Receiving a JMS Text Message
This topic provides instructions for building a Message-Driven Bean (MDB) that will monitor a designated queue on a JMS destination (of the JMS Server) in order to receive JMS messages. Upon receipt of the a JMS message, the MDB will print out the content of the message if it is of the type TextMessage.
Perform the following steps to receive a JMS text message:
 To Create an Admin Object Resource
To Create an Admin Object Resource
For this example, the message is being received from Queue1, so you need to create the corresponding JMS Queue object resource in GlassFish.
-
Start the GlassFish server and use a browser to connect to the Admin Console.
The URL for the Admin Console is http://HostName:PortNumber. The default port number is 4848.
-
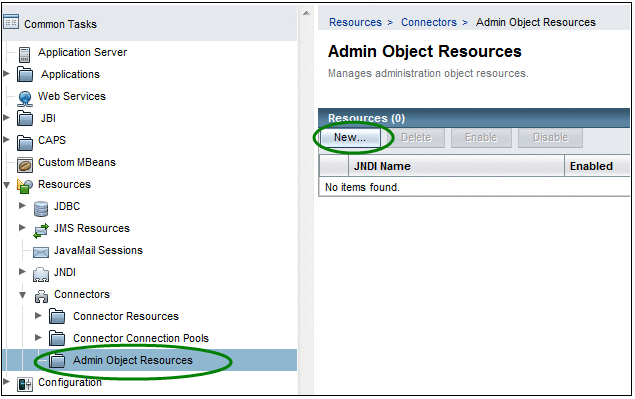
In the left navigation bar, expand Resources and Connectors and then select Admin Object Resources.
Figure 1 Admin Object Resources
-
Click New.
The New Admin Object Resource window appears (Step 1 of 2).
-
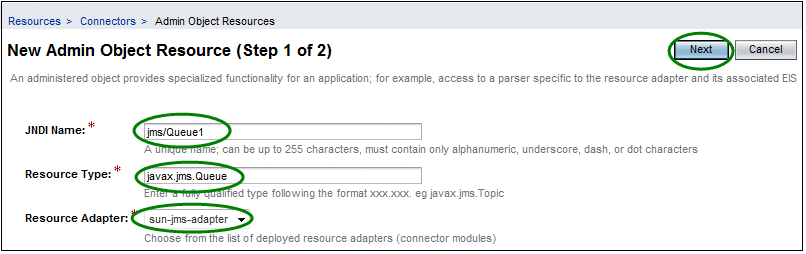
Fill in the required fields.
For the purposes of this exercise, use the following values:
-
JNDI Name = jms/Queue1
-
Resource Type = javax.jms.Queue
-
Resource Adapter = sun-jms-adapter
Figure 2 New Admin Object Resources (Step 1 of 2)
-
-
Click Next.
-
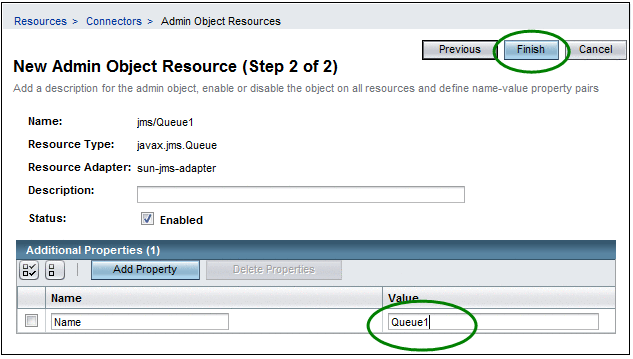
Enter a name for the resource.
For this exercise, enter Queue1. This is the physical destination name of the resource.
Figure 3 New Admin Object Resources (Step 2 of 2)
-
Click Finish.
 To Create the EJB Module Project
To Create the EJB Module Project
-
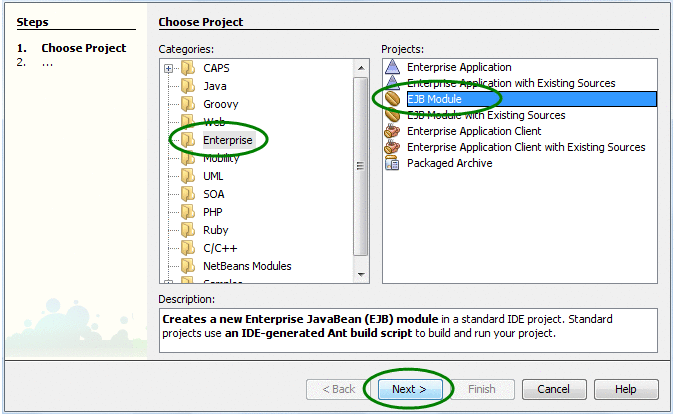
Right–click in the Projects Panel of the NetBeans IDE and select New Project.
