Chapter 10 Using Proxy Cache Services
The Netra j server can be used as a proxy cache for another HTTP (web) server on your network. This chapter explains how to configure, administer, and monitor proxy cache services on the Netra j server.
Proxy Cache Server Features
Netra j implements a full-featured proxy cache server that you can incorporate seamlessly into your organization's internal network. The Netra j proxy cache server includes the following features:
-
Compatible with Squid, Harvest, and CERN proxy standards.
-
Supports the Inter Cache Protocol (ICP).
-
Caches HTTP 1.0, FTP, and Gopher objects. This list includes, among other types, GIF, JPEG, and.exe.
-
Supports Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) tunneling.
-
Supports persistent HTTP connections, commonly referred to as "keep-alives."
-
The cache persists across reboots.
-
Provides configurable cache-object expiration times. The proxy cache software ages and deletes a cache object based on attributes specified in its uniform resource locator (URL). The product offers a flexible scheme for cache-object expiration.
-
Offers a flexible scheme for setting a cache object to non-cacheable, based on its URL.
-
Supports dynamic parent failover: If the proxy cache server has multiple parents and is connected to a parent that fails, the server fails over to the next available parent. Furthermore, the proxy cache server detects when the original parent comes back online.
-
Supports conditional retrievals; for example, can retrieve an object if it has been modified in the last day. You can modify the time threshold to suit your needs.
-
Caching software imposes no limit on the amount of data cached.
-
Enables you to build hierarchies of proxy servers. See "Hierarchies".
-
Offers a number of auditing features, including hit statistics, detailed user access logs, bandwidth usage statistics, and a number of other proxy- and cache-related statistics.
-
Ships with an SNMP MIB and agent, so that you can manage a Netra j proxy cache server from an SNMP-conformant management platform, such as Solstice(TM) Domain Manager(TM).
-
Offers a variety of filtering features, including blocking and redirecting of HTTP requests based on URL, host name, or user.
-
Ships with a set of web-based tools for product configuration and monitoring.
Hierarchies
With the Netra j proxy cache server you can create hierarchies of proxy cache servers simply by pointing proxy cache servers to succeeding proxy cache servers as you proceed toward a firewall.
The following figure illustrates a simple hierarchy of proxy cache servers.
Figure 10-1 Simple Hierarchy
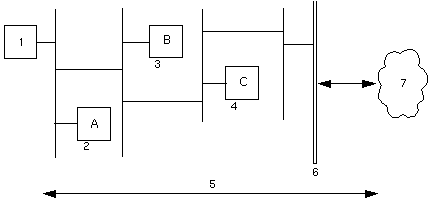
Legend:
-
Client browser
-
Netra j proxy cache server A
-
Netra j proxy cache server B
-
Netra j proxy cache server C
-
HTTP Requests/Responses
-
Firewall
-
Internet
Browser (1) points to proxy A. Proxy B is parent to A. Proxy C is parent to B.
In this sample hierarchy, assume the client browser requests a web object that originated somewhere in the Internet and is, at the moment, not in Netra j proxy cache server A's cache. The following sequence ensues:
-
Machine A checks with its parent, machine B.
-
Likewise, B does not have the object in its cache and checks its parent, machine C. If C does not have the object, it goes out through the firewall to the web server to obtain it.
-
Machine C returns the object--obtained from a remote web server or its local cache--to machine B.
-
Machine B returns the object to machine A.
-
Machine A returns the object to the requesting client.
If the object is cacheable, each proxy stores a copy upon receipt. Note that communication between parent proxies is over TCP connections.
Netra j proxy cache software also supports a variation of the preceding scenario. This variation is shown in the following figure.
Figure 10-2 Multiple Parent Proxies
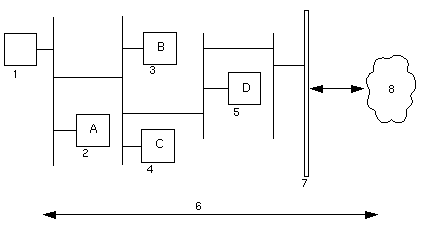
Legend:
-
Client browser
-
Netra j proxy cache server A
-
Netra j proxy cache server B
-
Netra j proxy cache server C
-
Netra j proxy cache server D
-
HTTP Requests/Responses
-
Firewall
-
Internet
Browser (1) points to A. Proxy B and proxy C are parents to A. Proxy D is parent to B and C.
In this example, if a client requests an object of its proxy server, machine A, that is not in A's cache, machine A relays the request to its two parents, machines B and C. If one of the parents has the object, it returns the object to A. If neither has the object, machine A forwards the request to the parent that responds faster, assuming that machine to be less loaded and/or have a better network connection.
If you configure multiple parents, the Netra j proxy cache software enables you to give greater weight to one or the other, or to set up one as the default. When no parent (of multiple parents) has a requested object, the "child" proxy always forwards the request to the default parent.
