| C H A P T E R 6 |
 Powering On the System
Powering On the System |
This chapter includes instructions for booting the server and for enabling the system controller network management port.
The following topics are included:
This section provides an overview and instructions for powering on your system the first time.
When you power on the system, the boot process begins under the control of the Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) system console. The system console displays status and error messages generated by firmware-based tests during system startup.
| Note - To see these status and error messages, connect a terminal or terminal emulator to the serial management port (SERIAL MGT). For a basic procedure to connect a terminal or terminal emulator, see To Power On the System for the First Time. |
For a more detailed discussion on configuring the system console and connecting terminals, refer to the Sun Netra T5220 Server Administration Guide.
After the system console finishes its low-level system diagnostics, the ILOM service processor initializes and runs a higher level of diagnostics. When you access the ILOM service processor using a device connected to the serial management port, you see the output of the ILOM diagnostics.
By default, the network management port is configured to automatically retrieve network configuration using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and to allow connections using Secure Shell (SSH).
| Note - If you are unable to use DHCP and SSH on your network, you must connect to the ILOM service processor using the serial management port to reconfigure the network management port. See Configuring the Service Processor Network Management Port. |
Once the network management port (NET MGT) has been assigned an IP address, you can connect to the ILOM service processor using SSH.
When connecting to the ILOM service processor for the first time using the serial or network management ports, the default CLI is ILOM, the default user account is root, and the default password is changeme. Examples in this document use the default ILOM CLI.
ILOM also provides an Advanced Lights Out Management (ALOM) compatability CLI that uses commands that resemble the ALOM CMT CLI commands. To access the ALOM compatability CLI, you must first create an admin account with the role of administrator. Once you create the admin account, assign the ALOM compatability CLI as the default CLI (role=administrator, cli=alom). For more information on using the ALOM compatability CLI, refer to the Integrated Lights Out Management 2.0 (ILOM 2.0) Supplement for Sun Netra T5220 Server.
|

The service processor runs on the 3.3V standby voltage. As soon as AC power is connected to the system, the service processor powers on, runs diagnostics, and initializes the ILOM firmware.
1. Connect a terminal or a terminal emulator (PC or workstation) to the service processor serial management port.
Configure the terminal or terminal emulator with these settings:
2. Turn on the terminal or terminal emulator.
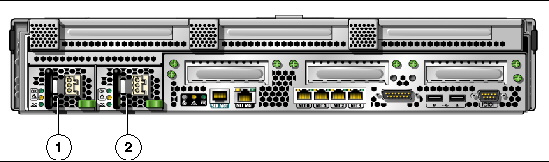
3. Connect the AC power cables to Power Supply 0 and Power Supply 1. Watch the terminal for system messages.
FIGURE 6-1 Rear Panel Power Connectors of a Sun Netra T5220 Server
After the service processor boots, the service processor login prompt is displayed on the serial console. The following example shows a partial output from the service processor boot sequence leading to the login prompt.
In hard drive HDD0, the Solaris OS is preinstalled.
 If you do not want to start the preinstalled OS, set the OBP parameter auto-boot? to false. For example from the ILOM CLI:
If you do not want to start the preinstalled OS, set the OBP parameter auto-boot? to false. For example from the ILOM CLI:
The service processor network management port is not operational until you configure network settings for the service processor. Configure the service processor in this order:
1. After the service processor boots, access the ILOM CLI through the serial management port. See To Log In To the Service Processor Using the Serial Management Port.
2. Configure the service processor. See Configuring the Service Processor Network Management Port.
3. Commit the changes to the service processor parameters. See Step 7 in To Power On the System for the First Time.
You can now use the network management port at any time to access the service processor. See To Log In To the Service Processor Using the Network Management Port.
If you are powering on the system for the first time after installation, use the service processor serial port to power on the system and run POST. See To Log In To the Service Processor Using the Serial Management Port.
If the network management port has already been configured, you can use it instead of the serial management port. See To Log In To the Service Processor Using the Network Management Port.
|
After the service processor boots, access the ILOM CLI to configure and manage the system. The ILOM CLI prompt (->) is displayed at the first time the service processor is booted. The default configuration provides an ILOM CLI root user account. The default root password is changeme. Change the password using the service processor ILOM CLI password command.
1. If this is the first time the system has been powered on, use the password command to change the root password.
| Note - After the root password has been set, on subsequent reboots, the ILOM CLI login prompt is displayed. |
2. Enter root for the login name followed by your password.
| Note - If your network allows the use of DHCP and SSH, this configuration is performed automatically the first time you boot the system. |
In this procedure, you connect to the ILOM service processor using the serial management port to manually reconfigure the network management port.
| Note - For more information on configuring ILOM, refer to the Integrated Lights Out Management 2.0 (ILOM 2.0) Supplement for Sun Netra T5220 Server. |
Set these network parameters according to the specific details of your network configuration:
Configure these parameters with the set command. The usage is as follows:
set target property=value where /SP/network is the target and pendingipaddress=xx.x.xx.xxx, for example, is the property=value. The following example sets the pending service processor IP address:
1. Set the /SP/network state parameter to enabled.
2. Enable and disable SSH connections as needed.
-> set /SP/services/ssh state=enabled Set 'state' to 'enabled' -> set /SP/services/ssh state=disabled Set 'state' to 'disabled' |
See the Integrated Lights Out Management 2.0 (ILOM 2.0) Supplement for Sun Netra T5220 Server for more information about SSH support in ILOM.
