Process of Federation
The process of federation begins with authentication. A standard installation of Access Manager provides two options for user authentication: the proprietary Authentication Service and the Liberty-based Federation component. With the proprietary option, users attempting to access a resource protected by Access Manager are redirected to the Authentication Service via an Access Manager login page. After the users provide credentials, the Authentication Service allows or denies access to the resource based on the outcome.
Note –
For more information about the proprietary Authentication Service, see the Sun Java System Access Manager 7.1 Administration Guide.
The second option for user authentication is Liberty-based federation. When a principal attempts to access a web site that belongs to the trusted member provider of a configured authentication domain, the process of user authentication begins with the search for a valid Access Manager session token from the proprietary Authentication Service.
-
If no session token is found, the principal is redirected to a location defined by the pre-login URL to establish a valid session. See Pre-login Process for details.
-
If a session token is found, the principal is granted (or denied) access to the requested page. Assuming access is granted, the requested page contains a link so the principal can federate the Access Manager identity with the identity local to the requested site. If the principal clicks this link, federation begins. See Federation and Single Sign-On for details.
The following figure illustrates these divergent paths.
Note –
The process shown in the figure below is the default process when no application has been deployed. When an application is deployed and using Access Manager, the process will change based on the application's query parameters and preferences. For more information, see The Pre-login URL.
Figure 3–1 Default Process of Federation
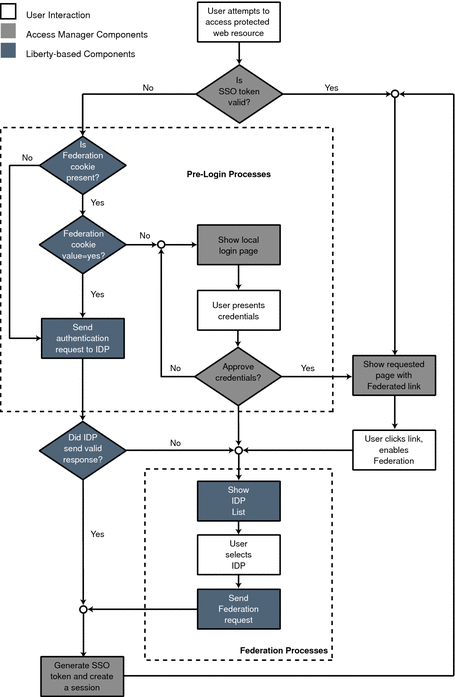
Pre-login Process
The pre-login process establishes a valid Access Manager session. When a principal attempts to access a service provider site and no Access Manager session token is found, Access Manager searches for a federation cookie. A federation cookie is implemented by Access Manager and is called fedCookie. It can have a value of either yes or no, based on the principal’s federation status.
Note –
A federation cookie is not defined in the Liberty Alliance Project specifications.
At this point, the pre-login process may take one of the following paths:
-
If a federation cookie is found and its value is no, an Access Manager login page is displayed and the principal submits credentials to the proprietary Authentication Service. When authenticated by Access Manager, the principal is redirected to the requested page, which might contain a link to allow for identity federation. If the principal clicks this link, federation begins. See Federation and Single Sign-On for details.
-
If a federation cookie is found and its value is yes, the principal has already federated an identity but has not been authenticated by an identity provider within the authentication domain for this Access Manager session. Authentication to Access Manager is achieved on the back end by sending a request to the principal’s identity provider. After authentication, the principal is directed back to the requested page.
-
If no federation cookie is found, a passive authentication request (one that does not allow identity provider interaction with the principal) is sent to the principal’s identity provider. If an affirmative authentication is received back from the identity provider, the principal is directed to the Access Manager Authentication Service, where a session token is granted. The principal is then redirected to the requested page. If the response from the identity provider is negative (for example, if the session has timed out), the principal is sent to a common login page to complete either a local login or Liberty-based federation. See Federation and Single Sign-On for details.
Note –
This pre-login process is the default behavior of Access Manager. This process might change based on parameters passed to Access Manager from the participating application. For more details, see the section on The Pre-login URL.
Federation and Single Sign-On
When a principal logs in to access a protected resource or service, Access Manager sends a request to the appropriate identity provider for authentication confirmation. If the identity provider sends a positive response, the principal gains access to all provider sites within the authentication domain. If the identity provider sends a negative response, the principal is directed to authenticate again using the Liberty-based federation process.
In the Liberty-based federation process, a principal selects an identity provider and sends credentials for authentication. After authentication is complete and access is granted, the principal is issued a session token from the Access Manager Authentication Service and redirected to the requested page. As long as the session token remains valid, the principal can access other service providers in the authentication domain without having to authenticate again.
Note –
Common Domain Services for Federation Management are used by a service provider to determine the identity provider used by a principal in an authentication domain that contains multiple identity providers. See Chapter 4, Common Domain Services for Federation Management for details.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
