| C H A P T E R 2 |
|
System Controller Navigation Procedures |
This chapter explains step-by-step procedures with illustrations describing how to:
Topics covered in this chapter include:
This section describes how to obtain the following:
There are two types of connections: telnet and serial. If you are using a telnet connection, configure the system controller network settings before using telnet.You can access the system controller main menu using either the telnet or serial connections.
From the main menu, you can select either the platform shell or one of the domain consoles.
You can also bypass the system controller main menu by making a telnet connection to a specific port.
This section describes how to obtain the platform shell.
Before you use telnet, be sure to configure the network settings for the system controllers.
1. Obtain the system controller main menu by typing telnet schostname (CODE EXAMPLE 2-1).
schostname is the system controller host name.
The system controller main menu is displayed. CODE EXAMPLE 2-1 shows how to enter the platform shell.
2. Type 0 to enter the platform shell.
The system controller prompt, schostname:SC>, is displayed for the platform shell of the main system controller. If you have a redundant SC configuration, the spare system controller prompt is schostname:sc>.
 At the machine prompt, type tip and the serial port to be used for the system controller session.
At the machine prompt, type tip and the serial port to be used for the system controller session.
machinename% tip port_name connected |
The main system controller menu is displayed.
1. Connect the system controller serial port to an ASCII terminal.
The system controller main menu is displayed.
2. From the main menu type 0 to enter the platform shell.
This section describes the following:
1. Obtain the system controller main menu by typing telnet schostname (CODE EXAMPLE 2-2).
The system controller main menu is displayed.
schostname is the system controller host name.
CODE EXAMPLE 2-2 shows entering the shell for domain A.
2. Enter a domain. Type 1, 2, 3, or 4 to enter the appropriate domain shell.
The system controller prompt for the domain shell you connected to is displayed. CODE EXAMPLE 2-2 shows entering the shell for domain A, whose prompt is
schostname:A>.
3. If the domain is active (the domain keyswitch is set to on, diag, or secure which means you are running the Solaris operating environment, or are in the OpenBoot PROM), perform the following steps:
a. Press and hold the CTRL key while pressing the ] key, to get to the telnet> prompt.
b. At the telnet> prompt type send break (CODE EXAMPLE 2-3).
ok Ctrl-] telnet> send break |
If the domain is active and the domain keyswitch is set to on, diag, or secure (you are running the Solaris operating environment, are in the OpenBoot PROM, or are running POST), perform the following steps:
1. Press and hold the CTRL key while pressing the ] key, to get to the telnet> prompt.
2. At the telnet> prompt type send break.
CODE EXAMPLE 2-4 shows obtaining the shell for domain A from the domain console. Because the domain is active, you will not see a prompt.
ok Ctrl-] telnet> send break |
This section explains how to navigate between the:
To return to the originating shell, use the disconnect command. In a domain shell, to connect to the domain console, use the resume command. To connect to a domain shell from the platform shell, use the console command.
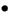
FIGURE 2-1 shows how to navigate between the platform shell, the domain shell, the domain console by using the console and disconnect commands. FIGURE 2-1 also shows how to connect to both the domain shell and platform shell from the operating environment by using the telnet command.
In the telnet command in FIGURE 2-1, 5000 is the platform shell and
In the console command, domainID is a, b, c, or d.
|
Note - By typing telnet schostname 500x, you will bypass the system controller main menu and directly enter the platform shell, a domain shell or a domain console. |
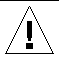
FIGURE 2-2 illustrates how to navigate between the Solaris operating environment, the OpenBoot PROM, and the domain shell. FIGURE 2-2 assumes that the Solaris operating environment is running.
|
Caution - Note that in FIGURE 2-2, typing the break command suspends the Solaris operating environment. |
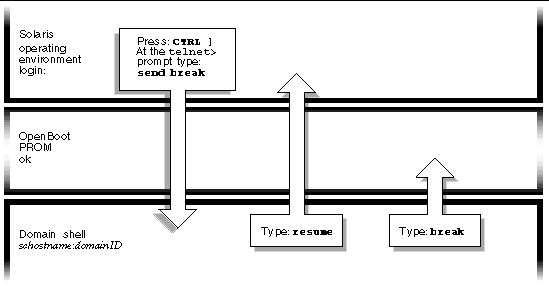
FIGURE 2-3 illustrates how to navigate between the OpenBoot PROM and the domain shell. This figure assumes that the Solaris operating environment is not running.
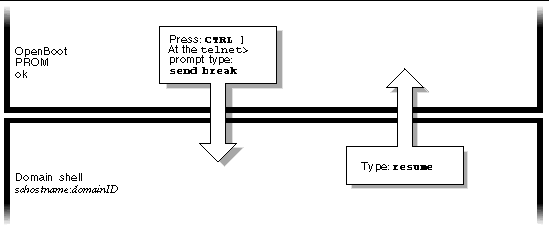
When you connect to a domain, you will be connected to the domain shell unless the domain is active, in which case you will be connected to the domain console. When you connect to the console, you will be connected to the Solaris operating environment console or the OpenBoot PROM, depending on which of these is currently executing.
|
|
 Type setkeyswitch on in the domain shell.
Type setkeyswitch on in the domain shell.
schostname:A> setkeyswitch on |
The domain console is available only when the domain is active. To make the domain active, you must turn the keyswitch on. You will be automatically switched from the domain shell to the domain console.
This action powers on and initializes the domain. The domain will go through POST and then the OpenBoot PROM. If the OpenBoot PROM auto-boot? parameter of the setupdomain command is set to true, the Solaris operating environment will boot. For details on the domain parameters, refer to the setupdomain command description in the Sun Fire 6800/4810/4800/3800 System Controller Command Reference Manual.
1. Press and hold the CTRL key while pressing the ] key to get to the telnet> prompt (CODE EXAMPLE 2-5).
2. Type send break at the telnet prompt.
ok Ctrl-] telnet> send break |
schostname:D> resume |
Note that because the domain is active, you will get a blank line.
2. Press the Return key to get a prompt.
|
Note - If the domain is not active, (the Solaris operating environment or the OpenBoot PROM is not running), the system controller stays in the domain shell and you will obtain an error. |
schostname:SC> console -d a Connected to Domain A Domain Shell for Domain A schostname:A> |
If the OpenBoot PROM is running, you are returned to the console for domain A. If the keyswitch is set to off or standby, you are returned to the shell for domain A.
|
Note - To enter another domain, type the proper domainID b, c, or d. |
This section describes how to terminate system controller sessions.
 Type the disconnect command at the domain shell prompt.
Type the disconnect command at the domain shell prompt.
Your system controller session terminates.
schostname:A> disconnect Connection closed by foreign host. machinename% |
This example assumes that you are connected directly to the domain and not from the platform shell.
If you are connected to the System Controller board with the serial port, use the disconnect command to terminate the system controller session then use a tip command to terminate your tip session.
1. At the domain shell or platform shell prompt, type disconnect.
schostname:A> disconnect |
2. If you are in a domain shell and are connected from the platform shell, type disconnect again to disconnect from the system controller session.
schostname:SC> disconnect |
The system controller main menu is displayed.
3. Type ~. to end your tip session (CODE EXAMPLE 2-6).
Copyright © 2003, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.