network conditions.
Nerve Center activities are based upon user-defined request templates, which are rules-based configuration files that tell Solstice EM how to interrogate for network component information, and how to respond to the information received. In this context, the term request should not be confused with the common object-oriented use of the term as it relates to GET and SET methods; a Nerve Center request is a set of programmatic rules, whereas an object-oriented request refers to a specific set of methods for manipulating object properties.
The Solstice EM Advanced Requests tool, and the Simple Requests function in Network Views, provide advanced and simple tools, respectively, for viewing, creating, and managing Nerve Center Request templates. The Advanced Requests tool is described in this Guide; Simple Requests are described in Chapter 3 of Managing Your Network.
1.4.3.3 More About PMI and MPAs
Although there are potentially many interfaces to Solstice EM, only one is required by the Solstice EM architecture. This primary interfaces is the high-level Portable Management Interface (PMI). The PMI defines the management protocol, services, and transport mechanisms for all Solstice EM components. Specifically, the PMI provides the following features:
- Protocol-independent management applications--management applications can communicate with managed objects via the PMI regardless of the protocol used by the managed object.
- Distributed, multi-user access--multiple users can access and modify objects and object definitions in the MIS.
- Proxy agent support--proxy agents can use the Management Protocol Adapter (MPA) library to access managed objects over protocols other than CMIP or SNMP.
MPAs translate information between managed objects and the MIS. For example, if you have a network component that uses SNMP, then the SNMP MPA receives data from an SNMP agent, translates the data into the PMI, and sends the data to the MIS.
Solstice EM includes the following three MPAs:
- CMIP--Common Management Information Protocol
- SNMP--Simple Network Management Protocol
- RPC--SunNet/Site/Domain Manager Remote Procedure Call
Solstice EM also supports other MPAs; see Chapter 11 in Developing C++ Applications for information about adding MPAs to your Solstice EM environment.
1.4.3.4 MIS Ancillary Services
In addition to the MIS database and Nerve Center, an MIS provides ancillary services that make information about managed objects available and modifiable by network management applications and agent software. These services are invoked at MIS startup with the em_services command.
Note – Solstice EM MIS services are usually run on one or more of the network's workstations. It is not necessary to dedicate a machine to running MIS services, although Solstice EM requires at least one MIS to be running somewhere on the network. As mentioned previously, you can run multiple MISs on a network
Specifically, the Solstice EM MIS provides the following ancillary services:
- Protocol and location transparency--a network management tool provides a managed object name, and the Solstice EM services determine what protocol to use to access the object, and what address to use within that protocol. This means that management clients do not need to know where an object is physically located or what protocol to use to communicate with it.
- Coordinate requests from multiple tools--Solstice EM supports concurrent access to MIS data from multiple network management clients.
- Persistent storage--data in the MIS database is not lost when an MIS host is shut down.
- SNMP traps and events--event handling for SNMP traps and events, and a registry mechanism that allows applications and objects to register interest in an event.
- Log management services--keep track of what is happening where on the network. Solstice EM provides detailed logging services, which are maintainable through Solstice EM's Event Logs tool.
1.4.3.5 More About MIS Data Access
One of the primary functions of an MIS is to make managed object data available to network management tools and agent software. A related function is to make this data transparently available across multiple MIS machines on multiple subnetworks.
In Solstice EM, all managed objects are accessed through the MIT. There is one global tree, with a single naming scheme for all data. The MIT is constructed according to the rules provided by OMNIPointTM, and has a single root branch. The shape of the tree descended from this root branch is arbitrary, and may vary widely from one MIS to another. The tree's structure is hierarchical and based on parent/child containment relationships; below any given object are one or more related subordinate objects.
A Solstice EM MIS makes MIT data accessible both through the naming conventions that come from the managed resources it describes, and from a resource-independent naming convention, in which identifiers are specified using Fully Distinguished Names (FDNs). FDNs enable Solstice EM MIS to provide transparent access to managed objects.
Managed objects in the Solstice EM environment may be stored locally, in an MIS database. However, Solstice EM also supports access to remote objects that are stored outside a given MIS. When representing a remote object, a Solstice EM MIS stores information about that object's physical location, along with a description of the address and protocol required to access that object. When getting or setting properties for a given object, Solstice EM handles the address and protocol resolution transparently, without user intervention, whether the object is local or remote to the MIS.
