About Logon and Logoff
To perform SunLink Server Solaris administrative tasks or Windows NT administrative tasks--whether from the SunLink Server console, the SunLink Server Manager tool, or from a remote client--you must be authorized by the server. Network resources are protected at several levels by different processes.
Depending on what type of privileges that the administrative task you want to accomplish requires, you need to log on by identifying yourself with both a special user name and a password that accompanies it. Purely SunLink Server administrative tasks, such as changing the name of a SunLink Server system, require that you log on with the Solaris "superuser" name, root. Windows NT administrative tasks, such as creating file and printer shares, also require special Windows NT administrator privileges and passwords.
Windows NT and Solaris root Logon Privileges
To administer Windows NT data, some of your network users may be designated as account operators, print operators, or server operators. These users have limited Windows NT administrative or operator privileges that enable them to perform specific tasks. These privileges are sufficient to use the net command to administer a local server at the SunLink Server command prompt, as well.
However, remote Windows NT administrative access to a SunLink Server computer is protected by additional logon security, which requires you to be a member of a specially privileged group, administrators. Once you have identified yourself to the computer, it checks your user name and password against the computer directory database.
You can use SunLink Server Manager or the Solaris command line to log on to, or log off from, your SunLink Server system. To perform any administrative task, you must log on as root first, and then, in some cases, also provlde your Windows NT administrator name and password. Note that using the SunLink Server command line requires you first to log on as root to the Solaris system that hosts the SunLink Server program, and then, using your Windows NT administrator user name and password, to log on to the network with the net command.
How to Start SunLink Server Manager
-
Do one of the following, depending on the computer you are using:
-
Using a Microsoft Windows system, select SunLink Server Manager folder from the Programs menu, and then double-click the SunLink Server Manager icon.
-
Using a Solaris system, enter the following at the command prompt: /opt/lanman/sbin/slsmgr
-
How to Add a Server to SunLink Server Manager
-
From the Action menu, select Add Server.
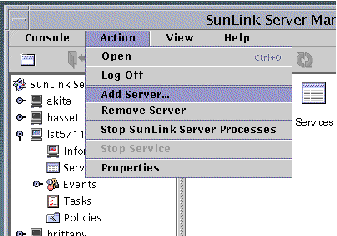
The following screen appears.
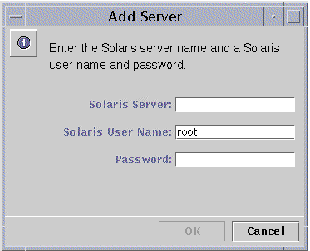
-
Type in the Solaris name of the SunLink Server system that you want to add to SunLink Server Manager.
-
Enter the root password for the system (the root user name is already entered by default), then click OK.
The specified server is added to the list of SunLink Server systems. Note that you must still log on to the specific SunLink Server system to make changes to it, or to view information about it.
How to Log On Using SunLink Server Manager
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the Servers list in the Navigation pane (left side) of SunLink Server Manager, click the name of any SunLink Server system; or
-
Highlight a system name in the View pane (right side) of SunLink Server Manager, and select Log On from the Action menu; or
-
With the mouse pointer over the icon of a SunLink Server system in the View pane, right-click and select Log On.
Note -The step above assumes that this is not the first time that you have run SunLink Server Manager. If this is the first time, then you need to add a server as the first step. See "How to Add a Server to SunLink Server Manager".
The Server Log On dialog box appears.
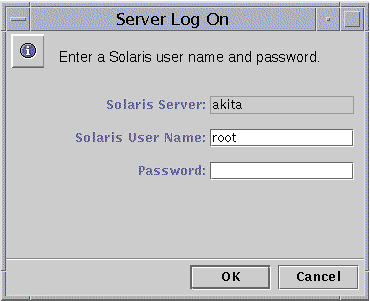
Note -The Server Log On dialog box will also appear whenever you attempt to perform an administrative task on a SunLink Server system to which you are not logged on. To make any changes, you must log on as root (the user name that appears by default).
-
-
In the text field provided, type the root password.
Although you can log on with a non-root user name, SunLink Server administrative functions require root privileges. A root account in a Solaris system is equivalent to an Administrators group account in a Windows NT system, with full administrative privileges. Therefore, if you log on with a user name other than root (the default), you will not be able to make any administrative changes to the system.
-
Click OK.
How to Log On From the Command Line
-
At the Solaris prompt of the system that hosts the SunLink Server program, enter the following command:
system% su Password: system#
-
At the new system prompt, log on to the network as Administrator or as a user with administrative privileges by entering the following command:
system# net logon username password
Substitute a privileged user name for username, and substitute the privileged user's correct password for password.
Note -
To perform administrative tasks on any remote SunLink Server system, you must be logged on as a member of the Administrators group. Operator privileges are not sufficient for remote administration.
How to Log Off Using SunLink Server Manager
-
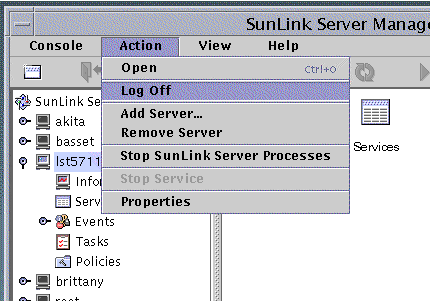
With the SunLink Server system name highlighted, select Log Off from the scrolldown list in the Action menu.
How to Log Off From the Command Line
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
