How Backup Performs an Archive
The implementation of the archive process differs across operating system platforms. Backup uses two types of archives:
-
PC style archive
You cannot schedule a PC-style archive from the Backup server; it is initiated by the client's save program. This style of archive also gives the user the option to delete the original files after the files are archived. To provide cross-platform compatibility with Solaris servers, the Backup server for Solaris has a preconfigured PC Archive volume pool to receive data generated by archives from non-UNIX clients.
Refer to the Backup User program online help for instructions on how to make an archive request from a Windows NT or PC client.
-
On UNIX, you can use the archive program (nwarchive) for manual archives from the client, or you can schedule archives from the server. (Refer to the online help for details explaining how to use the Backup programs to start an archive.) Whether you initiate the archive on the client or the server, the archive is performed by the client's nsrarchive program, which is initiated by the client's nsrexecd daemon. Figure 6-1 illustrates the UNIX-style archive implementation.
You cannot select the Store Index Entries option in the Pools resource for UNIX-style archives. If you select the option and then apply your changes, you receive an error message. With a UNIX-style archive, you can only retrieve the entire archive save set; you cannot browse or retrieve individual files from within the archive save set.
Figure 6-1 UNIX Archive Operation
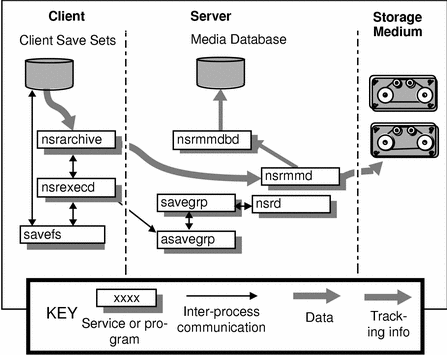
During the archive operation, the data is written to storage volumes of the archive pool type. The archive volume can be in a device attached to the Backup server or a device attached to a storage node (called a remote device). Information about the archive data, including the annotation that you entered as part of the archive request, is tracked in the Backup server's media database. The client file index entries that are generated during an archive are backed up during the next scheduled backup, to volumes from the Default pool. Index entries are not made for a UNIX-style archive.
You can select the verification, grooming, and cloning options for an archive operation. If you select verification, Backup checks the integrity of the data on the storage volume against the original data on the client system. If you select grooming, Backup deletes the archived save sets from the source client machine. If you select cloning, a copy of each archive save set is written to a volume from an Archive Clone pool, similar to the process of cloning backup save sets. You can select cloning, verification, and grooming for an archive in either the Archive Options window of the Backup archive program or the Archive Request resource in the Backup administration program for UNIX-style archives.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
