| Solstice Enterprise Manager 4.1 Management Information Server (MIS) Guide |
Managing MIS
This chapter provides information and procedures for managing MIS. Many of the applications and tools in Solstice Enterprise Manager (Solstice EM) are used with MIS. For some topics in this chapter, references to related publications are provided. These related publications provide detailed information and instructions for performing tasks affecting MIS.
This chapter describes the following topics:
- Section 4.1 Setting Up MIS on Your Network
- Section 4.2 Controlling Access
- Section 4.3 Customizing the MIS Configuration
- Section 4.4 Starting MPAs
- Section 4.5 Detecting Events and Conditions
- Section 4.6 Troubleshooting
4.1 Setting Up MIS on Your Network
After Solstice EM is installed, you may want to customize your installation, especially the implementation of MIS. For detailed information, refer to the Customizing Guide.
If your network has many resources to manage, you may want to implement a multiple-MIS architecture. For examples and information about implementing a multiple-MIS architecture on your network, refer to Chapter 3.
4.2 Controlling Access
Using the Security application, you control who has access to applications, MIS, and the database. To administer access control, refer to Chapter 6 in Managing Your Network. This guide provides information and instructions for performing access control administration.
4.3 Customizing the MIS Configuration
For information and procedures on how to customize your MIS configuration, refer to the Customizing Guide
4.4 Starting MPAs
Depending upon the options selected by the user who installed Solstice EM, you may have the following MPAs installed on your system:
- CMIP
- RPC and SNMP
- MPA
The installed MPAs start automatically when Solstice EM is started or restarted. If you want to use an MPA that was not installed, refer to the Installation Guide for installation procedures, and use the following procedures to start the applicable MPA.
4.4.1 Starting CMIP
To use the Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP), install the CMIP MPA package (SUNWemcpa) and start the CMIP MPA daemon (em_cmip) as root by running the following command:
The CMIP MPA (em_cmip) starts automatically during package installation or whenever the machine on which it is installed is re-booted, provided the license is available.
4.4.1.1 Registering CMIP Agents
In order to recognize an agent for the CMIP MPA, the agent must first be registered in the configuration file. This process is performed through the CMIP Autoregistration application.
The CMIP autoregistration application is customizable. The application currently looks for an entry in the configuration file based on the Network Service Access Point (NSAP). It can be customized to look at the entire presentation address.
The entry in the configuration file is based on the Network Service Access Point (NSAP) of the agent. The event emitted by the CMIP MPA is emIdentifyAgent, and contains the information show in the following code example.
CODE EXAMPLE 4-1 CMIP Autoregistration
EMIdentifyAgent ::= SEQUENCE {aETitle AE-title OPTIONALpSelector GraphicString,sSelector GraphicString,tSelector GraphicString,nSAP GraphicString
To Register an Agent in the Configuration File
1. Create an entry for an agent in the configuration file by typing the following command:
Note – For more information on the CMIP autoregistration application, refer to the Customizing Guide.
2. Start the CMIP Autoregistration application by typing the following command:
4.4.1.2 Configuring

To Configure a toponode
1. To configure a toponode as a CMIP agent, use one of the following methods.
- The Object Properties window will display.
- In the Network Tools window select Viewer and then add a device to the Network Views using the default procedure in the Object Properties (using only the hostname).
- From the command line interface use one of the following commands:
2. Select Agent.3. Select CMIP.
- When an agent establishes an association with the CMIP MPA, the CMIP MPA sends an event to the CMIP Autoregistration application. The event contains addressing information for that agent. Based on the event information, the CMIP Autoregistration application looks for the corresponding entry in the configuration file. If it finds the entry, it creates an entry for the agent in the CMIP table.
4. Click Add in the Agent subwindow.
- The CMIP agent version of em_oct will display.
5. Fill in the CMIP agent entry with the appropriate information according to the field description in following table.
Note – The Network SAP in this case is the value of the IP address of the CMIP Agent represented in hexadecimal.
6. Click Apply.7. Click OK.
- The Object Properties window displays again.
8. Click Apply.9. Click OK.
Note – You can verify that the Agent is properly added to the toponode by clicking the toponode in Network Views.
4.4.2 Starting RPC and SNMP
The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) and SNMP MPAs start automatically during package installation or whenever the machine on which they are installed is re-booted, provided the license is available.

To Start RPC and SNMP Independently
- If you want to start RPC and SNMP independently, start the MPA daemon as root by running the following command:
4.4.3 Starting MPAs on a Remote Machine
To prepare the system for starting an MPA on a remote machine, the remote machine must have the MPA package installed.

To Setup and Start a Remote MPA
1. Make sure the MPA packages are installed on the remote machine (SUNWemipa SNMP and RPC, and/or SUNWemcpa for CMIP).
- Both of these packages depend on the Solstice Enterprise Manager Common Libraries, so the SUNWemalb package must also be installed on the remote machine.
- Additionally, the CMIP MPA requires a license file. Set the LM_LICENSE_VARIABLE environment variable on the remote machine so that it points to the license file (for example, license.dat), which in turn points to the machine where the license server is installed (usually, the same machine as MIS).
2. In the Network Tools window select Administration \xd4 Security.
Note – This step needs to be done on the primary machine or the machine where the MIS process is running.

To Start an MPA on a Remote Machine
Note – This must be done on the machine where the MIS process is running.
1. In the Network Tools window, select Administration \xd4 Security as illustrated in the FIGURE 4-1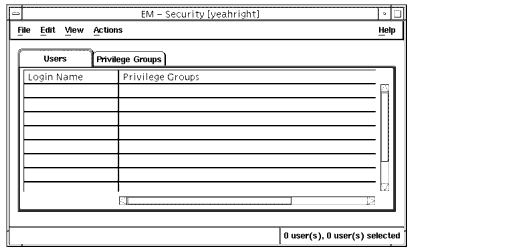
FIGURE 4-1 Security Window2. Select Actions \xd4 Security Defaults to display the Security Defaults window, as illustrated in the following figure.
- If Security is set to Off, the message "EM Security is currently disabled in the MIS" is displayed. You can turn Access Control back on from the Defaults window.

FIGURE 4-2 Security Defaults Window3. Use the Security Off/On toggle switch to set the security function.4. Under Security Defaults set the following defaults to either Deny with response, Deny without response, Abort association, or Allow:
- Action
- Create
- Delete
- Get
- Set
- Filter
- Multiple Object Selection
- Events
- And set Events to either Allow or Deny.
5. Set Security Logging and Audit Logging to Off, Summary, or Detailed.6. Type the Trusted Host name in the text field.
- The Trusted Host is the remote machine that has MPA installed. When superusers connect from a remote machine, for full access to be granted the remote host must be defined as a Trusted Host.
7. Click Add.8. Click OK.9. Login as root on the remote machine and start the MPA by typing the following command:
The <mpa variable> represents the name of the MPA you want to start. Specify cmipmpa to start the CMIP MPA, or ipmpa to start the IP MPA.
Note – You must start the MIS process before you start the MPAs.
4.4.4 Stopping MPAs
You can stop the MPAs by typing the following command:
where the <mpa variable> is either cmipmpa or ipmpa. 4.4.5 Using em_topo_args for Third Party Integration
The command em_topo_args is used to pass arguments to applications that are launched from the Object Menu of a device. Refer to the following example.
In this example, serviceProvider is an attribute added to the topoNodeUserData of a device type and so em_topo_args can be used to extract its value.
The em_topo_args command was written for backwards compatibility, although it can be used for non-backward compatible applications. The % is from SNM. % in SNM is how you pass an element type (glyph) schema attribute to the command line.
There are also some limitations on what you can pass on to an application. If the topoNodeUserData type is a SET OF xxx, it will not work since topoargs does not have a way to pull out individual members of a SET. It does work for SEQ.
4.5 Detecting Events and Conditions
For information about detecting events and conditions in your network, refer to the C++ API Reference.
4.6 Troubleshooting
If you encounter messages or unusual behavior with MIS, refer to the Customizing Guide.. This guide contains helpful information for determining the cause and resolution of MIS issues.
One of the most common errors occurs when you or another user makes changes that require restarting Solstice EM, and you or the other user do not restart the system. For example, when adding shared memory and semaphores, you have the option of automatically or manually rebooting the system. If you choose the manual option, then later forget to reboot, you'll see a database error when you attempt to start MIS.
A simple way to check is to look for the /reconfigure and /tmp/reboot files in the directory where Solstice Enterprise Manager was installed. (Use the command ls -l at the appropriate directory level). If either file exists, then the host must be rebooted.
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Copyright information. All rights reserved.
Doc Set | Contents | Previous | Next | Index