| Interval Arithmetic Programming Reference |
Glossary
- An order relation other than certainly, possibly, or set not equal. Affirmative relations affirm something, such as a < b.
- An affirmative relational operator is an element of the set: {<,
, =,
, >}.
- An anti-affirmative relation is a statement about what cannot be true. The order relation
is the only anti-affirmative relation in Fortran.
- The Fortran
.NE.and /= operators implement the anti-affirmative relation. The certainly, possible, and set versions for interval operands are denoted.CNE.,.PNE., and.SNE., respectively.
- An assignment statement is a Fortran statement having the form:
V =expression. The left-hand side of the assignment statement is the variable, array element, or array,V.
- See relational operators: certainly true.
- A closed interval includes its endpoints. A closed interval is a closed set. The interval [2, 3] = {z | 2
z
3} is closed, because its endpoints are included. The interval (2, 3) = {z | 2 < z < 3} is open, because its endpoints are not included. Interval arithmetic, as implemented in
f95, only deals with closed intervals.
- In a closed mathematical system, there can be no undefined operator-operand combinations. All defined operations on elements of a closed system must produce elements of the system. The real number system is not closed, because division by zero is undefined in this system.
- A closed set contains all limit or accumulation points in the set. That is, given the set, S, and sequences,
, the closure of S is
, where
denotes an accumulation or limit point of the sequence {sj}.
- The set of real numbers is the open set {z | -
< z < +
}, because it does not include -
and +
. The set of extended real numbers,
, is closed.
- Given the expressions f, g, and h, with
,
- the closure-composition equality states that
.
- The closure of
at the point x0 is equal to the composition of its component's closures,
and
.
- The closure of the expression f of n-variables, evaluated over the set
is denoted
, and for
is defined:
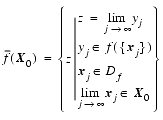
- For
.
- The accumulation points,
xj, of all sequences, {
}, are elements of the set, X0. The closure of f is the set of all possible accumulation points of f given the conditions on the right-hand side of the above defining expression are satisfied.
is defined for all
.
- The connected set of numbers between and including two values, a
b, contains all the values between and including a and b.
- Forming a new expression, f, (the composite expression) from the given expressions, g and h by the rule f({
}) = g(h({
})) for all singleton sets, {
} = {x1}
{xn} in the domain of h for which h is in the domain of g. Singleton set arguments connote the fact that expressions can be either functions or relations.
- A constant expression in Fortran contains no variables or arrays. It can contain constants and operands. The expression
[2,3]+[4,5]is a constant expression. IfXis a variable, the expressionX+[2,3]is not a constant expression. IfYis a named constant,Y+[2,3]is a constant expression.
- The containment constraint on the interval evaluation, f([x]), of the expression, f, at the degenerate interval, [x], is:
- f([x])
cset(f,{x}),
- where cset(f,{x}) denotes the containment set of all possible values that f([x]) must contain. Because the containment set, cset(x ÷ y, {(1, 0)}) = {-
, +
}, [1] / [0] = hull({-
, +
}) = [-
, +
]. See also containment set.
- A containment failure is a failure to satisfy the containment constraint. For example, a containment failure results if [1]/[0] is defined to be [empty]. This can be seen by considering the interval expression
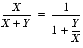
- for X=[0] and Y, given
. The containment set of the first expression is [0]. However, if [1]/[0] is defined to be [empty], the second expression is also [empty]. This is a containment failure.
- The containment set, cset(h, {x}), of the expression h is the smallest set that does not violate the containment constraint when h is used as a component of any composition, f({x}) = g(h({x}), {x}).
- For h(x, y) = x ÷ y,
- cset(h, {(+
, +
)}) = [0, +
].
- See also cset(expression, set).
- Given any expression f({x}) = f({x1}
{xn}) of n-variables and the point, x0, then cset(f, {x0}) = f({x0}), the closure of f at the point, x0.
- Two expressions are containment-set equivalent if their containment sets are everywhere identical.
- Let eval(f, {x}) denote the code-list evaluation of the expression f, using individual composition closures to compute the value of every sub-expression, whether it is the value of an operation, function, or relation. Given the expression, f({x}) = f({x1}
{xn}), whether f is a function or a relation, then for all
, cset(f, {x0})
eval(f, {x0}).
- The internal approximation of an
INTERVALconstant under widest-need expression processing is context dependent, because it is a sharp interval with KTPV that equals KTPVmax. Any approximation for the interval constant [a, b] can be used, provided,- [a,b]
ev(
[a,b]),- where ev(
[a,b]) denotes the external value of the interval constant, [a, b]. Choosing any internal approximation is permitted, provided containment is not violated. For example, the internal approximations,[0.1_4],[0.1_8], and[0.1_16], all have external value, ev(0.1) = 1/10, and therefore do not violate the containment constraint. Under widest-need expression processing the internal approximation is used that has the same KTPV as KTPVmax.
- The notation, cset(expression, set), is used to symbolically represent the containment set of an expression evaluated over a set of arguments. For example, for the expression, f(x, y) = xy, the containment constraint that the interval expression [0] × [+
] must satisfy is
- [0] × [+
]
cset(x × y, {(0,+
)}) = [-
, +
].
- A degenerate interval is a zero-width interval. A degenerate interval is a singleton set, the only element of which is a point. In most cases, a degenerate interval can be thought of as a point. For example, the interval [2, 2] is degenerate, and the interval [2, 3] is not.
- Directed rounding is rounding in a particular direction. In the context of interval arithmetic, rounding up is towards +
, and rounding down is towards -
. The direction of rounding is symbolized by the arrows,
and
. Therefore, with 5-digit arithmetic,
2.00001 = 2.0001. Directed rounding is used to implement interval arithmetic on computers so that the containment constraint is never violated.
- Two disjoint intervals have no elements in common. The intervals [2, 3] and [4, 5] are disjoint. The intersection of two disjoint intervals is the empty interval.
- The empty interval, [empty], is the interval with no members. The empty interval naturally occurs as the intersection of two disjoint intervals. For example, [2, 3]
[4,5] = [empty].
- The empty set,
, is the set with no members. The empty set naturally occurs as the intersection of two disjoint sets. For example, {2, 3}
{4, 5} =
.
- The notation ev(
literal_constant) is used to denote the external value defined by a literal constant character string. For example, ev(0.1) = 1/10, in spite of the fact that an internal approximation of 0.1 must be used, because the constant 0.1 is not machine representable.
- In the IEEE 754 floating-point standard, an exception occurs when an attempt is made to perform an undefined operation, such as division by zero.
- Two expressions are exchangeable if they are containment-set equivalent (their containment sets are everywhere identical).
- In widest-need expression processing, the two attributes that define expression context are the expression's type and the maximum KTPV (KTPVmax).
- See strict expression processing.
- See widest-need expression processing.
- The term extended interval refers to intervals whose endpoints can be extended real numbers, including -
and +
. For completeness, the empty interval is also included in the set of extended real intervals.
- The external representation of a Fortran data item is the character string used to define it during input data conversion, or the character string used to display it after output data conversion.
- The external value of a Fortran literal constant is the mathematical value defined by the literal constant's character string. The external value of a literal constant is not necessarily the same as the constant's internal approximation, which, in the Fortran standard, is the only defined value of a literal constant. See ev(literal_constant).
- See interval hull.
- The infimum of a set of numbers is the set's greatest lower bound. This is either the smallest number in the set or the largest number that is less than all the numbers in the set. The infimum, inf([a, b]), of the interval constant [a, b] is a.
- An interval algorithm is a sequence of operations used to compute an interval result.
- In Fortran, the internal approximation of a literal constant is a machine representable value. There is no internal approximation accuracy requirement in the Fortran standard.
- Interval arithmetic is the system of arithmetic used to compute with intervals.
- An interval box is a parallelepiped with sides parallel to the n-dimensional Cartesian coordinate axes. An interval box is conveniently represented using an n-dimensional interval vector, X = (X1, . . ., Xn)T.