1.4.3.6 More About Object Orientation
As mentioned previously, Solstice EM MIS services are based on an ISO-standard ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) object-oriented architecture. Specifically, Solstice EM:
- Describes managed objects in terms of OMNIPoint and ISO terminology
- Uses C++ objects for internal storage and manipulation of network data
The following list describes some object-oriented terms as they relate to Solstice EM.
- Class--C++ classes, as described in the Annotated C++ Reference Manual (Margaret Ellis and Bjarne Stroustrop; Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Reading, MA; copyright 1990 by AT&T Bell Laboratories).
- Instance--memory that is allocated for a C++ class according to its definition. A variable name is usually associated with a particular instance of a class.
- Managed resource--an actual physical device or entity that exists in a network or system. This is consistent with the OSI/Network Management Forum (NMF) definition of the term.
- Managed Object (MO)--is a set of services and attributes that describes a type of managed resource. This is also consistent with the OSI/NMF definition of the term.
- Managed Object Class (MOC)--within the Solstice EM development environment, this term refers to the internal representation of a managed object, as described by the OSI/NMF. An MOC is based on the GDMO description, which could itself be a translation of an SNMP MIB or SunNet Manager schema description--that is, the MOC represents the attributes and behaviors for particular types of manageable objects. The MOC defines the type of data stored and the behaviors that can be taken, but does not represent the actual data for any managed object. The MOC is the internal representation used by the Solstice EM MIS.
- Managed Object Instance (MOI)--relates to a managed object class in the same way as an instance relates to a class, where the MOC determines the type of attributes and behaviors available to operate on an object of this type, and MOI refers to actual data that represents an object being managed by the MIS. An MOI is also an internal representation used by the Solstice EM MIS.
1.4.4 Network Management Protocols
In order to be able to pass management data from component to agent to MIS to management tool and back again, all components in the environment must agree on and understand how and what data is being exchanged. The rules defining such exchanges are referred to as protocols.
As mentioned previously, Solstice EM is based on the ISO-standard agent/station network management model, and supports the following common protocols:
- CMIP--Common Management Information Protocol
- SNMP--Simple Network Management Protocol
- RPC--SunNet/Site/Domain Manager Remote Procedure Call
Solstice EM also provides full conformance with Telecommunications Management Networks (TMN) standards.
SNMP and RPC are network management protocols used to manage resources in a TCP/IP network environment. CMIP is the protocol used in ISO networks. Both protocols specify ASN.1 as the language used to encode and decode object request and response messages.
Note – When you install Solstice EM, you are asked if you want support for IP management, CMIP management, or both. The choice you make depends on the types of devices on your network, and the network management protocols they support.
1.4.4.1 More About RPC
Solstice EM includes a suite of agents developed for the SunNet/Site/Domain Manager (SNM) platform. These agents communicate with Solstice EM using RPC protocols, and are included primarily to provide a migration path from SNM installations to Solstice EM.
In addition to migrating to Solstice EM, however, SNM agents communicating over RPC can be a useful part of your network management strategy. Specifically, SNM agents can act as proxies for communicating via older protocols.
1.4.4.2 About MIBs
Part of the SNMP protocol includes attribute definition files called MIBs (Management Information Base). MIBs define:
- Attributes or types of data that can be supplied by an agent to a manager
- Actions performed by an agent that can be requested by a manager
- Behavior exhibited by the agent
- Notifications--unsolicited information the agent can send to a manager
The ISO standards organization defines a MIB in ISO/IEC 7948-4 as follows: "The conceptual repository of management information within an open system." A network management package normally contains management information describing each type of agent the manager is capable of managing. This information typically includes Internet MIB definitions and ISO GDMP definitions for managed objects and agents. An agent typically presents or contains management information for one type of device, although this information can include descriptions and data for several types of devices.
1.5 Solstice EM APIs
In addition to the network management tools shipped with Solstice EM, you can define your own tools and applications to work with Solstice EM through the Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) included with Solstice EM.
If an application developer also provides access to a managed object type not previously known to the MIS, the MIS must be informed of the Managed Object Class through the use of GDMO ASN.1 documents.
The Solstice EM APIs provide a rich set of functions for the application programmer. The libraries, written in C++, contain the objects and methods necessary to communicate with the MIS and obtain information about the managed resources it controls. The APIs provide the following services:
- Initialization, including establishment of a distributed message passing interface to the MIS
- Event subscription
- Remote caching and cache control
- Local object cache management for applications
- Encoding and decoding of parameters into ASN.1
- Encoding and encapsulation of data into a format (message class) passed to the MIS
1.5.1 API Modules
The Solstice EM APIs consist of several different groupings or modules, as summarized in the following table. Refer to the Developing C++ Applications and Developing Java Applications for detailed information about developing applications that interact with Solstice EM.
1.5.2 Application Development Support Tools
In addition to the API classes and methods described in the preceding table, Solstice EM includes the following application development support tools:
- Object Development Tools (ODT)--provide a simple and automated framework developers can use to add and write behaviors for managed objects that reside in the MIS. Refer Chapter 10 in Developing C++ Applications for detailed information.
- Compilers--Solstice EM includes several compilers that developers and, in some cases, system administrators need to use. The compilers provide a means by which you can add new managed object definitions to the MIS. Solstice EM includes the following compilers:
- ASN.1 (em_asn1)--Compile descriptions of managed objects into the MDR. These descriptions are provided as ASN.1 documents.
- GDMO (em_gdmo)--Compile new GDMO object descriptions and then add them to the MDR.
- Concise MIB (em_cmib2gdmo)--Convert object descriptions written in Concise MIB format to GDMO for use in Solstice EM.
- Schema (em_snm2gdmo)--Convert object descriptions written in SunNet Manager schema format to GDMO for use in Solstice EM.
- em_debug--Solstice EM includes a dynamic debugging function that helps you track information going in to and out of the MIS.
1.6 Related Reading
Depending on what you want to do in Solstice EM, one or more of the following Solstice EM manuals may interest you:
- Installation Guide--complete instructions on installing all Solstice EM components and utilities, including agent software.
- Managing Your Network--information about using the Solstice EM tools to perform day-to-day management tasks.
- Customizing Guide--detailed information about advanced Solstice EM configuration and customization.
- Management Information Server (MIS) Guide--advanced information about MIS servers.
- Developing C++ Applications--information for developers who want to write custom applications that can be integrated with Solstice EM.
- Troubleshooting Guide--solutions to problems you encounter with Solstice EM.
- CORBA Gateway Administration Guide--provides information on installing, configuring, and using SEM CORBA ToolKit to build and package the SEM CORBA Gateways.
- Glossary--a glossary of network management terms as they relate to Solstice EM.
1.7 Solstice EM Tools--Complete Listings
The remainder of this chapter provides a quick-reference table that briefly describe all of the Solstice EM network management tools, along with pointers to the books in which you can find more detailed information.
Refer to the preceding sections in this chapter for information about general Solstice EM network management concepts, and explanations of how the major Solstice EM tools work together.
The following table lists the Solstice EM tools, sorted by binary name. All tools listed here are located by default in /opt/SUNWconn/em/bin ($EMHOME/bin).
TABLE 1-3 Solstice EM Tools - Complete List, Sorted by Binary Name build_oid Build Object IDs SunNet Manager (SNM) SNMP utility; creates an Object ID Database (/var/usr/SUNWconn/snm/oid.dbase. This Guide build_tt Build Textual Convention Types Builds the textual convention types database; used by the mib2schema utility to look for new IMPORT definitions local to a MIB. Developing C++ Applications create_admin *** *** *** db_services Initialize Database Services Initializes MIS database services; usually run as part of the em_services command. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em Network Tools Primary Solstice EM tools window; Solstice EM and custom network tools can be started, added, and removed from this window. Managing Your Network em_accesscmd Access Control - command line interface Command-line Access Control tool; lets you manage user access to Solstice EM tools and objects. Managing Your Network em_accessmgr Access Control - graphical interface Graphical Access Control tool. Managing Your Network em_add_db_server Add Database Server Lets you specify an MIS database server to use instead of or in addition to the default. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_admintool Administration Access advanced administration functions; for example, MIS connections and parameters, database backup and restore, request template designer, etc. This Guide em_alarmmgr Alarms View and manage object alarms. Managing Your Network em_asn1 ASN.1 Compiler ASN.1 object compiler. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_autod Automatic Management Daemon Automatic management daemon; monitors creation and deletion of MIS objects; starts and stops requests when objects are added and deleted. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_autoexd Database Table Extender MIS daemon that automatically extends database tables when they get full. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_automgr Request Controllers Automatic management configuration tool; used in conjunction with em_autod. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_auxdb *** *** This Guide em_clear_alarms Clear Alarms - command line interface Command-line utility for clearing alarms against a specified range of toponodes. Managing Your Network em_cmib2gdmo Concise MIB Compiler Converts MIB files in Concise MIB format to GDMO and ASN.1 formats. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_cmip CMIP Management Protocol Adapter Implements CMIP MPA functions; starts during product installation. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_cmipautoreg CMIP Autoregistration Automatically registers CMIP agents in the MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_compose_all Compose/Load GDMO Bindings Compose and load all name bindings from a GDMO file. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_compose_oc Instantiate Volatile Class Instantiates a new MIS object class with volatile data storage. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_compose_poc Instantiate Persistent Class Instantiate a new MIS object class with persistent data storage. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_datacollector Data Collections Create and manage data collection entry objects, and display data gathered from requests. Managing Your Network em_datad Data Collection Daemon Daemon used in conjunction with em_datacollector. Managing Your Network em_dataviewer RPC/CMIP Data View and manage RPC, CMIP, and SNM managed objects. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_db_abort Abort Database Script to abort an Informix database on the specified MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_db_create Create Database Script to create a new Informix database on the specified MIS Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_db_drop Drop Database Tables Script to drop log or non-log tables from an Informix database on the specified MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_db_start Start Database Server Script to start a database server on the specified MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_db_stop Stop Database Server Script to stop the database server on the specified MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_dbarchive Database Backup/Restore Graphical administration tool for backing up and restoring MIS databases. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_dbbackup Database Backup - command-line interface Command-line interface for MIS database backup. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_dbrestore Database Restore - command-line interface Command-line interface for MIS database restore. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_debug Solstice EM Debugging Tool Command-line debugging tool that supports the Solstice EM remote dynamic debugging feature. Cooperative Consoles Administration Guide em_discover Network Discovery Discover components on your network and update the MIS database. This Guide em_eds Event Distribution System Distributes events from event sources to event listeners. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_gdmo GDMO Compiler GDMO compiler; lets you extend Solstice EM capabilities with new GDMO object class descriptions. This Guide em_grapher Grapher Create graphs from alarm and agent data. Managing Your Network em_help Help Solstice EM help system. Online Help em_imex Log File Import/Export Import and export log objects from and to ASCII files. Managing Your Network em_java2gdmo Java GDMO Compiler Compile Java classes in GDMO format. This Guide and Developing Java Applications em_jdmk_config Configure Java Agents Configure Solstice EM to work with Java-based agents. This Guide and Developing Java Applications em_jdmkfwd Forward Java Events Forwards Java events to the Solstice EM MIS for processing. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_layout Network Views Layout Define how object views are laid out in Network Views; commonly invoked from Network Views. Managing Your Network em_load_name_bindings Load Name Bindings Loads object name bindings; allows the MIS to resolve MIT object names. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_load_nc_templates Load Nerve Center Templates Script that invokes the em_ncimport -file command; loads Solstice EM Nerve Center templates. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_loaddefs Load Object Definitions Load MIB, GDMO, and SunNet Manager schema files into the MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_log Initialize Log Server Initializes log server MPA functions. This Guide em_log2hist Save Log Entries Saves logs in history files. Managing Your Network em_log2rdb.ifmx Transfer Log Histories Daemon - Informix Daemon that reads and transfers log histories to an Informix database. Managing Your Network em_log2rdb.orcl Transfer Log Histories Daemon - Oracle Daemon that reads and transfers log histories to an Oracle database. Managing Your Network em_log2rdb.sybs Transfer Log Histories Daemon - Sybase Daemon that reads and transfers log histories to an Sybase database. Managing Your Network em_login Login Daemon Listens for Solstice EM connection requests for password authentication. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_logmgr Event Logs Create, modify, and delete log objects. Managing Your Network em_logview View Logs View logs and log objects. Managing Your Network em_mis MIS Services Core Primary Solstice EM services; commonly invoked from the em_services command. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_mismgr MIS Manager Manage MIS parameters and connections. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_mpa_jdmk Initialize JDMK MPA functions. Initializes JDMK MPA functions on the MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_mpa_rpc Initialize RPC MPA functions. Initializes RPC MPA functions on the MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_mpa_snmp Initialize SNMP MPA functions. Initializes SNMP MPA functions on the MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_ncam Nerve Center Daemon Daemon that handles nerve center actions, such as sending email or executing UNIX commands. This Guide em_ncexport Nerve Center Export Export Nerve Center templates to an ASCII file. This Guide</br> em_ncimport Nerve Center Import Import Nerve Center templates that have been previously exported with em_ncexport. This Guide em_nnadd Global Nickname Service Addition Enable a global nickname server on the MIS; generally started with em_services. Developing C++ Applications em_nnconfig Global Nickname Configuration Populate the global nickname translation server. Developing C++ Applications em_nnmpa Global Nickname Service Daemon Starts the global nickname translation server. Developing C++ Applications em_ns_server Debug Nickname Services Debug global nickname translation services. Developing C++ Applications em_obcodegen Object Code Generator Used to generate object behavior code from GDMO and ASN.1 definitions. Developing C++ Applications em_obed Object Editor View and edit objects in the MIT; see also em_oct. This Guide em_objop Object Operations Utility Command-line utility for sending CREATE, SET, DERIVE, and DELETE requests; primarily used by init_platform to create and modify MIS objects at MIS startup. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_oct Network Views Object Configuration Tool View, modify, and create managed objects; commonly run from a Network Views window; see also em_obed. Managing Your Network em_panel Network Tools Starting point for Solstice EM general network management applications; usually invoked with the em command and em -host Managing Your Network em_purged Alarm Deletion Daemon Periodically deletes alarms based on severity, stat, time, etc. Managing Your Network em_purgemgr Alarm Deletion Controller Sets up conditions for em_purged to delete alarms. Managing Your Network em_reqedit Request Template Designer View, modify, create, and delete Nerve Center request templates. This Guide em_restart Restart MIS Services Restart MIS services. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_services Initiate MIS Services Initiate MIS services; starts the MIS server and several related daemons. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_simplerequests Network Views Simple Requests View, modify, and create simple MIS request templates; generally invoked from Network Views. Managing Your Network em_snm2gdmo SNM Schema to GDMO Compiler Convert SNM schema files to GDMO descriptions. This Guide em_snm_type_import Import SNM Object Types Import SNM object types into the Solstice EM environment. This Guide em_snmdb_import Import SNM Topology Imports SNM topology databases into an Solstice EM MIS. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_snmfwd Forward SNM Events Forwards SNM events to the Solstice EM MIS for processing. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_snmp-trap Listen for SNMP Traps Daemon Daemon that listens on port 162 for SNMP traps. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_snmpbrowser SNMP Data Get, set, view, and modify SNMP agent attributes. Managing Your Network em_sql Log In to SQL Database Login process for SQL databases. This Guide em_srm *** *** *** em_startup Start MIS Server Start the MIS server; usually invoked as part the em_services command. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_topo_args Modify Toponodes Command-line interface for modifying topoNode objects. This Guide em_topoimex Topology Import/Export Import or export MIT topology information. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide em_topoimex_BC Convert Legacy Topology Information Converts topology information from prior versions of Solstice EM. This Guide em_trapd Initialize Topology Services Initializes topology services on the MIS; commonly invoked as part of em_services. This Guide em_viewer Network Views View, organize, modify, and create managed objects. Managing Your Network emenv.csh Environment Configuration - C Shell Source this file to configure Solstice EM environment variables, such as $EMHOME, license server, etc.; C Shell environment only. Managing Your Network emenv.sh Environment Configuration - Korn/Bourne Shell Source this file to configure Solstice EM environment variables, such as $EMHOME, license server, etc.; Korn or Bourne shell. Managing Your Network get_local_host Find Local MIS Host Display the name of the current local MIS host. This Guide hyperhelp Help Viewer Bristol HyperHelpTM Viewer; Solstice EM online help isin HyperHelp format. Managing Your Network jme_jre JME Services helper script Helper script for jme_services; do not invoke directly. Management Information Server (MIS) Guide jme_services JME Services Start and stop Solstice EM Java daemons Management Information Server (MIS) Guide mib2schema SNMP MIB to SNM Schema compiler Convert SNMP MIB files to SNM scheme format. This Guide snm_br Results Browser List RPC, CMIP, or SNMP data collected with the Data Collections tool. This Guide snm_cmd Manage SNM Agents - command-line interface Command- line manager for Site/SunNet/Domain Manager agents. This Guide snm_cmdtool Run Command from SNM Session Run a UNIX command from an SNM session. This Guide snm_exec Execute command via EVAL from SNM Uses the Bourne shell's eval to execute a UNIX command from an SNM session. This Guide snm_gr Grapher Display and graph SNM data. This Guide snm_kill Stop SNM Agent Requests Stop one or more SNM agent requests. This Guide snm_version SNM Version Information Displays information about the current version of SunNet Site/Domain Manager software. v2mib2schema SNMP2 MIB to Schema Compiler Convert SNMP2 MIBs to SNM schema format. This Guide var-install Install Solstice EM Packages on Remote Install Solstice EM packages on another machine. Installation Guide var-obj-install Install Solstice EM object Definitions Install Solstice EM object definitions. This Guide
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. |
Doc Set | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |