Chapter 1 Introduction to ONC+ Technologies
This section is a short introduction to ONC+ technologies, the Sun Microsystem's open systems distributed computing environment. The ONC+ technologies are the core services available to developers who implement distributed applications in a heterogeneous distributed computing environment. ONC+ technologies also includes tools to administer client/server networks.
Figure 1-1 shows an integrated view of how client-server applications are built on top of ONC+ technologies, and how they sit on top of the low-level networking protocols:
Figure 1-1 ONC+ Distributed Computing Platform
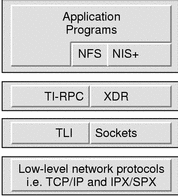
Brief Description of ONC+ Technologies
ONC+ technologies consist of a family of technologies, services, and tools. It is backward compatible, and interoperates with the installed base of ONC services. The main components are described. This guide covers the technologies that require the use of programming facilities.
TI-RPC
Transport-independent remote procedure call (TI-RPC) was developed as part of the UNIX System V Release 4 (SVR4). It makes RPC applications transport-independent by allowing a single binary version of a distributed program to run on multiple transports. Previously, with transport-specific RPC, the transport was bound at compile time so that applications could not use other transports unless the program was rebuilt. With TI-RPC, applications can use new transports if the system administrator updates the network configuration file and restarts the program. Thus, no changes are required to the binary application.
XDR
External data representation (XDR) is an architecture-independent specification for representing data. It resolves the differences in data byte ordering, data type size, representation, and alignment between different architectures. Applications that use XDR may exchange data across heterogeneous hardware systems.
NFS
NFS is the Sun Microsystems distributed computing file system that provides transparent access to remote file systems on heterogeneous networks. In this way, users can share files among PCs, workstations, mainframes, and supercomputers. As long as they are connected to the same network, the files appear as though they are on the user's desktop. The NFS environment features Kerberos V5 authentication, multithreading, the network lock manager, and the automounter.
NFS does not have programming facilities, so it is not covered in this guide. However, the specification for NFS is available through anonymous ftp. See "Related Books and Sites" for more information.
NIS+
NIS+ is the enterprise naming service in the Solaris environment. It provides a scalable and secure information base for host names, network addresses, and user names. It makes administration of large, multivendor client/server networks easier by being the central point for adding, removing, and relocating network resources. Changes made to the NIS+ information base are automatically and immediately propagated to replica servers across the network; this ensures that system uptime and performance is preserved. Security is integral to NIS+. Unauthorized users and programs are prevented from reading, changing, or destroying naming service information.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
