| C H A P T E R 3 |
|
Registering, Upgrading, and Initially Setting Up the Array |
This chapter provides an overview of the management software and the steps required for first time you log in. It contains the following sections:
The Sun StorageTek Common Array Manager provides two interfaces for accessing the configuration software and the monitoring software for the array:
For access instructions, see Logging In and Out Using the CLI.
For access instructions, see Logging In Using the Browser Interface.
When you register an array in Common Array Manager, the wizard analyzes the firmware installed on the array. If the firmware placed on the host is newer than the firmware installed on the array, the wizard performs an array firmware upgrade.
The following explains how to log in to and out of a remote host using the CLI. Do so either by remotely logging in to a management software station or by using the Solaris remote client on a remote host.
|
Note - Be sure to add the /opt/SUNWsesscs/cli/bin directory to your path. |
2. Log in by typing the following command:
% sscs login -h cam-hostname -u username
You can now use CLI commands to perform the same software operations as those available in the browser interface. For more information:
|
Note - To locate the sscs(1M) man page, you must update your MANPATH variable or use the -m option with the man command. |
3. Log out by typing the following command:
You can start the management software on any system that is connected to the user LAN. Before you log in, you need to set up a storage role or group in your OS and assign users to it. See Adding Users And Assigning Roles
1. Open a supported web browser.
|
Note - For information about supported web browsers, see the Sun StorageTek Common Array Manager Release Notes. |
2. Enter the IP address of the management host using this format:
https://cam-management-host:6789
cam-management-host is the IP address of the host where you installed the Sun StorageTek Common Array Manager software.
3. Login with the root or storage user name.
You need root and storage users on the system. For more information about user names and roles, see Adding Users And Assigning Roles.
For Solaris and Linux, root already exists for the machine on which you installed the software.
For Windows, you will have to create a root user name. with Windows administrative privileges. For more information about adding users and roles to Windows, see Adding User Roles and New Users to Windows.
The Java Web Console page is displayed.
At this point, you are logged in to the system.
|
Note - The connection closes automatically if there is no activity for approximately 15 minutes. |
5. Select Sun StorageTek Common Array Manager from the Storage section of the Sun Java Web Console page.
The first time you open the Common Array Manager after a first-time installation, the Site Information page displays.
Fill out the required fields(indicated by an asterisk: *) and click Save.
Once you have saved the Site Information page, on all subsequent logins to the Common Array Manager the Storage System Summary page is displayed. The first time the Storage System Summary page is displayed, it comes up blank with no arrays listed.
If you need help navigating the software or the online help, refer to Using the Browser Interface.
From here, you can carry out the setup tasks described in the following sections, including registering arrays, upgrading the array firmware, naming arrays, setting the array password, setting the system time, and adding new users.
When you first log into the array's management software, select Storage Systems in the left navigation pane and on the Storage Summary page, click Register. The Array Registration wizard starts and you can choose to either search the subnet for arrays that are not already registered or to manually register an array as noted in the following sections:
At the end of the registration wizard, you can upgrade the array firmware for initial installations.
The registration wizard will automatically discover arrays that are on the same subnet as the management host, or you can point the wizard to the array if it is not on the same subnet as the management host.
If searching for arrays on a subnet, the discovery process displays the percentage of completion while the array management software polls devices in the network to determine whether any new arrays are available. When complete, a list of discovered arrays is displayed.
The Storage System Summary page is displayed.
The Register Storage System wizard is displayed.
3. In the Register Storage System wizard, select the storage system discovery method you want to use and click Next.
The management software will scan the subnet it is on for unregistered arrays, or you can specify a specific IP address for the array if the array is outside of the storage system subnet. Additionally, you can have it use the default password for arrays or you can enter a password if you have already changed the password on the array.
|
Note - The password of the array is not a required entry. No array is shipped with a default password. This field is used only if the array being registered is one that was previously managed and had a set password. To give the array a password, see Setting an Array Password. |
The wizard then finds one or more unregistered arrays and adds it to the Storage System Summary page. The following figure is an example Summary page.
|
Note - It takes approximately 2 minutes for the software to discover each array. |
The Analyze Arrays page shows you the firmware version available from the Common Array Manager, and the firmware version currently installed on the array. You can select the action you want the software to take with respect to the firmware:
5. Select an upgrade action from the Action menu and click Next.
A Review page displays a summary of your action selection.
6. Review the summary and click Finish.
The registration (and firmware upgrade, if selected) completes and the results are displayed on a Results page.
7. Click Close to close the Results page.
You remove an array from the management software by unregistering the array.
The Storage System Summary page is displayed.
2. Select the check box to the left of the array you want to remove from the list of registered arrays.
This enables the Remove button.
The array is unregistered and removed from the Storage System Summary.
You can upgrade your array firmware by either:
You can choose to modify the array firmware later with the next option.
As part of the installation of the Common Array Manager software, the script puts the array firmware files in a directory on the management host (/var/sadm/swimages/). When you upgrade the firmware, the software analyzes the firmware installed on the array. If the firmware on the host is newer, and you choose to upgrade, the software performs an array firmware upgrade.
|
Note - For optimal performance, Sun Microsystems recommends that the firmware on all arrays be at the level of the current firmware baseline. |
1. On the Storage System Summary page, click the checkbox of the array you want to upgrade.
The Upgrade Firmware button is enabled.
The management software launches the Analyze and Upgrade Array Firmware wizard. Step 1, the Overview, is displayed.
Step 2, Analyze Arrays, is displayed.
4. In the Action field, specify the type of upgrade, and click Next.
Step 2.1 verifies that the array password is correct.

|
Caution - All management operations for the array should stop prior to the firmware upgrade. Disk I/O must be quiesced. |
6. Review the current selections, and click Finish.
7. When the upgrade is complete, click Close.
To set up the array for basic operation, perform the procedures outlined in the following sections:
The Administration page contains other features that you may decide to configure. See the online help for more information before you change any default settings.
Open the Administration page to perform array administration functions.
1. In the navigation pane, click on the array you want to work with to expand the navigation tree.
The navigation tree expands to display the configuration options for the selected array, including Administration.
2. Click on Administration, under the array you have selected.
The Administration page for that array is displayed.
After making any changes on the Administration page, click Save to save the changes.
A new Sun StorageTek array is shipped with a blank, or empty, password field. Sun recommends that you establish an array password during initial setup for security purposes. The password prevents other management hosts from unauthorized access to the configuration of the array.
1. On the Administration page, click Manage Passwords.
The Manage Passwords page is displayed.
2. Select Change Array Password.
3. Leave the Old Password field blank.
This is the only time you can leave this field blank, when you establish a password for a new array.
4. Enter a new password consisting of up to 30 characters for the array.
5. Enter the password again to confirm the new password.
The Administration page is redisplayed.
The management software stores an encrypted copy of the array password, known as the local password, on the management host.
Each array requires a unique name to be identified on the subnet.
In the Name field on the Administration page, enter a unique name consisting of up to 30 characters.
Hot spare drives are used by a controller to replace a disk that has failed. It is a good practice to define a hot spare before initiating storage on the array.
From the drop-down menu on the Administration page, select a drive to serve as a hot spare drive to provide alternative drive space in case of a failure. Refer to the online help for information about this and other advanced configuration features.
You can also update the system time and date on the Administration page for the array in the browser interface. When you set the time and date for a selected array, the values are updated for all arrays registered with this management software.
There are two ways in which you can update the system time and date:
1. On the Administration page, scroll down to the System Time section.
2. Select the current hour and minute according to a 24-hour clock.
3. If the date is incorrect, change the month, day, and year to the current date.
4. Click Save to save your changes.
The Administration page is refreshed, and Success message is displayed at the top of the page.
For more information about the fields and buttons on the Administration page that you can use after you set up your system, see the online help.
The General Configuration page contains information about the site, rather than the array, and differs from the Administration page. Enter the following information for your site:
The fault management features of the Sun StorageTek Common Array Manager software enables you to monitor and diagnose your arrays and storage environment. Alarm notification can be provided by:
1. In the navigation pane, under General Configuration, choose Notification.
The Notification Setup page is displayed:
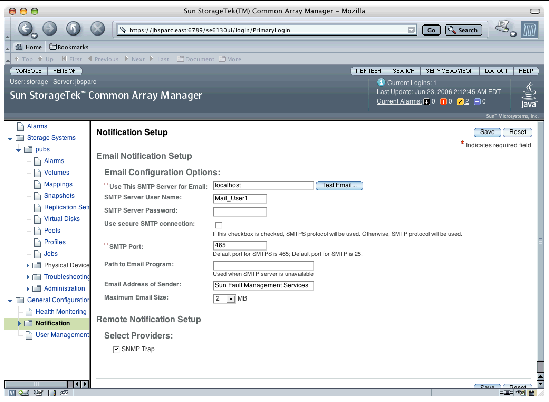
a. Enter the name of the SMTP server.