Monitoring and Managing Proxy Services
The Netra j proxy cache server offers three different types of tools for monitoring the state of proxy-caching services:
-
You can monitor proxy cache services through web pages. See "Monitoring a Netra j Proxy Cache Server" for a description of the monitoring web pages.
-
You can monitor proxy cache services through web-based log tracing tools. See "Proxy Cache Log Files" for a description of the various types of logs available.
-
You can use any SNMP-conformant management platform (such as Solstice Domain Manager) to monitor and manage a Netra j proxy cache server through Management Information Bases (MIBs) included in the Netra j proxy cache software. The software also supports a set of traps that notify you of critical events, ranging from a down server to a failure report on a server component. See "Configuring SNMP Services".
Basic Proxy Cache Setup and Shutdown
The Basic Proxy Cache page provides a simple 3-step questionnaire that sets up a fully functional proxy-caching server. If you decide to turn off proxy cache services, you can use the Unconfigure Proxy Cache page.
To Set Up Basic Proxy Cache Services
-
From the Main Administration page, click Proxy Cache Service.
-
In the Proxy Cache Administration page, click Basic proxy cache configuration.
The Basic Proxy Cache page is displayed.
-
Enter the HTTP port number and click the forward arrow icon.
Most sites use the default value of 8080 for the HTTP port number. Conventions may differ at your site.
-
List the domains inside your corporate firewall and click the forward arrow icon.
Most corporate intranets are inside a firewall. If you are not inside a firewall, simply proceed to the next step.
If you are inside a firewall, you have the option of listing domains that are inside the firewall. For URLs containing domains not in this list, the software does not perform a DNS lookup for the host specified in the URL and always fetches the object from a parent cache.
-
List the parent proxy servers and click the forward arrow icon.
The basic setup questionnaire does not require the proxy server to have a parent, but if you are inside a firewall, it probably does have one.
The Netra j proxy cache server supports multiple parents. For a given transaction, your machine might make requests to all of its parents. It would then use the parent that responded the fastest.
-
Click the up-arrow icon to return to the Proxy Cache Administration page.
To Unconfigure the Proxy Cache
-
In the Proxy Cache Administration page, click Unconfigure proxy cache.
-
In the Unconfigure Proxy Cache page, click OK.
A confirmation window verifies that proxy services have been unconfigured.
Viewing and Modifying Advanced Configuration Properties
You can view or modify advanced proxy cache configuration properties in pages accessed through the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page. This section assumes you have completed the basic setup of your Netra j proxy cache server. See "Basic Proxy Cache Setup and Shutdown".
To View or Modify Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration Properties
-
From the Main Administration page, click Proxy Cache Service.
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Advanced proxy cache configuration.
The Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page presents a list of links, each of which corresponds to a category of proxy cache properties. For all categories, you follow the same procedure for viewing or modifying a property.
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click the link for the category in which a property resides.
-
In the page for that category, view or make changes to the value of a property.
Most properties have editable fields. A few have toggles (either one value or another) or pulldown menus.
-
At the bottom of the category page, click OK.
A page is displayed indicating the success or failure of your change. If a change fails, the page is redisplayed with the error indicated. Correct the error and click OK again. With some errors, a new page containing an error message is displayed. If this occurs, click the Back button on your browser to return to the category page.
If you click Reset, the values for the properties on a page revert to what they were when you first loaded the page.
-
After a successful change, click the up arrow icon to return to the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page.
Alternatively, you can click the home icon to return to the Netra j Main Administration page.
The remainder of this chapter is a description of the advanced proxy cache properties, broken down by the categories reflected in the links on the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page.
To View or Modify Primary Configuration Properties
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Primary Configuration.
The Primary Configuration page is displayed.
-
In the Primary Configuration page, accept or modify values for the following properties.
Table 10-1 Primary Configuration PropertiesProperty
Description
Proxy Webmaster
An e-mail address of the person or group who is to receive notices of abnormal conditions in the Netra j proxy cache server. The default postmaster is root, which means that the recipients you specified for the Netra System Administrator Alias will receive mail bound for the Proxy Webmaster.
Visible Hostname
Error messages generated by the Netra j proxy cache server contain the host name you specify here. The default is the return from the hostname command.
Append Domain Name to Unqualified Host Name
If a URL refers to a host name without a . (period) in its name, the domain name you specify for this property is appended to the host name to form a fully qualified domain name.
Port for HTTP Client Requests
The port number at which the Netra j proxy cache server listens for HTTP requests. Most users can accept the default of 8080. Do not use 81; the Netra j proxy cache uses this number for administrative purposes.
Port for Neighboring Cache ICP requests
The number of the port on which the proxy cache server will receive and process ICP (InterCache Protocol) requests by other proxy servers that support the ICP protocol.
Port for Proxy Cache Server Statistics Requests
The TCP or UDP port on which the Netra j proxy cache server provides statistics. The SNMP subagent shipped with the product uses this feature to export the statistics via SNMP. Setting this property to 0 (zero) disables the providing of statistics. The default is 3140. Entering a non-zero value enables proxy cache monitoring, which is described in "Proxy Cache Monitoring".
Receive ICP Requests on this Address
If you enter an address, the Netra j proxy cache server accepts ICP requests only at the IP address specified here.
Send ICP Requests from this Address
If you enter an address, the Netra j proxy cache server sends ICP requests from the IP address specified here.
Operation Mode
Choose between Proxy+Cache (the default) and Proxy Only. If you choose Proxy Only, the Netra j proxy cache server does not cache any objects.
To View or Modify Proxy Cascade Properties
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Proxy Cascade.
The Proxy Cascade page is displayed.
-
In the top portion of the Proxy Cascade page, accept or modify values for the following properties.
Table 10-2 Proxy Cascade PropertiesProperty
Description
Table of Parent Proxy Caches
When you load the Proxy Cascade page, the table of parents contains the hosts you entered when you last performed basic proxy cache configuration. See "Table of Parent Proxy Caches".
Query Parent Cache for Domains
The Netra j proxy cache server contacts parents specified for this property only for matching domain names. An alternative form enables you to specify a host for non-matching domain names. See "Query Parent Cache for Domains".
Domains Inside Firewall
When you load the Proxy Cascade page, the Domains Inside Firewall field contains the domains you entered when you last performed basic proxy cache configuration.
The Netra j proxy cache server considers domains you list for this property as being inside a firewall. For URLs containing domains not in this list, the software does not perform a name service resolution (for example, a DNS lookup) of a host name specified in a URL. Also, for domains not in this list, if the Netra j proxy cache server does not have a requested object in its local cache, it always tries to fetch the object from a parent cache.
-
Scroll down to the remaining properties in the Proxy Cascade page.
Table 10-3 Remaining Proxy Cascade PropertiesProperty
Description
IP Addresses Inside Firewall
The Netra j proxy cache server considers addresses you list for this property as being inside a firewall. When you specify one or more addresses, the Netra j proxy cache server performs a host name resolution (for example, a DNS or NIS lookup) of the address specified in a URL for all requests, to determine whether the address is inside the firewall. For addresses not in this list, if the Netra j proxy cache server does not have a requested object in its local cache, it always tries to fetch the object from a parent cache.
Note that using this property degrades server response time because of the overhead associated with host name resolutions.
Source Ping
Choose between off (the default) and on. By default, when the Netra j proxy cache server receives a request, it pings (sends ICP requests to) its parents. If Source Ping is on, the software also pings the host specified in the URL of an object it retrieves. This feature can be useful where parents are overloaded and the source web server is not. Note that Source Ping packets are never sent beyond a firewall.
Wais Relay Host
Enter the host name of the proxy server to which WAIS URLs will be relayed.
Wais Relay Port
Enter the port number on the above-named host name to which WAIS URLs are to be relayed.
Max. Relay Object Size (MB)
Enter the maximum size (in MB) of a WAIS object that can be received from the Wais Relay Host. The Netra j proxy cache server does not relay WAIS objects that exceed this limit.
Local Domains Inside the Firewall
When you load the Proxy Cascade page the Local Domains Inside the Firewall contains the domains you entered for the Domains Inside Firewall field when you last performed basic proxy cache configuration.
The Netra j proxy cache server retrieves URLs containing the domains you specify here directly from the source and not from a parent. These domains should be the same as or a subset of the domains you specify for Domains Inside Firewall (see description above). Specify here domains to which you have good network connectivity, and from which users request relatively small objects.
Local IP Addresses Inside the Firewall
The Netra j proxy cache server retrieves URLs containing the IP addresses you specify here directly from the source and not from a parent. These addresses should be a subset of the addresses you specify for IP Addresses Inside Firewall (see description above). Specify here addresses to which you have good network connectivity, and from which users request relatively small objects.
Note that using this property degrades server response time because of the overhead associated with host name resolutions.
Table of Parent Proxy Caches
The table of parent proxy caches contains the hosts you entered when you last performed basic proxy cache configuration. If you have multiple parent proxies that do not support ICP, the proxy cache service contacts those parents in the order you list them here. If you have multiple parents that do support ICP, the proxy cache service determines the "closest" parent by comparing response times to its ICP queries.
The headings in the table of parent caches are as follows:
-
Proxy Name - Fully qualified host name of the parent proxy cache host. If this host is not in the same domain as the Netra j proxy cache host, you must specify the domain name; for example: webcache.eng.acme.com
-
HTTP Port - The HTTP port number on which the parent listens for HTTP requests.
-
SSL - A checkbox indicating whether a host supports the tunneling of the Secure Sockets Layer protocol.
-
Persistence - A checkbox indicating whether a host supports the HTTP persistent connections feature, sometimes referred to as "keep-alive."
Query Parent Cache for Domains
This property enables you to specify parents the Netra j Proxy Cache Server will contact only for URLs with matching domain names or, alternatively, with non-matching domain names.
Entries have the form hostname domain_name or hostname !domain_name. For example, if you have a parent wbyeats, in the same domain as the Netra j proxy cache server, to which you want directed all traffic related to URLs that contain the domain names sales.acme.com and eng.acme.com, you make an entry:
wbyeats sales.acme.com eng.acme.com
If you have multiple entries for one host--for example, in addition to the above, if you had: wbyeats fin.com--the domains in those entries are combined to form a single list.
You can also have a reverse match on domain names, so that requests related to URLs that contain domain names that do not match the specified domains are directed to the specified host. So, for example, if you want wbyeats to field all requests related to domains other than the domain names sales.acme.com, you make an entry:
wbyeats !sales.acme.com
Note that with the reverse-match feature, you can specify only one domain name, either as the only domain name in an entry or as the last domain name in an entry. If you want to prevent use of a given parent for multiple domains, specify additional entries. For example:
wbyeats !sales.acme.com wbyeats !eng.acme.com
To View or Modify Cache Policy Properties
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Cache Policy.
The Cache Policy page is displayed.
-
Under the Cache Policy heading, enter or accept values for the properties described below.
The properties are divided into groups reflected in the following sections.
HTTP Policy
There are three HTTP Policy properties.
Table 10-4 HTTP Policy Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Time To Live (min) |
The limit on the length of time an HTTP object can remain in the cache. The default is 720 minutes (12 hours). |
|
Max Object Size (MB) |
The limit on the size of an HTTP object for caching. The Netra j proxy cache server proxies for, but does not cache, HTTP objects that exceed this limit. The default is 4 MB. |
|
Do not Cache URLs Containing |
The Netra j proxy cache server does not cache HTTP URLs containing strings you add to this list. The defaults are: /cgi-bin/ /htbin/ /www-bin/ ? |
Gopher Policy
There are three Gopher Policy properties.
Table 10-5 Gopher Policy Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Time To Live |
The limit on the length of time a Gopher object can remain in the cache. The default is 4320 minutes (three days). |
|
Max Object Size |
The limit on the size of a Gopher object for caching. The Netra j proxy cache server proxies for, but does not cache, Gopher objects that exceed this limit. The default is 4 MB. |
|
Do not Cache URLs Containing |
The Netra j proxy cache server does not cache Gopher URLs containing strings you add to this list. The default is ? (question mark). |
FTP Policy
There are three FTP Policy properties.
Table 10-6 FTP Policy Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Time To Live |
The limit on the length of time an FTP object can remain in the cache. The default is 4320 minutes (three days). |
|
Max Object Size |
The limit on the size of an FTP object for caching. The Netra j proxy cache server proxies for, but does not cache, FTP objects that exceed this limit. The default is 4 MB. |
|
Do not Cache URLs Containing |
The Netra j proxy cache server does not cache FTP URLs containing strings you add to this list. There are no defaults. |
URL Policy
There are two URL Policy properties.
Table 10-7 URL Policy Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Do not Query Neighbors for URLS Containing |
For URLs containing strings you add to this list, the Netra j proxy cache server looks in its own cache and does not query parent caches. |
|
TTL Selection Based on URL |
The Netra j proxy cache server enables you to set the Time To Live for URLs containing strings that you specify (see below). |
Setting the TTL for URLs
You can specify a URL's Time To Live in either of two ways: as an absolute value or as a percentage of an object's age. Entries have the following form:
| reg_expression absolute_TTL percentage maximum_TTL |
where:
-
reg_expression is a regular expression that is matched against a URL. See "Rules for Pattern Matching for TTL Selection Property" for rules for the regular expression.
-
absolute_TTL is the TTL (in minutes) used by the Netra j proxy cache server if the percentage method is not used.
-
percentage is the percentage of the duration between an object's last-modified timestamp and the current time.
-
maximum_TTL is the upper limit (in minutes) on the TTL.
The proxy cache uses the percentage method of determining the TTL if a matched object has a last-modified timestamp. If an object does not have such a timestamp, the absolute TTL is used instead. You can specify a negative value for absolute_TTL thereby forcing the percentage method to be used. If a matched object then does not have the required timestamp, the TTL is set from a value set under Cache Policy (see Step 2 in "To View or Modify Cache Policy Properties").
If neither the absolute TTL nor percentage methods result in a TTL for a matched object, the TTL is determined from the values set in the Cache Policy properties.
The Netra j proxy cache server checks all patterns in the list and uses the last match.
The following is an example of a TTL-selection entry:
^http:// 1440 20 43200
The preceding example matches URLs that start with http://. If a URL contains a last-modified timestamp, the TTL for that URL is set to 20% of the difference between the timestamp and the current time. If the URL does not have such a timestamp, the TTL is set to 1440 minutes. In any event, the URL will not stay in the cache longer than 43200 minutes.
Other
Two properties are outside the scope of the previous categories.