-
On the New Project Wizard, select Java EE under Categories, and then select EJB Module under Projects.
Figure 4 Choose New Project
-
Click Next.
The Name and Location window appears.
-
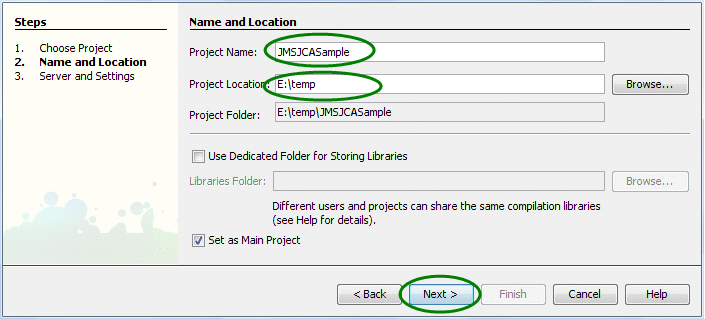
Enter the Project Name and Location fields.
For the purposes of this exercise, enter the following values:
-
Project Name = JMSJCASample
-
Project Location = the location to store NetBeans project files
Figure 5 EJB Module Project Name and Location
-
-
Click Next.
The Server and Settings window appears.
-
In the Server and Settings window, keep the default values for all fields.
-
Click Finish.
 To Create the JCA Message-Driven Bean
To Create the JCA Message-Driven Bean
-
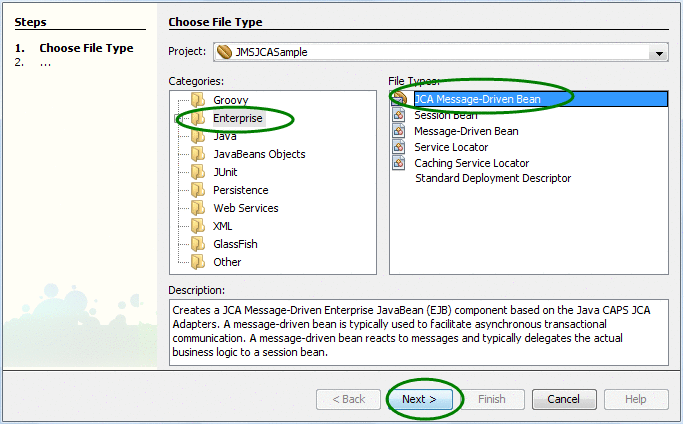
Right-click on the Project node, and then select New->Other.
-
On the wizard, select Java EE under Categories, and select JCA Message-Driven Bean under File Types.
Figure 6 Choose JCA Message-Driven Bean
-
Click Next.
The JCA Message-Driven Bean Name and Location window appears.
-
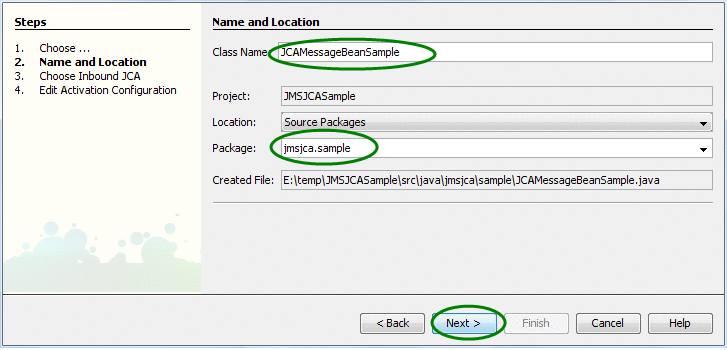
Enter the Name and Location fields.
For this exercise, enter the following values:
-
Class Name = JCAMessageBeanSample
-
Package = jmsjca.sample
Figure 7 JCA Message-Driven Bean Name and Location
-
-
Click Next.
The Choose Inbound JCA window appears.
-
Select JMS Adapter and click Next.
Note –Currently only JMS Adapter can be selected in the window.
The Edit Activation Configuration window appears.