3. Choose one of these methods to configure the service processor using information from your network administrator:
4. If you choose to use DHCP, set pendingipdiscovery to dhcp.
Go to Step 6.
5. If you choose to use a static IP configuration, set the parameters pendingipdiscovery, pendingipaddress, pendingipgateway, and pendingipnetmask as follows.
a. Set the service processor to accept a static IP address.
b. Set the IP address for the service processor.
-> set /SP/network pendingipaddress=service-processor-IPaddr Set 'pendingipaddress' to 'service-processor-IPaddr' |
c. Set the IP address for the service processor gateway.
d. Set the netmask for the service processor.
This example uses 255.255.255.0 to set the netmask. Your network environment subnet might require a different netmask. Use a netmask number most appropriate to your environment.
6. Use the show /SP/network command to verify that the parameters were set correctly.
| Note - After setting the configuration parameters, you must enter the set /SP/network commitpending=true command for the new values to take affect. |
7. Commit the changes to the service processor network parameters.
|
It is not necessary to reset the service processor for new network values to take effect. To commit the changes to the service processor network parameters, use the
set /SP/network commitpending=true command. See Step 7 in Configuring the Service Processor Network Management Port.
You are prompted to confirm that you want to reset the service processor. Reply y when prompted.
| Note - You can specify the -script option to bypass the confirmation question, for example, reset -script /SP. |
The service processor resets, runs diagnostics, and returns to the login prompt.
|
| Note - You must configure the service processor parameters shown in Configuring the Service Processor Network Management Port before you can use the network management port. |
 Open an SSH session and connect to the service processor by specifying its network address.
Open an SSH session and connect to the service processor by specifying its network address.
| Note - For more information on using the ILOM service processor, refer to the Integrated Lights Out Management 2.0 (ILOM 2.0) Supplement for Sun Netra T5220 Server. |
|
1. Perform the following steps to verify that there are no faults:
a. Set the virtual keyswitch to diag mode so that POST will run in Service mode.
b. To initiate the power on sequence, type the start /SYS command.
You see an ILOM CLI alert message on the system console. This message indicates that the system has reset.
c. Switch to the system console to view POST output.
Watch the POST output for possible fault messages. The following output is a sign that POST did not detect any faults:
2. Check the POST execution result with the following command:
3. Use the set /SYS keyswitch_state=normal command to return the virtual keyswitch to Normal mode (default) so that the system can power on and start the boot process.
|
Output from POST, OpenBoot, and the Solaris OS is displayed in the system console using the network console on the service processor.
 Type the start /SP/console command.
Type the start /SP/console command.
Multiple users can be connected to the console, but only one can be attached.
-> start /SP/console Are you sure you want to start /SP/console (y/n)? y Serial console started. To stop, type #. |
| Note - For more information about POST output, refer to the Sun Netra T5220 Server Service Manual. |
|
After you issue the start /SYS command, the CPU and memory controllers initialize, and eventually OpenBoot initializes. After a number of system console messages, the ok prompt appears, or the system will boot into the Solaris OS.
| Note - System behavior depends on how the auto-boot variable is set. See the Sun Netra T5220 Server Service Manual for more information. |
The following example output is a small section of the complete output.
To understand the various devices and their path names as represented in the OpenBoot device tree, refer to TABLE 6-1 for disks and TABLE 6-2 for optional PCI cards.
|
Logical Device Name[1] |
||
|---|---|---|
The Solaris OS is preinstalled on the servers on the disk in slot 0. The Solaris OS is not configured (that is, the sys-unconfig command was run in the factory). If you boot the system from this disk, you will be prompted to configure the Solaris OS for your environment.
|
1. At the ok prompt, boot from the disk that contains the Solaris OS.
2. Type the boot command at the ok prompt.
Use the value from Step 1 to construct the boot command. You must append the target to the disk path.
In the following example, the system is being booted from disk 0 (zero) on a Sun Netra T5220 server from Oracle. Thus, @0,0 is appended to the disk path.
|
 If it is necessary to reset the system, use the shutdown -g0 -i6 -y command.
If it is necessary to reset the system, use the shutdown -g0 -i6 -y command.
It is not necessary to power the system off and on to simply reset the system.
|
If a simple reset does not clear a system problem, you can power the system off and on with this procedure.
At the Solaris OS prompt, type the shutdown -g0 -i0 -y command and then type h when prompted to halt the Solaris OS and to return to the ok prompt.
2. Switch from the system console prompt to the service processor console prompt by issuing the #. escape sequence.
3. Using the ILOM CLI, type the stop /SYS command to perform a graceful shutdown of the system.
4. Type the start /SYS command.
| Note - To force a power on sequence, use the start -script /SYS command. |
5. Reconnect to the system console with the start /SP/console command.
-> start /SP/console Are you sure you want to start /SP/console (y/n)? y Serial console started. To stop, type #. |
The systems displays various messages, followed by the ok prompt.
After powering on the system for the first time, you can use the Sun Validation Test Suite (SunVTS ) software to verify the functionality and performance of any installed components, as well as its network connections. Refer to the SunVTS documentation at http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/indexes/documentation/index.html for more information.
) software to verify the functionality and performance of any installed components, as well as its network connections. Refer to the SunVTS documentation at http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/indexes/documentation/index.html for more information.

Copyright © 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.