Table 10-8 Other Properties|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Max Request Size |
The maximum size of a request, in KB. The default is 100. This value should be large enough to accommodate users who use the POST method to upload files. |
|
Quick Abort |
By default, the Netra j proxy cache server completes the retrieval of an object even when the request for that object is aborted. This is potentially a benefit because the cache will then have the object should it be requested subsequently and the machine resources and bandwidth consumed to the point of the aborting of the request are not wasted. However, this feature can be a detriment where you have slow links or very busy caches. This feature also allows for the possibility of impatient users tying up a URL by repeatedly aborting and re-requesting non-cachable objects. You have the option of turning this "quick abort" feature on (meaning that object retrieval ceases if the request is aborted). The default is off. |
To View or Modify Access Control Properties
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Access Control.
The Access Control page is displayed.
-
Under the Access Control heading, enter or accept values for the properties listed below.
Enter access control definitions one to a line. To edit an entry, click the entry in the table, and then make any changes you want.
Table 10-9 Access Control PropertiesProperty
Description
Access List Definition
Access lists enable you to control access to the functions of the Netra j proxy cache server based on characteristics of a request. See "Access List Definition".
Client Access Control
This and the following properties are used in conjunction with the access lists you create. For a given access list, you can allow or deny access to the HTTP port on the Netra j proxy cache server.
The Client Access Control property takes an entry of the form:
allow (or deny) access_list . . .
The default values for Client Access Control are:
deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
allow all
Access to Cache Via ICP
An entry of the form:
allow (or deny) access_list . . .
The default for Access to Cache via ICP is to allow all accesses.
ACLs for the Cache Host
An entry of the form:
cache_server access_list . . .
Enables you to limit the ICP queries sent to a given host (such as ICP-capable parent proxy), based on the contents of an access list. If you specify multiple access lists, the Netra j proxy cache server applies the first list that matches for a given URL.
URL Redirection
An entry of the form:
access_list . . . : HOST hostname PATH path
Enables you to redirect a URL to a specified host and path. The access lists must be of types domain, service, or pattern. For example, the entry:
games : HOST restricted.acme.com PATH /restricted.html
redirects a URL that matches the games access list to:
http://restricted.acme.com/restricted.html
To create a URL Redirection entry, enter:
-
The name of one or more access lists, followed by a colon
-
The word HOST and a fully-qualified host name
-
The word PATH and an absolute path name
-
Access List Definition
Access lists enable you to control access to the functions of the Netra j proxy cache server based on characteristics of a request. To create an access list, you create a name (an arbitrary string), specify the type of access list (types are described below), and specify an argument that is used to match against the request. After creating an access list, you can specify that list for the following properties:
-
Client Access Control
-
Access to Cache via ICP
-
ACLs for Cache Host
-
URL Redirection
These properties are described below.
Access list definitions have the following form:
name type argument
Access list types are as follows:
-
src Matches on the source address in a request. It takes an argument of the form: ip_address/netmask. You can specify multiple pairings of IP address and netmask.
-
domainMatches on the domain specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: .domain_name. You can specify multiple domain names.
-
timeMatches on a time period specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: day_of_the_week start_time-end_time. The variable day_of_the_week is expressed as one of the following abbreviations:
|
S |
Sunday |
|
M |
Monday |
|
T |
Tuesday |
|
W |
Wednesday |
|
H |
Thursday |
|
F |
Friday |
|
A |
Saturday |
The start_time-end_time variables are expressed as hour:minutes, using a 24-hour clock. For example, to express a period in the mid-afternoon, you specify 14:15-16:30, meaning from 2:15 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.
-
patternMatches on a pattern specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: pattern_to_be_matched. You can specify multiple patterns.
-
portMatches on a port number specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: port_number. You can specify multiple port numbers.
-
protoMatches on a protocol specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: protocol (HTTP, FTP, Gopher, or WAIS). You can specify multiple protocols.
-
methodMatches on a method (CONNECT, HEAD, POST, or GET) specified in a URL. It takes an argument of the form: method_name. You can specify multiple methods.
-
serviceMatches on the service specified in a request. It takes an argument of the form: ip_address/netmask. "Service," in this context, is an instance of a service on a Netra j proxy cache host, as identified by a service address and netmask.
Note -If you have multiple access lists of the same type, the Netra j proxy cache server, when determining which list a URL is in, works from top to bottom and stops after the first match.
The following is an example of an access list:
games domain game.com
This example creates an access list named games of type domain. This list includes all URLs containing a destination domain of game.com. In the HTTP Access property (described in Table 10-9), you can, for example, deny access to the games list.
To View or Modify Storage Management Properties
-
In the Advance Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Storage Management.
The Storage Management page is displayed.
-
Under "Storage Management," enter or accept values for the following properties.
Table 10-11 Storage Management PropertiesProperty
Description
High-water mark for Memory (%)
Removing of the least recently used objects in memory begins when the high-water mark is reached and ends when enough objects are removed so that the low-water mark (see following property) is reached. Note that objects removed from memory remain on disk. Enter a percentage. The default is 90%.