-
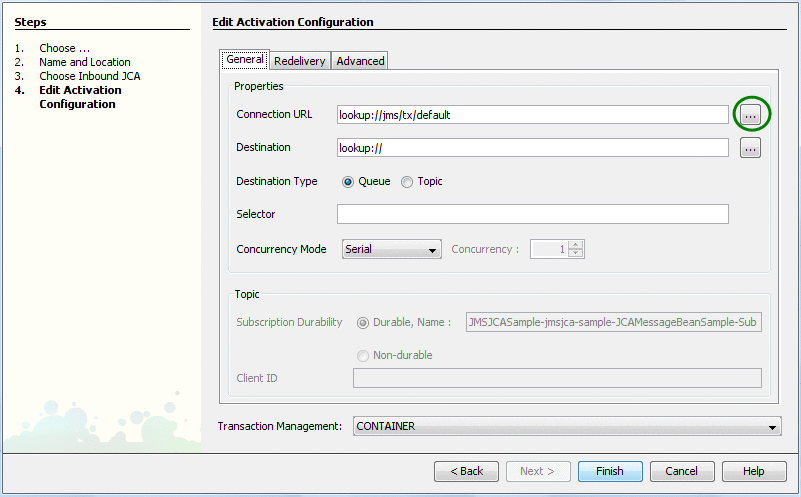
Configure the Inbound JMS connection by clicking on the ellipsis button next to the Connection URL box (as shown below).
You can configure many different options for the Inbound JMS connection, such as the JNDI name of the JMS connection resource or the JNDI name of the JMS destination. You can also configure the more advanced options such as message re-delivery, selector, concurrency mode, and so on. In this simple case, only the Connection URL and Destination options for our sample code to work.
Figure 8 Edit Activation Configuration
-
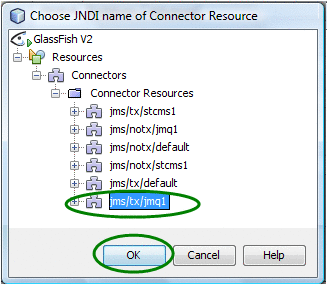
Expand the tree node all the way and select jms/tx/jmq1 (as shown below).
This resource connects the embedded Sun MQ JMS server inside the GlassFish server and is created by default with the installer. The default connection URL is mq://localhost:7676.
Figure 9 Connector Resource — Connection URL
-
Click on the ellipsis button next to Destination box.
The Connector Resource dialog box for the Destination appears.
-
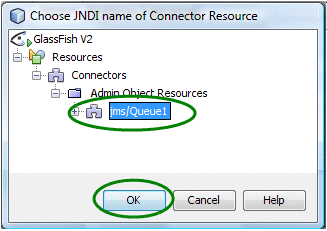
Expand the tree node all the way and select jms/Queue1 (as shown below).
This is the Admin Object Resource created earlier for the Queue1 destination using the GlassFish Admin Console.
Figure 10 Connector Resource — Destination
-
Click Finish.
A Java source file is created and opened in the editor view. The source file is a skeleton file with most of the boilerplate code already generated, as shown below.
Figure 11 Java Source Code
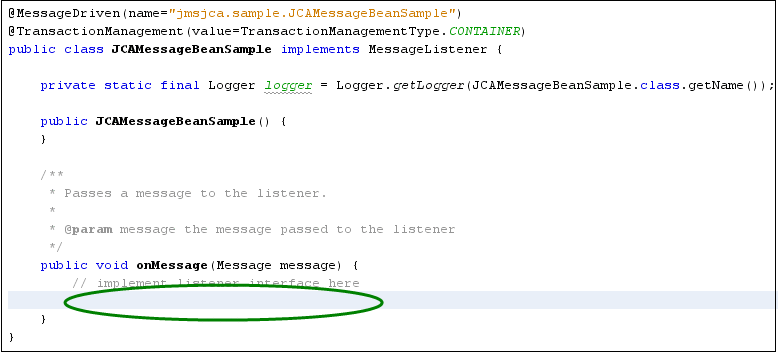
Any JMS messages sent to the Queue1 destination are passed to the onMessage(...) method in this Java file. The login can be processed inside the onMessage() method as needed. Because the purpose of this task is to simply print out the message content of the JMS message (if the message is of type javax.jms.TextMessage), the implementation code would be similar to the following:
public void onMessage(Message message) { try { if (message instanceof javax.jms.TextMessage) { logger.log(Level.INFO, "JMS message conecnt is: " + ((javax.jms.TextMessage) message).getText()); } } catch (JMSException ex) { Logger.getLogger(JCAMessageBeanSample.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); return; } }
Note –The above code has been wrapped to fit the page.
-
Click Save when you are done editing the file.
 To Test the Sample Code
To Test the Sample Code
-
Right-click the Project node and select Build.
-
When the build process is complete, right-click the Project node and select Undeploy and Deploy.
-
Use a JMS client to send a text message to Queue1 on the to JMS server (located at mq://localhost:7676, by default).
The contents of the message is logged in the server log file.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