- An
INTERVALconstant is the closed corrected set: [a, b] ={z | az
b} defined by the pair of numbers, a
b.
- An
INTERVALconstant's external value is the mathematical value defined by the interval constant's character string. See also external value.
- In
f95, anINTERVALconstant's internal approximation is the sharp internal approximation of the constant's external value. Therefore, it is the narrowest possible machine representable interval that contains the constant's external value.
- The interval hull operator,
, on a pair of intervals
, is the smallest interval that contains both X and Y (also represented as
). For example,
- [2, 3]
[5, 6] = [2, 6].
- In
f95, anINTERVAL-specific function is an interval function that is not an interval version of a standard Fortran function. For example,WID,MID,INF, andSUP, areINTERVAL-specific functions.
- Interval width, w([a, b]) = b - a.
- In Fortran, there are four intrinsic numeric data types:
INTEGER,REAL,DOUBLEPRECISIONREAL, andCOMPLEX. With the command line option-xiaor-xinterval,f95recognizesINTERVALas an intrinsic data type.
- In
f95, there are a variety of intrinsic INTERVAL-specific functions, including:WID,HULL,MID,INF, andSUP.
- In Fortran, each intrinsic data type is parameterized using a kind type parameter value (KTPV), which selects the kind (precision) of the data type. In
f95, there are threeINTERVALKTPVs: 4, 8, and 16. The default interval KTPV is 8.
- See kind type parameter value (KTPV).
- In widest-need expression processing of interval expressions, all intervals are converted to the maximum value of the KTPV of any data item in the expression. This maximum value is given the name KTPVmax.
- The left endpoint of an interval is the same as its infimum or lower bound.
- In
f95, an interval literal constant is the character string used to define the constant's external value.
- In
f95, an interval literal constant's external value is the mathematical value defined by the constant's character string. See also external value.
- In
f95, an interval literal constant's internal approximation is the sharp machine representable interval that contains the constant's external value.
- See infimum (plural, infima).
- When written in scientific notation, a number consists of a mantissa or significand and an exponent power of 10. The
Eedit descriptor in Fortran displays numbers in terms of a mantissa or significand and an exponent, or power of 10.
- A mixed-KTPV INTERVAL expression contains constants and/or variables with different KTPVs. For example,
[1_4]+[0.2_8]is a mixed-KTPVINTERVALexpression. Mixed-KTPV interval expressions are permitted under widest-need expression processing, but are not permitted under strict expression processing.
- A mixed-mode INTERVAL expression contains data items of different types and KTPV. For example, the expression
[0.1]+0.2is a mixed-mode expression.[0.1]is anINTERVALconstant with KTPV = 8, while0.2is aREALconstant with KTPV = 4.
- A mixed-type INTERVAL expression contains data items of different types. For example, the expression
[0.1]+0.2D0is a mixed-typeINTERVALexpression, because[0.1]is anINTERVAL, and0.2D0is aDOUBLEPRECISIONconstant. They both have the same KTPV = 8.
- A multiple-use expression (MUE) is an expression in which at least one independent variable appears more than once.
- A named constant is declared and initialized in a
PARAMETERstatement. Because the value of a named constant is not context dependent, a more appropriate name for a data item in aPARAMETERdeclaration is "read-only variable."
- Let the interval [a, b] be an approximation of the value
. If w[a, b] = b - a, is small, [a, b] is a narrow-width interval. The narrower the width of the interval [a, b], the more accurately [a, b] approximates
. See also sharp interval result.
- An opaque data type leaves the structure of internal approximations unspecified.
INTERVALdata items are opaque. Therefore, programmers cannot count onINTERVALdata items being internally represented in any particular way. The intrinsic functionsINFandSUPprovide access to the components of an interval. TheINTERVALconstructor can be used to manually construct any valid interval.
- A point (as opposed to an interval), is a number. A point in n-dimensional space, is represented using an n-dimensional vector, x = (x1, . . . , xn)T. A point and a degenerate interval, or interval vector, can be thought of as the same. Strictly, any interval is a set, the elements of which are points.
- See relational operators: possibly true.