If the host running this software has the sendmail daemon running, you can accept the default server, localhost, or the name of this host in the required field.
b. Specify the other optional parameters, as desired.
c. If you have changed or entered any parameters, click Save.
d. (Optional) Click Test Local Email to test your local email setup by sending a test email.
If you need help on any of the fields, click the Help button.
3. Set up local email notification recipients.
a. Click Administration > Notification > Email.
The Email Notification page is displayed.
The Add Email Notification page is displayed.
c. Enter an email address for local notification. At least one address is required to begin monitoring events. You can customize emails to specific severity, event type, or product type.
4. (Optional) Set up remote notifications by SNMP traps to an enterprise management application.
a. Select SNMP as the provider.
5. Perform optional fault management setup tasks:
To set up the array for basic operation, perform the procedures outlined in the following sections:
The first time that you access your array software, you sign on as an administrator:
You then assign a user role of storage or guest to each user of the software. The storage role allows a user access to all of the software features related to storage device configuration and array management.
The storage and guest roles must be added to the management host using its OS software. For Solaris OS, consult system administration documentation. For Windows, add groups for storage and guest and assign members to those groups. Refer to Adding User Roles and New Users to Windows for additional information about adding roles in Windows.
The user role assigned to a user determines that user's access to the management functions for the array. TABLE 3-1 describes the valid user names and user role functions and the requirements for each.
1. Setting up with an administrative role.
In Solaris or Linux, by default, root has a storage role that allows full privileges. Before you can add other user and assign that user a user role, the user name must be defined in the Linux or Solaris Operating System /etc/passwd file or network information server (NIS).
In Windows, you can set up an administrative role with full privileges. You can even call it root, as noted in Adding User Roles and New Users to Windows.
2. Restrict use of the administrator role.
To maintain security on the server running the management host software, the root or administrator user name and password should be used only the first time you log in. At that time, create at least one user with a storage user role. Thereafter, that created user can perform all available management functions, including adding or modifying users.
3. Make rules for multiple users with storage roles.
Multiple instances of the same user name can be logged in concurrently. However, because users with the storage user role have write privileges, there is a risk that the changes of one logged-in user will overwrite previous changes of another logged-in user. Therefore, you should develop policies about who can make changes and how to notify others.
1. To view the list of defined users, choose General Configuration > User Management in the navigation pane.
The User Summary page is displayed.
2. To add a new user, click the Add button.
The Add New User page is displayed.Common Array Manager Add New User page where you can add a user name and assign a user role.
3. In the User Name field, enter a valid user name.
The user name must be defined in the /etc/passwd file or NIS.
4. From the User Role list, select the role you want to assign for this user.
You can assign a user to one of the user roles identified in TABLE 3-1.
The User Summary page is displayed with a success message, and the name is added to the list.
|
Note - Newly added users should enter the same password for the Sun Java Web Console that they use in their Linux or Solaris accounts. |
Refer to Adding User Roles and New Users to Windows.
Sun Connection is a remote notification service that submits device registration and fault event data to a Sun Microsystems service database. Common Array Manager provides the interface to activate Sun Connection on behalf of the devices it manages. It also provides the fault telemetry to notify the Sun service database of fault events on those devices. Depending on the Service Offering implemented by your service group, the data can be used to monitor the health and performance of your storage devices, improve system performance, and enable Sun service to respond faster and more accurately to critical on-site issues.
When you register for Sun Connection through the Common Array Manager, all the devices registered in Common Array Manager are registered to Sun Connection.
To register for Sun Connection:
1. In the navigation pane, under General Configuration, choose Sun Connection.
The Sun Connection Configuration page displays.
2. Enter your Sun online account name and password in the appropriate fields. If you do not have a Sun online account, register by clicking Sun Online Account Registration.
3. Identify the internet connection type your system uses. Choices are:
|
Note - If your computer uses a network proxy to connect to the Internet, check your computer's network proxy preferences for values for these parameters. |
If your system requires proxy authorization, select the Enable Proxy Authentication check box. Then you must also provide:
4. Select the Sun Connection Services you wish to receive. Choices are:
These services will apply to all storage systems managed by this Common Array Manager.
5. Once you have completed these fields to your satisfaction, read the Purpose Statement and click the OK button.
The registration parameters are saved and submitted to Sun Connection.
You are now ready to review the planning concepts that will help you to configure storage. If you are familiar with the concepts, you can proceed to Configuring Basic Storage.
Copyright © 2007, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.