| C H A P T E R 5 |
|
Sun Java System RFID Information Server Configuration |
This chapter includes the following topics:
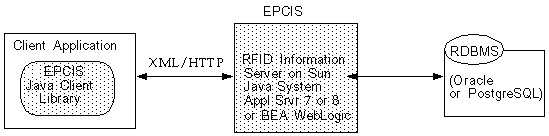
The Sun Java System RFID Information Server is a J2EE application that serves as an interface for capture and query of EPC-related and non-EPC data. As outlined below in "Information Tables", EPC-related data can include RFID tag observation data from Event Managers as well as information that maps EPCs to higher-level business data. The Sun Java System RFID Information Server is typically used to translate a set of low-level observations into higher-level business functions, as described in Chapter 1.
Alternatively, one may look at EPC-related data as being either static or timestamped. Static data includes serial-level and product-level attributes of tagged items, such as the GTIN number of a box of detergent. Timestamped data is collected over a period of time and typically changes more often than static data. An example of timestamped data is the relationship between an EPC and a business transaction, such as an Advanced Shipment Notice.
The Sun Java System RFID Information Server runs on the Sun Java System Application Server 7 or 8. Other applications interface with the Information Server through XML message exchange. The Information Server also supports HTTP and JMS message transports. The Information Server persists all data in a relational database. Any RDBMS that is supported by JDBC can be used as the data store. However, the Sun Java System RFID Information Server has only been tested with Oracle 8.1.7, Oracle 10g, and PostgreSQL 7.4.6.
The Sun Java System RFID Information Server stores EPC-related information which includes:
Refer to the Sun Java System RFID Software 2.0 Installation Guide for details on setting up sample databases and the database scripts that are available with the product.
Refer to the Sun Java System RFID Software 2.0 Developer's Guide for API information on accessing the RFID Software databases.
This section describes server configuration information. Ths following topics are described in this section:
The file, EpcisDbSchema.xml, describes the database schema in a database-independent manner. This schema is used by the client and the server to perform type checking and data validation at run time. This file also specifies extended attributes for the UNIT, PRODUCT and ORGANIZATION tables outlined in the section Database Information Tables.
All <table> elements have a fixed attibute section that lists the columns in the table. The UNIT, PRODUCT and ORGANIZATION table elements also have an extended attribute section.
The file, EpcisDbSchema.xml,is located in the document root of the J2EE application. In a standard (non-bundled) installation of Application Server the document root of the Information Server is:
/var/opt/SUNWappserver7/domains/domain1/server1/applications/j2ee-apps/epcis_1/epcis_war
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/domains/domain1/server1/applications/j2ee-apps/epcis_1/epcis_war
BEA_install_dir/rfid/sun-rfid-si.ear/sun-rfid-is.war where the variable represents your BEA WebLogic server installation path.
|
Note - The application server installation path may vary depending on the version and platform that you are using. |
1. Save a copy of EpcisDbSchema.xml in a permanent location.
2. Modify the file to add or delete extended attributes.
3. Copy the modified file to the docroot of the application server.
4. Restart the application server.
Note that the EpcisDbSchema.xml file is intended to be modified once at deploy time. If changes are made to the file after the database has been populated it may result in inconsistent data in the database.
In this example the PRODUCT has one extended attribute - 'SIZE_OZ' - (bold-faced) which is of type FLOAT.
The template for an extended attribute is as follows:
<attribute extended="true"> <name></name> <dbName></dbName> <type></type> <paramNum>3</paramNum> </attribute> |
To add extended attributes using the template:
1. Enter the name of the attribute in the name and dbName sections.
2. Enter the type of the attribute. The type can be one of:
STRING, FLOAT, LONG, TIMESTAMP, INTEGER or BOOLEAN
The logging parameters are set using Application Server's administration interface. Refer to the Application Server administration guide for more details.
In general the log service is an element within the J2EE Service Element category in the server.xml file, as described in the Sun Java System Application Server Configuration File Reference. The log service is used to configure the system logging service, which can include the following log files:
Configuration of the system logging service can include specifying values for various attributes of the log service element. Using Application Server's administration interface, you can configure any of the following attributes for the log service element:
For general usage with production systems, reset the Default Log Level to WARNING . For debugging purposes set the Log Level to INFO or finer granularity.
The Sun Java System RFID Information Server client library - shown in FIGURE 5-1 as "EPCIS Java Client Library" - requires two Java system properties.
1. From Application Server Admin Console, choose Application Server  JVM Settings
JVM Settings  JVM Options.
JVM Options.
3. Type the following option value:
5. Click Add JVM Option and type the following:
7. Click Save to save the options.
Using Sun Application Server Administration Server, you can manage user access to RFID Information Server. Basic Authentication is the first step to securing RFID Information Server. Please refer to Sun Java System Application Server 8 Developer's Guide, Chapter 2, "Securing J2EE Applications" for basic security terminology. This book can be found at: http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/doc/817-6087
Quoting from the Developer's Guide:
"A role is different from a user group in that a role defines a function in an application, while a group is a set of users who are related in some way. For example, members of the groups astronauts, scientists, and (occasionally) politicians all fit into the role of SpaceShuttlePassenger.
The EJB security model describes roles (as distinguished from user groups) as being described by an application developer and independent of any particular domain. Groups are specific to a deployment domain. It is up to the deployer to map roles into one or more groups for each application or module."
Component level security encompasses web components and EJB components. A secure web container authenticates users and authorizes access to a servlet or JSP by using the security policy laid out in the servlet XML deployment descriptors (web.xml and sun-web.xml files).
For the RFID Information Server, two roles are defined in WEB-INF/web.xml: readonly and readwrite. The users under the readonly role can only find tags from RFID Information Server. The users under the readerwrite role can also modify the RFID Information Server database for tags. The default realm used is the file realm. The realm can be changed to ldap or other supported realms.
Two role-mappings are predefined in WEB-INF/sun-aplication.xml. Where, a principal user guest and a group viewer are mapped to the role readonly. A principal user tester and a group modifier are mapped to the role readwrite. Using this definition, you can use the Application Server admin console to add a new user or assign existing users to group viewer or modifier in file realm for coresponding access previledge.
The Sun Java System RFID Information Server installation script creates the following JMS resources on the application server:
Sun Java System RFID Information Server clients can be configured to use the JMS interface using a file system JNDI provider (Java Naming and Directory Interface) as well.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.