- Quality of implementation, is a phrase used to characterize properties of compiler support for intervals. Narrow width is a new quality of implementation opportunity provided by intrinsic compiler support for
INTERVALdata types.
- Radix conversion is the process of converting back and forth between external decimal numbers and internal binary numbers. Radix conversion takes place in formatted and list-directed input/output. Because the same numbers are not always representable in the binary and decimal number systems, guaranteeing containment requires directed rounding during radix conversion.
- A read-only variable is not a defined construct in standard Fortran. Nevertheless, a read-only variable is a variable, the value of which cannot be changed once it is initialized. In standard Fortran, without interval support, there is no need to distinguish between a named constant and a read-only variable. Because widest-need expression processing uses the external value of constants, the distinction between a read-only variable and a named constant must be made. As implemented in
f95, the symbolic name that is initialized in aPARAMETERdeclaration is a read-only variable.
- The certainly true relational operators are {.
CLT., .CLE., .CEQ., .CNE., .CGE., .CGT.}. Certainly true relational operators are true if the relation in question is true for all elements in the operand intervals. That is [a, b] .Cop. [c, d] = true if x .op. y = true for all.
- For example, [a, b] .
CLT. [c, d] if b < c.
- The possibly true relational operators are {.
PLT., .PLE., .PEQ., .PNE., .PGE., .PGT.}. Possibly true relational operators are true if the relation in question is true for any elements in operand intervals. For example, [a, b] .PLT. [c, d] if a < d.
- The set relational operators are {.
SLT., .SLE., .SEQ., .SNE., .SGE., .SGT.}. Set relational operators are true if the relation in question is true for the endpoints of the intervals. For example, [a, b] .SEQ. [c, d] if (a = c) and (b = d).
- See supremum (plural, suprema).
- See widest-need expression processing: scope.
- Set theoretic is the means of or pertaining to the algebra of sets.
- A sharp interval result has a width that is as narrow as possible. A sharp interval result is equal to the hull of an expression's containment. Given the limitations imposed by a particular finite precision arithmetic, a sharp interval result is the narrowest possible finite precision interval that contains the expression's containment set.
- Single-number input/output, uses the single-number external representation for an interval, in which the interval [-1, +1]uld is implicitly added to the last displayed digit. The subscript uld is an acronym for unit in the last digit. For example 0.12300 represents the interval 0.12300 + [-1, +1]uld = [0.12299, 0.12301].
- Single-number INTERVAL data conversion is used by the
Yedit descriptor to read and display external intervals using the single-number representation. See single-number input/output.
- A single-use expression (SUE) is an expression in which each variable only occurs once. For example
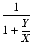
- is a single use expression, whereas
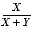
- is not.
- Under strict expression processing, no automatic type or KTPV changes are made by the compiler. Mixed type and mixed KTPV
INTERVALexpressions are not allowed. Any type and/or KTPV changes must be explicitly programmed.
- The supremum of a set of numbers is the set's least upper bound. This is either the largest number in the set or the smallest number that is greater than all the numbers in the set. The supremum, sup([a, b]), of the interval constant [a, b] is b.
- In single number input/output, one unit in the last digit (uld) is added to and subtracted from the last displayed digit to implicitly construct an interval.
- One unit in the last place (ulp) of an internal machine number is the smallest possible increment or decrement that can be made using the machine's arithmetic. Therefore, if the width of a computed interval is 1-ulp, this is the narrowest possible non-degenerate interval with a given KTPV.
- See supremum (plural, suprema).
- A valid interval result, [a, b] must satisfy two requirements:
- In Fortran, an assignment statement computes the value of the expression to the right of the assignment of value operator, =, and stores the value in the variable, array element, or array to the left of the assignment of value operator.
- Under widest-need expression processing, automatic type and KTPV changes are made by the compiler. Any non-interval subexpressions are promoted to intervals and KTPVs are set to KTPVmax.
- In Fortran, scope refers to that part of an executable program where data and/or operations are defined and unambiguous. The scope of widest-need expression processing is limited by calls to functions and subroutines.
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. Feedback |
Library | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |