Chapter 3 Sharepoint Integration With Sun GlassFish Web Space Server
Once you install the Sharepoint Add-On users can access Sharepoint services through Web Space Server. Windows Sharepoint Services 3.0 is a built-in component of Windows Server 2003. Microsoft Windows Sharepoint Services 3.0 is a versatile technology that organizations and business units of all sizes can use to increase the efficiency of business processes and improve team productivity. With tools for collaboration that help people stay connected across organizational and geographic boundaries, Windows Sharepoint Services gives people access to information they need.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Prerequisites for Sharepoint Integration
The following are the prerequisites for Sharepoint integration:
-
Microsoft Windows 2003 Enterprise Server SP2 installed on a host that is configured as a domain controller.
-
Microsoft Windows SharePoint Services version 3 installed on the domain controller or on a separate host within the domain.
-
Sun GlassFish Web Space Server software installed on a separate host.
You need the following information:
-
Name of the Windows domain.
-
Hostname of the Windows domain controller and the credentials for Active Directory access.
-
Hostname where the SharePoint Services are installed and administrator credentials.
-
Sun GlassFish Web Space Server software installed on a separate host with users having the same email address as defined in the Windows domain. The Email address is needed for LDAP authentication. If ldap://nicp123.wss.test.com:389 is the Base Provider URL, the domain controller in the LDAP directory contains dc=wss,dc=test,dc=com.
Introduction to Sharepoint Integration
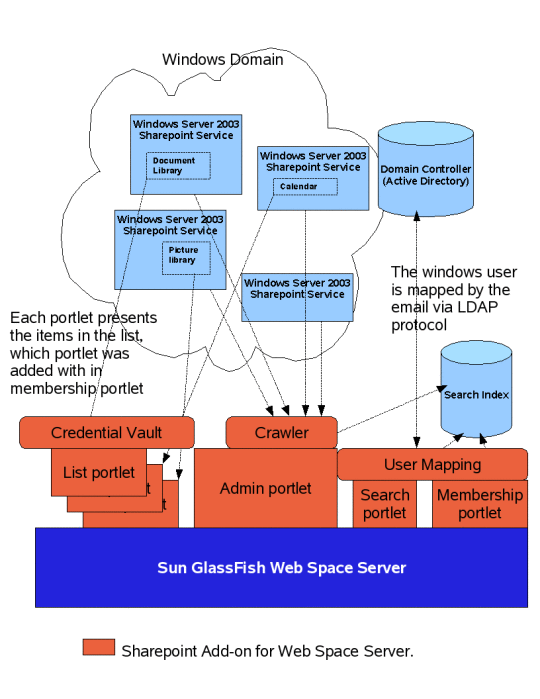
Windows Sharepoint Services 3.0 is freely available for Windows Server 2003, so any machine running Windows Server 2003 can download and install Sharepoint Service 3.0. Web Space Server provides a set of services similar to Sharepoint, such as Calendar, Discussion, Tasks, Announcement, Wiki and Blog. For the users who want to keep existing services/data, the solution we provide here is to allow users to access Sharepoint services through Web Space Server. Sharepoint integration is provided by the Sharepoint Add-on, which can be installed on Web Space Server.
The add-on itself is in a single war file, so the installation is simple. The deployed war file includes the following components:
Table 3–1 Components in the WAR file for Sharepoint Add-On|
Add-On Component |
Description |
|
Admin portlet |
Configures/controls user mapping and crawler. |
|
Sharepoint Crawler |
Aggregates sharepoint sites data into Web Space Server search index. |
|
User Mapping |
Maps a portal user to a sharepoint services active directory user. |
|
Search portlet |
Provides a search user interface for indexed Sharepoint data. |
|
Membership portlet |
Uses the metadata of indexed sites and user mapping to present expandable list of sites (which can be added as WSS List portlets) to portal users who has membership (with contribute privilege). |
|
WSS List portlet |
Portlet to access a Sharepoint List. Multiple portlets can be added via the UI in membership portlet on a selected Sharepoint List, such as Calendar, Document Library. |
Figure 3–1 Sharepoint integration architecture
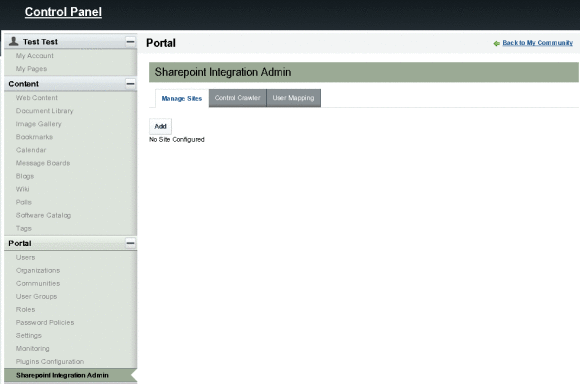
Using the Sharepoint Integration Admin Portlet
The Sharepoint Integration Admin portlet provides Manage Sites, Control Crawler, and User Mapping tabs.
Figure 3–2 Sharepoint Integration Admin Portlet
Manage Sites Tab
Manage Sites tab enables you to add/modify/delete sharepoint sites. You need to authenticate the site that you add by providing its administrator user name and password. You can enable or disable the site for crawling.
 To Add a Sharepoint Site
To Add a Sharepoint Site
-
Log in to Web Space Server as the admin user.
-
From the Welcome menu, navigate to Control Panel -> Sharepoint Integration Admin under Portal category.
-
Click the Add button on the Manage Sites tab.
-
In the Sharepoint site window, type the URL of the Sharepoint site, and the user name and password of the Active Directory administrator.
This example illustrates adding a Sharepoint site named http://nicp123.wss.test.com. Administrator is the username of the Active Directory administrator.
Figure 3–3 Adding a Sharepoint Site
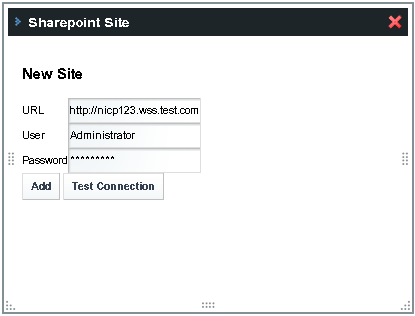
-
Click the Test Connection button.
-
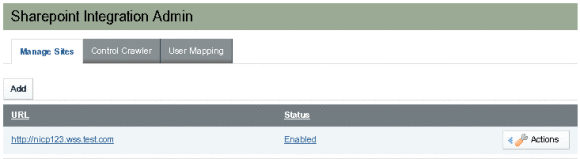
When a site is added successfully, its URL and status are displayed in the Manage Sites tab.
The site is Enabled by default. You can switch the status from Enabled to Disabled and back again. The Actions button next to a site name enables you to edit or delete the site.
Figure 3–4 Sharepoint Site Added Successfully
Control Crawler Tab
You can start or stop the crawler from this tab. You can start the crawler after you add a Sharepoint site. The crawler crawls the information available on the Sharepoint site added from the Manage Sites tab in the Sharepoint Integration Admin portlet.
Web Space Server uses the Sharepoint search crawler to examine Sharepoint site URLs and associated network resources such as Sharepoint lists (like calendars and alerts), so that they can be indexed in a site search database and a content search database used by the membership and the search portlets.
Figure 3–5 Control Crawler Tab
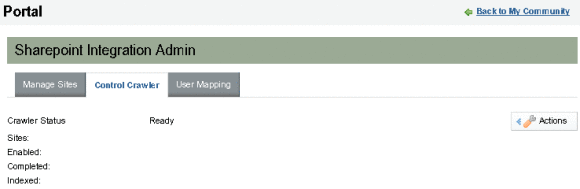
The Ready status means that the crawler has not started. To start crawling Sharepoint sites, click Start Crawler from the Actions menu. After the crawling is complete, the Crawler status is Stopped.
It also displays the other information related to crawling status, including the number of sites crawled, the number of sites which are enabled for crawling, and the number of sites for which the crawling is completed.
Indexed displays the number of metadata items collected. When a new metadata item is added, all the metadata is automatically reindexed. But if changes are made only in the Active Directory, the crawler might not reindex the metadata. If this situations occurs, choose Clean Running Status, and Remove Index from the Actions menu. Then restart the crawler by selecting Start Crawler.
Figure 3–6 Crawling a Sharepoint Site
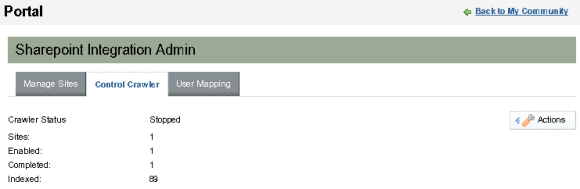
Choosing Actions Menu Options
The Actions menu has Start Crawler, Clean Running Status, and Remove Index options.
- Start Crawler
-
When you select Start Crawler, the crawler starts indexing all the metadata. The Crawler Status changes from Ready to Running, and when the crawling is completed, it changes to Stopped.
- Clean Running Status
-
The "Status" records the last-modified of a crawled object (site, list or item), so the next crawl will only update the index of those items changed since last crawl. When need to crawl all objects disregarding the time stamp, then we need to clean the status (database). Running Clean Running Status cleans the status.
- Remove Index
-
After cleaning the status, the crawler runs just as the very first time. If you want to re-index all the metadata, you need to select the Clean Running Status and Remove Index options consequently. If the Sharepoint site has no changes, you will see exactly the same number of indexed items.
User Mapping Tab
The User Mapping tab enables you to map the users on the Sharepoint site with the users on Web Space Server. This page allows you to define Active Directory authentication for the users defined in the Sharepoint Active Directory. An authentication search filter is applied to map users in Web Space Server with the users in the Sharepoint Active Directory. For example, if mail=@email_address@ is the authentication search filter, all users who have a common email address in both Sharepoint and Web Space Server are mapped together.
Figure 3–7 User Mapping Tab
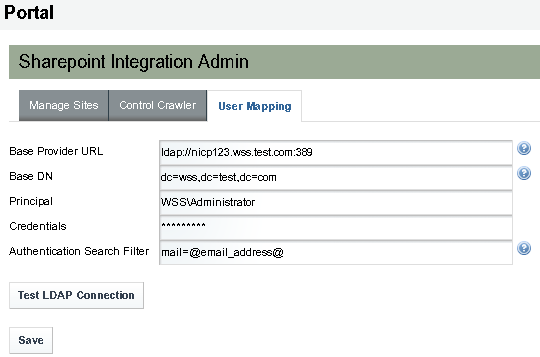
Defining Active Directory Authentication
You need to provide information in the following fields in the User Mapping tab to define Active Directory authentication.
Table 3–2 Defining Active Directory Authentication|
Attribute |
Vaule |
Description |
|
Base Provider URL |
ldap://host:389 For example, ldap://nicp123.wss.test.com:389 |
Active directory URL of domain controller |
|
Base DN |
domain_name |
Base DN of Active Directory domain (such as dc=wss,dc=test,dc=com) This specify the initial search context for users. Specifying the base DN is optional. |
|
Principal |
admin_name with Domain For example, WSS/Administrator, where WSS is the domain controller domain name in wss.test.com |
Active directory administrator user name |
|
Credentials |
admin_password |
Active directory administrator password |
After you define the Active Directory Authentication, click the Test LDAP connection button. If the connection is authenticated, the Web Space has successfully connected to the Active Directory servermessage appears.
Defining the Authentication Search Filter
If @email_address@ is the search token during runtime, the system looks for the users in the Active Directory with the same email address as in their Web Space Server user account, and such users are authenticated.
In this example, type mail=@email_address@ as the Authentication Search Filter. LDAP search authentication requires selecting mail=@email_address@ as the Authentication Search Filter.
The Authentication Search Filter can also use other tokens, such as @company_id@, @screen_name@, and @user_id@.
How Does Crawler Work?
Just like a web crawler, a set of site collection URLs are defined through the admin portlet as starting points. The crawler, however, is using the web service provided in Sharepoint service for retrieving data. It keeps track of timestamps of each site, list and item to avoid unnecessary data retrieving and indexing. The data collected are indexed into Web Space Server as search index. ACL and Membership are part of metadada indexed, so it is import that all Sharepoint services should run in a single windows domain; the same domain defined in the user mapping described in the next section.
User Mapping Between Web Space Server and Sharepoint Service
Microsoft Windows uses its domain controller (Active Directory) to manage user identity, and most of the applications from Microsoft and many other third party vendors use Active Directory by default. For example, Sharepoint uses the authentication model built-in with IIS, for user authentication and permission. In a out-of-box environment, there is no form based authentication (by session cookie) for a web application, so any client application communicating with the web server must use either Basic Authentication (if enabled in IIS), NTLM or Kerberos.
Web Space Server has the capability of using the same Active Directory for authentication, which can be configured via control panel of administrator. It can also import Active Directory users into Web Space Server user database. However, in order to loosen the dependency on this configuration, Sharepoint add-on has its own Active Directory configuration for user mapping.
The mapping is to retrieve a user name in windows domain for a given portal user with matching email by default. Consider that an Active Directory lookup by email id is defined in the user attribute of Web Space Server. If the email id is found, the user name will be available in DOMAIN\USRENAME format. This user name is used to perform secure search on indexed Sharepoint data in both Membership portlet and Search portlet.
 To Add a User on Active Directory to Web Space Server
To Add a User on Active Directory to Web Space Server
Consider that Active Directory on the Sharepoint site (in this example, nicp123.wss.test.com) has a user named Paul with the email ID paul@wss.test.com. To add the user to Web Space Server, you need to create a new user on Web Space Server with paul@wss.test.com as the email ID. Then you need to login to Web Space Server, with paul@wss.test.com as the username, and add the Sharepoint Membership Portlet to your page. The Sharepoint Membership Portlet displays the Sharepoint sites for which the user is registered.
Note –
When an email ID is defined as the Authentication Search Filter (that is when the Authentication Search Filter is mail=@email_address@), only the email ID of the user registered on Web Space Server and the email ID of the user in the Active Directory on the Sharepoint site need to match. Any other user information and the password are not required to be identical.
-
Log in to Web Space Server as the admin user.
-
Navigate to Control Panel -> Users under Portal category.
-
Click Add.
-
Specify the user details.
In this example, type paul@wss.test.com as the email ID.
-
Click Save.
-
Select Password under User Information.
-
Specify a password and click Save.
CredentialVault Service
Sharepoint service is a web application running on Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), and it suites the authentication model within IIS. There are different ways of authentication on IIS, but out-of-box, it supports Basic Authentication (if enabled in IIS), NTLM and Kerberos if enabled. While talking to Sharepoint service in WSS List portlet via its web service interface, it needs to be able to handle those authentication schema in a http connection as well.
The CredentialVault service is used to store user credentials (such as user name and password) for the Sharepoint sites where you have an account. You can use the CredentialVault service to define the scope (realm) that user credentials are accepted (such as a Sharepoint site URL). For example, when you specify user credentials for the site http://nicp123.wss.test.com, it defines the realm for all the services listed under the site, while all added WSS List portlets within the site use the stored credential for communicating with the web service.
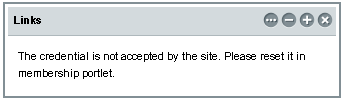
If you add a Sharepoint Service (List) as a portlet when the credential is not set in the site url, or if the credentials are wrongly set, the portlet do not display any of the resources, and displays a message saying The credential is not accepted by the site. Please reset it in membership portlet. The following is an example of a Sharepoint Service added as a portlet, when CredentialVault is set improperly:
Figure 3–8 The message displayed on a WSS List portlet when the CredentialVault is not set
Using the Sharepoint Search Portlet
The Sharepoint user on Web Space Server can use the Sharepoint Search portlet to search the indexed Sharepoint data as the windows user he/she is mapped. The search query syntax is based on the underlying search engine. Lucene is the default search engine on Web Space Server, and the Sharepoint Search portlet users the Lucene search syntax by default.
 To Use the Sharepoint Search Portlet
To Use the Sharepoint Search Portlet
-
Log in to Web Space Server as the user mapped to the Sharepoint Active Directory.
In this example, log in with paul@wss.test.com as the user name.
-
From the Welcome menu, navigate to My Places -> My Community -> Private Pages.
-
Choose Add Application from the Welcome menu, and add the Sharepoint Search portlet to the page.
-
Specify a search key, and click Search.
All the resources associated with the search key are displayed.
Using the Sharepoint Membership Portlet
After creating a Web Space Server user with an email id which is same as the email id of the user in the Active Directory on a Sharepoint site, login to Web Space Server as the new user, and add the Sharepoint Membership portlet to a page. The Sharepoint Membership portlet uses the metadata of indexed sites and user mapping to present expandable list of sites (which can be added as WSS List portlets) to portal users who has membership (with contribute privilege).
 To Use the Sharepoint Membership Portlet
To Use the Sharepoint Membership Portlet
-
Log in to Web Space Server as the user mapped to Sharepoint Active Directory.
In this example login with paul@wss.test.com as the user name.
-
From the Welcome menu, navigate to My Places -> My Community -> Private Pages.
-
Select Add Page to add a new page, specify a name for the Page, and click Save.
In this example, name the page Sharepoint View.
-
Choose Add Application from the Welcome menu, and add the Sharepoint Membership portlet to the page.
The page lists the mapped Sharepoint site, and all the subdomains in the mapped Sharepoint site. In this example, Team Site is the Sharepoint site, and PSQA Team Site is a subdomain of the Sharepoint site.
Figure 3–9 Sharepoint Membership Portlet
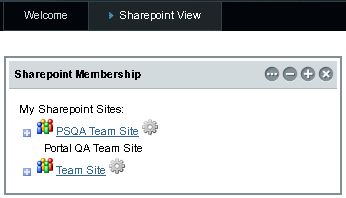
You need to authenticate a Sharepoint site before you can access it.
-
Click the “wheel” icon next to each Sharepoint site.
The Add Credentials window appears.
Figure 3–10 Authenticating a Sharepoint Site
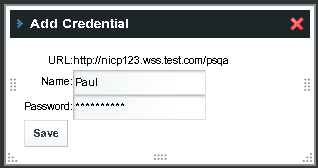
-
Specify the credentials for the Sharepoint site, and click Save.
This uses the CredentialVault Service. See CredentialVault Service for more details.
In case the user typed the credentials wrongly in Add Credentials, he/she can modify the value by clicking the "Wheel" icon (Credentials) to update with correct values.
-
Expand a Sharepoint site to view all the Sharepoint Services (list) associated with it.
Figure 3–11 Sharepoint Services Associated With a Sharepoint Site
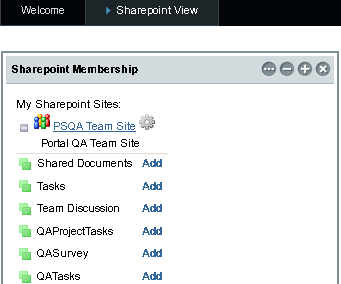
Web Space Server presents the Sharepoint services associated with a Sharepoint site as WSS List portlets. You can add a WSS List portlet to your page to access the corresponding Sharepoint service. These WSS List portlets form the interface for Sharepoint services on Web Space Server.
-
Click the Add button next to a selected Sharepoint service.
In this example, click the Add button next to Links.
The Sharepoint service is added to your page as a WSS List portlet.
-
Expand the portlet to view the associated resources.
In this example, the Links portlet is added to your page.
Figure 3–12 A Sharepoint Service as a Portlet on Web Space Server
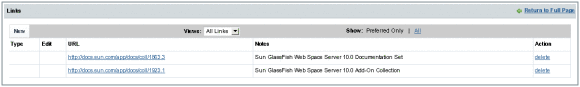
This WSS List portlet lists all the links that are currently available. You can add or remove a link. In the same way, any Sharepoint service listed on Web Space Server as a WSS List portlet, enables you to view and access existing resources, and to make changes to the resources. You can set the access configuration of a portlet from the control menu of the portlet.
Supported Features of Windows Sharepoint Services 3.0
Sun GlassFish Web Space Server integrates with Windows SharePoint Services (WSS) 3.0. This section lists the WSS 3.0 features that are supported and not supported in Web Space Server.
-
Add, Delete, and Display for Lists, Document/Forms/Picture Libraries, Meeting Sites, and Meeting Items are the functions that are supported. However, the Edit feature is not supported for all Items.
-
The supported Lists are Announcements, Calendar, Links, Contacts, Issues, Tasks, Discussions, Surveys, and Custom Lists. The unsupported Lists are Alerts, Wikis, and Blogs.
-
The supported Libraries are Document, Form, Picture, and Shared Documents.
-
The supported Meeting Items are Objectives, Agenda, Attendees, Directions, Things to Bring, Discussions, Document Library, and Picture Library. The Pages (Multi-Page Meeting) is not supported.
-
Views are supported. However, Windows based views (for example, SlideShow View, Explorer View) and Calculation based views (for example, Count, Total, Sub-Total) are not supported. Moreover, Views are not supported for Document, Forms, and Picture Libraries functions.
-
Workspaces and Related Issues are not supported, while you add Items to the List.
-
Discussions - Threading Field is not supported.
-
Adding Recurrence Event is supported with a workaround.
-
Adding metadata during Picture Upload for Picture Libraries is not supported.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