Low-water mark for Memory (%)
See the description of the high-water mark, above. Enter a percentage. The default is 75%.
High-water mark for Disk Cache (%)
Replacement of the least recently used objects in the disk cache begins when the high-water mark is reached and ends when enough objects are removed so that the low-water mark (see following property) is reached. Enter a percentage. The default is 90%.
Low-water mark for Disk Cache (%)
See the description of the high-water mark, above. Enter a percentage. The default is 75%.
Garbage Collection (GC) Rate (min)
Specifies how often, in minutes, the Netra j proxy cache server runs a full garbage collection. Garbage collection involves checking the expiration time of every object in the cache. In the course of normal operation, the Netra j proxy cache server removes expired objects so that explicit garbage collection is not necessary. This feature can be helpful if you have a frequent need to reclaim disk space. Note that the server does not process client requests during garbage collection. Enter a number of minutes if you want to use this feature, or leave the field blank to disable garbage collection.
Time of Day for GC (HH:MM:SS)
Enables you to schedule garbage collection at an off-peak time. Time is expressed on a 24-hour clock. For example, if you want garbage collection to occur at 3:30 a.m., enter 03:30:00.
To View or Modify Timeouts
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Timeouts.
The Timeouts page is displayed.
-
Under "Timeouts," enter or accept values for the following properties.
Table 10-12 Timeout PropertiesProperty
Description
ICP Neighbor Timeout
The period of time after which ICP (InterCache Protocol) requests made to parent proxies will time out. The default is two seconds.
Timeout for Server Connections (sec)
The maximum duration, in seconds, the server waits for a connection to be established. The default is two minutes. See "Proxy Cache Connect Timeout and Parent Failover" for a discussion of the relationship of this property to the operating system's TCP connect timeout.
Read Timeout (min)
The duration beyond which the Netra j proxy cache server disconnects a connection on which no activity is occurring. The default value is 15 minutes.
Client Lifetime (min)
The maximum duration a client (browser) is allowed to remain connected to the cache process. This timeout prevents clients that go away without shutting down from consuming software resources. The default is 200 minutes (3 hours, 20 minutes). If you have high-speed client connectivity or occasionally run out of file descriptors, you might want to reduce the default number.
TTL for Negative Caching of Objects (min)
The server caches the fact that a cache request failed (for example, the object identified by a specified URL cannot be found). This negative caching lasts for the number of minutes specified for this property. The default is five minutes.
TTL for Successful DNS Lookups (min)
The server caches the result of a successful host name lookup for the duration specified for this property. The default is six hours. Note that the proxy cache service does not observe the TTL specified in a DNS record.
TTL for failed DNS Lookups (min)
The server can cache the fact that a host name lookup failed. The default is zero minutes, which means that, by default, the server does not perform this type of negative caching.
To View or Modify Log File Options
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Log File Management.
The Log File Management page is displayed. For instructions on using this page, see "Administering Proxy Cache Service Log Files".
To View or Modify Web Server Accelerator Options
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click Web Server Accelerator Options.
The Web Server Accelerator Options page is displayed.
-
Under "Web Server Accelerator Options," enter or accept values for the following properties.
Table 10-13 Web Server Accelerator Properties
To View or Modify External Program Options
-
In the Advanced Proxy Cache Configuration page, click External Program Options.
The External Program Options page is displayed.
-
Under the External Program Options heading, enter or accept values for the following properties.
Table 10-14 External Program PropertiesProperty
Description
FTP User
The string supplied as the login password for anonymous ftp. This enables you to supply an informative address, if you want.
Options for `ftpget'
The arguments supplied to the ftpget command. The ftpget command retrieves FTP data for the cache. HTTP and Gopher protocol support are built into the proxy cache software. To view a list of valid ftpget arguments, invoke /opt/SUNWcache/lib/ftpget, with no arguments.
No. of Processes for DNS Lookups
The number of processes spawned by the Netra j proxy cache server to service DNS name lookups. This number indicates the maximum number of concurrent DNS lookups. On heavily loaded caches, you might want to increase this value from the default of 5 to 10. The maximum is 32.
Configuring SNMP Services
The SNMP Configuration page enables you to set up user groups with permissions for performing the following SNMP actions:
-
Reading variables from the Netra j proxy cache server Management Information Base (MIB)
-
Changing the settings of variables from that MIB
-
Receiving traps generated by the Netra j proxy cache server agent
To Configure SNMP Services
-
In the Proxy Cache Administration page, click SNMP configuration.
The SNMP Configuration page is displayed.
-
Under the SNMP Configuration Parameters heading, enter or accept values for the following properties.
Table 10-15 SNMP Configuration ParametersParameter
Description
SNMP Manager
SNMP Managers are hostnames of machines that will receive SNMP traps from the Netra j proxy cache server agent. This should be the same set of machines that is running your SNMP management platform.
SNMP Read Community
The name of a user group with permission for reading variables from the Netra j proxy cache server MIB.
SNMP Write Community
The name of a user group with permission for changing the settings of variables read from the Netra j proxy cache server MIB.
SNMP Trap Community
The name of a user group with permission for receiving traps generated by the Netra j proxy cache server agent.
Backing Up and Restoring the Proxy Cache Service Configuration
This section describes the procedures for backing up and restoring the Netra j proxy cache configuration.
Backing Up Your Configuration
You can back up your proxy server configuration by using the Save/Restore link in the Netra j Main Administration page.
To Back Up a Proxy Cache Configuration
-
Insert your backup diskette in the diskette drive of the host being restored.
-
In the Netra Main Administration page, click Save/Restore.
-
In the Save/Restore page, click Save configuration to diskette.
Restoring Your Configuration
Assuming you have backed up your configuration to diskette (see the preceding section), you can subsequently restore that configuration to your server. Use the Save/Restore link in the Netra j Main Administration page (see the preceding procedure).
Monitoring a Netra j Proxy Cache Server
This section explains how to monitor a Netra j proxy cache server through the Netra Administration web pages. You can also monitor the server through log traces or through an SNMP-conformant management platform. See "Proxy Cache Log Files" and "Configuring SNMP Services".
To Load the Host Status or Proxy Cache Monitoring Pages
-
In the Proxy Cache Administration page, click Host Status to monitor the server, or Proxy Cache Monitoring to view statistics related to the operation of the proxy cache service.
Host Status
When you click the Host Status link in the Proxy Cache Administration page, the Host Status page is displayed.
When you load the Host Status page, a snapshot of current host activity is displayed. To obtain the latest statement of host activity, click on your browser's Reload button to refresh the latest host activity statistics.
There is a single table in the Host Status page.
Table 10-16 Table on Host Status Page|
Table |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Test Objects |
A test object is a software object that runs on a host to test a specific component of that host, such as the integrity of an interface or the existence of a process. A test object returns OK (yes) or not-OK (no) for the object it tests. There is a man page for each test object. |
Proxy Cache Monitoring
When you click the Proxy Cache Monitoring link in the Proxy Cache Administration page, the Proxy Cache Monitoring page is displayed. This page presents a snapshot of current proxy cache statistics. Click on your browser's Reload button to refresh the latest proxy cache statistics.
The tables in the Proxy Cache Monitoring for Host page are listed below.
Table 10-17 Tables on the Proxy Cache Monitoring for Host Page|
Table |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Proxy Cache URL Statistics |
Provides statistics on the rate of URL requests and the extent to which requests are serviced from the local cache. |
|
Proxy Cache Connection Statistics |
Provides statistics on HTTP and SSL connections. |
|
Cached Object Statistics |
Provides statistics on the number of objects cached, for each type of object. |
The headings for these tables are described in the following tables.
In the Proxy Cache URL Statistics table, under Totals (since start):
Table 10-18 Proxy Cache URL Totals|
Total |
Description |
|---|---|
|
# URLs accessed |
The number of requests for a URL fielded by the Netra j proxy cache server. |
|
# Hits |
The number of URL requests for which the Netra j proxy cache server was able to return an object from its own cache. |
|
% Hits |
The number of URLs accessed divided by the number of hits. This number tells you the extent to which the Netra j proxy cache server is able to respond to URL requests from the local cache. |
Under Delta (since reset counter):
Table 10-19 Proxy Cache URL Deltas|
Delta |
Description |
|---|---|
|
URLs/sec |
The rate at which URL requests are being fielded by the Netra j proxy cache server since the reset counter was last set to zero. |
|
Hits/sec |
The rate at which the Netra j proxy cache server was able to find requested objects in a local cache, since the reset counter was last set to zero. |
|
% Hits |
The number of URLs accessed divided by the number of hits, since the reset counter was last set to zero. |
In the Proxy Cache Connections Statistics table:
Table 10-20 Proxy Cache Connections Statistics|
Statistic |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection Type |
Has rows for HTTP and SSL connections and for established connections. |
|
Totals (since start) |
The total number of connections for each connection type, HTTP and SSL, since the last reboot of the host. |
|
Current |
The number of current connections for each connection type, HTTP and SSL, and the number of current established connections. |
In the Cached Object Statistics table:
Table 10-21 Cached Object Statistics|
Statistic |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection Type |
HTTP, FTP, WAIS, or Gopher. |
|
Size (KB) Cached |
The size of all objects cached for a given object type. |
Under Number of Objects Cached:
Table 10-22 Statistics on Number of Objects Cached|
Statistic |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Total Cached Disk & Main Memory |
The total number of objects cached on a host for a given object type. |
|
Cached in Main Memory |
The number of objects cached in main memory. |
Proxy Cache Log Files
This section explains how to view and manage the proxy cache service log files. These log files are distinct from the log files accessed through the Log Files link on the Netra j Main Administration page. The log files described in this section relate only to the activity of the proxy cache service.
To Load the Proxy Cache Log Administration Page
-
In the Proxy Cache Administration page, click Log Files.
A page of administration options is displayed.
You can view or clear each type of log file listed. If you choose to clear a log file, you are prompted to confirm the operation.
-
Click OK to confirm.
Note -Clearing a log file truncates the log file.
The log file types are described in the following table:
Table 10-23 Log File Types|
Log File |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Proxy Cache Server log |
Lists status messages related to the activity of the proxy cache service. By default, this log is turned on. |
|
Proxy Cache Access log |
Lists records of all client accesses to the Netra j proxy cache server. By default, this log is turned on. |
|
Proxy Cache Hierarchy log |
Contains information about which parent satisfied each request. By default, this log is turned off. See "To Enable Hierarchy and Store Logging". |
|
Proxy Cache Store log |
A log of items stored in and removed from the cache, with type (protocol), size, and timestamp. By default, this log is turned off. See "To Enable Hierarchy and Store Logging". |
|
Configuration Installation Error Log |
A log of errors or exceptional events that occurred when new configuration details were supplied to the proxy cache service via the Netra user interface. |
|
Administration Client Error log |
A log of errors that occur when the cgi-bin programs run from the administration web pages. This log can be useful when you encounter an unexpected and inexplicable failure when interacting with the web pages. |
|
Administration Server log |
A log of the daemon that maintains the configuration database. |
|
Administration Server Error and Exception log |
Records the stdout and stderr of the daemon referred to in the preceding item. Of use primarily to trained technical personnel. |
To Enable Hierarchy and Store Logging
-
In a text editor, open the file proxycache.conf, stored in /etc/opt/SUNWoam/config/proxy.
-
Uncomment the line corresponding to the log file you want to enable.
For example, to enable both types of logging, uncomment the lines for cache_hierarchy_log and cache_store_log.
-
In the uncommented lines, replace the word none with the location of the proxy cache service log files.
In the preceding example, the edited lines display as follows:
cache_store_log /var/opt/SUNWcache/cachelogs/store.log cache_hierarchy_log /var/opt/SUNWcache/cachelogs/hierarchy.log
Administering Proxy Cache Service Log Files
From the Log File Management page, you can set up automatic rotation and backup of the following proxy cache service log files (each log type is shown in parentheses):
-
Proxy Cache Server log (log type: cache)
-
Proxy Cache Access log (log type: access)
-
Proxy Cache Hierarchy log (log type: hierarchy)
-
Proxy Cache Store log (log type: store)
At the time of day you specify, log files are rotated so that the current log file, type.log, becomes type.log.0; type.log.0 becomes type.log.1; type.log.1 becomes type.log.2; and so on. The highest-numbered (and oldest) file, type.log.9, is overwritten by type.log.8.
The log files are then stored locally or on a remote server, according to your settings.
To Administer Proxy Cache Service Log Files
-
In the Proxy Cache Log Administration page, click Administer Proxy Cache Server, Access, Hierarchy, and Store Logs.
-
In the Log File Management page, set file location and time of day options.
Table 10-24 File Location and Time of Day OptionsOption
Description
Maintain available space
Specifies that log files are stored in the local directory /var/opt/SUNWcache/cachelogs. This option enforces a minimum disk space allowance (the default value is 10 MB). If necessary, log files are deleted (starting with the oldest) until the specified amount of space is reached.
Transfer logs via FTP
Specifies that log files are transferred after rotation to a specified directory on a remote server via FTP.
Time of day
The time of day at which you want the log files to be rotated.
-
Set parameters for local file maintenance or FTP delivery.
-
If Maintain available space is selected and you click Set Parameters, the following option is displayed.
Option
Description
Set Minimum Available Space To
The minimum amount of disk space that must be available in /var/opt/SUNWcache/cachelogs in addition to the log files.
-
If Transfer logs via FTP is selected and you click Set Parameters, the following options are displayed.
Option
Description
Logs To Transfer
The log file types (described earlier in this section) that will be transferred to the remote server.
Transfer Method
The mode (binary or ASCII) in which the FTP service will transfer the log files.
Hostname
The hostname of the remote system to which log files will be transferred.
Username
The username for the FTP account to be used for the transfer.
Password
The password for the FTP account to be used for the transfer.
Remote Directory
The remote directory to which log files will be transferred.
Log Filename Extension
An extension to be added to all log file names.
-
-
Click Set log file options, and enter or accept values for the following properties:
Table 10-27Option
Description
Emulate HTTPD Log
By default, the server emulates the log file format used by many HTTP servers. Accept the default of on or select off to turn this feature off.
No. of Logfile Rotations
Specifies the number of log file rotations the server performs. With the default of 10, the software creates log files with extensions from 0 through 9. Set this property to 0 to turn off log file rotation.
Log Directory
You do not have the option to change the default log-storage directory, /var/opt/SUNWcache/cachelogs, in the current release.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
